Veterinary Anatomy: Pelvic Limb
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Os Coxae
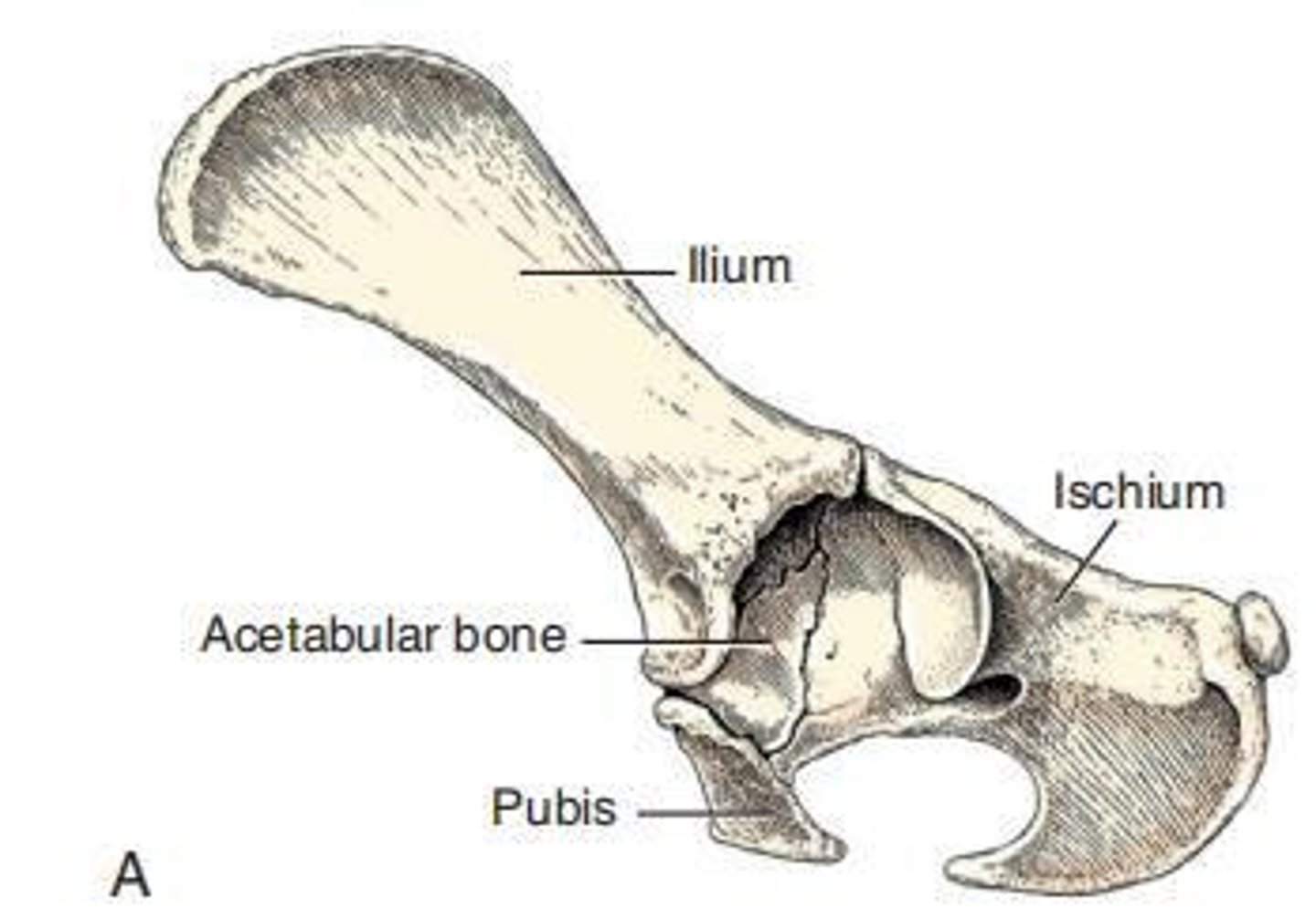
The___, or hip bone, is composed of four distinct bones developmentally: the ilium, ischium, pubis, and acetabular bone. They fuse during the twelfth postnatal week, forming the socket that receives the head of the femur in creation of the hip joint.
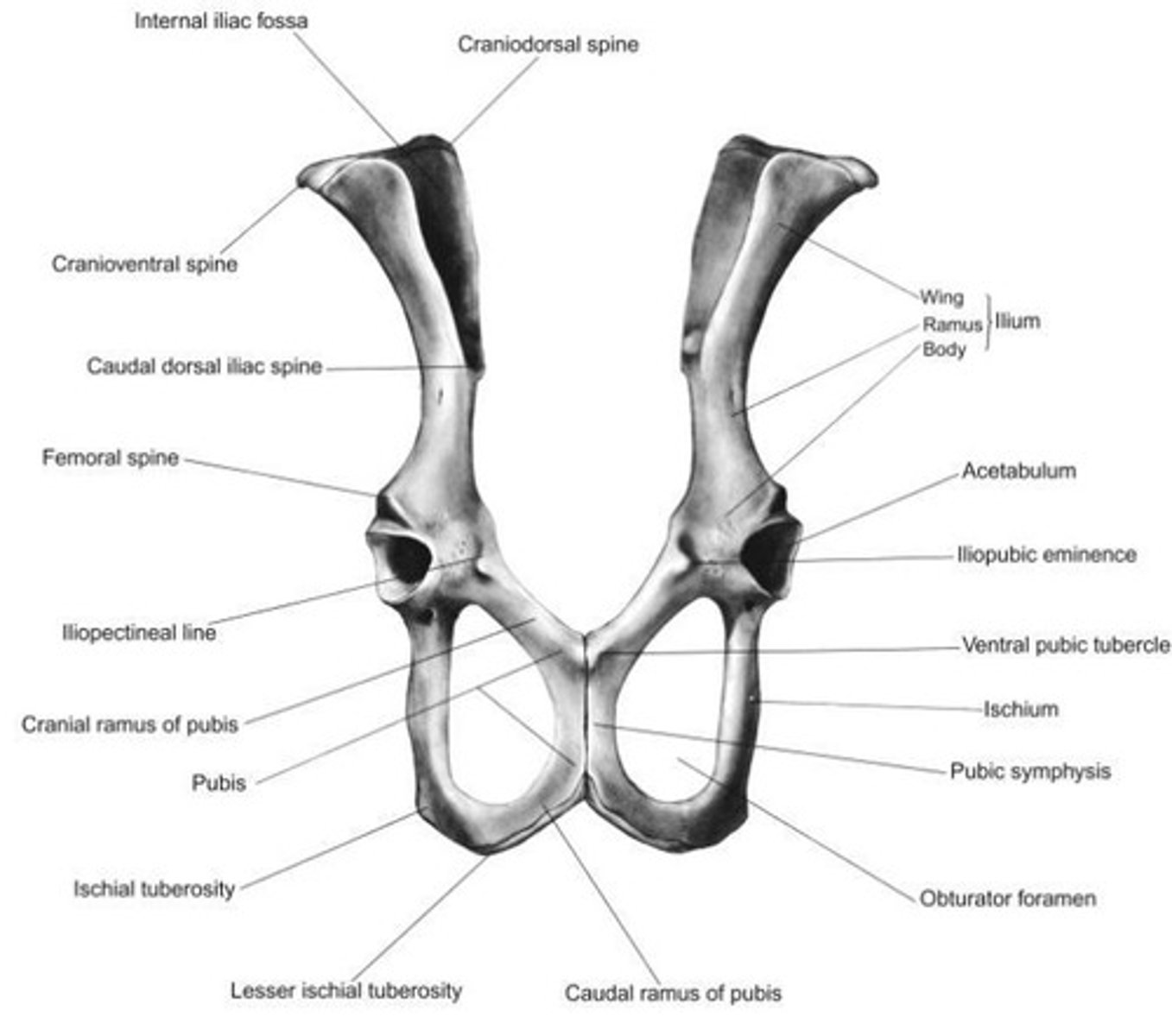
Acetabulum
The ___ is a deep, cotyloid cavity that forms the socket for the head of the femur in the hip joint.
Ilium
The ___ is the largest and most cranial of the bones that compose the os coxae, divided into a cranial wing and a narrow caudal body.
Iliac Crest
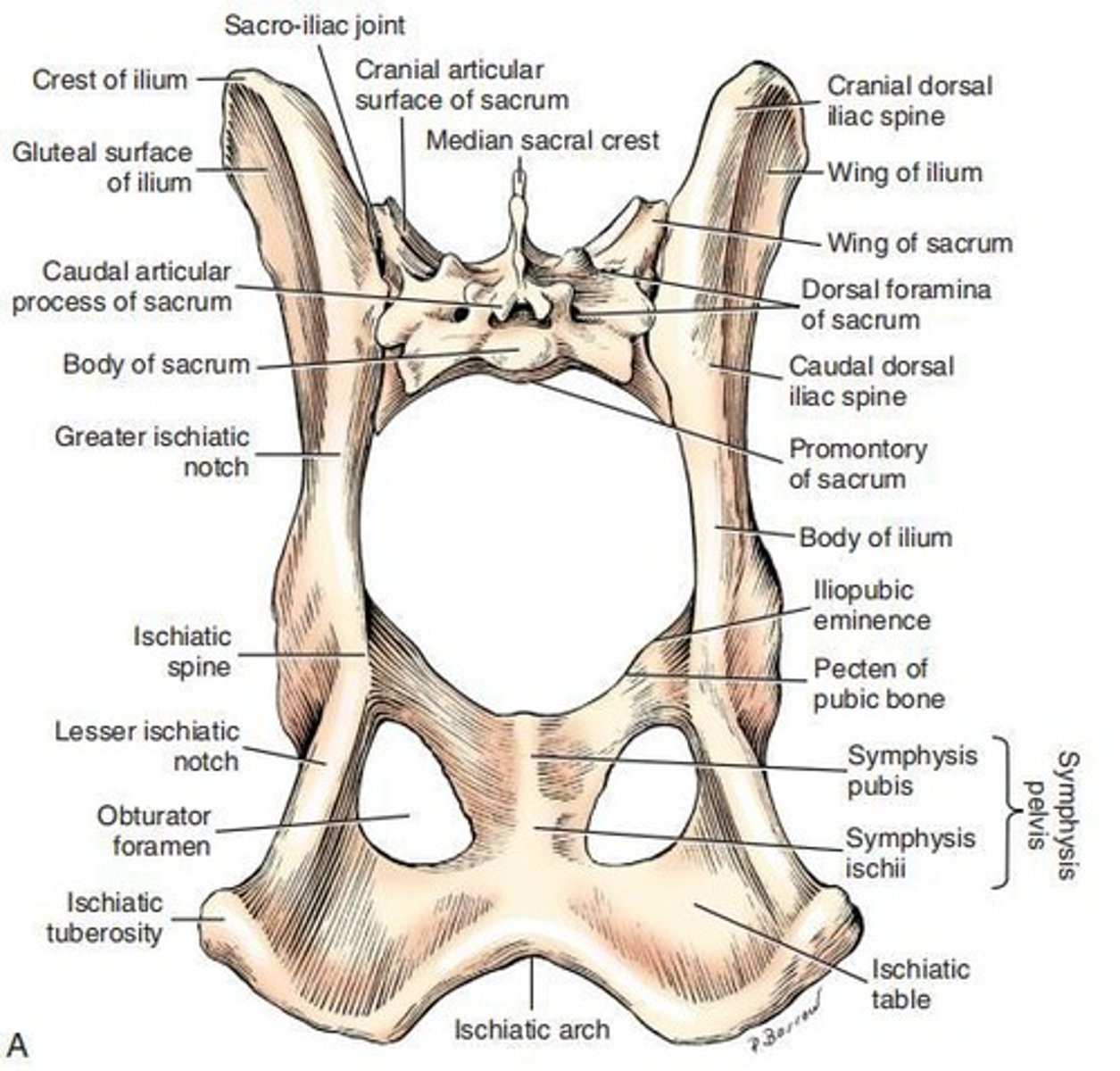
The ___ is composed of the tuber sacrale and tuber coxae and forms the cranial border of the ilium.
Ischium
The ____of a body, ramus, table, and tuberosity, forming the caudal third of the os coxae and contributing to the acetabulum, obturator foramen, and symphysis pelvis.
Ischiatic Spine
The ____ is formed by the thick dorsal border of the ischium, which continues with the dorsal border of the ilium.
Ischiatic Table
The ____ is the largest component of the ischium, continuous with the ramus of the ischium and forming part of the deep ischial arch.
Ischiatic Tuberosity
The ____ is the caudolateral part of the ischium, located caudolateral to the ischiatic table and lateral to the ischial arch.
Pubis
The ___ is a dorsoventrally compressed, curved bar of bone that extends from the ilium and ischium laterally to the symphysis pubis medially.
Cranial Ramus of Pubis
The ____ of the pubis fuses with the ilium and contributes to the formation of the acetabulum.
Caudal Ramus of Pubis
The ___ forms the medial border of the obturator foramen and fuses with the opposite side to form the symphysis pubis.
Ventral Pubic Tubercle
The ___ is located on the cranioventral surface of the pubis adjacent to the pubic symphysis.
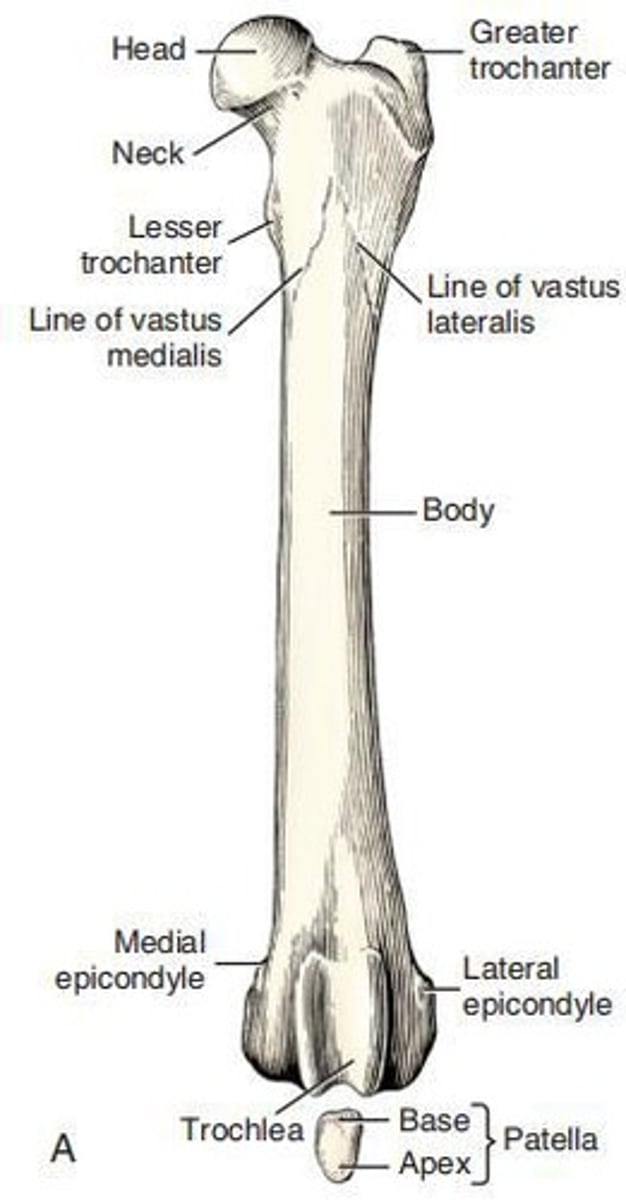
Femur
The ___ is the heaviest bone in the skeleton, slightly shorter than the tibia and ulna in well-proportioned breeds, but about one-fifth longer than the humerus.
Proximal End of Femur
The ___ consists of a head, neck, and two processes or trochanters.
Tarsus
The ____ is one of the bones of the pelvic limb, specifically numbered as 6.
Metatarsus
The ___ is one of the bones of the pelvic limb, specifically numbered as 7.
Sesamoid Bones of the Stifle Joint
The ___ are one of the bones of the pelvic limb, specifically numbered as 3.
Phalanges
The ___ are one of the bones of the pelvic limb, specifically numbered as 8.
Tibia
The ___ is one of the bones of the pelvic limb, specifically numbered as 4.
Fibula
The ___ is one of the bones of the pelvic limb, specifically numbered as 5.
Sesamoid Bone
The ___ is one of the bones of the pelvic limb, specifically numbered as 9.
Greater Trochanter
The largest tuber of the proximal extremity of the femur, located directly lateral to the head and neck.
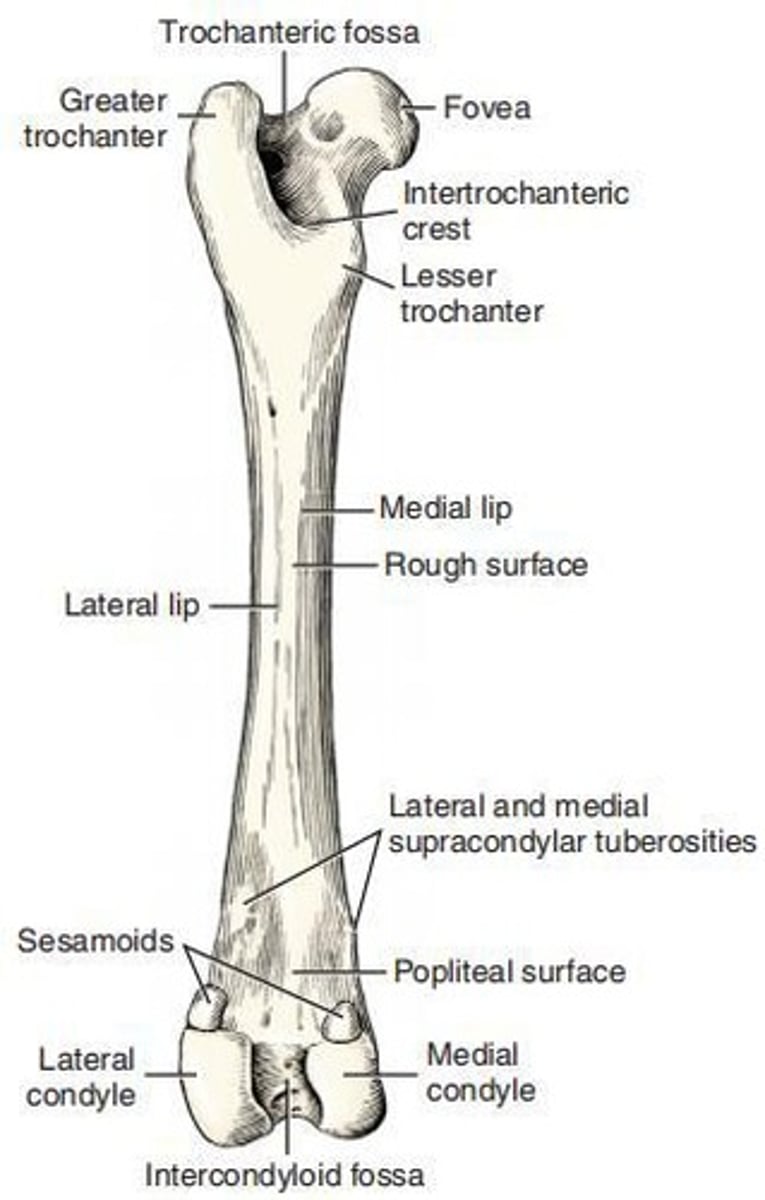
Lesser Trochanter
A distinct, pyramid-shaped eminence that projects from the caudomedial surface of the proximal extremity near its junction with the body of the femur.
Third Trochanter
A small lateral eminence of the proximal body of the femur approximately 2 cm distal to the apex of the greater trochanter at approximately the same level as the lesser trochanter.
Lateral Condyle
A convex structure of the femur in both the sagittal and the transverse planes.
Medial Condyle
A smaller and less convex structure of the femur in both the transverse and the sagittal planes.
Femoral Trochlea
The smooth, wide articular groove on the cranial surface of the distal extremity of the femur that is continuous with the articular surfaces of the condyles.
Patella
The largest sesamoid bone in the body, ovate in shape and curved to articulate with the trochlear of the femur.
Base of Patella
The blunt proximal end of the patella that may extend beyond the adjacent articular surface.
Apex of Patella
The distally located pointed end of the patella that does not extend beyond the articular surface.
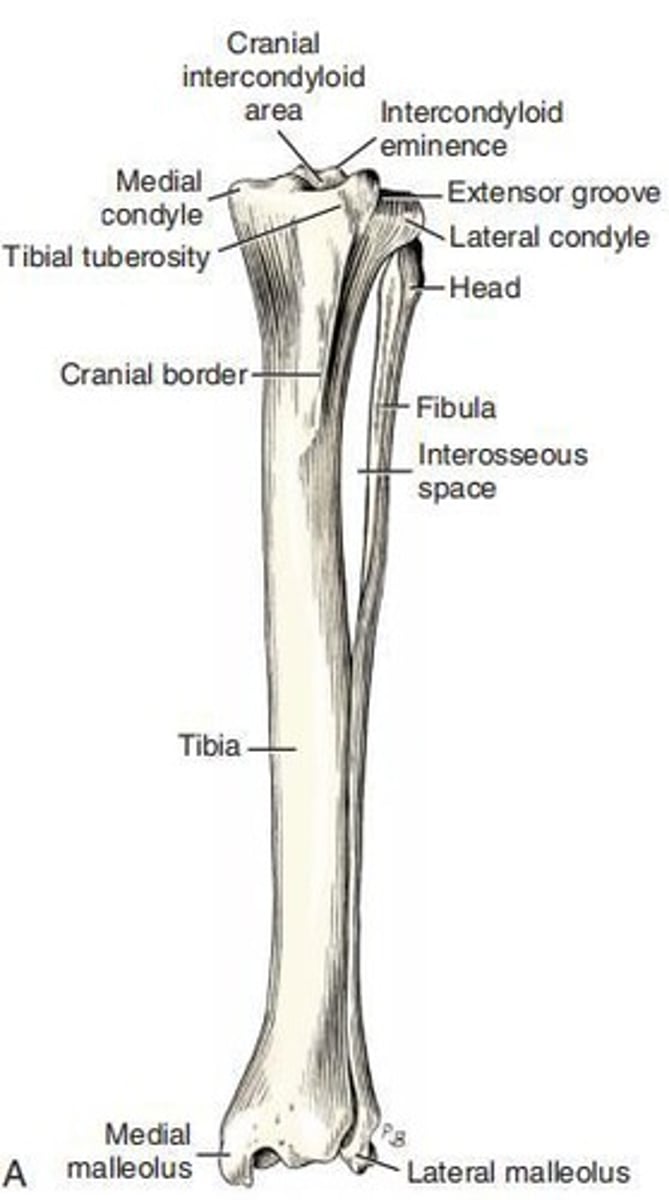
Intercondylar Eminence
A structure for ligamentous attachments that lies between the condyles of the tibia.
Extensor Groove
A smaller notch that cuts into the lateral condyle of the tibia as far as the articular surface.
Tibial Tuberosity
The large, quadrangular, proximocranial process of the tibia that provides insertion for the m. quadriceps femoris and parts of the mm. biceps femoris and sartorius.
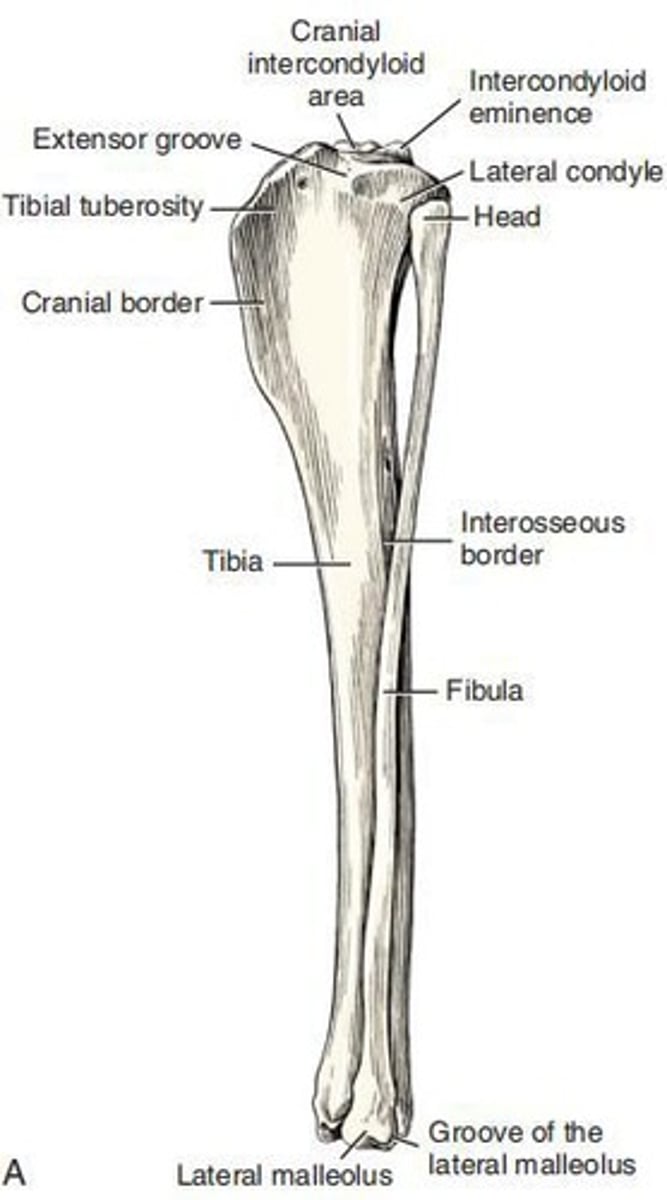
Head of Fibula
The flattened transversely expanded part of the fibula that is beyond the planes through the borders of the body.
Body of Fibula
The slender and irregular part of the fibula.
Cranial Margin of Fibula
The interosseous border of the fibula.
Lateral malleolus
The distal end of the fibula.
Articular surface
The surface that articulates with the distal lateral surface of the tibia, the lateral surface of the trochlea of the talus, and the craniolateral surface of the calcaneus.
Hindpaw
The skeleton of the ___ (pes) is composed of the tarsal and metatarsal bones, the phalanges, and the sesamoid bones associated with the phalanges.
Talus
The second largest of the tarsal bones that articulates proximally with the tibia and fibula, distally with the central tarsal, and on the plantar side with the calcaneus.
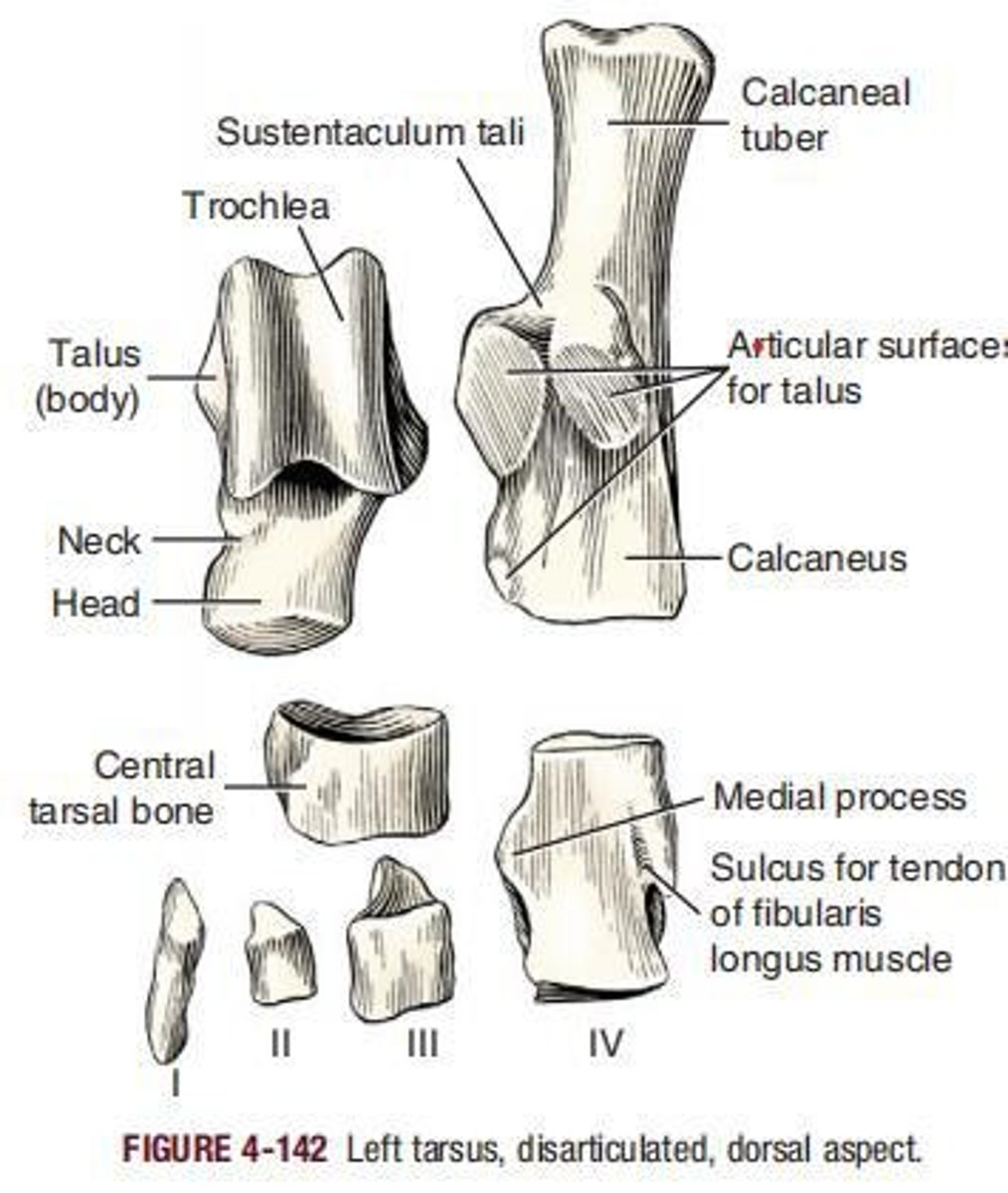
Calcaneus
The largest and longest bone of the tarsus, formerly called the os calcis or fibular tarsal bone.
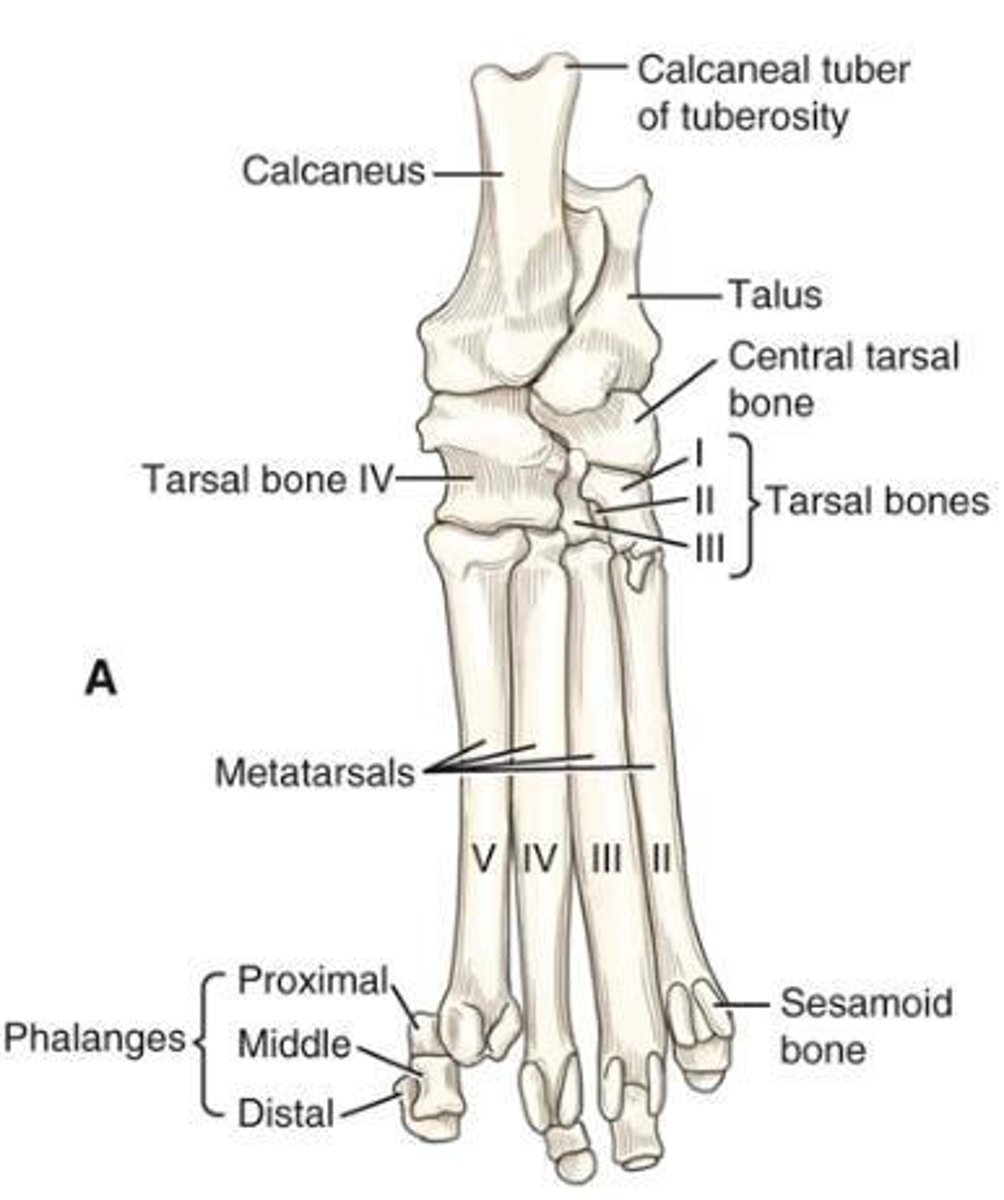
Central tarsal bone
(os tarsi centrale) lies in the medial part of the tarsus between the proximal and the distal rows.
First tarsal bone
Normally articulates with the central tarsal, the second tarsal, and the first metatarsal.
Second tarsal bone
The smallest of the tarsal bones, a wedge of bone that extends toward the plantar side only a short distance.
Third tarsal bone
Nearly three times larger and two times longer than the second tarsal bone.
Fourth tarsal bone
As long as the combined dimensions of the central and third tarsals, with which it articulates medially.
Metatarsal bones
The ___ resemble the corresponding metacarpal bones in general form, but are longer.
Shortest main metatarsal bone
Metatarsal II, which is about as long as the longest metacarpal bone.
First metatarsal bone
Usually atypical and will be described with the phalanges of the first digit.
Typical metatarsal bone
Consists of a proximal base, which is transversely compressed and irregular, and a shaft, or body, which in general is triangular proximally.
Distal end of each main metatarsal bone
Has a ball-shaped head (caput), separated from the body dorsally by a deep transverse sesamoid fossa (fossa sesamoidalis).
Dewclaw
The variably developed first digit of the hindpaw of the dog.