econ 1020- competitive equilibrium, consumer surplus, total surplus
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
what is a competitive market
a market with many buyers and sellers where no one controls the price and everyone is a price taker
price taker
one who accepts the price as given and cannot change it by oneself
what is competitive equilibrium
the consumers buy their preferred amount and the consumers sell their preffered amount. qunaityt demanded = quanity supplied(market clearing). it is a price quantity paring such that conumers maximise utility (demand) and firms maximise profit (supply)
why is competitive equilibrium important
because it provides positive predictions of how prices change after a shock (comparative statics). it also provides a normative benchmark; under perfect competition equilibrium outcomes are efficient (first welfare theorem)
consumer surplus
difference between what consumers are willing to pay and what they actually pay. (under demand curve above market price)
producer surplus
difference between market price and marginal cost ( the minimum price consumers are willing to accept) (area above the supply curve and below the market price)
total surplus (social welfare)
w = CS +PS measures the total gain enjoyed by the oncumer and producer
competitve equilibrium efficient (fist welfare theoreom)
consumers’ marginal willingness to pay = firm's marginal cost
All units where benefits exceed cost are produced. No mutually beneficial trade remains unexploited.
show consumer and producer surplus on a diagram

what is deadweight loss
reduction in total surplus when quantity traded differs from the efficiency level.
explain dead weight loss
represents the trades that should have happend but didint or the trades that have happend but shouldnt have
deadweight loss diagram
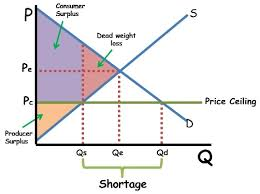
how does tax affect welfare
raises the price consumers pay lowers the price producers recieve, reduced the tradec quanity, creates government revenue