Adaptations for transport in plants
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What are the 3 theories of how water moves up the xylem
root pressure, cohesion-tension and adhesion
Root pressure theory
Endodermal cells actively transport ions into the xylem vessels, lowering the WP so water enters the xylem by osmosis. This creates hydrostatic pressure that forces water up the stem.
Cohesion-tension theory
Water evaporates from the spongy mesophyll into the air spaces and diffuses out the stomata down a WP gradient. This sets up a WP gradient across the leaf from a higher WP in the xylem to a lower WP in the air spaces.
Adhesion theory
Xylem vessels are very narrow and have a hydrophilic lining. Water molecules are strongly attracted and adhere to these walls, causing water to move up the vessel by capillarity.
what are the 3 pathways that water takes across cells
apoplast, symplast and vacuolar
apoplast pathway
water is transported inbetween cell walls and the spaces between cells
symplast pathway
water is transported between cytoplasms of adjacent cells via the plasmodesmata
vacuolar pathway
water is transported between the vacuoles of adjacent cells
Adaptations of the phloem
parenchyma and fibres provide structural support
plasmodesmata between sieve tubule and companion cell (un)loading of solutes
sieve pores allow phloem sap to flow between sieve tube elements
What 4 types of cell are phloem made up of
sieve tube elements, companion cells, fibres and parenchyma
Adaptations of the xylem
waterproofed strengthened wall by lignin
fibres and parenchyma provide structural support
no cell contents so little resistance to water flow
What 4 types of cell are xylem made up of
vessels, tracheids, fibres and parenchyma
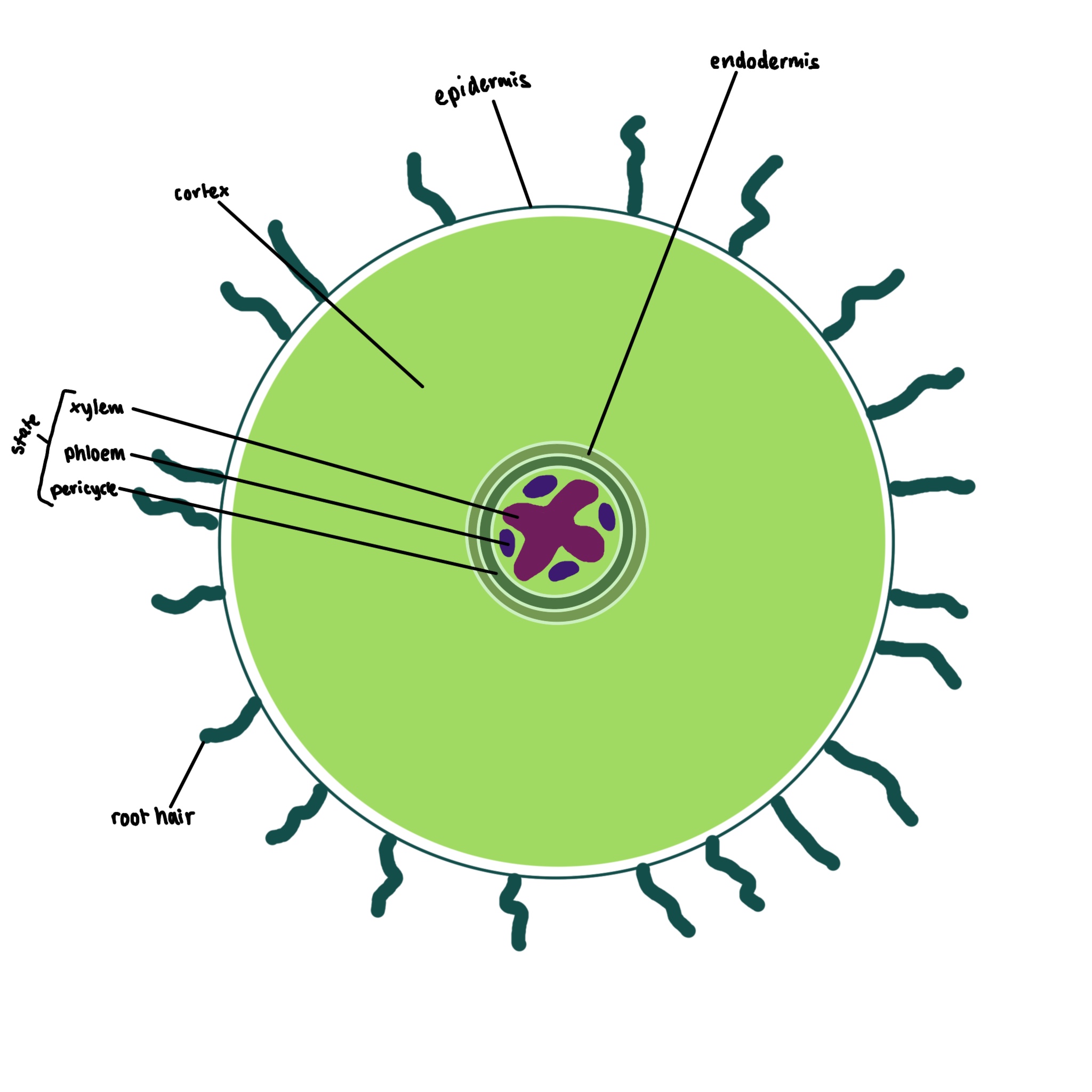
What type of cell is this
root
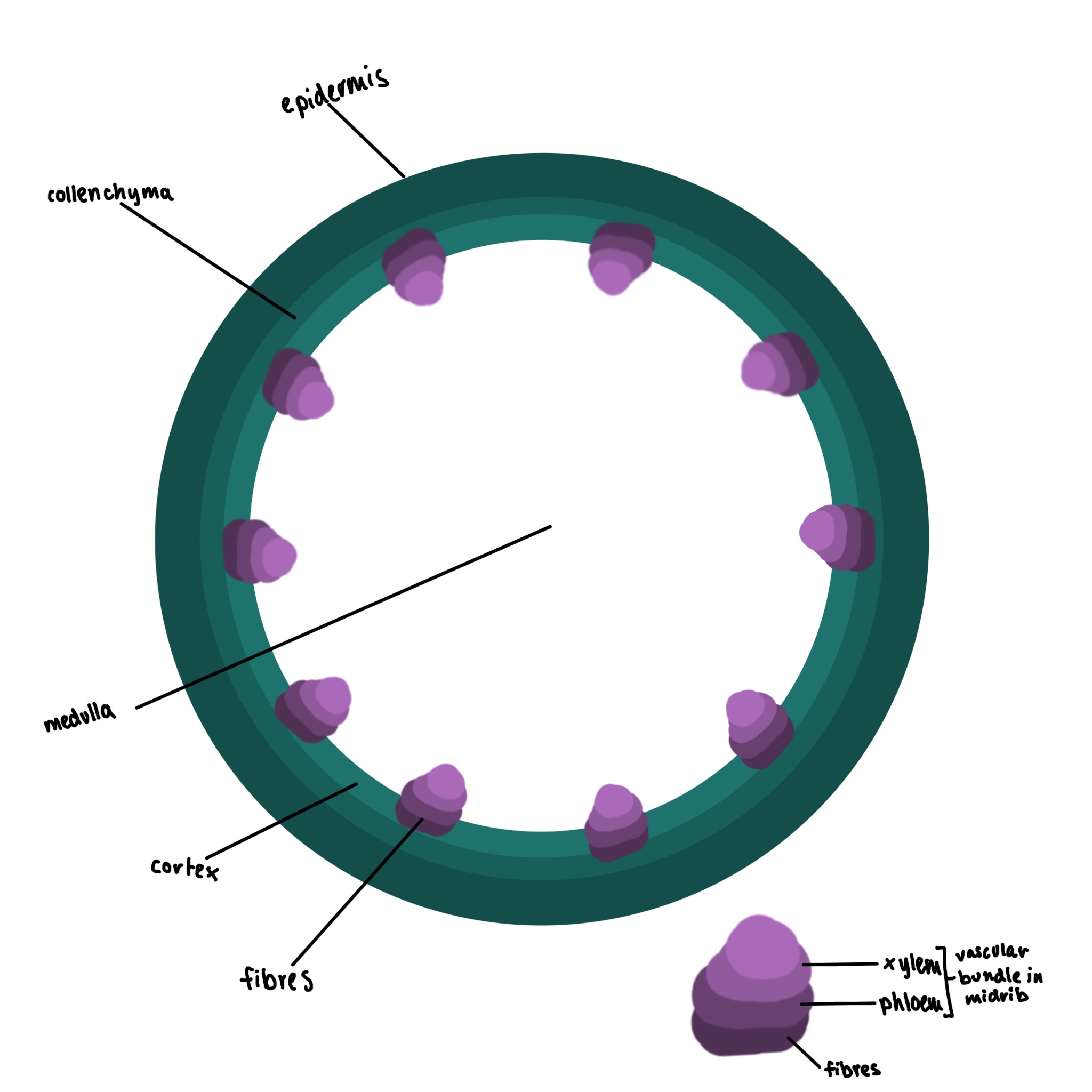
What type of cell is this
stem
what is the pericycle
contains the vascular tissues xylem and phloem
what examples of organic solutes does the phloem transport
sucrose, amino acids
What is the evidence for translocation
sucrose is transported in the phloem, sucrose is transported bi-directionally through the stem, the rate of transpiration is faster than diffusion
Mass flow theory
translocation of solutes through phloem due to differences in hydrostatic pressure. It suggests that translocation is a passive process however the presence of large numbers of mitochondria in companion cells and translocation having only been observed in living tissue imply that translocation is partly active and used ATP
what is the pressure flow hypothesis
suggests that translocation involves a combination of active transport and mass flow, it takes place in three stages.
1st stage of pressure flow
photosynthesis in leaf produced glucose, converted to sucrose. Sucrose actively transported from leaf into phloem sieve tubes. Loading carried out by companion cells which contain many mitochondria.
2nd stage of pressure flow
presence of sucrose in sieve tube lowers WP, causing water to enter the phloem from the xylem by osmosis. As hydrostatic pressure in the phloem sieve tube increases, mass flow occurs and sap moves through phloem. Pores in sieve plates allow large molecules to pass through, enabling unrestricted mass flow.
3rd stage of mass flow
sucrose at sinks is actively transported out phloem and either converted to stored starch or respired glucose. Loss of sucrose from phloem increases WP causing water to pass out phloem, reducing hydrostatic pressure and maintaining the pressure gradient from source to sink.
What is a criticism of the pressure flow theory
substances cannot flow in opposite directions in the same sieve tube. However they can flow in opposite directions in different sieve tubes.
Cytoplasmic streaming
in individual sieve tube elements, the cytoplasm circulates around the cell. Solutes may then be actively transported across the sieve plate, either upwards or downwards.
In the potometer practical, what steps are important in setting up
cut shoots under water so the transpiration stream isn’t disrupted, seal the bung with vaseline, ensure air bubble is at the end of the capillary tube.
In the potometer practical, what measurements need to be made
distance air bubble moves along capillary tube, diameter of capillary tube and time
What factors affect transpiration
temperature, humidity, wind speed and light intensity