hematology lab
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
how many hours should dog be fasted before blood collection
6-8 hrs
2 hr for water
what should be avoided before blood collection
excerize/ play
stress
hemolysis interference with blood parameters
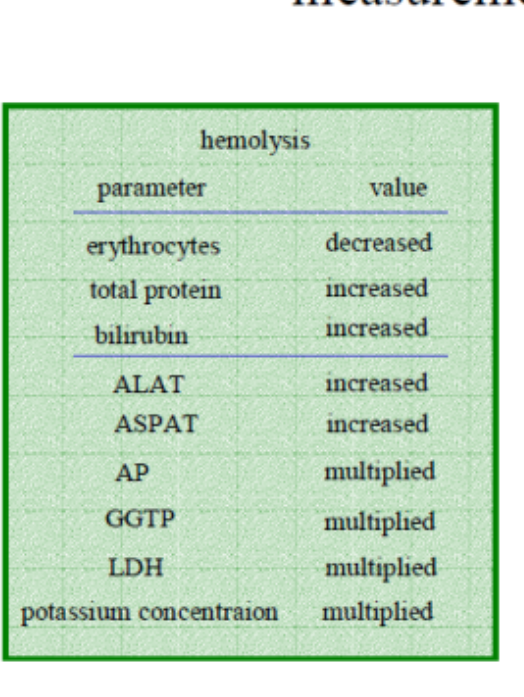
hemolysis free hemoglobin
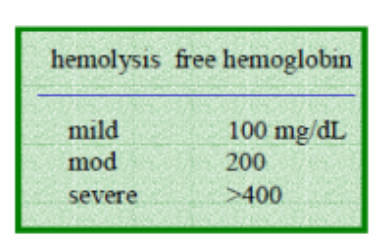
mild hemolysis free hemoglobin
100mg/dl
moderate hemolysis free hemoglobin
200
severe hemolysis free hemoglobin
>400
when dose primitive hematopoiesis take place
in visceral yolk sac (extraembryonic mesoderm)
dog breeds asso w macrocytosis
Miniature and Toy Poodles.
dog breed asso w microcytosis w/o anemia
Akita, Shiba Inu, and Chow Chow, and potentially the Siberian Husky
dog breed asso w stomatocytosis
Alaskan Malamutes, Drentse Patrijshonds, and Miniature Schnauzers
when dose definitive hematopoiesis take place
takes place in AGM region of embryo
what was a good Cv system important for
activity in warmer waters and in air conditions => also the hemopoetic system (blood-forming system)
conserved pattern (similar traits) found in
vertebrates (high and lower)
what was key to survival of stem cells
different potencies (mutli-toti-puli) key to survival
what helped remodell chromatin
conserved structure of H1 in chromosomes (a key part in genetic material)
HSC molecular diagnostics
CD 34 ag- used to identify and isolate hematopoietic stem cells (HSC)
GATA 1 gene- transcription factors essential for development of RBC, plts and mast cells
CD 34 ag
used to identify and isolate hematopoietic stem cells (HSC)
GATA 1 gene
transcription factors essential for development of RBC, plts and mast cells
how can CD34+ cells from 3 week old be done
using canine anti-CD34 mAB
after female dog with XSCID (Canine X-linked Severe Combined Immunodeficiency) received CD34+ male cells they showed improved
lymphocyte counts and T-cell and B-cell response (immune resp) after 2 months
how was male origin of cells confirmed
male donor T cells contained SRY gene
what is critical for normal RBC and PLT formation
GATA-1
GATA-1 mutant (changes) effect on erythroid precursor
GATA-1 mutants (a mutation/ change) have blocked committed erythroid precursors maturation and undergo aptosis (RBC precursors cant mature and die)
megakaryocytes (cells that become plts) stay immature and proliferate
if case with laboratory marrow and blood results above (RBC aptosis and megakaryocytes immature and proliferating
GATA1 mutation should be preformed
what is erythropoeisis influenced by
EPO
GATA1
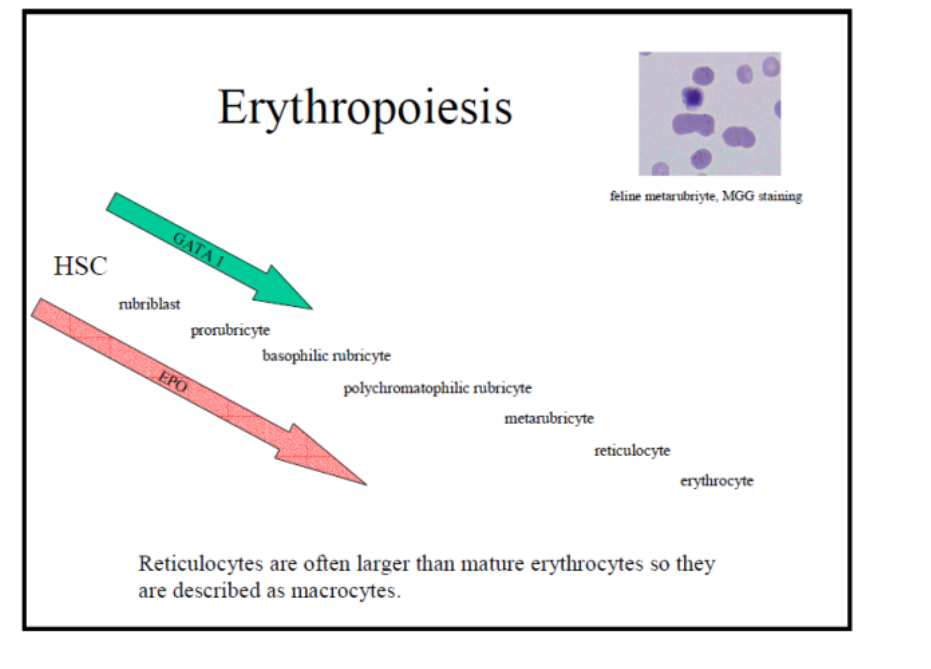
feline metarubriyte, MGG staining
metarubriyte- aka nucleated red blood cell or NRBC
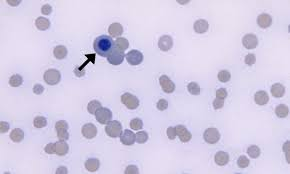
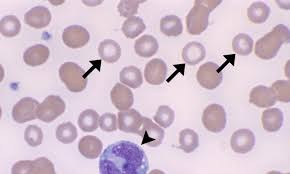
are reticulocytes larger or smaller than mature erythrocytes
larger = described as macrocytes
what regualtes erythropoisis
EPO
EPO
growth factor
glycoporteins (165 aa)
where is EPO (erythropoietin) produ
produ by fibroblasts of kidney in adult mammals
terminolgy
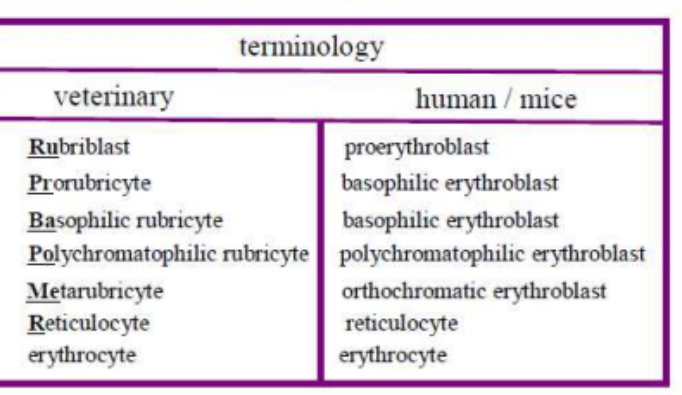
rubriblast
proerythroblast
prorubricyte
basophilic erythroblast
basophilic rubricyte
basophilic erythroblast
polychromatophilic rubricyte
polychromatophilic erythroblast
metarubricyte
orthochromatic erythroblast
feline blood smear
erythro smaller
varible in size (ansiocytosis)
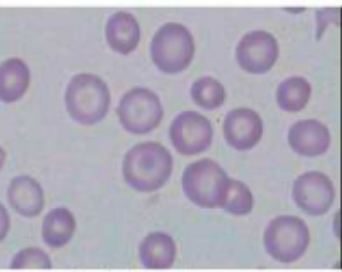
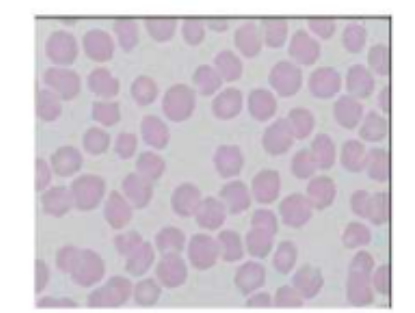
canine blood smear
larger than feline
more uniform in size
more pronounced central pallor
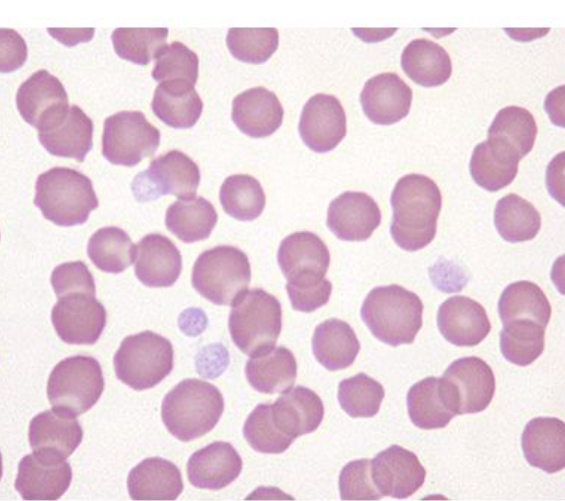
equine blood smear
largest of both
distinct central depression rather than clear cental pallor
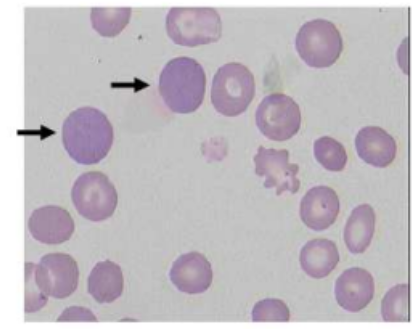
polychromasia
RBCs exhibit a bluish-gray tint when stained with specific dyes, indicating an increased number of immature red blood cells (reticulocytes).
This is often a sign of the bone marrow responding to anemia or other conditions by releasing these immature cells prematurely into the bloodstream.
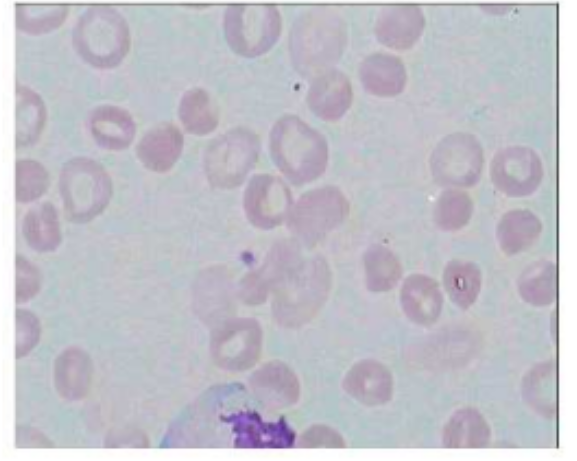
hypochromasia
red blood cells that have less color than normal under a microscope. This usually indicates a reduced amount of hemoglobin, the protein responsible for carrying oxygen in the blood, within the red blood cells. A common cause of hypochromia is iron deficiency.
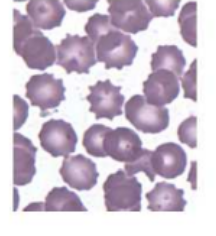
echinocytes
indicate:
kidney failure- uremia
liver diease- prob w lipid metab'
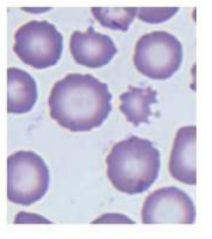
acantocytes
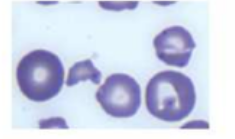
schistocytes
fragmented
various shapes
iregular/ spikey edges
indicate:
microangiopathc hemolytic anemia (MAHA)
TTP
HUS
DIC
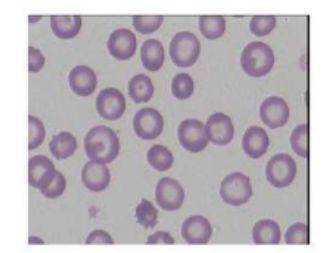
microcytosis
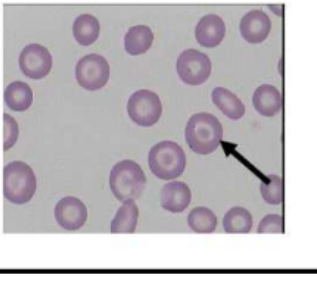
codocytes
have central, round dark area of hemoglobin
pale ring
outside of pale ring there is darker ring
=> look like target
indicate
liver disease
post haemorr regen
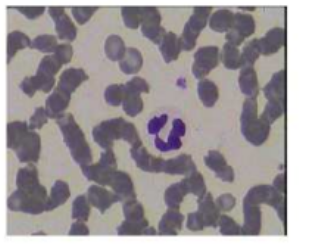
rouleax
rouleax
stacking of RBC
what animals have circulating reticulocytes in health
dogs and cats
what animals have circulating reticulocytes during regenerative response only
cow
sheep
laboratory markers for diag of anemia
HCT
RBC
HGB
severity of anemia
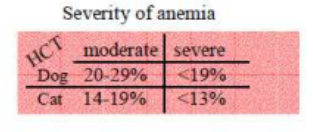
level of HCT in dog in moderate anaemia
20-29%
level of HCT in dog in severe anaemia
<19%
level of HCT in cats in moderate anaemia
14-19%
level of HCT in cats in severe anaemia
<13%
indication body is responding to anemia
high reticulocyte (young RBC) count => suggesting regeneratuve response
non regen reticulocyte count in anemia
normocytic nomochromic cells in blood smear
bone maroow aspirate evaluation- test to asses bone marrows ability to regenerate blood cells
in cattle what reflects regneration
nucleated RBC
in ru what do howell jolly bodies suggest
regenerative anemia
what can cause howel jolly bodies and NRBC
glucocorticoud treatment
prolonged storage of EDTA blood
mild anemia in equine
30-33%
moderate anemia in quine
20-29%
severe anemia equine
<19%
in horses what suggests response to anemia
macrocytosis
ansiocytosis
cause of regen anemia
haemorrhage
hematolysis (hemolytic anemia)
TP conc during haemorrhage
decrease
TP conc during hematolysis- the breakdown or destruction of red blood cells
increase in TP
cause of hematolysis
immune mediated autoagglutination- coombs test
heinz bodies
young age/ worms
heinz bodies
clumps of damaged hemoglobin in RBC
aggregates of oxidised, precipitated hemoglobin
strong indicator of IMHA
spherocytosis
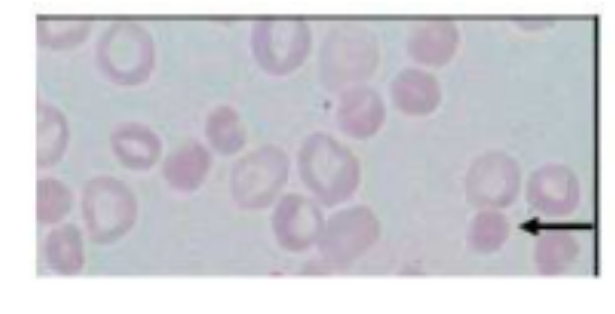
coombs test
RBC w IgG and C3 bound to cell membrane
incubation w ab anti-C3 and anti-IgG (coombs reagent)
purpose of coombs test
detect antibodies in surface of RBC which can indicate immune mediated hemolysis (Immune-mediated hemolytic anemia)
ab present in positive commbs test
IgM and IgG
heinz bodies
aggregates of oxidized, precipitated hemoglobin
monocyte
left shift results in increase in…
bands (more immature cells such as metamyelocytes and myelocytes)
degenerative left shift
more band neutrophils are counted than segmented neutophils
acute leukemia
cytopenias, blast (immature blood cells) present
more that ~25 of blast- AML or ALL
chronic leukemias
cytophilia of involved cell types
cell hyperplasia- CML or CLL
diag tool for leukemia
blood smea
bone marow
immunophenotyping/ cytochemistry
PARR
flow cytometry
markers if AmMegL (acute megakaryroblastic leukemia)- subtupe of AML
mAB anti CD61 and myeloperoxidase
blastic cells- immature cells
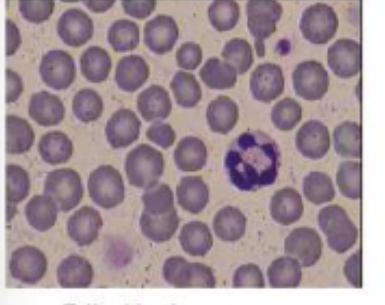
stained feline blood smear
SNAP tetst
an example of monoclonal ab use
what could steroid cause
neutrophilia
deccrease in lymphocyte count (lymphopenia)
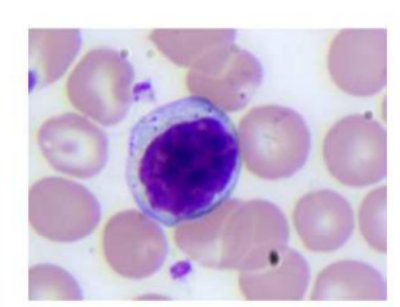
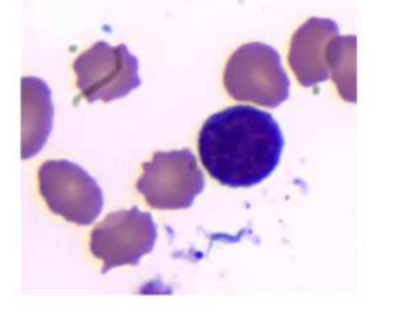
granularity
reactive lymphocyte
increase in number in response to infections or inflammation
help fight infection
parasites in blood
white intracellular EHrlichia canis infection
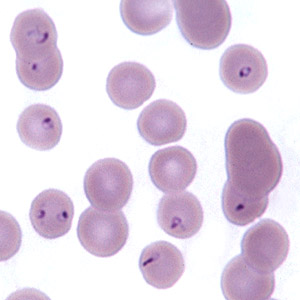
babesia canis
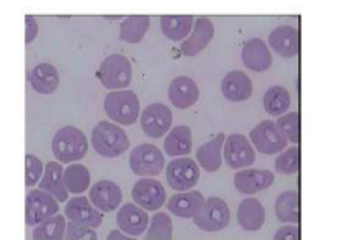
babesia canis
pear/ teardrop shape
what are piroplasms
parasitic protozoa
transmitted by ticks and infect RBCs
cause babesia
ex.
babesia
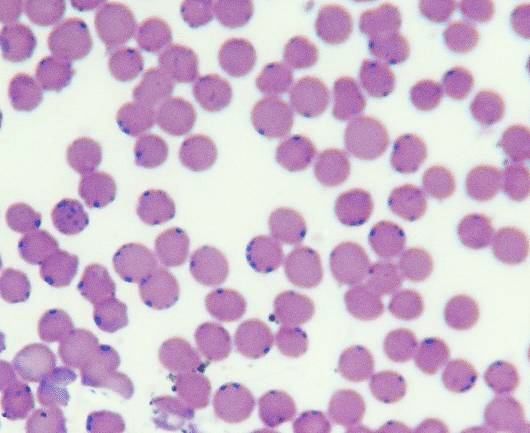
Cytauxzoonosis felis
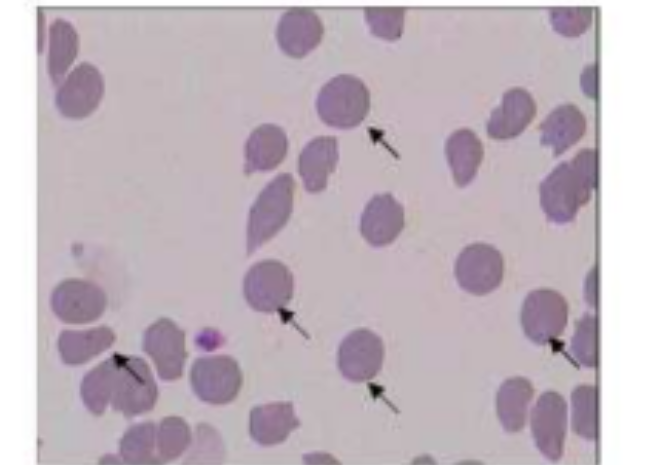
Cytauxzoonosis felis
(more clear image can see black dots which are parasite)
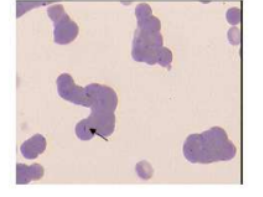
bacteria in blood- haemobartonella felis
appearing as small, blue cocci, rings, or rods, typically on the edges or surfaces of red blood cells
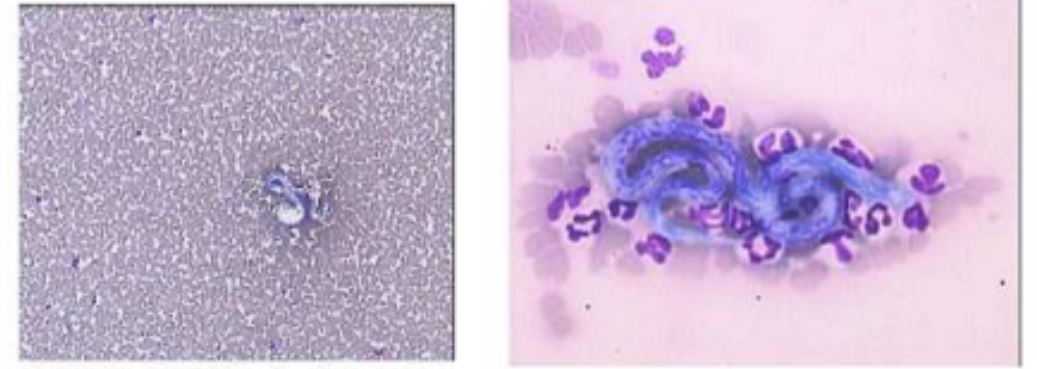
microfilaria- blood worms
change in PLT count
thrombocytosis
thrombocytopenia
clinical signs of thrmobocytopenia
petechiation
ecchymosis (bruising)
hematuria
Na- EDTA
dependent pseudothrombocytoenia
plts clump together → EDTA = atrifically low plt count, hence pseudo,
in blood colection what is added to APTT
kaolin
cephalin
to inittiate intinsic pathway coagu cascade
in blood colection what is added to PT
thromboplastin
to initate extrinsic pathwway of caogu cascade
incubation at
37