AP Psych Unit 3 - Sensation & Perception
1/144
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
Psychophysics
the study of how environmental energy can cause a change in emotion and behavior
Reception (step 1 of sensation)
absorption of environmental stimuli (energy) with sensory receptors (eyes, ears, etc.)
Transduction (step 2 of sensation)
physically converting environmental stimuli/energy into neural inpulses
Transmission (step 3 of sensation)
the process of relaying neural impulses to the brain via sensory neurons
Selection (step 1 of perception)
(in hindbrain) the process of filtering the neural impulses via the Reticular Formation
Coding (step 2 of perception)
(in midbrain) organizing stimuli & relaying filtered stimuli to cerebral cortex
Interpretation (step 3 of perception)
(in forebrain) comprehension, analysis, and evaluation of stimuli
Bottom-Up Processing
Thick slicing
sensing something before you are able to perceive it
only method children use to perceive world
Top-Down Processing
Thin slicing
cognitive assumptions (expectations based upon experiences & perceptual memory)
perceiving something first, then being able to sense it
Our conscious mind can process…
40-50 bits per second
Our unconscious mind can process…
11 million bits per second
If there was no natural stimuli filter…
sensory overload
inability to focus
delayed physical reactions
cognitive delay
psychosis
Sensory reduction
minimizing the amount of energy absorption at the sensory level
Sensory adaptation
cognitive filtering and adaptation when incoming sensory messages within an environment remain constant & mundane; desensitization within afferent neurons
picking and choosing selection at hind brain level
Habituation
cognitive filtering when exposed to repeated stimuli over extended periods of time; learning to desensitize due to constant exposure
learned from experience
Absolute threshold
the lowest limit of stimulus energy that can be physically detected with +50% accuracy
Difference threshold
the measurement of a stimulus’ lowest amount of detectable change of intensity
Weber’s law
states that the just noticeable difference between two stimuli is a constant proportion of the intensity of the original stimulus
Ex. you would need to add 10 pounds to feel a difference between a 100 pound weight rather than adding 1 pound to feel a difference from a 10 pound weight
Signal detection
consciously adjusting thresholds to become sensitive to specific signals; consciously selecting what signals to pay attention to will accelerate response time
Analgesia
the general inability to experience physical pain
Biological & cognitive purposes of pain…
acts as a warning that something has gone wrong in the body
learning mechanism, to promote avoidance behavior to ensure species survival
Nociceptor cells
specialized pain receptor cells; specialized afferent neurons
Substance P
the neurotransmitter responsible for pain sensation
Endorphins
the body’s natural painkillers
Gate control theory of pain
a mechanism, in the spinal cord, in which pain signals can be sent up to the brain to be processed to accentuate the possible perceived pain, or attenuate it at the spinal cord itself
Anticipatory pain
fear and anxiety preceding physical injury; top-down processing
Phantom pain (illusory pain)
false perceptions of pain typically related to limbs / body parts that have been amputated
Sympathy pain
perceiving pain that has been experienced by other people
Wavelength (vision)
horizontal distanced between a wave (light)
1 cycle = measurement from crest to crest
Spectrum of visible light
380nm-750nm / 430 Thz - 790 Thz
Frequency (vision)
the number of wavelength cycles that pass through a fixed point per second (vision)
Hue
colors or shades
Low frequency wavelengths (vision)
wavelengths that produce red color (~430Thz)
Infrared waves
light wave frequencies < 430Thz (~1mm-750nm); too low of frequency for human detection
High frequency wavelengths (vision)
wavelengths that produce the color violet (max ~790Thz)
Ultraviolet waves
light wave frequencies > 790Thz (~380-350nm); too high frequency for human detection
Amplitude (vision)
the vertical height of the wave that measures the energy intensity within the wave; provides brightness/darkness or dullness of a color
low = darker; high = brighter
Saturation
the intensity of the hue
Eye lid
the external protective shield of the eye that blocks debris and light, and cleans/moisturizes the eye
Cornea
internal shield of the eye
very sensitive
reflects light waves
highest concentration of nerve endings
Pupil
an adjustable tunnel through which light enters the eye
Iris
the colored, donut shaped muscle that regulates the pupil’s diameter; sensitive to amplitude of light wave; melanin protects the retina
Lens
the flexible, transparent disk that focuses light waves onto retina; contour of shape is adjusted by ciliary muscles
Vitreous humor
a clear, gelatinous fluid that fills the ocular chamber to prepare the eye’s spherical shape
Aqueous humor
a clear, gelatinous fluid between the cornea and iris
Retina
projection screen of the lens; transduces light waves into neural impulses
Rods
~120 million per eye; concentrated in the outer rims of the retina
peripheral vision
twilight vision
shades of grey
sensitive to low amplitude
Cones
~6 million per eye; concentrated in inner core of retina
color detection
acuity (fine detail)
sensitive to high amplitude
3rd layer of retina
Macula
center of retina
contains the highest concentration of cone photoreceptors
Fovea
the centermost place of the macula (ideal focal point)
Optic nerve
the nerve connecting the retina to the reticular formation; transmits neural impulses to the brain
Blind spot
the place on the retina where the optic nerve is attached and can’t see light
Sclera
the outer membrane of the eye where ocular muscles & blood vessels are attached
Visual accommodation
the ability of the lens to change the contour of it’s shape to allow focus far and near
ciliary muscles relax, allowing the lens to stretch/flatten for far distance focus
contraction causes lens to thicken/round for short range focus
How eyes see with limited light…
Iris muscles contract causing pupil openings to dilate
Photoreceptor sensitivity transfers from the cones to rods
Presbyopia
transitional blindness
inability for the lens to accommodate rapidly as it ages and loses flexibility
Myopia (nearsightedness)
visual impairment at a distance (far things are blurred)
image is focused at a point in front of the retina
Hyperopia (farsightedness)
inability to focus images at a close range (troubling seeing things up close)
image is focused beyond/behind the retina
Astigmatism
misshaped eye (cornea)
creates multiple focal points causing visual impairment
Feature detection
the process by which the brain breaks down complex stimuli into specific visual features, such as color, shape, motion, and edges
Selective Attention (Cocktail party phenomenon)
perceptual ability to consciously identify/isolate a single stimuli among a complex mixture of environmental information
Inattentional blindness
failure to detect features within the environment when trying to maintain concentrated focus on a selected stimuli
Change blindness
perceptual phenomenon that occurs when a change in visual stimulus is introduced and the observer is unable to notice it
Illusions
sensory misperceptions that result when cognitive assumptions are proven wrong
Form perception
type of top-down processing strategy that quickly provides the perception of an image based upon it’s relationship between the figure & ground
Figure-ground illusion
misperceptions resulting when distinctions between an image’s figure and ground become blurred
Reversible figure illusions
1 picture that contains 2 images depending on which you perceive as the figure and ground
Closure illusions
perceptual tendency to complete or finish an image when the figure & ground are indistinguishable
Impossible figure illusions
images of objects impossible to construct or design because of laws of physics
Perceptual adaptation
top down ability to adjust to images when presented in a distorted, obstructed, or incomplete view
Perceptual set illusions
perceptual adaptation illusions resulting when our cognitive assumptions are proven wrong when top-down processing an image in a distorted view compared to when processed bottom-up
Thatcher effect
perceptual set illusion involving distorted view of a person’s face
Frame of reference perception
values of an image are perceived based upon how they relate to a frame of reference
Perceptual constancy illusions
despite having equal/constant values, the perceived traits appear to change relative to different frames of reference
size, shape, and color/brightness constancy illusions
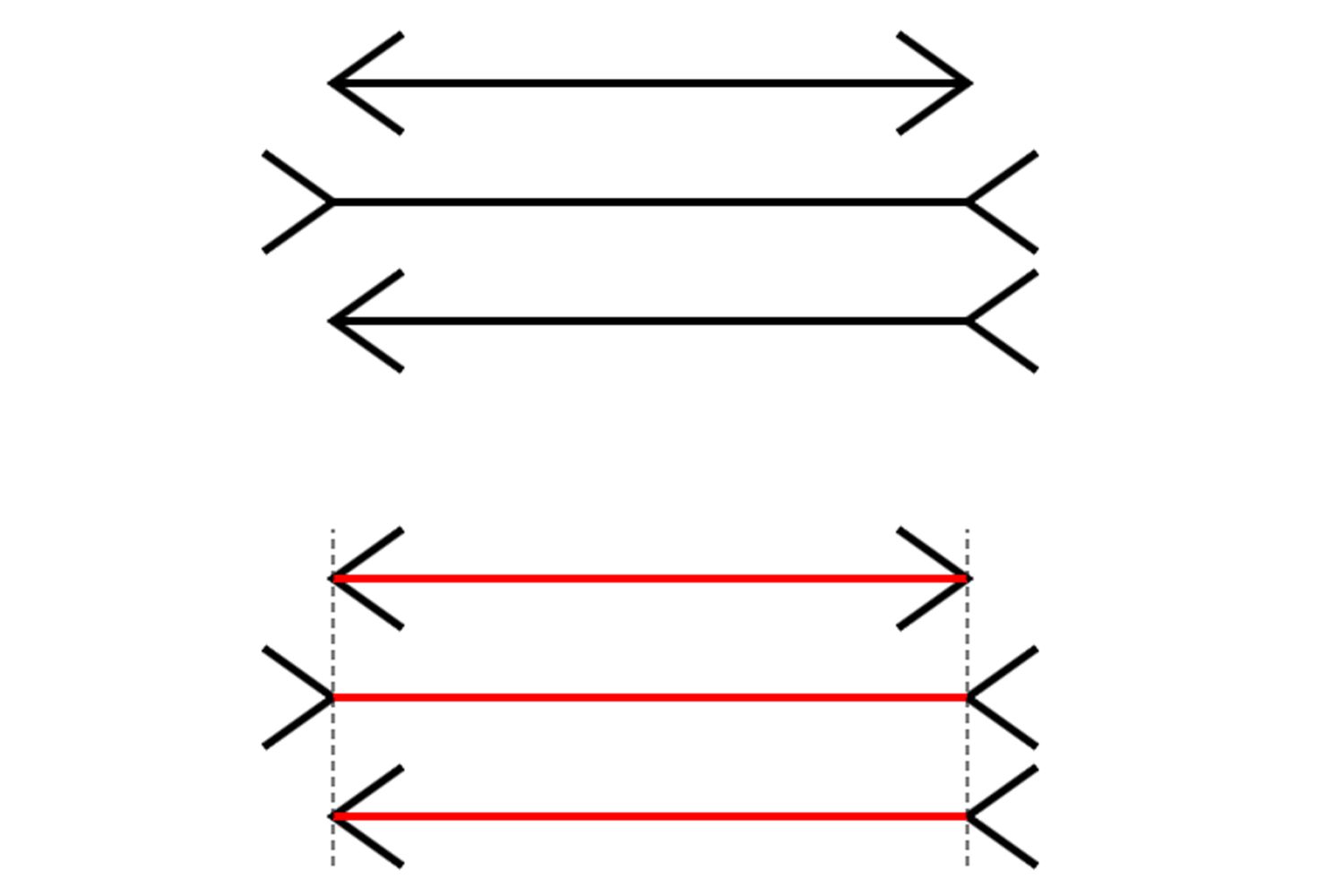
Muller-Lyer Illusion
an example of a size constancy illusion
Parallel processing
the ability of the brain (angular gyrus) to cognitively multitask & process dual functions required by multiple brain structures simultaneously
Perceptual interference illusions
disruptions, delays, & processing failure resulting from conflicts when processing multiple cognitive tasks simultaneously
The Stroop Effect
interference resulting when a singular task requires the use of both cerebral hemispheres simultaneously

The Phi Phenomenon
perceptual illusion of motion caused when stationary images or pulses of light are presented in alternating, rapid succession & are unable to be perceived individually
After image illusions
the residual phantom appearance of an image that temporarily persists after prolonged exposure or because of bad color contrast
Maximum amount of colors and shades of hue that the human color-vision system can detect
~7 million colors/hues
Color blindness
genetic defect affecting the sensitivity of the cones
Monochromatic (can only see grey)
Dichromatic (unable to distinguish two colors)
V1 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (V1 LGN)
feature detector in occipital lobe
responsible for the perception of color
Ganglion cells
(1st layer of retina) sensory neurons sensitive to specific frequencies for color detection
Bipolar cells
(2nd layer of retina) sensory neurons that connect photoreceptors to ganglion cells
Opponent Process Theory of Color
Bipolar cells are responsible for detecting colors in opposite pairs; when sensing frequencies of 1 color for prolonged periods of time, the other colors overcompensate
Trichromatic theory
says that cone receptors come in red, green, & blue; each is sensitive to specific light frequency
Depth perception
the ability to gauge approximate size, distance, and relative motion of objects within a 3D space
Linear perspective
monocular cue
visual appearance of parallel lines converging as they reach a point in distance
Interposition
monocular cue
depth cue caused when multiple objects overlap, creating an appearance of relative distance or order of position
Motion parallax
monocular cue
depth perception cue while in motion
perception of motion is based upon planes of depth
objects near appear to travel faster than objects far away
Retinal disparity
binocular cue
measurement between pupils
provides the brain with horizontal span of distance needed to triangulate depth
Visual convergence
binocular cue
ocular muscles angle inward to focus on near objects, causing the line of sight in both eyes to converge
provides information the brain needs to triangulate vertical distances
Ames room illusion
example of an illusion that limits stereoscopic vision because it eliminates binocular cues
Wavelength & Frequencies (audition)
measured as vibrations per second
as wavelength decreases, frequency increases
Long wavelengths (audition)
low frequency, low pitch sound
min threshold ~20 Hz
Short wavelengths (audition)
high frequency, high pitch sound
max threshold ~20,000 Hz
Amplitude (audition)
vertical height of a wave
provides volume of a sound
measurement of energy intensity within the wave
Range (tone)
the complexity of a sound when mixed with multiple waves of various frequencies and amplitudes
Timbre
quality/clarity of a sound