Unit 2 Cell biology
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
All living thing have at least 1 cell
t/f
true
All living thing have at least 1 cell
Cell structure correlated to ____ ____
cell function
______ descend from existing cells
All cells
3 Domains of Life on Earth
ARCHAEA BACTERIA EUKARYA
Prokaryotic cells
No nucleus, no membrane-bounded organelles
Cyanobacteria were on Earth at least
3.5 bya
Cyanobacteria
Photosynthetic
Enabled evolution of oxygen-requiring life forms
Eukaryotic cells at least 2.7 BYA
2.7 BYA
EUKARYOTIC CELLS (DOMAIN Eukarya)
DNA in nucleus
Organelle
Cytoplasm = fluid + organelles
1665 Hooke
coined the word “cell”
Plasma (cell) membrane
selective barrier allows passage of oxygen, nutrients, waste….
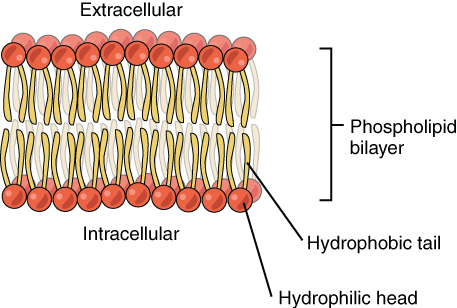
what is this
Phospholipid bilayer
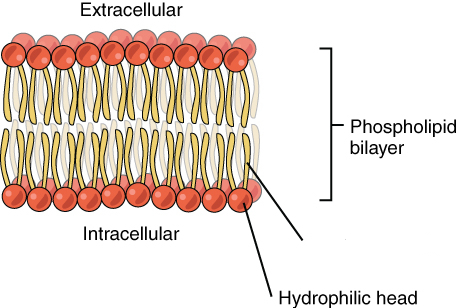
what is missing
Hydrophobic tail
Cells have a high surface to
Volume ratio
Larger organisms do have larger cells
t/f
false
Nuclear envelope (NE)
Double membrane; each a bilayer
Pores regulate entry and exit of molecules
Chromatin
is in the nucleus; chromosomes are DNA and associated proteins
Nucleolus
Assembles ribosomes
Ribosomes
Protein Factories
Assemble amino acids into polypeptides
• free ribosomes
• bound ribosomes – bound to NE and ER
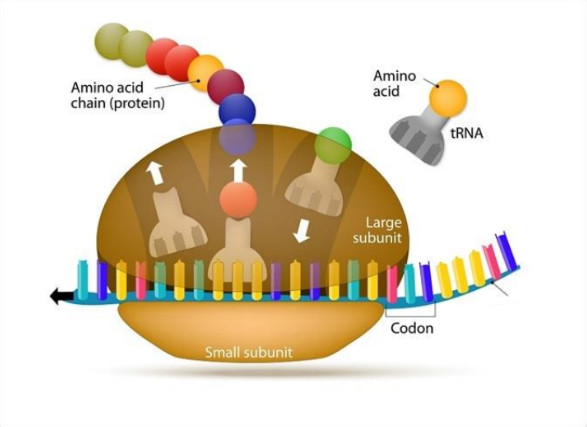
what isn’t labeled
mRNA
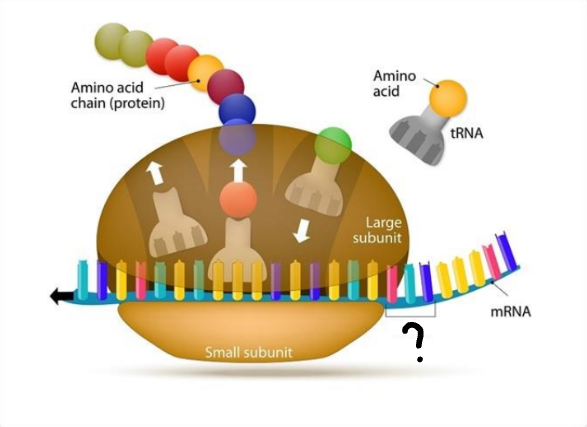
what is the ?
Codon
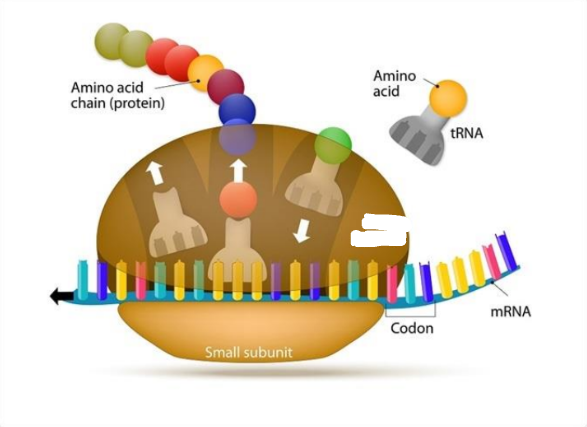
what is the ?
large subunit
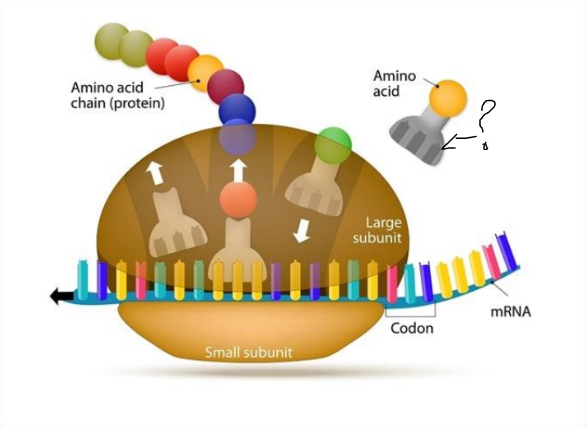
what is the ?
tRNA
The Endoplasmic Reticulum
• >half of total membrane
• continuous with nuclear envelope
Smooth ER
lacks ribosomes
Rough ER (RER)
has ribosomes
RER
1. Ribosomes assemble amino acids to make a protein
2. New protein enters the ER lumen
3. Protein folds in the ER lumen
The Golgi Apparatus
flattened membranous sacs called cisternae
Golgi has
a cis and a trans face
vesicle with protein from ER Vesicle ____ from the trans Golgi
budding
_____ proteins from ER
Modifies
Functions of the Golgi apparatus
• Modifies proteins from ER
• Add sugars, phosphate, sulfur etc…
• Sorts and packages protein into vesicles PROTEIN
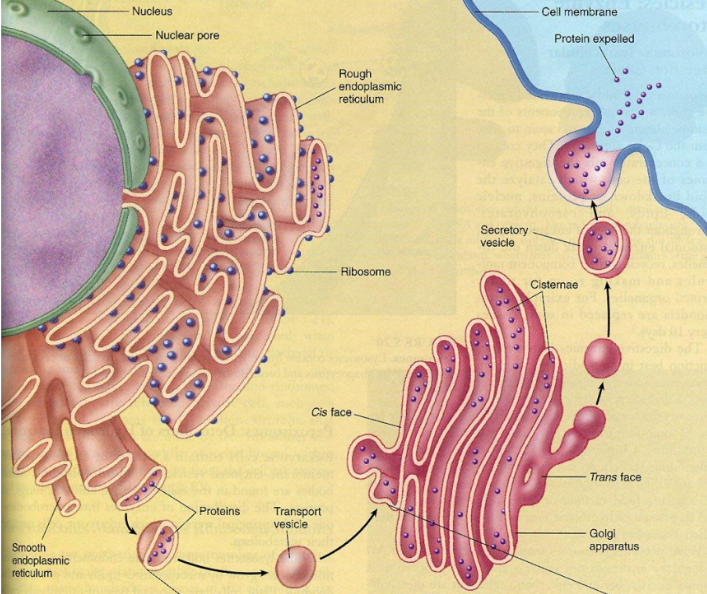
what is happening?
protein synthesis
protein synthesis steps
mRNA "reads" the gene and carries the message to the ribosomes either free in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum
At the ribosomes on the RER, DNA's message gets uncoded and Proteins are produced (with the help of tRNA transfering amino acids (the building units of proteins) to the ribosomes
The proteins produced will be transport to the Golgi apparatus which will package the proteins
export proteins to the cell or other cells.
Lysosomes
membranous sac of enzymes that digest macromolecules
What do they do?(Lysosomes)
1. get rid of phagocytosed invaders
2. recycle cell parts (autophagy)
3. digest food in single celled organisms
Food vacuole formed via phagocytosis →
lysosome fuses with food vacuole and digests food
Vacuoles
-- Food vacuoles
-- Contractile vacuoles
Contractile vacuoles
• freshwater protists
• pump excess water out of cells
Central vacuoles
•found in many plant cells
• hold starch/water
Mitochondria
cellular respiration generates ATP (energy)
• contain mtDNA
• all eukaryotic cells have mt
• Some have 1, some 1000s
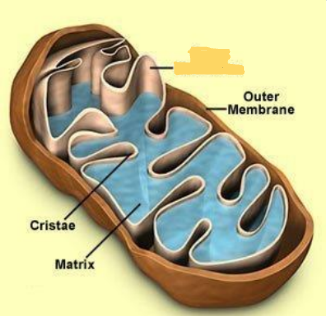
what is gone?
inner membrane
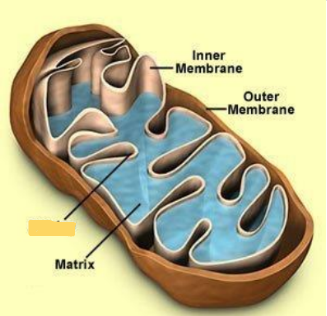
what is gone?
cristae
Plastids
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts
•plants and algae
•sites of photosynthesis
Cytoskeleton
•Network of protein fibers
•Anchors organelles
•Maintains cell shape
3 proteins of the cytoskeleton
microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments
Cytoskeleton
interacts with motor proteins/kinesins to transport cargo
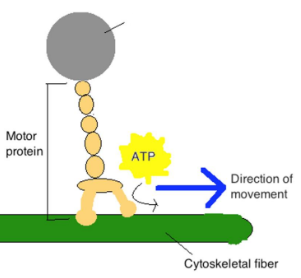
what is missing
Cargo
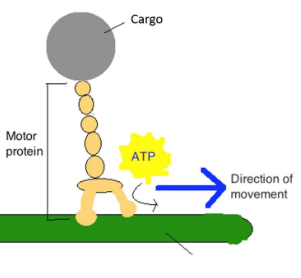
missing?
cytoskeletal fiber
Centrioles
Microtubules involved in cell reproduction
Cilia and Flagella
For movement
• Controlled by microtubules
• Found in many protists
Extracellular materials
external to plasma membrane
Plants - cell wall
Composed mainly of cellulose
Composed mainly of ______
cellulose
Animal cells can have a ___ extracellular matrix (ECM)
large
The ECM _____ _____ ____ the cells
anchors and supports
Intercellular Junctions
• Adherence of one cell to another
• Communication through direct physical contact