AP Human Geography- Unit 2 review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SLAYYYYYY
Last updated 11:25 PM on 5/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards
2
New cards
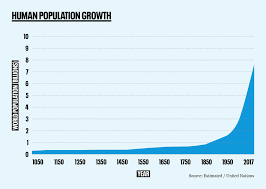
Natural Rate of Increase (NRI)
the percentage by which a population grows in a year
3
New cards
Formula for Natural Increase Rate
Number of births - Number of deaths = NIR
4
New cards
What is Doubling Time
the time it would take for a population to double at current natural growth rates
* formula: 70/NRI
* formula: 70/NRI
5
New cards
Economic factors that influence growth/decline
* economic boom
* economic bust
* job availability
* housing
* economic bust
* job availability
* housing
6
New cards
Political factors that influence growth/decline
* unstable governments
* war
* child policies
* war
* child policies
7
New cards
Environmental factors that influence growth/decline
* natural disasters
* drought
* disease
* famine
* drought
* disease
* famine
8
New cards
Cultural factors that influence growth/decline
* family traditions
* religion
* social norms
* religion
* social norms
9
New cards
Why are women’s childbearing years reduced in core countries?
* they rather establish their careers
10
New cards
Increases in (blank) for women may (blank) maternal & infant mortality rates.
“political power”, “decrease”
11
New cards
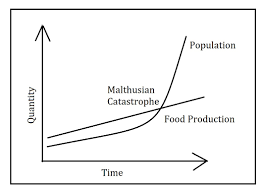
Thomas Mathus’ theory
* population grows exponentially, while food production grows arithmetically (overpopulation)
* he believed that the world was headed towards a population disaster because there was more people than food
* he believed that the world was headed towards a population disaster because there was more people than food
12
New cards
What checks did Malthus suggest in order to prevent a worldwide famine?
1) Positive Checks- external acts that will decrease population
2) Preventative Checks- internal actions that people/society can take
2) Preventative Checks- internal actions that people/society can take
13
New cards
Evidence that supports Malthus’ theory
* there has been a population explosion
* repeated wars & famines in Sahel region of Africa suggest population growth has outstripped food supply
* WHO says that more than 800 million people are chronically malnourished
* repeated wars & famines in Sahel region of Africa suggest population growth has outstripped food supply
* WHO says that more than 800 million people are chronically malnourished
14
New cards
Did his theory ever occur?/ What are the limitations?
NOOO!!!!
* ignored advances in agriculture/healthcare technology
* not useful at broader scale
* ignored advances in agriculture/healthcare technology
* not useful at broader scale
15
New cards
Neo-Malthusians
People in the 1960s whom began worrying about the population disaster
16
New cards
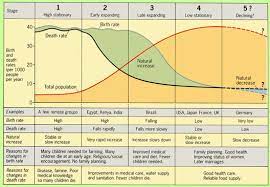
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
based on historical population trends of two demographic characteristics (birth/death rate) to suggest that a country’s total population growth rate cycles through states as that country develops economically
17
New cards
Limitations of DTM
* not all of a country progresses at the same rate
* it is based solely on the experience of Western Europe and may not be applicable to other parts of the world
* some critics feel it implies causes & effects that do not exist
* it is based solely on the experience of Western Europe and may not be applicable to other parts of the world
* some critics feel it implies causes & effects that do not exist
18
New cards
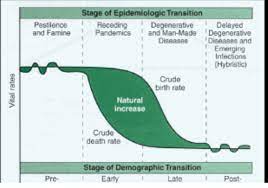
Epidemiological Transition Model (ETM)
describes changes in fertility, mortality, life expectancy, and population age distribution, largely as the result of changes in causes of death
19
New cards
Limitations of ETM
* focuses only on health-related factors, and almost exclusively on disease
* oversimplifies the causes and patterns of disease and mortality
* overlooks the role that poverty plays in determining disease risk & mortality
* does not address changes that are occurring in how people live
* it is unknown how human-caused environmental factors might affect the causes of mortality as described in the ETM
* oversimplifies the causes and patterns of disease and mortality
* overlooks the role that poverty plays in determining disease risk & mortality
* does not address changes that are occurring in how people live
* it is unknown how human-caused environmental factors might affect the causes of mortality as described in the ETM
20
New cards
Antinatalist
policies are designed to curb population growth by discouraging citizens from having children
Incentives:
* contraceptive education
* family planning support
* financial/social incentives
* restriction on family size
Countries:
* India
* Nigeria
* Rwanda
* China
Incentives:
* contraceptive education
* family planning support
* financial/social incentives
* restriction on family size
Countries:
* India
* Nigeria
* Rwanda
* China
21
New cards
Pronatalist
policies that encourage births and aim to accelerate population growth
Incentives:
* financial support
* free daycare
* cash money per child
* fully paid maternity/paternity leave
Countries:
* denmark
* singapore
* russia
* hungary
* japan
Incentives:
* financial support
* free daycare
* cash money per child
* fully paid maternity/paternity leave
Countries:
* denmark
* singapore
* russia
* hungary
* japan
22
New cards
China’s One Child Policy
* couples had to apply to have a child
* men could not marry until 22, women: 20
* having only one child would result in increased social benefits like money from the government, free food, and expended job opportunities
* having a second child could result in massive fines and a reduction in social benefits
* men and women could receive large sums of money for undergoing sterilizations. In the late 1980s, some sterilizations in rural areas were forced
* men could not marry until 22, women: 20
* having only one child would result in increased social benefits like money from the government, free food, and expended job opportunities
* having a second child could result in massive fines and a reduction in social benefits
* men and women could receive large sums of money for undergoing sterilizations. In the late 1980s, some sterilizations in rural areas were forced
23
New cards
Consequences of the One Child Policy
* population & birth rates declined significantly
* skewed sex ration that favored males to females. this led to sex selective abortions & the abandonment of millions of baby girls.
* upside down dependency ration. far too many elderly with few young to support them
* skewed sex ration that favored males to females. this led to sex selective abortions & the abandonment of millions of baby girls.
* upside down dependency ration. far too many elderly with few young to support them
24
New cards
Land degredation
long-term damage to the soil’s ability to support life
Examples:
* soil exhaustion
* soil erosion
* deforestation
Examples:
* soil exhaustion
* soil erosion
* deforestation
25
New cards
Social consequences of an aging population
* reduced crime rate
* larger need for doctors, nurses, hospitals and nursing homes
* younger generation forced to care for elders
* larger need for doctors, nurses, hospitals and nursing homes
* younger generation forced to care for elders
26
New cards
political consequences of an aging population
* more conservative voters
* elder care a top priority in votes
* elder care a top priority in votes
27
New cards
Environmental consequences of an aging population
* more public transportation usage
* parks needed
* parks needed
28
New cards
Economic consequences of an aging population
* less workers contributing to the economy
* high medical costs
* low/no growth
* high medical costs
* low/no growth
29
New cards
Mobility
a general term that refers to all types of movements
30
New cards
Circulation
movements that occur on a regular basis, like a daily commute to school/work
31
New cards
Human Migration
a permanent move to a new location
32
New cards
Emigration
E = exit: migration from a location
33
New cards
Immigration
I = into: migration to a location
34
New cards
Net Migration
the difference between the number of immigrants and emigrants in a location (IN-OUT)
35
New cards
Countries with Net-Out Migration
* asia
* latin america
* africa
* latin america
* africa
36
New cards
Countries with Net-In Migration
* north america
* europe
* oceania
* europe
* oceania
37
New cards
Ravenstein’s Laws of Migration
* Migration is typically over a short distance
* Migration occurs in steps, like from a rural area to a nearby city, and then perhaps on to a larger city
* Long-distance migrants often move to places of economic opportunity (urban areas)
* Migration occurs in steps, like from a rural area to a nearby city, and then perhaps on to a larger city
* Long-distance migrants often move to places of economic opportunity (urban areas)
38
New cards
What is the Gravity Model
* based on Ravenstein’s work & Newton’s law of universal gravitation
* It suggests that as the population of a city increases, migration to the city increases, and as the distance to a city grows, migration to that city decreases
* It suggests that as the population of a city increases, migration to the city increases, and as the distance to a city grows, migration to that city decreases
39
New cards
Push Factors
motivates migrants to leave their location of origin
40
New cards
Pull Factors
attracts migrants to a new location
41
New cards
Political Push Factors
* political persecution
* intolerance of dissent
* abuse of power by ruling parties
* open violence/conflict
* intolerance of dissent
* abuse of power by ruling parties
* open violence/conflict
42
New cards
Political Pull Factors
* peace
* greater freedoms from government oversight
* greater freedoms from government oversight
43
New cards
Economic Push Factors
* poor job prospects
* low wages
* weak national economy
* no opportunities for the highly skilled/educated
* low wages
* weak national economy
* no opportunities for the highly skilled/educated
44
New cards
Economic Pull Factors
* better employment opportunities
* high wages
* low unemployment
* strong national economy
* high wages
* low unemployment
* strong national economy
45
New cards
Cultural Push Factors
* religious persecution
* racial/ethnic/identity-based discrimination
* countries that limit female emigrants
* racial/ethnic/identity-based discrimination
* countries that limit female emigrants
46
New cards
Cultural Pull Factors
* freedom of religion
* racial/ethnic/identity recognition
* fair emigration
* racial/ethnic/identity recognition
* fair emigration
47
New cards
Demographic Push factors
* overpopulation
* lack of access to needed services
* lack of access to needed services
48
New cards
Demographic Pull Factors
* imbalance in gender ratio (ability to find a spouse)
* low population
* low population
49
New cards
Environmental Push factors
* drought
* flooding
* crop failures
* flooding
* crop failures
50
New cards
Environmental Pull factors
* desirable climate
* fertile soil
* flat land
* fertile soil
* flat land
51
New cards
International Migration
permanent move from one country to another
52
New cards
What is the biggest reason for voluntary migration?
Economic reasons
53
New cards
What is the biggest reason for forced migration?
war, oppression, or natural disasters
54
New cards
Internal Migration
permanent move within the same country
55
New cards
Interregional Migration
Movement between regions of a country
56
New cards
Intraregional Migration
Movement within the same region
57
New cards
Chain Migration
when people move to a new area or country because a family has moved there
58
New cards
Example of Chain Migration
Irish Potato Famine: Ireland → America
59
New cards
Step Migration
when a person makes small, incremental moves to their ultimate migration goal
60
New cards
Intervening Obstacles
an occurrence that causes a migrant to pause their journey. This can be done by choice (intervening opportunity; jobs) or by force (obstacle; barriers/documentation)
61
New cards
Guest Worker Programs (circular migration)
* seasonal migration: workers from poor countries move to richer countries work in specific areas like manufacturing or agriculture
62
New cards
Refugees (Forced Migration)
forced to migrate to avoid a potential threat to his or her life, and they cannot return for for fear of persecution
63
New cards
Asylum Seeker (forced migration)
someone who has migrated to another country in hope of being recognized as a refugee
64
New cards
Internally Displaced Person (IDP) (forced migration)
someone who is forced to flee his or her home but who remains within his or her country's borders
65
New cards
Climate refugee
people forced to flee by natural disasters or global warming
* not entitled to same protections as traditional refugees
* not entitled to same protections as traditional refugees
66
New cards
Human Trafficking
the recruitment, transportation, harboring, or receipt of persons by improper means such as force, abduction, fraud, or coercion. it is modern day slavery
67
New cards
Why would it be difficult to obtain a refugee status
* limited language skills
* trauma
* illness
* lack of documentation
* real vs perceived threat
* overly taxed system
* trauma
* illness
* lack of documentation
* real vs perceived threat
* overly taxed system
68
New cards
Where may refugees seek asylum?
* any of the 145 countries that have ratified the United Nation’s 1951 Refugee Convention
69
New cards
What is a host country expected to provide?
* civil rights
* the right to work
* access to social services
* the right to work
* access to social services
70
New cards
Repatriate
return to their home country
* fewer refugees have been able to repatriate
* fewer refugees have been able to repatriate
71
New cards
Indian Removal Act of 1830
authorized the US Army to force tribes off their land to be replaced by white settlers (Trail of Tears)
72
New cards
The Great Migration
6 million African Americans migrated from the agrarian South to the industrialized North of the US
73
New cards
Reasons for the Great Migration
* racial discrimination
* pestilence on cotton crops
* better jobs in north
* join family that had already moved
* pestilence on cotton crops
* better jobs in north
* join family that had already moved
74
New cards
Great Migration → __Kinship Links__
networks of relatives and friends that led migrants to follow similar settlement patterns
75
New cards
International/Intraregional Migration Example: Somali
* Somali Resettlement: fled war & famine in Somali and began resettling in the US in the 1990s.
* Refugees are located in cities like Houston, Minneapolis, Atlanta, and Boston.
* Kinship Links are used to create communities
* Refugees are located in cities like Houston, Minneapolis, Atlanta, and Boston.
* Kinship Links are used to create communities
76
New cards
International/Intraregional Migration Example: Hmong
* Hmong citizens fought alongside US soldiers during the Vietnam War
* Many Hmong were being killed by Laos government, so many fled to California, Minnesota, and Wisconsin.
* Chain Migration + Kinship Links
* Many Hmong were being killed by Laos government, so many fled to California, Minnesota, and Wisconsin.
* Chain Migration + Kinship Links
77
New cards
What drives migration policies
* meet labor market demands within the country
* increase diversity
* limit the numbers of immigrants from specific countries or regions
* possible xenophobia
* policies aimed at protecting women & children (high risk immigrants)
* increase diversity
* limit the numbers of immigrants from specific countries or regions
* possible xenophobia
* policies aimed at protecting women & children (high risk immigrants)
78
New cards
The European Union is facing a massive influx of asylum seekers. What is their policy?
* asylum seekers must apply in the first EU country they enter
79
New cards
What strict laws were enacted in the US after 9/11?
* 2017 restriction on foreign nationals from 7 Muslim-majority countries
* 2017 repeal of deferred action for childhood arrivals
* 2018 “zero-tolerance” immigration policy that resulted in family separations
* 2017 repeal of deferred action for childhood arrivals
* 2018 “zero-tolerance” immigration policy that resulted in family separations
80
New cards
Positive Economic Consequences of Migration
* decreasing the dependency age in their new home country
* large number of people willing to work for low wages
* increase population numbers in new home country
* migrants who move into rural areas offset the urbanization of cities and slow down overpopulation of areas
* free up services like health care and food in their country of origin
* large number of people willing to work for low wages
* increase population numbers in new home country
* migrants who move into rural areas offset the urbanization of cities and slow down overpopulation of areas
* free up services like health care and food in their country of origin
81
New cards
Negative Economic Consequences of Migration
* skills gap- shortage of trained people in a particular industry
* population decline
* low wage, unsafe jobs
* remittances- send money abroad to family (does not add to country’s economy)
* brain drain- loss of trained or educated people to the lure of work in another, often richer, country
* population decline
* low wage, unsafe jobs
* remittances- send money abroad to family (does not add to country’s economy)
* brain drain- loss of trained or educated people to the lure of work in another, often richer, country
82
New cards
Relocation Diffusion
the spread of ideas and culture traits through migration
83
New cards
Population Distribution
where people live within a geographic area
84
New cards
Population Distribution Patterns
* uniform
* random
* clustered
* linear
* random
* clustered
* linear
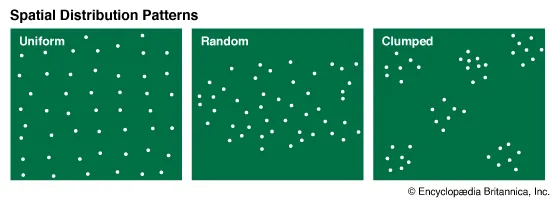
85
New cards
Ecumene Zone
places hosting permanent human settlement
86
New cards
What kind of physical environments do humans avoid?
* dry lands
* wet lands
* cold lands
* high lands
* wet lands
* cold lands
* high lands
87
New cards
Climate
the long-term patterns of weather in an area that greatly affect population distribution in direct/indirect wars
88
New cards
Weather
the condition of the atmosphere at a particular location and time
89
New cards
Human Factors that Influence Population
* Economic: humans will always go where they can make the most money for themselves or their families
* Political: Humans want the ability to live in peace & have fair balanced trade & human rights
* Cultural: Belonging to a community of people who share common values & beliefs
* Historical: communities that have been established for thousands of years will continue to exist
* Political: Humans want the ability to live in peace & have fair balanced trade & human rights
* Cultural: Belonging to a community of people who share common values & beliefs
* Historical: communities that have been established for thousands of years will continue to exist
90
New cards
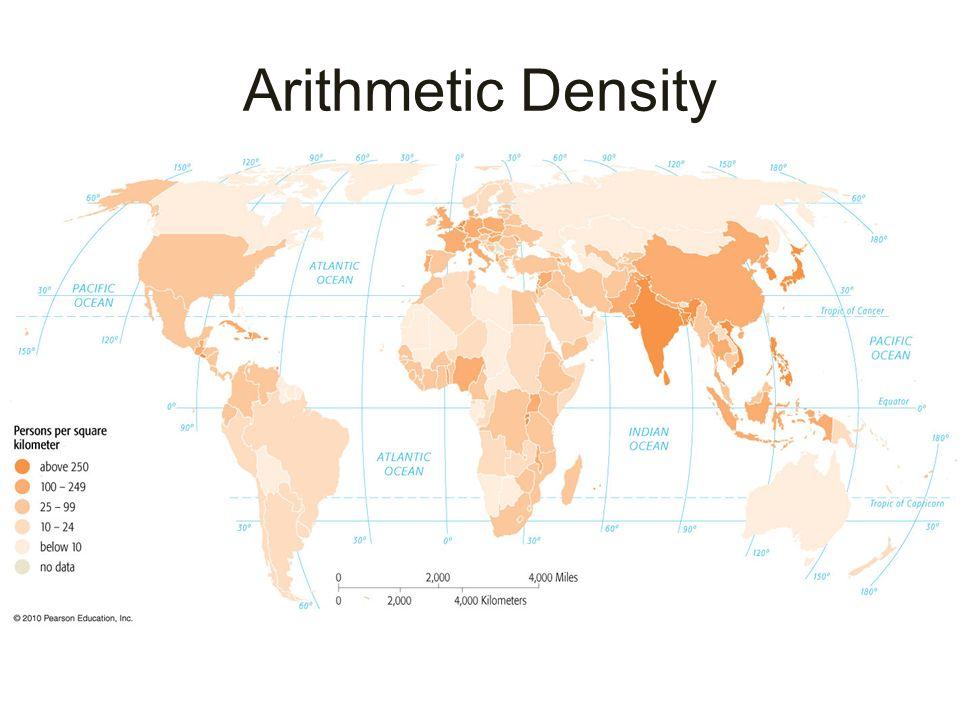
Arithmetic Density
* useful for comparing different countries or areas
91
New cards
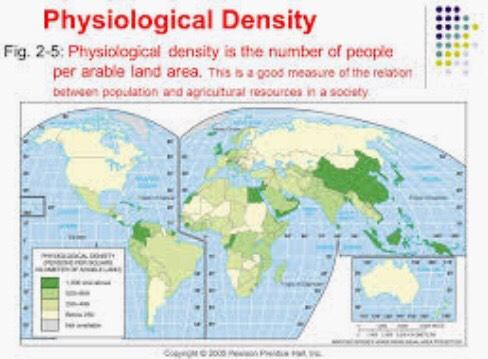
Physiological Density
* useful for analyzing food availability in different places
92
New cards
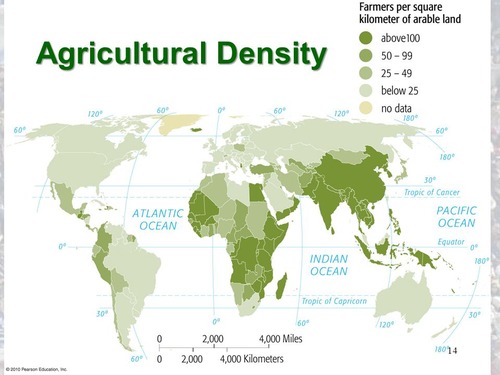
Agricultural Density
* an indicator of development- less farmers support more people in the developed world
93
New cards
What kind of country would evenly & densely populated areas tend to be?
* core countries
94
New cards
What kind of country would scattered populations tend to be?
* periphery countries
95
New cards
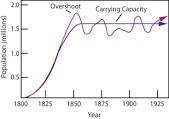
Carrying Capacity
the maximum population size an environment can sustain
* these environments will have high levels of poverty & famine/starvation
* these environments will have high levels of poverty & famine/starvation
96
New cards
Dependency Ratio
the number of people who are too young/old to work, compared to the number of people in their productive years
* if a country has more dependents than workers, it will struggle economically.
* if a country has more dependents than workers, it will struggle economically.
97
New cards
Sex Ratio
the number of males per 100 females in the population
98
New cards
Factors that affect sex ratio
* in peripheral countries, the number of women who die in childbirth contributes to a lower percentage of women
* countries with a high rate of emigration of men have higher percentages of women
* deaths of men in wars lead to a higher percentage of women
* cultural preference for boys results in higher percentage of men
* countries with a high rate of emigration of men have higher percentages of women
* deaths of men in wars lead to a higher percentage of women
* cultural preference for boys results in higher percentage of men
99
New cards
Fertility
the ability to produce children
* better education & job opportunities tend to lead to lower fertility rates
* better education & job opportunities tend to lead to lower fertility rates
100
New cards
Crude Birth Rate
the number of births in a given year per 1,000 people in a given population