Chapter 30: Atomic Physics
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
angular momentum quantum number
a quantum number associated with the angular momentum of electrons
atom
basic unit of matter, which consists of a central, positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons
atomic de-excitation
process by which an atom transfers from an excited electronic state back to the ground state electronic configuration; often occurs by emission of a photon
atomic excitation
a state in which an atom or ion acquires the necessary energy to promote one or more of its electrons to electronic states higher in energy than their ground state
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Bohr radius
the mean radius of the orbit of an electron around the nucleus of a hydrogen atom in its ground state
Brownian motion
the continuous random movement of particles of matter suspended in a liquid or gas
cathode-ray tube
a vacuum tube containing a source of electrons and a screen to view images
double-slit interference
an experiment in which waves or particles from a single source impinge upon two slits so that the resulting interference pattern may be observed
energies of hydrogen-like atoms
Bohr formula for energies of electron states in hydrogen-like atoms: 𝐸𝑛=−𝑍2𝑛2𝐸0(𝑛=1,2,3,…)
energy-level diagram
a diagram used to analyze the energy level of electrons in the orbits of an atom
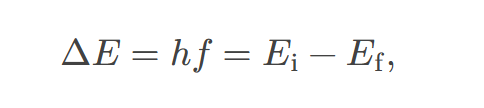
fine structure
the splitting of spectral lines of the hydrogen spectrum when the spectral lines are examined at very high resolution
fluorescence
any process in which an atom or molecule, excited by a photon of a given energy, de-excites by emission of a lower-energy photon
hologram
means entire picture (from the Greek word holo, as in holistic), because the image produced is three dimensional
holography
the process of producing holograms
hydrogen spectrum wavelengths
the wavelengths of visible light from hydrogen; can be calculated by 1𝜆=𝑅(1𝑛2f−1𝑛2i)
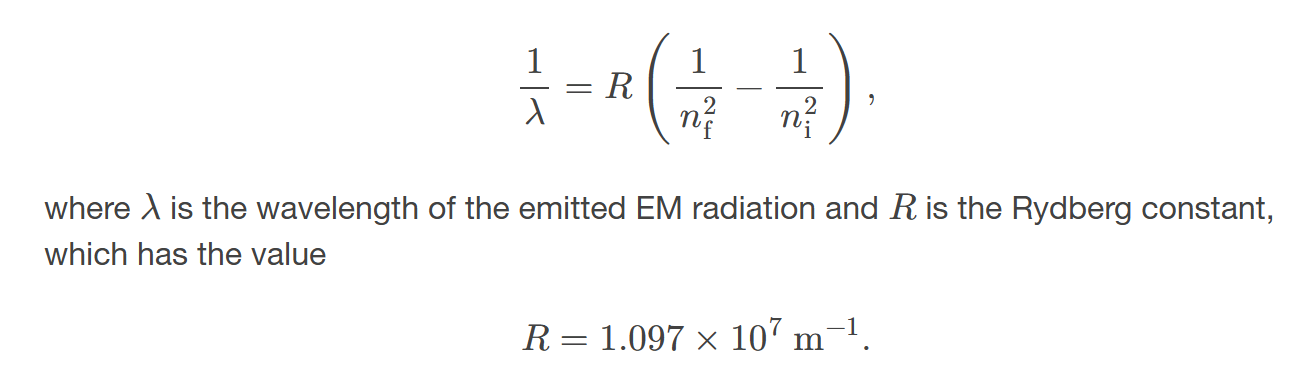
hydrogen-like atom
any atom with only a single electron
intrinsic magnetic field
the magnetic field generated due to the intrinsic spin of electrons
intrinsic spin
the internal or intrinsic angular momentum of electrons
laser
acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation
magnitude of the intrinsic (internal) spin angular momentum
given by 𝑆=√𝑠(𝑠+1)ℎ2π
metastable
a state whose lifetime is an order of magnitude longer than the most short-lived states
orbital angular momentum
an angular momentum that corresponds to the quantum analog of classical angular momentum
orbital magnetic field
the magnetic field generated due to the orbital motion of electrons
Pauli exclusion principle
a principle that states that no two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers; that is, no two electrons can be in the same state
phosphorescence
the de-excitation of a metastable state
planetary model of the atom
the most familiar model or illustration of the structure of the atom
population inversion
the condition in which the majority of atoms in a sample are in a metastable state
quantum numbers
the values of quantized entities, such as energy and angular momentum
Rydberg Constant
a physical constant related to the atomic spectra with an established value of 1.097×107m−1
shell
a probability cloud for electrons that has a single principal quantum number
space quantization
the fact that the orbital angular momentum can have only certain directions
spin projection quantum number
quantum number that can be used to calculate the intrinsic electron angular momentum along the 𝑧-axis
spin quantum number
the quantum number that parameterizes the intrinsic angular momentum (or spin angular momentum, or simply spin) of a given particle
stimulated emission
emission by atom or molecule in which an excited state is stimulated to decay, most readily caused by a photon of the same energy that is necessary to excite the state
subshell
the probability cloud for electrons that has a single angular momentum quantum number 𝑙
x rays
a form of electromagnetic radiation
x-ray diffraction
a technique that provides the detailed information about crystallographic structure of natural and manufactured materials
z-component of spin angular momentum
component of intrinsic electron spin along the 𝑧-axis
z-component of the angular momentum
component of orbital angular momentum of electron along the 𝑧-axis
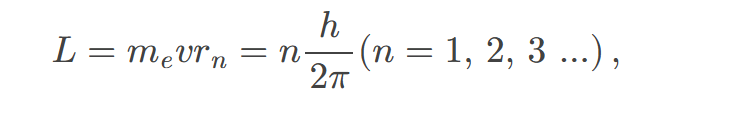
Zeeman effect
the effect of external magnetic fields on spectral lines
All electrons are identical and have a charge-to-mass ratio of
approximately 1.76 x 10^11 coulombs per kg.
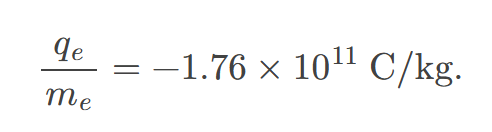
The positive charge in the nuclei is carried by particles called protons, which have a charge-to-mass ratio of
approximately 9.58 x 10^7 coulombs per kg.
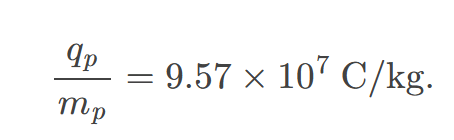
Mass of electron
approximately 9.11 x 10^-31 kg
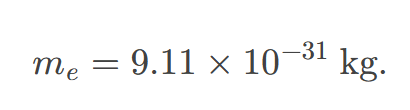
Mass of proton
approximately 1.67 x 10^-27 kg
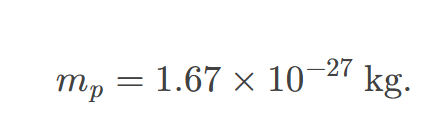
For all one-electron (hydrogen-like) atoms, the radius of an orbit
is given by the formula r = n²a₀, where n is the principal quantum number and a₀ is the Bohr radius.

energies of hydrogen-like atoms
are quantized and given by the formula E = -13.6 eV/n², where n is the principal quantum number.
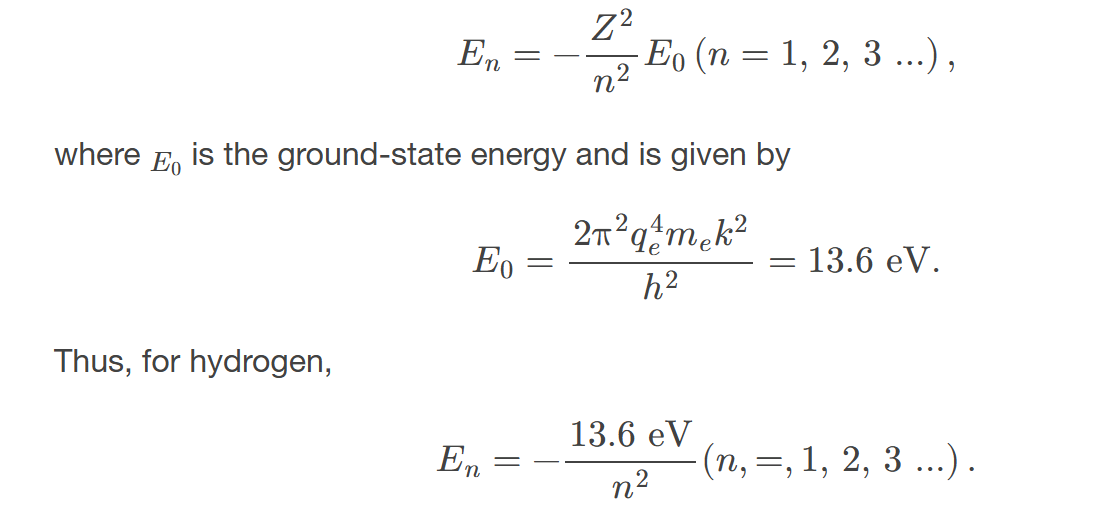
The maximum number of electrons that can be in a subshell is
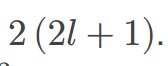
The maximum number of electrons that can be in a shell
2n², where n is the principal quantum number.