3.5 Newton’s Laws of Motion and Momentum
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Define Newton’s first law of motion
An object will remain at rest or in motion at constant velocity unless acted upon by a resultant force.
Define Newton’s second law of motion
The resultant force acting on an object is directly proportional to the rate of change of its momentum, and is in the same direction.
F ∝ (∆p) ÷ (∆t) → F = (∆p) ÷ (∆t)
What law is net force ∝ rate of change of momentum?
Newtons second law
F = (∆p) ÷ (∆t)
F = ma is a special case of which equation?
F = (∆p) ÷ (∆t)
Define Newton’s third law of motion
When two objects interact, they exert equal and opposite forces on each other
What are the four fundamental forces?
gravitational
electromagnetic
strong nuclear
weak nuclear
What is the equation for momentum?
momentum = mass x velocity
p = m v
What is the SI unit for momentum?
kgms^-1
Is momentum a vector or scalar quantity?
vector
As product of scalar (mass) and vector (velocity)
What is the principle of momentum?
The momentum before an even equals the momentum after the event.
The total momentum in a specified direction remains constant.
Investigating momentum
An air track is ideal as minimises friction, but can use trolleys and runway.
Velocity of object found using motion sensors/light gates + times/ruler + stopwatch. (v = s ÷ t)
use balance to find mass
momentum = mass x v
Define (perfectly) elastic collisions
Momentum, total energy and kinetic energy are all conserved
Define inelastic collisions
Momentum and total energy are conserved, but kinetic energy is NOT
Why is momentum conserved in collisions?
The net force acting in a closed system in 0
Due to 2nd law, ∆p of both objects = 0 so total p doesn’t change. Momentum is conserved.
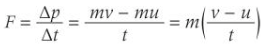
Define impulse
The product of force and the time for which this force acts on an object
impulse of force = change in momentum
∆p = F∆t
What is the equation for impulse?
∆p = F∆t
What is the unit of impulse
Ns or kgms^-1
What does the area under a force - time graph represent?
impulse or ∆p
What is conserved in collisions and interactions?
(linear) momentum