Animal Science Lecture Final Review
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Gestation
Process of carrying or being carried in the womb between conception and birth (pregnancy)
Parturition
The action of giving birth to young
Estrus
(Heat) Recurring period of sexual receptivity and fertility in many female mammals
Dam
Female parent
Sire
Male parent
Body Condition Score
A practical method of assessing an animal’s body fat by eye and touch
What is the critical score for BCS?
Between 4 and 5
(4 and under is bad, 5 and above is good)
During which trimester of pregnancy is the most weight gain
Third
Conception rate for a BCS 4 or under
19%
Conception rate for a BCS 5 and above
75%
Polygamy
One sire to many females
85 degrees F
Stress temperature for cattle
How does heat affect estrus?
Estrus can become shorter and less obvious
Monozygotic Twins
Genetically and physically identical
One fertilized egg splits into two identical halves during early embryonic stages
Dizygotic Twins
Fraternal
Formed from two completley different ova at the same time
Freemartin
Condition that can cause infertility in a female twin that also has a male twin
Broad Ligament
Suspends the female reproductive organs
Contains arteries, veins, and nerves
Ovaries
Primary female reproductive organ
Analogous to the testicles
Produce the female gamete ovum (egg)
Produces female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone)
Monotocous
One egg is released and fertilized (e.g. cattle)
Polytocous
Multiple follicles ruptured and fertilized (e.g. pigs)
Medulla
Receives the blood
Cortex
Contains the ova, where Graafian follicles develop, estrogen is produced, Cl develops, and produces progesterone
Primary Follicle
Surrounded by a single layer of follicular cells
Secondary follicle
Primary layer has multiplied into two layers
Tertiary “growing” follicle
Begins to form the antrum
Graafian follicle
Mature follicle appears as a blister, if ovulation does not occur the follicle will be broken down
Antrum
Cavity containing follicular fluid
Corpus Hemorrhagicum
Forms subsequent to ovulation to the follicle
Blood clot fills the cavity
Similar to a bruise
Collapsed follicle contains blood, lymph, granulosa, and theca cells
Corpus Luteum
Solid tissue which is composed of luteal cells that originate from granulosa and theca cells of the Graafian Follicle
Produces progesterone
Corpus Albicans
Connective tissue replaces the luteal cells (white)
Continues to get smaller with each day until they are not visible and process repeats
What do luteal cells produce?
Progesterone
What are the stages of follicle growth?
Primary Follicle
Secondary Follicle
Tertiary Follicle
Graaphian Follicle
Coprus Hemorrhagicum
Corpus Luteum
Corpus Albians
Oviduct
Paired, coiled tubes (fallopian tubes)
Spans from near the ovary to the tip of the uterine horn
Transports the gamete and is the location of fertilization
Is the oviduct tissue designed to support pregnancy?
No
What are the segments of the oviduct?
Infundibulum - funnel shaped opening near the ovary that picks up the egg at ovulation (“catcher’s mitt”)
Ampulla “neck” - ampullary isthmic junction is the specific site of fertilization
Isthmus - joins the uterus at the tubo-uterine junction
Uterus
Houses the fetus
Two horns with one common body
Extends from the tubo-uterine junction to the cervix
Carnucles
Button-like projections in the uterus that allow for nutrient flow to the fetus
Where do we want implantation to occur?
The uterus
Placentome
The specialized area of attachment between the fetal placental cotyledon and the maternal uterine caruncle
Which uterine classification is this?
Simplex
Primates & Humans
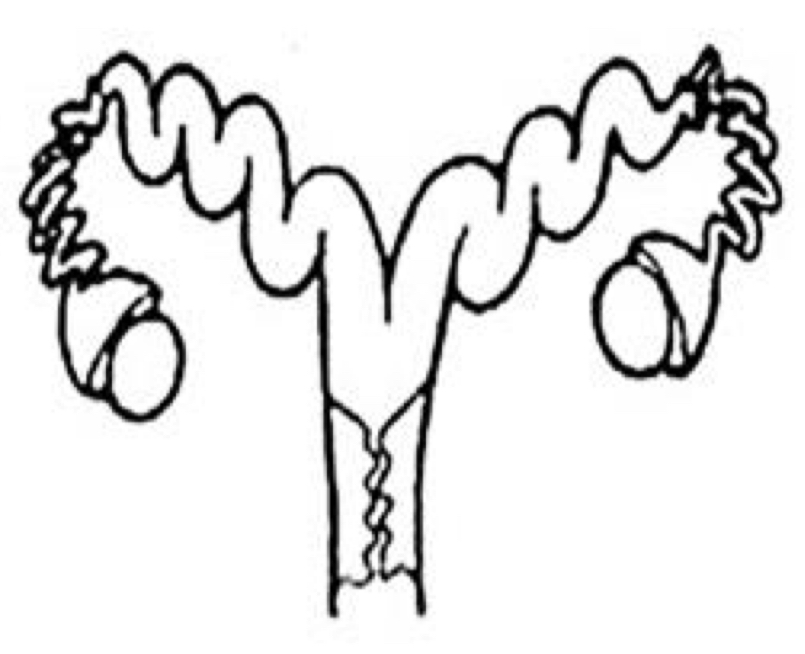

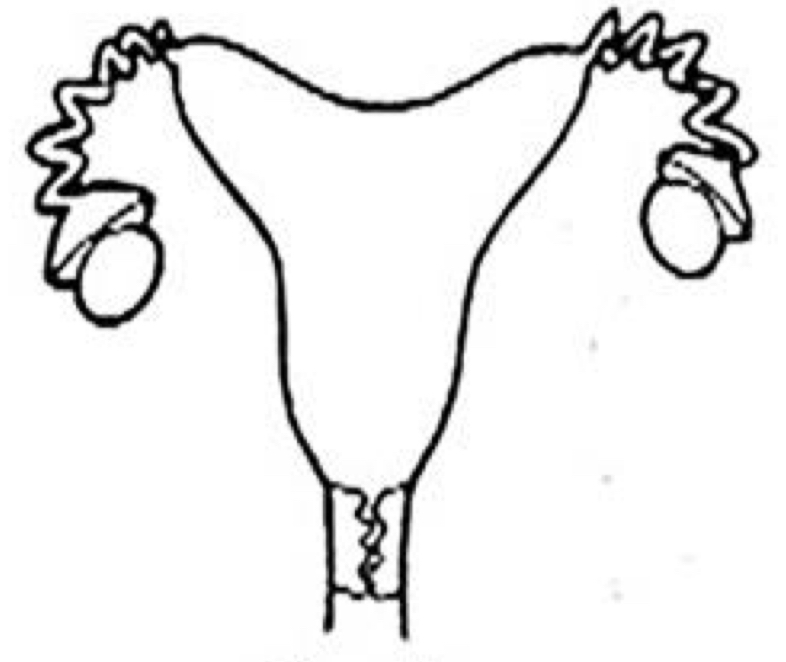
Which uterine classification is this?
Bicornuate (sow)
Horses, Sheep, and Swine
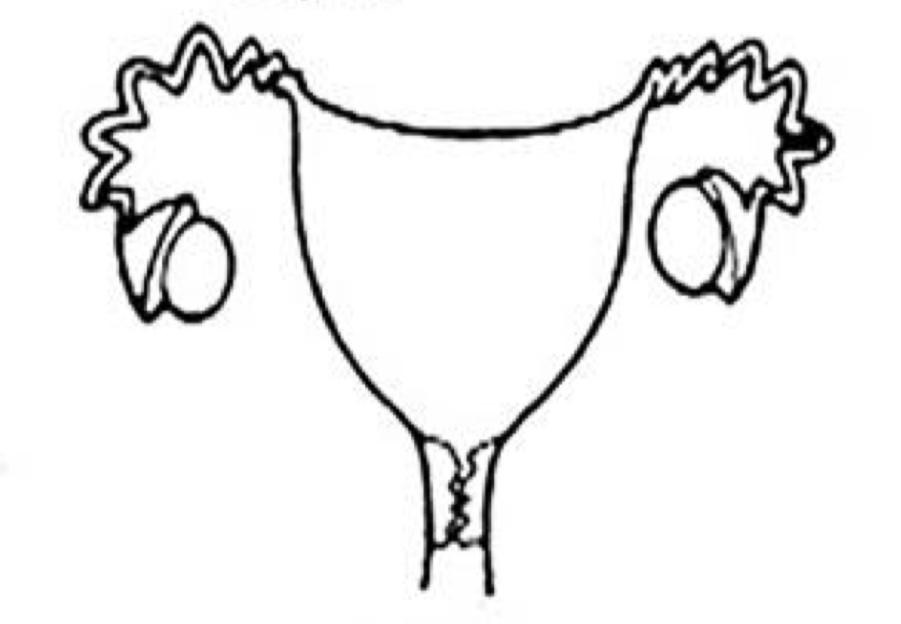
Which uterine classification is this?
Bicornuate (cow)
Cattle, Horses, Sheep
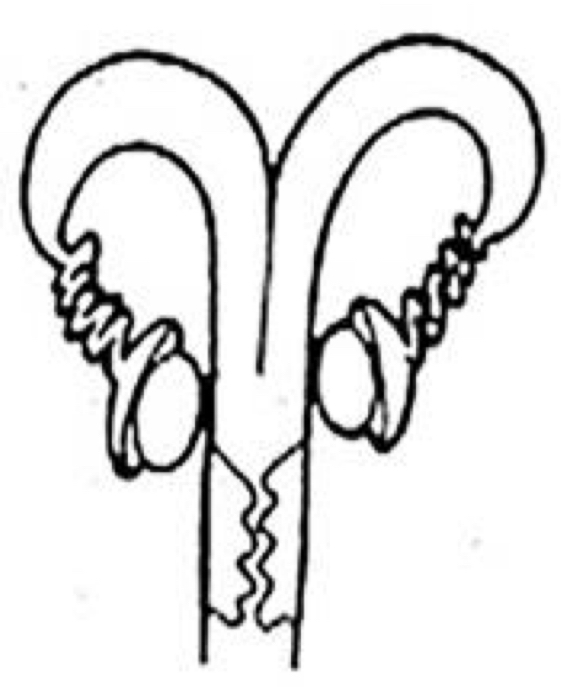
Which uterine classification is this?
Duplex
Rodents and Rabbits
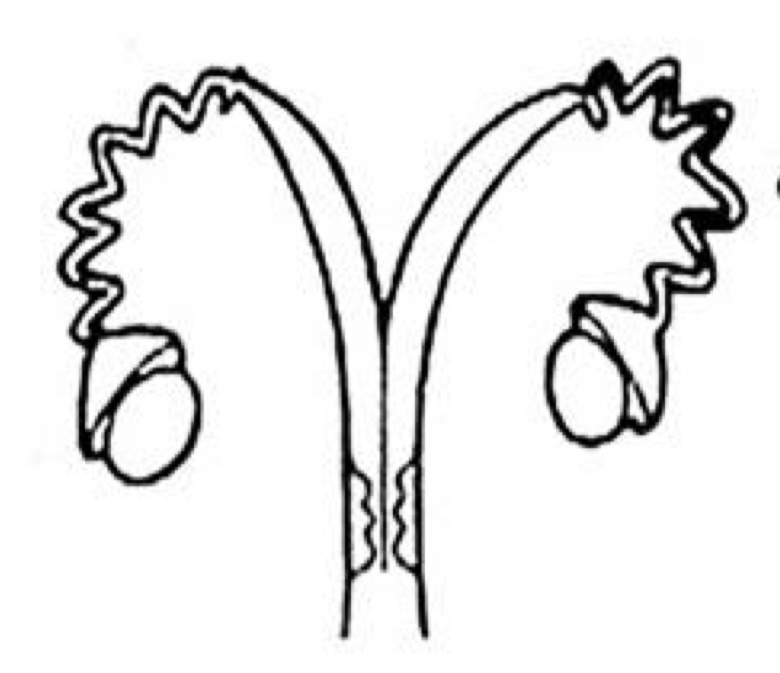
Which uterine classification is this?
Bipartite
Deer, Moose, Elk, and Cats
Cervix
Prevents contamination of the uterus and protects the fetus (cervical plug)
Thick walled tube (inelastic)
Posterior protrudes into the vagina
Fornix or “blind pouch”
Fold created by protrusion of the cervix into the vagina
Issue for A.I.
Which classification of cervix is this?
Annular Rings
Ewe and cow
Which classification of cervix is this?
Longitudinal Folds
Horses
Which classification of cervix is this?
Corkscrew
Swine
Matches boar’s spiral shaped penis
Vagina
Serves as the organ of copulation and the birth canal
Thin-walled tube (elastic)
Anterior vagina - location of semen disposition by the bull and ram
Vulva
External entrance to the reproductive organs
Clitoris
Analogous to the penis
Stimulates hormone release
Is the oviduct where fertilization or implantation takes place?
Fertilization
Testes
Primary organs of male reproduction
Analogous to the ovary
Produces the male gametes (sperm)
Produces the male sex hormone (testosterone)
Seminiferous Tubules
Produces the sperm cells in the testes
Sertoli cells
Line the seminiferous tubules and under the influence of FSH, nurture the developing sperm cells (testes)
Leydig cells
In the testes, sit across the blood-testes barrier from the Sertoli cells and produce testosterone, under the influence of LH, to aid in development of sperm cells
What temperature should be maintained to control testes?
5 degrees C below the body temp
Cryptorchid
One or both testes retained in the body cavity
Mechanisms for temperature regulation in the testes
Scrotal skin will wrinkle when the dartos muscle contracts
Cremaster muscle can pull the testes closer to the body
Pampiniform plexus is a network of blood vessels that will cool the blood going to the testicles
Thermoregulation by muscles
Rete Testes
Tubules that transport the spermatids from the seminiferous tubules to the epididymal duct
Epididymis
Aids in the maturation of the sperm and serves as storage until needed
3 segments
Head (caput) - maturation and concentration
Body (corpus) - maturation and concentration
Tail (cauda) - storage area for mature sperm
Located on the long axis of each testes
Deferent Duct (Vas Deferens)
Transports sperm from the epididymis to the pelvic urethra in preparation for ejaculation
Where we see vasectomies
Spermatic Cord
Composed of the deferent duct, blood vessels, and nerves (that support the testes) and the Cremaster muscle
Accessory Glands
Adds fluid portion of the semen (seminal plasma)
Vesicular
Prostate
Bulbourethral
Vesicular Glands (Seminal Vesicles)
Provide nutrients and buffering capacity to the semen
Prostate Gland
Produces thin, watery fluid to cleanse the urethra prior to ejaculation (urine is very detrimental to sperm)
Bulbourethral Glands (Cowper’s Glands)
Produce the gel portion of the semen and help force the semen from the urethra at ejaculation
Pelvic Urethra
Passageway for semen and urine
Penis
Organ of copulation
Glans Penis
Terminating end of the penis
Vascular type penis
Erectile tissue which engorges with blood to achieve erection
Fibroeleastic type penis
The retractor penis muscle relaxes to allow the rigid penis to extend from the prepuce, then contracts to pull the penis to the prepuce
Sheath
Outer skin containing hair and wool follicles
Bull Penis
Very rapid copulation with low volume and high concentration
Ram Penis
Has a filiform appendage (hair like projection) at the end of the glans penis, which sprays semen around the cervical opening. Rapid copulation, very low volume, and high concentration
Boar Penis
Has corkscrew shaped glans penis, long copulation, high volume, and low concentration
Stallion Penis
Moderate copulation time with high volume and relatively low concentration
Copulation
Gonadotropin-Released Hormone (GnRH)
Peptide hormone produced and released by the hypothalamus
Controls the release of FSH and LH from the anterior pituitary
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Peptide hormone produced and released by the anterior pituitary in response to GnRH
Female: Acts on the ovary to stimulate growth and development of follicles
Male: Acts on the Sertoli cells to stimulate sperm cell production
Works toward gamete production in each sex
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Peptide hormone produced and released by the anterior pituitary in response to GnRH
Female: Acts on the follicle to cause ovulation and subsequent formation of luteal cells that form the CL. Induces continued production of progesterone from CL
Male: Acts on the Leydig cells to induce production of testosterone
Progesterone
Steroid hormone produced by the corpus luteum
Prepares uterus to receive the embryo and maintains pregnancy
Responsible for the quiescence of the system during diestrus
Only found in females
Estrogen / Estradiol
Female: Steroid hormone produced by the developing and mature follicle
Responsible for the development of secondary sex characteristics during puberty
Relaxes the cervix during estrus
Responsible for behavioral signs of estrus
Male: Function not well understood, especially high in the stallion. Produced in testes.
Prostaglandin (PGF 2a)
Lipid hormone produced by the uterus in females
Causes regression of the corpus luteum if no pregnancy occurs
Causes uterine contractions at parturition or for cleansing of the uterus
Proestrus
Days17-21
Follicular growth, corpus luteum regression
Estrus
6-30 hours
Sexual receptivity
Growth and maturity of graaphian follicle (ovulation)
Metestrus
Days 1-3
Corpus luteum commences development
Diestrus
Days 4-16
Luteal development (progesterone)
Testosterone
Steroid hormone produced by the Leydig cells in the testes
Responsible for secondary sex characteristics in males
Males’ sexual behavior or libido
Maturation of sperm
Oxytocin
Produced by the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary
Released in response to stimulation of the mammary system to induce milk letdown
Released during parturition to cause uterine contractions to aid in fetal and placental expulsion
May also be released by the luteal cells in some species
Artificial Insemination
Semen is deposited in the female reproductive tract by artificial techniques rather than natural mating
Seminiferous Tubule
Tube #1
Rete Teste
Tube #2
Epididymis
Tube #3
80-90%
% AI in Dairy Cattle
Less than 5%
% AI in Sheep
95%
% AI in Turkeys
Genetic improvement through increased use of superior sires
Disease control (especially STD)
May be more economical
Improved record keeping
Eliminates need to keep bulls on farm
Major Advantages of AI
Time required for estrus detection
% of cows in estrus during breeding season
Trained personnel required
Can accentuate poor sires
Major Disadvantages of AI