Health, Wellness, and Safe Workplace
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A collection of vocabulary flashcards focusing on key concepts related to workplace health, safety, and wellness.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Due Diligence
The requirement for employers to take every reasonable precaution to prevent workplace accidents, incidents, or illness.
Compliance Processes
Methods used by regulators to enforce safety regulations, including workplace inspections, investigations of accidents, and issuing fines.
Management Responsibilities
Duties of management to ensure compliance with health and safety laws, maintain safety policies, and provide a hazard-free environment.
Employee Rights
Entitlements including the right to know about hazards, the right to participate in safety programs, and the right to refuse unsafe work.
Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS)
A system that provides information about hazardous materials in the workplace, including handling, storage, and disposal.
Eustress
Positive stress that is usually accompanied by excitement and boosts productivity.
Cumulative Trauma Disorders
Injuries caused by repetitive strain, often linked to improper ergonomic practices.
Psychosocial Hazards
Stressors in the workplace that can impact mental health, such as unclear job responsibilities and interpersonal conflicts.
Occupational Illnesses
Health conditions or disorders caused due to working conditions, such as exposures to harmful chemicals or stress.
Safety Training
Mandatory education for employees on safety rules, employer and worker responsibilities, and emergency procedures.
Supervisor responsibilities
Advising employees about potential workplace hazards, ensuring workers user safety equipment and devices. Provide written instructions and comply with due diligence protocols.
Health and safety committee
Supporting safety collaboration, inspections, work refusals, investigation of accidents and respond to concerns. Committees include union, management and employee representatives.
Workers compensation
No fault insurance, employers pay all premiums. Provide workers with compensation when they are unable to work.
Workers compensation formula
Premium owning = industry rating x employer experience rating x size of payroll.
Causes of hazard
Human factors, environmental factors and situational factors
Analytical tree
Positive tree shows the proper way of doing a job. Fault tree shows things that can go wrong.
Risk assessments consider
Frequency, severity, and probability.
Methods of controlling hazards include
Elimination - the best
Engineering controls - guards shields
Administrators control - proper processes instruction and training
Personal protective equipment- masks gloves etc
Safety performance
= ability + motivation + opportunity
Safety awareness
Visible reminders company booklets and safety messages. Most importance - safety crew talks - regular communication is best!
Employee commitment to safety increased when they are involved in
Setting safety standards, designing development of special safety training programs, participating in safety training, establishing safety incentives and rewards, investigating accidents.
Accident investigation
Is required by law.
Standard safety tracking formulas include
Frequency track record= # injuries x 200,00/ total hours worked
Severity track record = days lost to injuries x200,000/ total hours worked
sound pressure level meter
measures gross noise levels in decibels
octave brand analyser
measures noise frequency range
dosimeter
measure employee exposure as a percentage of work time
audiometer
measures employee hearing sensitivity
Types of vibration
segmental vibration - affecting only a particular body part and whole body vibration
vibration evaluated based on
frequency, intensity and duration
Exposure to heat can occur through
conduction - touching. convection - standing close, and radiation
Exposure to radiation
ionizing - e rats,gamma rays. non ionizing - ultraviolet, visible, microwave, radio..etc.
Pictogram Examples
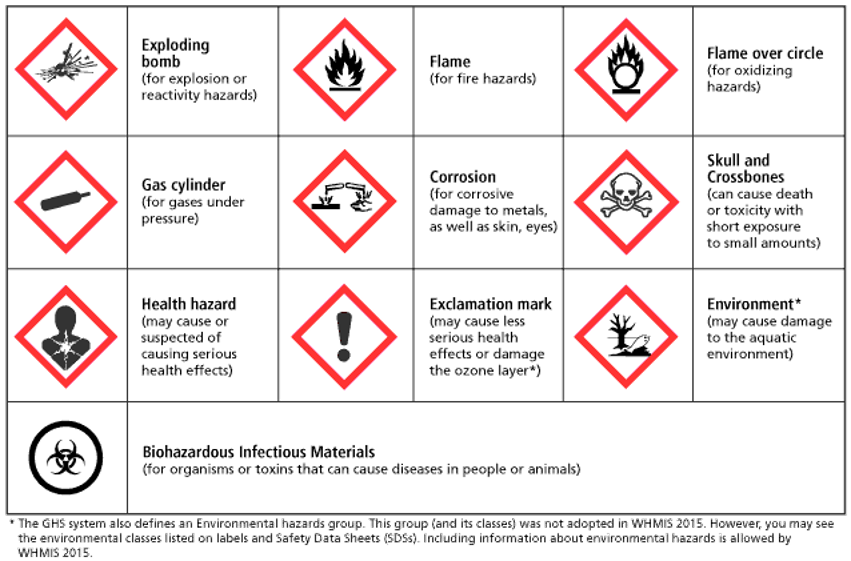
Cumulative Traume Disorders - repetitive strains injuries (RPI
caused by repeated motion or awkward positions over time, affecting hinge joints. Pre existing conditions are amplified. Ergonomics is a good preventative measure.
workplace violence: Type I
random - usually associated with a criminal act.
workplace violence: Type II
committed by clients or customers
workplace violence: Type III
committee by co-workers
workplace violence: Type IV
committed by a family member
psychosocial hazards - include stressors
acute stress (short term) chronic stress (long term) daily (regular) catastrophic (significant event)
Employee assistance programs (EAPs)
helping employees with personal and work-related problems. Access to specialists. strictly confidential.
Substance abuse
employers liable for ensuring safe work environment, acts of intoxicated employee, duty to accommodate.
Disability Management
a proactive approach to managing employee health issues, facilitating early return to work and accommodations. (Temp part timeworn, rehabilitation programs, physical aids, holding job open.. etc)
Return to work programs
light duties, gradual return to work, work trial, supported work, sheltered work. These programs assist employees in transitioning back to work after illness or injury by providing modified duties and support.