Chapter 14 – Ethers, Epoxides, Thioethers, and Silyl Ethers
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering core terms, reactions, solvents, and mechanistic concepts from Chapter 14 on ethers, epoxides, thioethers, and silyl ethers.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Ether
An R–O–R′ compound in which oxygen is bonded to two carbon atoms; lacks O–H bond and cannot hydrogen-bond as a donor.
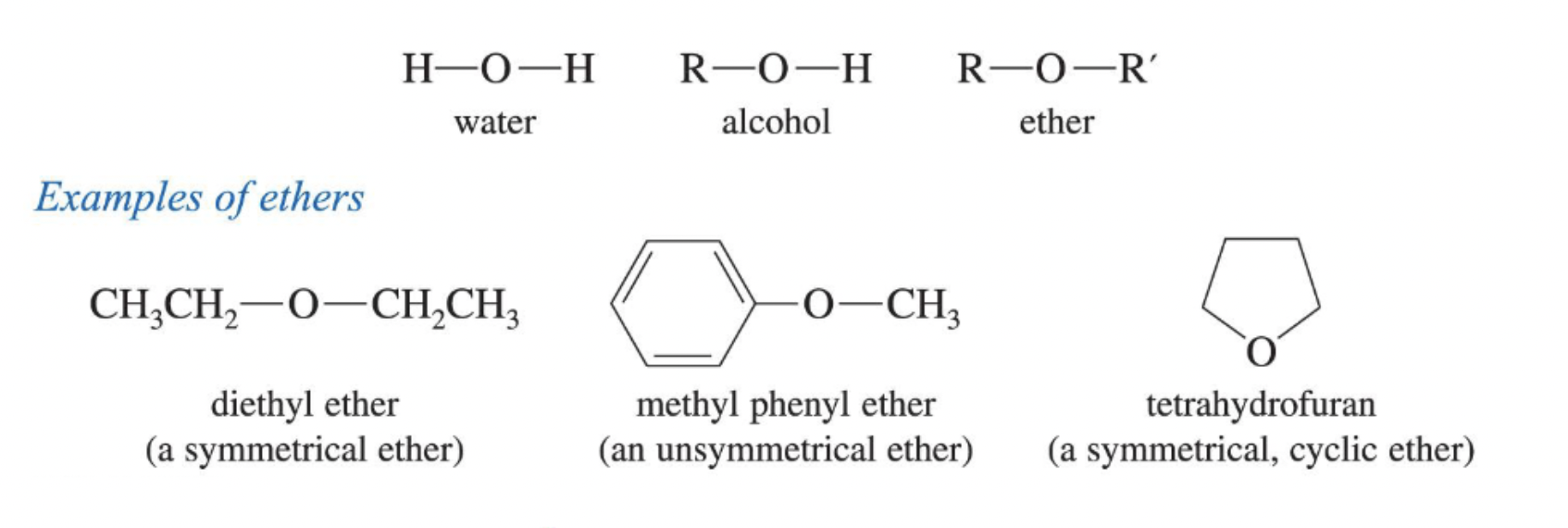
Symmetrical ether
An ether whose two alkyl (or aryl) groups are identical, e.g., diethyl ether.
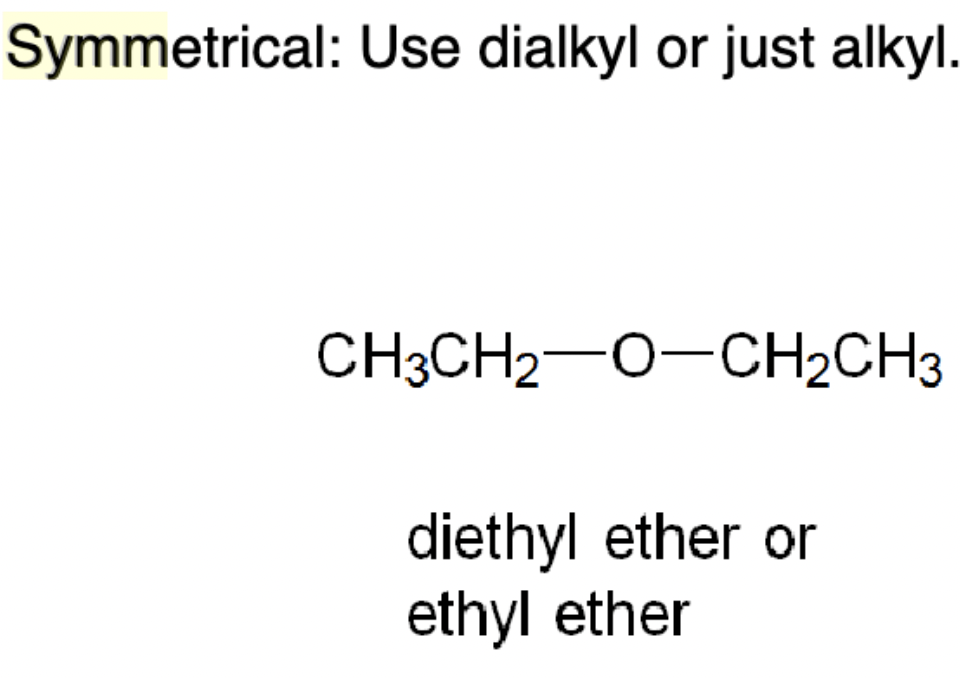
Unsymmetrical ether
An ether whose two substituents differ, e.g., methyl phenyl ether (anisole).
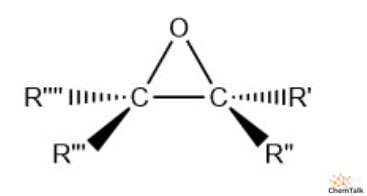
Epoxide (oxirane)
A three-membered cyclic ether with significant ring strain; formula C2H4O.
Furan
An aromatic five-membered heterocycle (C4H4O) with one oxygen; parent of the ‘oxole’ series.
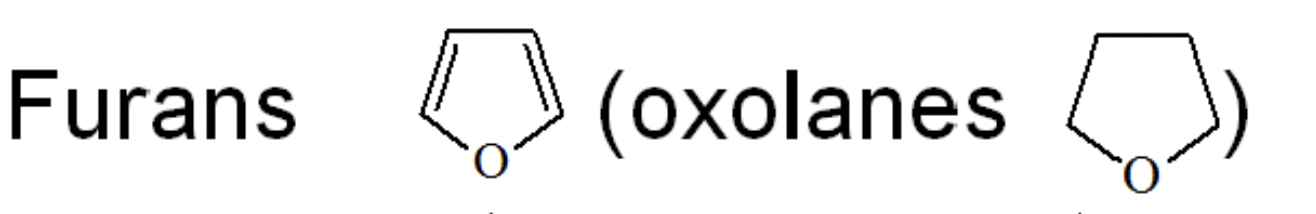
Tetrahydrofuran (THF)
A saturated five-membered cyclic ether (C4H8O); common polar aprotic solvent, bp 65 °C. (no hydrogen bonding)

1,4-Dioxane
A six-membered ring containing two opposite oxygens; higher-boiling (bp 101 °C) polar aprotic solvent.
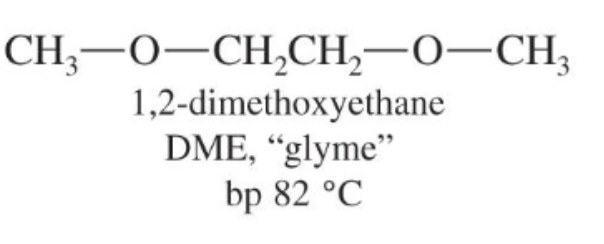
1,2-Dimethoxyethane (DME, glyme)
Linear diether (CH3OCH2CH2OCH3); polar aprotic solvent able to solvate cations.
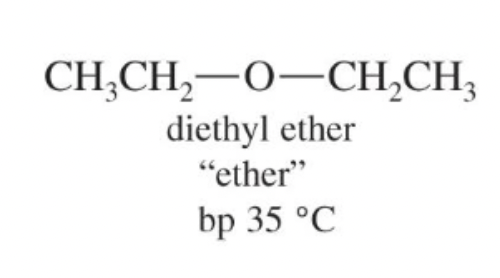
Diethyl ether
Classic laboratory solvent (bp 35 °C) that solvates cations well but cannot donate H-bonds.
Polar aprotic solvent
Medium with significant dipole moment but no acidic hydrogens; stabilises cations, e.g., ethers.
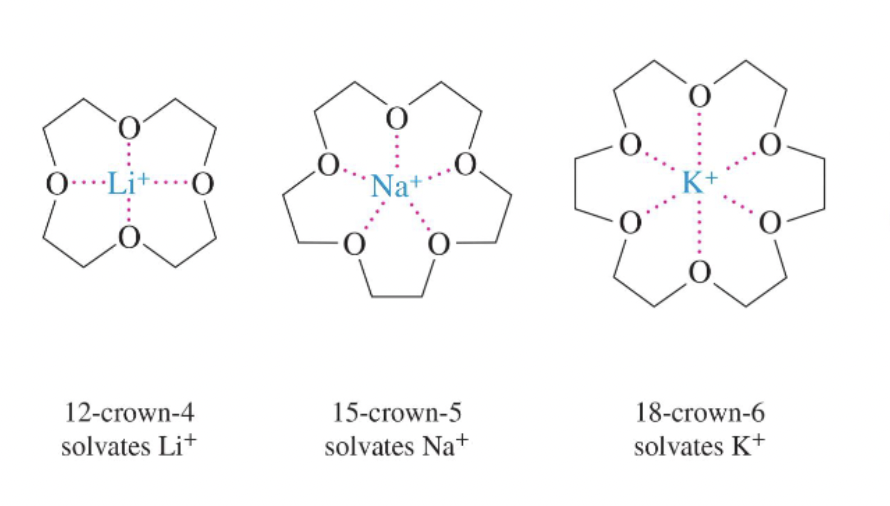
Crown ether
Macrocyclic polyether that wraps around metal cations via lone-pair donation (e.g., 18-crown-6 for K⁺).
Williamson Ether Synthesis
SN2 reaction between an alkoxide (RO–) and a 1° alkyl halide or tosylate to form R–O–R′.
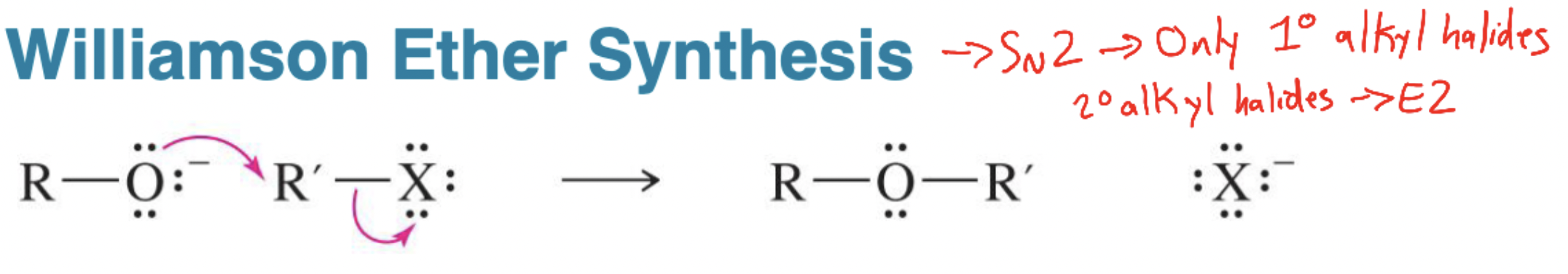
Phenoxide alkylation
Using a deprotonated phenol in Williamson synthesis; works only with aliphatic halides (no SN2 on aryl).
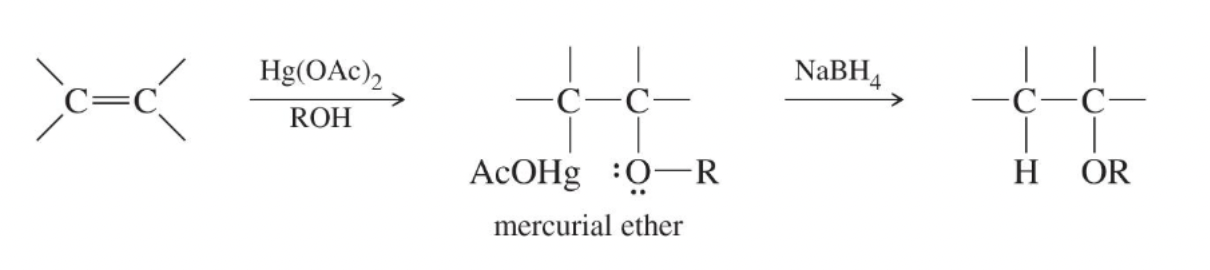
Alkoxymercuration–demercuration
Addition of ROH + Hg(OAc)₂ across an alkene followed by NaBH₄ to give Markovnikov ethers without rearrangement.
Acid-catalyzed condensation of alcohols
Bimolecular dehydration (H₂SO₄, 140 °C) of two 1° alcohols to form symmetrical ethers + water.
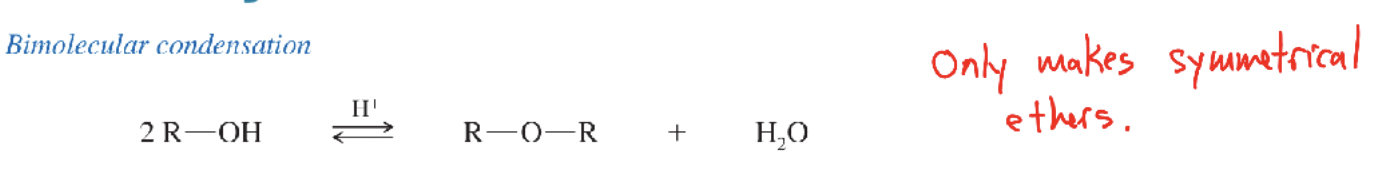
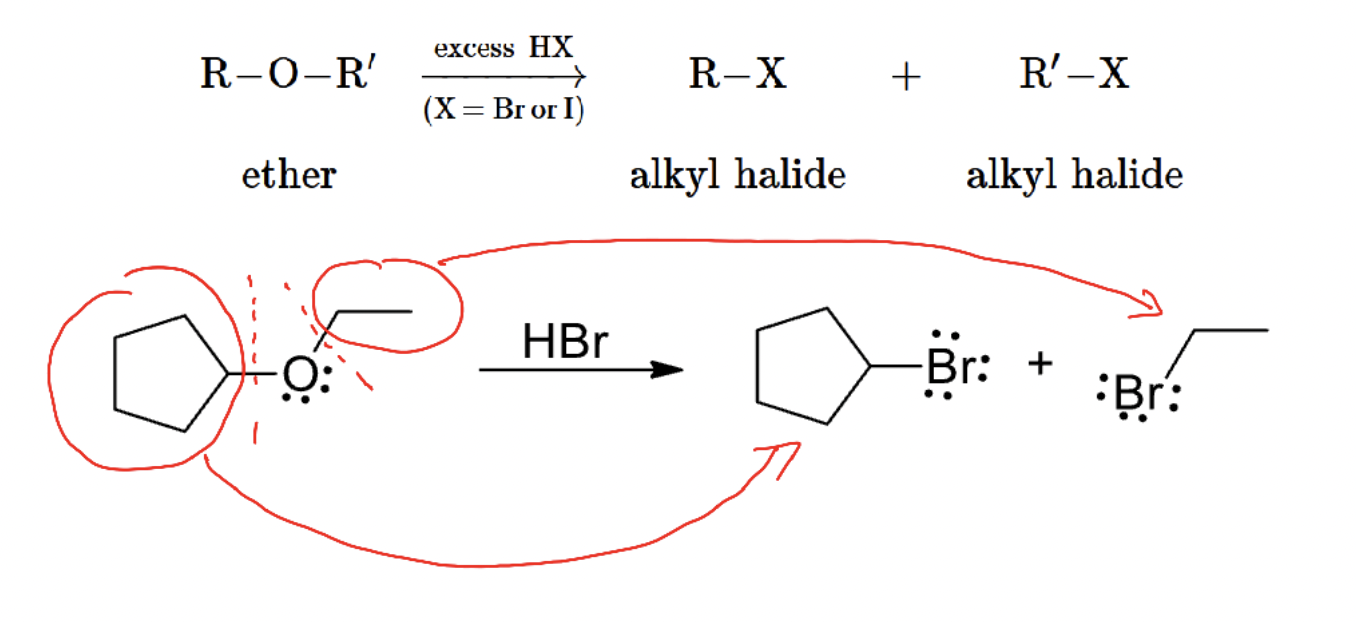
Cleavage of ethers by HBr/HI
Strong HX converts R–O–R′ into alkyl halides via protonation and SN1/SN2 pathways.
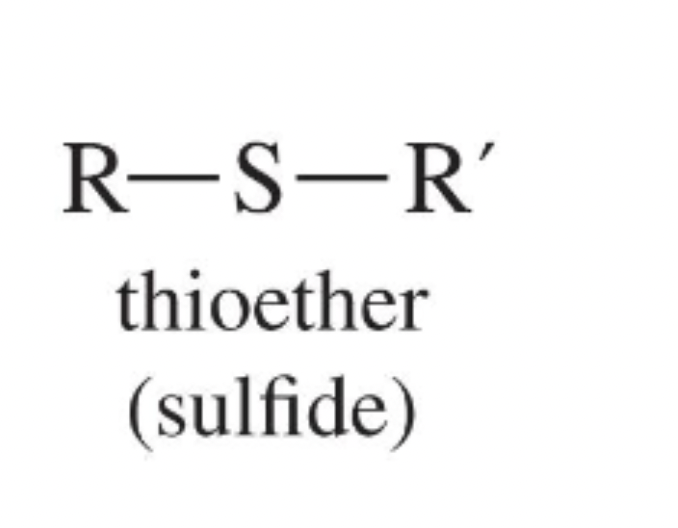
Thioether (sulfide)
Sulfur analogue of an ether, R–S–R′; more nucleophilic and easily oxidised.
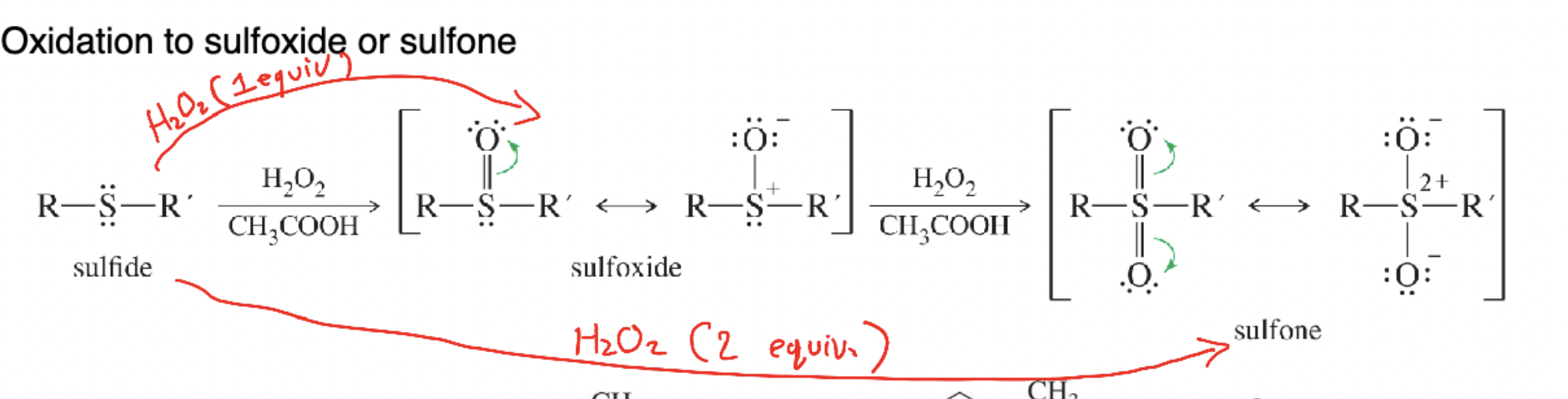
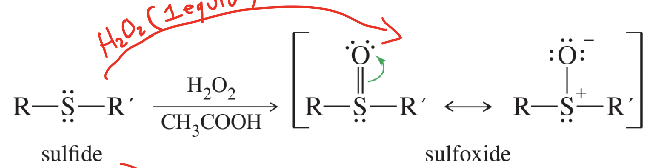
Sulfoxide
R–S(=O)–R′ produced by mild oxidation (1 equiv H₂O₂) of a sulfide.
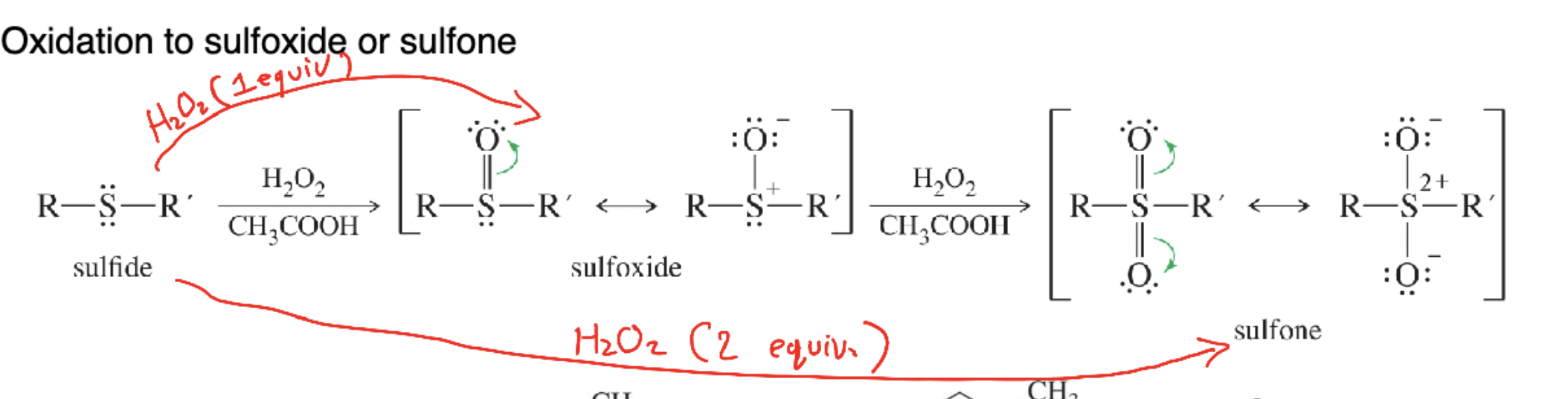
Sulfone
R–S(=O)₂–R′ formed by stronger oxidation (2 equiv H₂O₂) of a sulfide or sulfoxide.
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)
Polar aprotic solvent (CH₃)₂S=O; product of oxidising dimethyl sulfide.
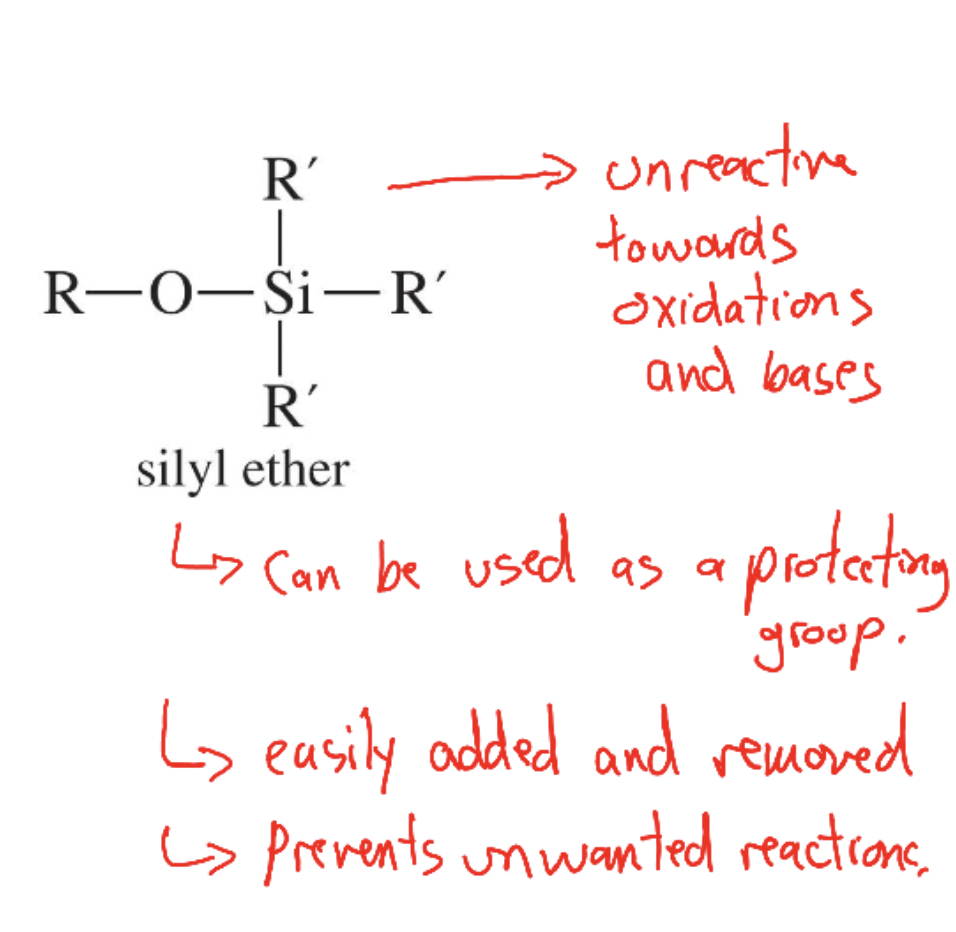
Silyl ether
R–O–SiR′₃ derivative used to protect alcohols from bases/oxidants; removed by fluoride or acid.
TIPS ether
Triisopropylsilyl-protected alcohol (R-O-Si(i-Pr)₃); introduced with TIPS-Cl and Et₂N, removed by TBAF.

Protecting group
Temporary modification that masks a functional group to prevent unwanted reaction during synthesis.
MCPBA
meta-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid; common peroxyacid for alkene epoxidation.
Halohydrin cyclization
Base-induced intramolecular SN2 of a halohydrin yielding an epoxide and halide ion.
Acid-catalyzed epoxide opening
Protonation followed by nucleophilic attack at the more-substituted carbon with inversion; SN1-like regioselectivity.
Base-catalyzed epoxide opening
Nucleophilic attack at the less-substituted carbon under SN2 control; occurs with alkoxides, OH⁻, etc.
Regioselectivity of epoxide opening
Acidic conditions → attack more-substituted carbon; basic conditions → less-substituted carbon.
Grignard/organolithium epoxide reaction
Strong carbanions open epoxides at the less-substituted carbon, extending the carbon chain by two atoms after protonation.
Autoxidation of ethers
Slow air oxidation to peroxides and hydroperoxides; explosive—avoid distilling anhydrous ether to dryness.
Squalene epoxidase
Enzyme that converts squalene to 2,3-epoxysqualene in steroid biosynthesis.
Epichlorohydrin
Chlorinated epoxide used with bisphenol A to make epoxy-resin prepolymers.
Epoxy resin
Thermosetting polymer formed by curing bis-epoxide prepolymer with amine hardeners.
Trimethylsulfonium ion (SAM)
In biochemistry, S-adenosylmethionine acts as a sulfonium methyl donor in methylation reactions.
Hydrogen-bond donor/acceptor in ethers
Ethers are H-bond acceptors only (no O–H); alcohols are donors and acceptors, leading to higher bps.
Diethyl ether as Grignard solvent
Co-ordinates to Mg²⁺ in RMgX, stabilising the reagent while remaining inert to strong bases.