INTRO IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
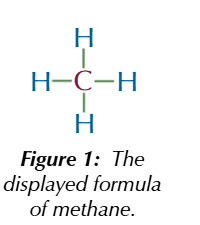
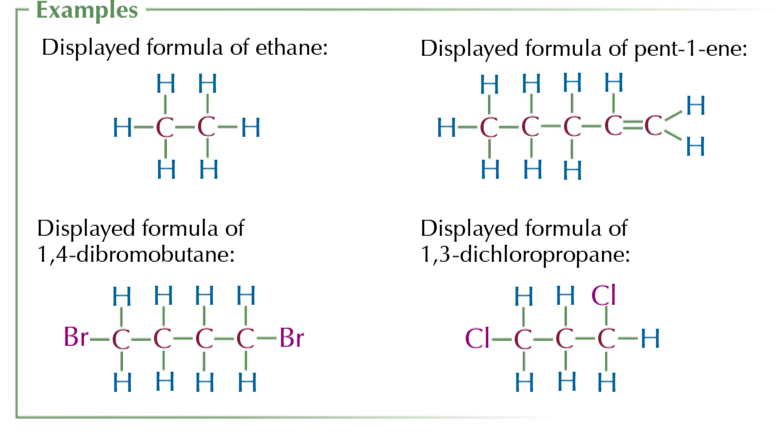
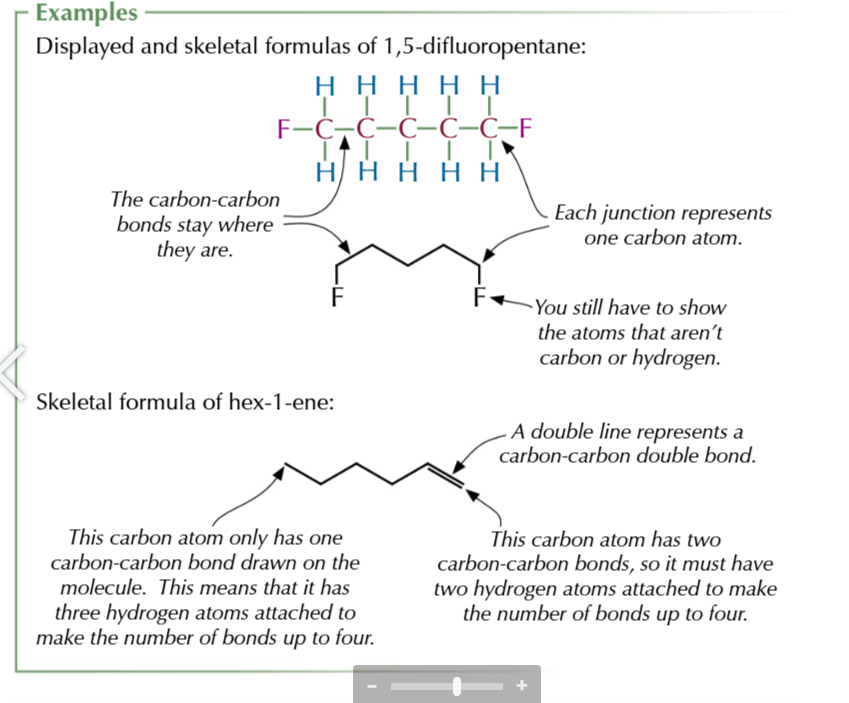
displayed formula
shows how all atoms are arranged and all the bonds between them
functional group o
a group of atoms responsible for the characteristic of the molecule

nomenclature
naming molecules using specific rules known as IUPAC
molecular formula
gives the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule

structural formula
shows the atoms CARBON BY CARBON with the attached hydrogens and functional groups in WRITTING and DOES NOT SHOW BONDS

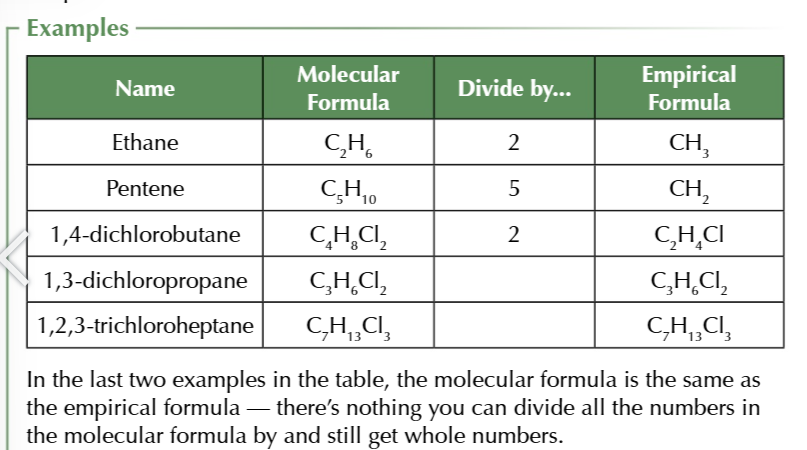
empirical formula
smallest whole number ratio of atoms of each elements in a compound
general formula
algebraic formula that can describe any member of a family of compounds AKA homologous series
Homologous series
a family of compounds that have the same functional group and general formula, consecutive members of a homologous series differ by -CH2- and you can predict their chemical properties

SKELETAL FORMULA
shows bonds of the carbon skeleton representing carbon atoms as lines and hydrogen atoms as vertices USEFUL FOR CYCLIC HYDROCARBONS
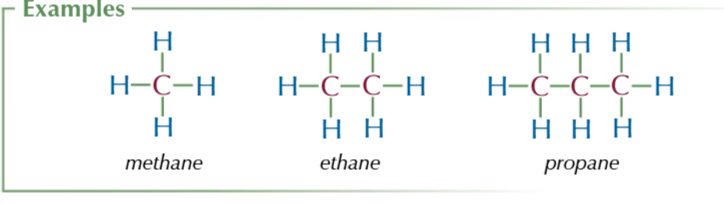
alkane general formula
CnH2n+2
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons
carbons have 4 bonds and molecule only contains hydrogen and carbon
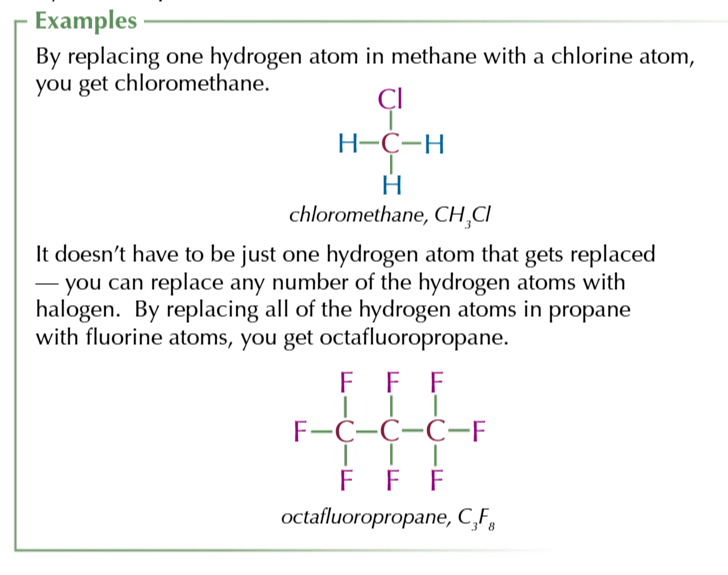
halogenoalkanes
similar to alkanes expect at least 1 hydrogen is replaced with a halogen atom
prefix- FLUORO-/CHLORO-/BROMO-/IODO-
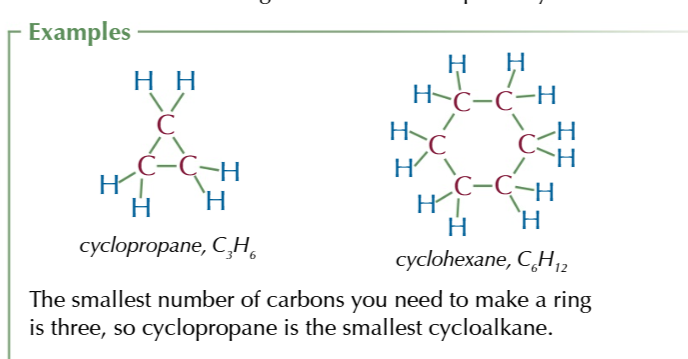
CYCLOALKANES
a ring of carbon atoms with 2 hydrogens attached to each
they have fewer hydrogen atoms that other alkanes therefore have a different general formula: CnH2n
saturatedprefix: CYCLO-
suffix: -ANE
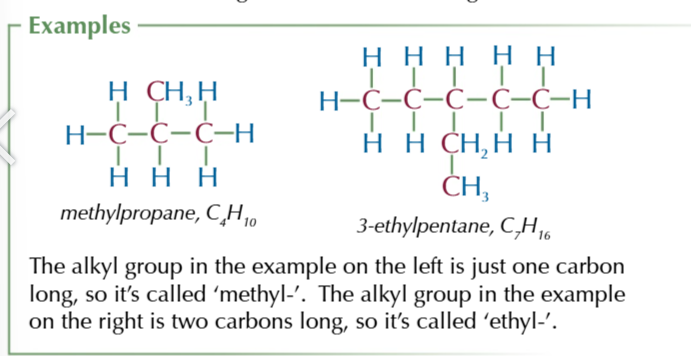
branched alkanes
the main carbon chain is the longest one
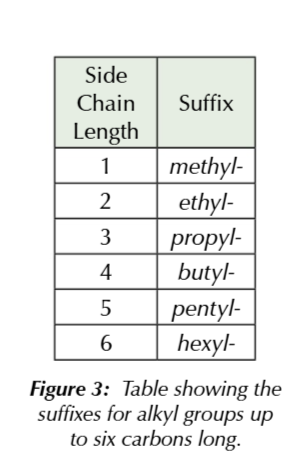
the branched chains are called ALKYL groups
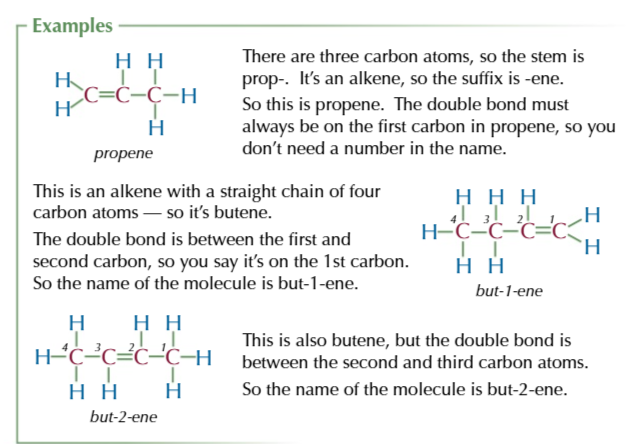
alkenes
hydrocarbons with a carbon carbon double bond
general formula: CnH2n
unsaturated because of double bond as carbon could form a 4th bond, making them fairly reactive

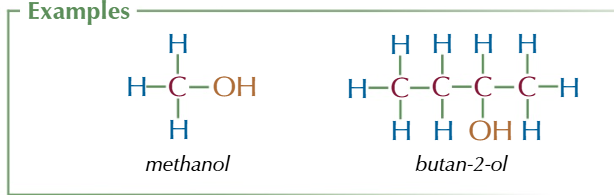
alcohols
-OH/ hydroxyl functional group
suffix: -ol
general formula CnH2n+1OH
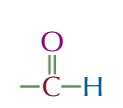
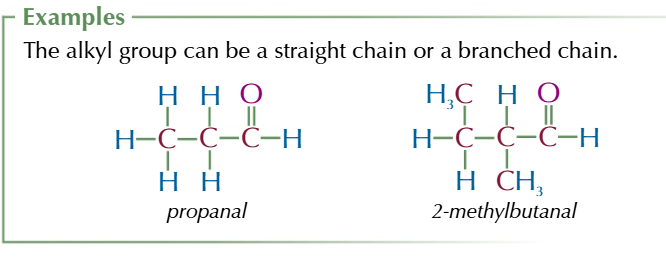
aldehydes
END CARBON HAS A DOUBLE BOND TO OXYGEN AND SINGLE BOND TO HYDROGEN
suffix:-al
general formula R-CHO
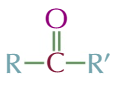
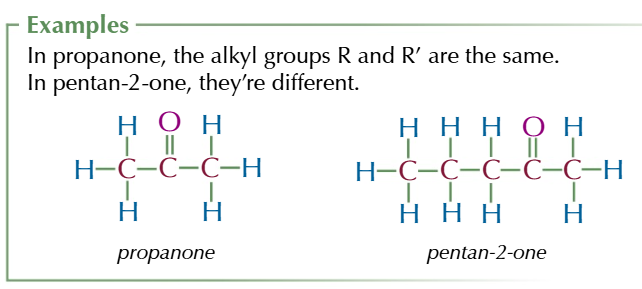
ketones
MIDDLE CARBON HAS DOUBLE BOND TO OXYGEN
general formula R-C=O-R’
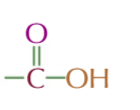
CARBOXYLIC ACID
functional group COOH
suffix: -OIC ACID
general formula R-COOH
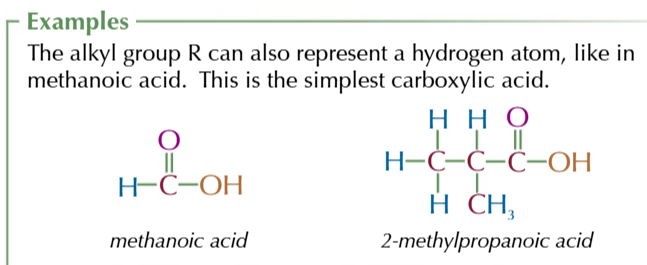
IUPAC system
allows scientific ideas to be communicated across the globe more effectively
nomenclature rules:
count the carbons in the longest continuous chain that contains the functional group
the main functional group of the molecules usually gives the suffix
number the carbons in the lowest carbon chain so that the carbon with the main functional group attached has the lowest possible number
write the carbon number that the functional group is on before the suffix EG: pentan-2-ol
any side chains or less important functional groups are added as prefixes at the start of the name in alphabetical order, with the number of the carbon atom each is attached to
if there’s 1 or more identical side chains/ functional groups use di-, trio- or tetra- before that part of the name
cycloalkanes have the same name as their straight chain equivalents
but with cyclo- attached to the front

if the cycloalkane has an alkyl group attached
its added as a alkyl prefix
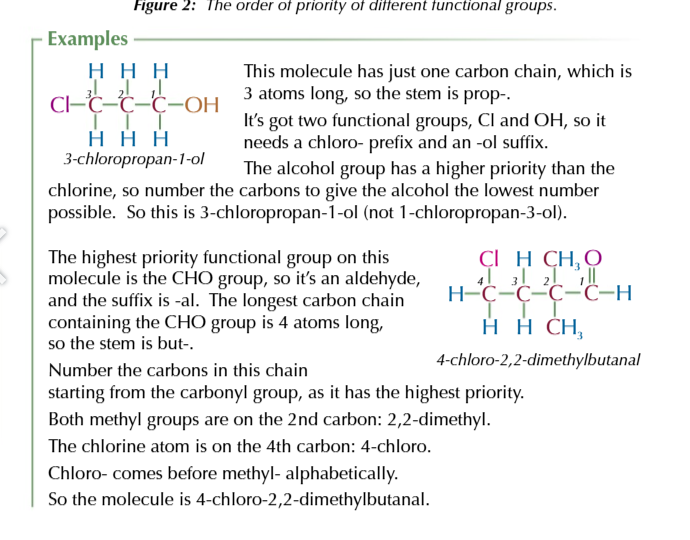
functional group priority list
(lowest) HALOGENS → ALKYL → ALKENES → OTHER FUNCTIONAL GROUPS (highest)

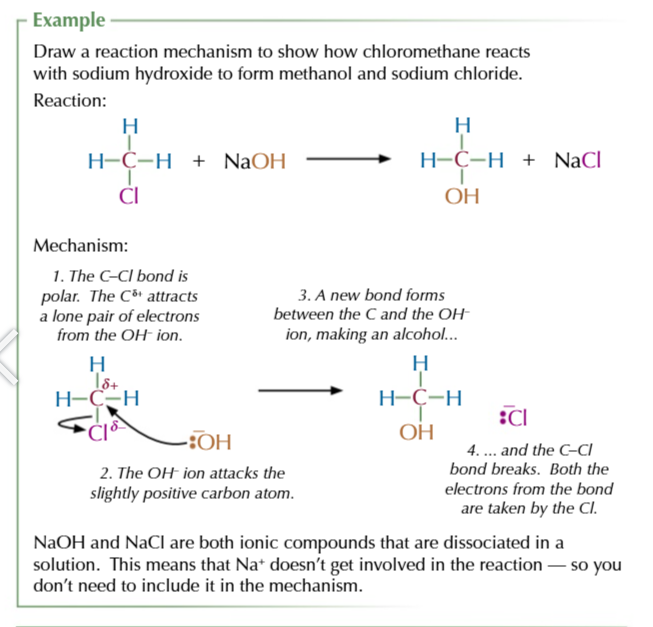
mechanisms break reactions down
into a sequence of stages
reaction mechanism diagrams show how molecules react together
by using curly arrows to show which bonds are made/broken

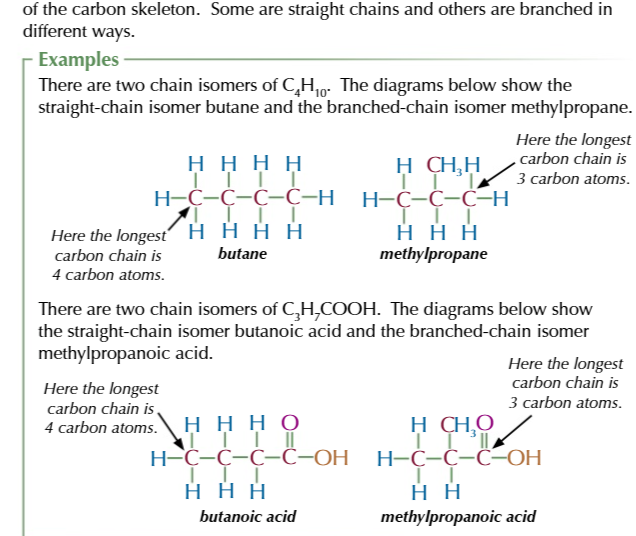
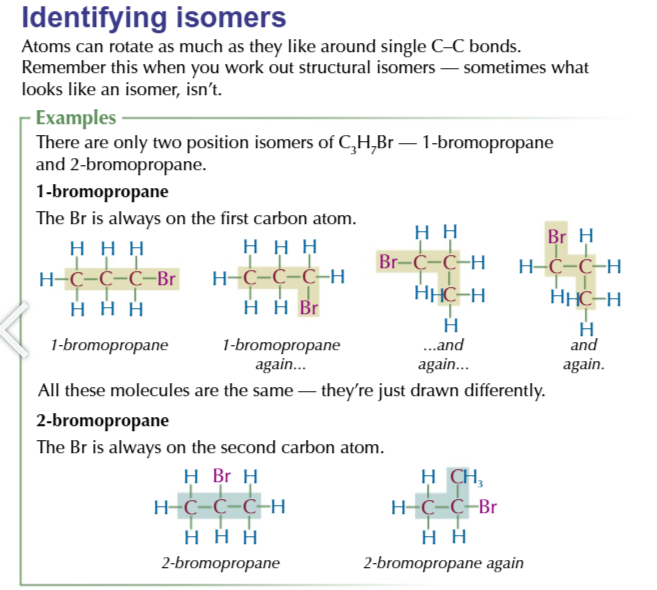
structural isomers
molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural formula
types of structural isomers
chain
position
functional
chain isomers
same functional groups but different arrangement of the carbon skeleton
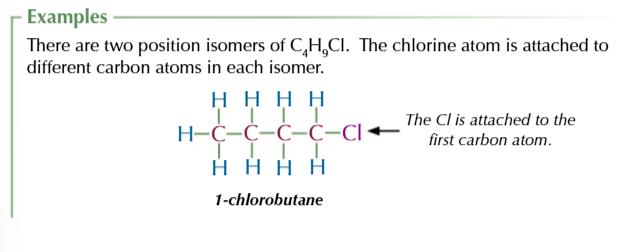
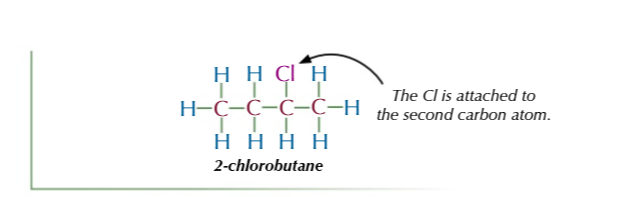
position isomers
same carbon skeleton but different placement of the functional group
functional group isomers
same atoms arranged into different functional groups
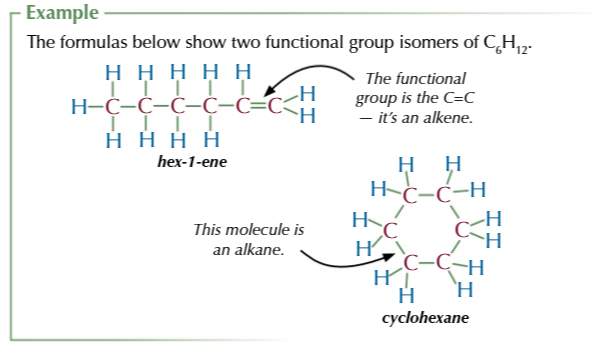
stereoisomers
same structural formula but different arrangement of atoms in space
types of stereoisomers
E/Z
geometric
E/Z isomerism
seen in C=C molecules
carbon atoms in a C=C and all atoms attached to them are on the same plane
the molecule is planar (trigonal planar to be exact)

in larger alkenes only the C=C unit is planar
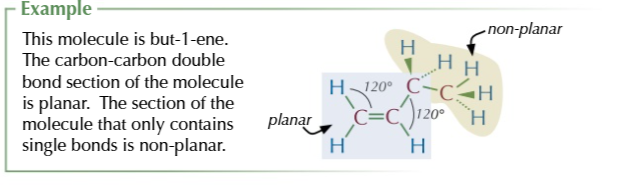
atoms cannot rotate around C=C bonds
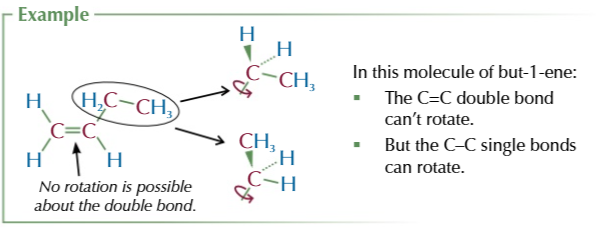
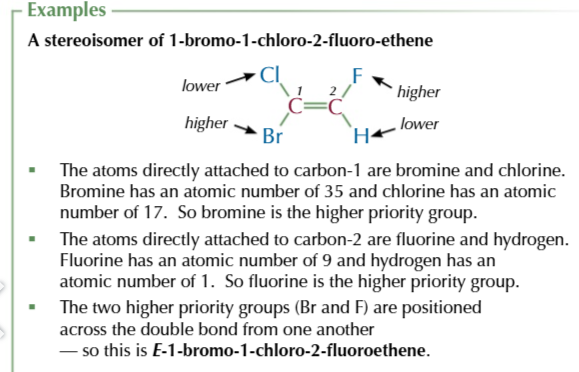
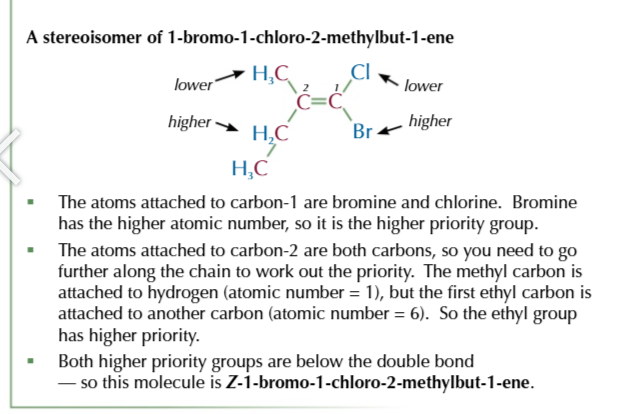
E-isomers
the same atoms are opposite/ diagonal each other
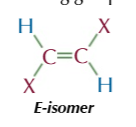
Z-isomers
the same atoms are on the same side as each other
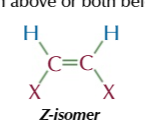
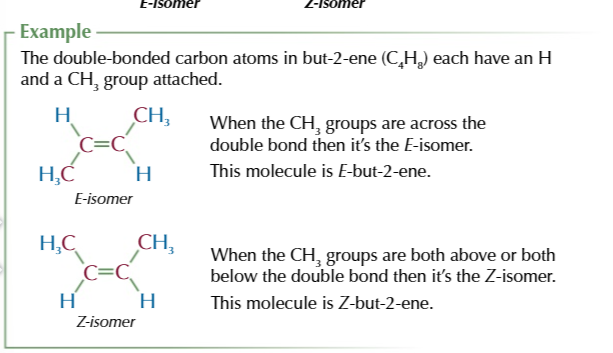
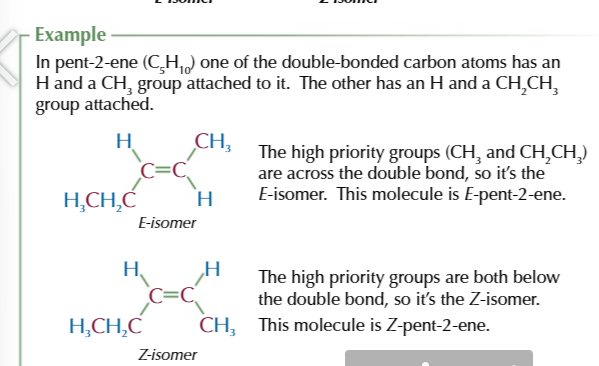
Cahn-ingold-prelog priority rule helps identify E/Z isomers
start by assigning a priority to the two carbon atoms in a double bond
the atom with the higher atomic number of each carbon is given a higher priority
if the atoms directly bonded to each carbon ar the same then you look at the next aotm in the groups to work out which has the higher priority
to work out which isomer you have, look at how the two higher proirity groups are arranged.
if they’re positioned across the double bond from each other (diagonal) then tis an E isomer
if they’re positioned both above or both below the double bond you have Z-isomer