Population Growth Dynamics in BIOL201
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What are the four processes that cause population change?
Births, immigration, deaths, and emigration.
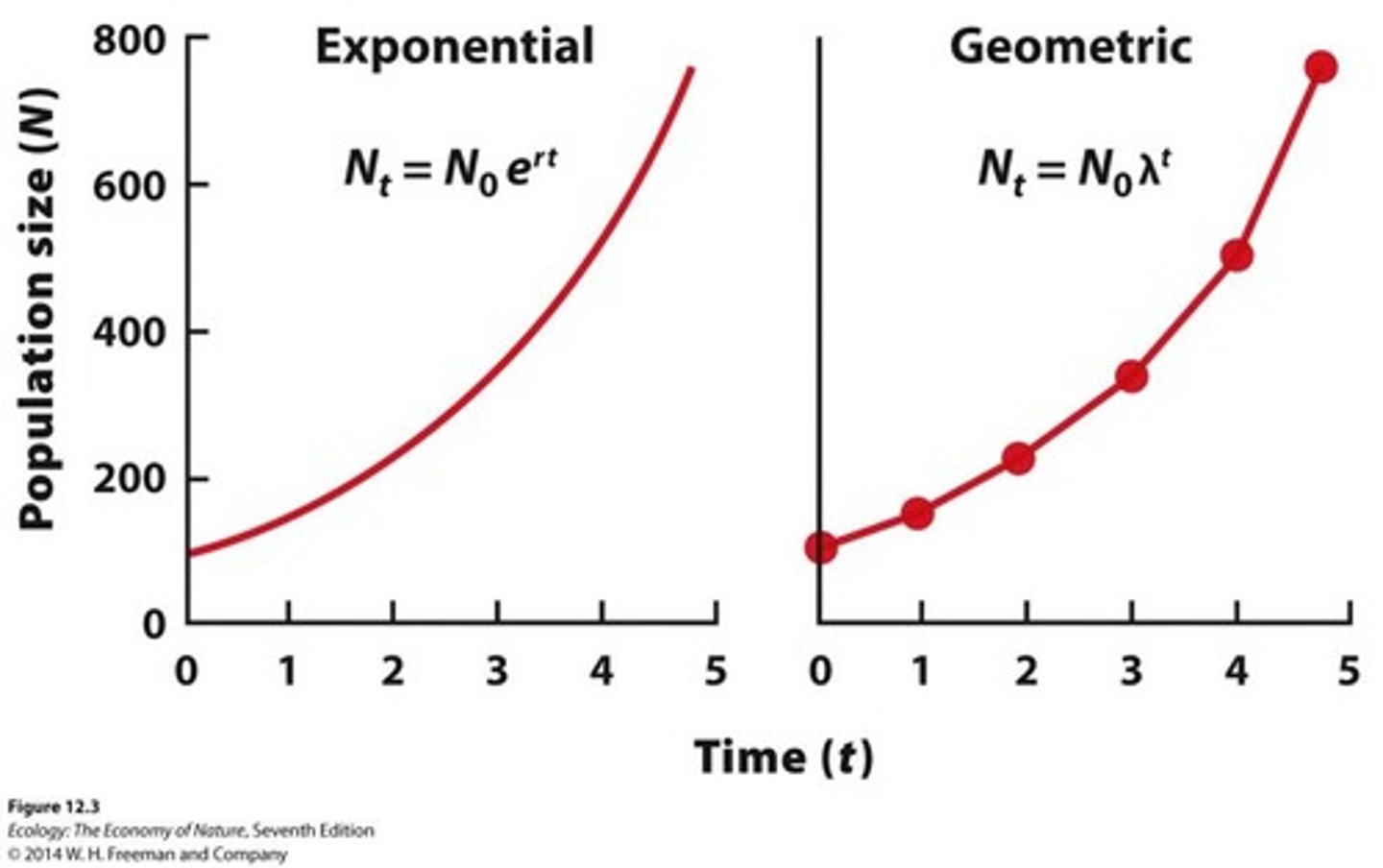
What is the difference between density-dependent and density-independent growth?
Density-dependent growth means the growth rate is a function of population size, while density-independent growth means the growth rate is the same regardless of population size.
What is positive feedback in population growth?
Positive feedback refers to an instantaneous growth rate that increases as population density increases, leading to autocatalytic growth.

What does the demographic balance equation represent?
N(t + Δt) = N(t) + (births + immigration - deaths - emigration) Δt.
What is the modified demographic balance equation when Δt = 1?
Nt+1 = Nt + B - D + I - E.
How is the change in population size (∆N) calculated?
∆N = B - D + I - E.
What does dN/dt represent in population growth modeling?
dN/dt represents the change in population size over an infinitesimally small time interval.
How do you calculate the number of births (B) in a population?
B = bN, where b is the instantaneous birth rate and N is the number of individuals in the population.
What factors determine the death rate (D) of a population?
D depends on the instantaneous death rate (d) and the number of individuals in the population (N), calculated as D = dN.
What is the intrinsic rate of increase (r) in population growth?
r = (b - d), where b is the birth rate and d is the death rate.
What is the equation for exponential population growth?
dN/dt = (b - d)N.
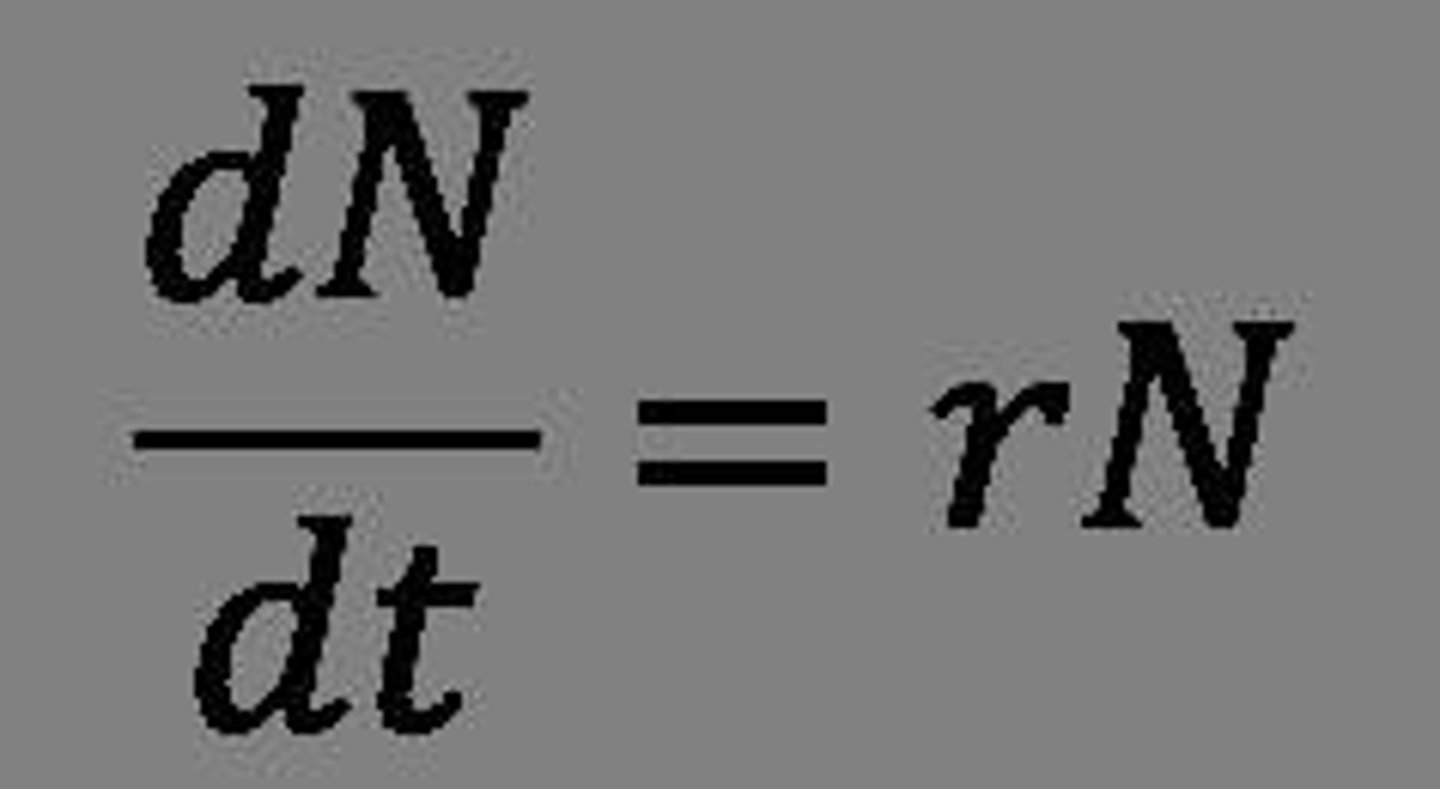
What is the significance of doubling time in population growth?
Doubling time is the time it takes for a population to double in size.
What is the relationship between population growth rate and time interval (Δt)?
The population growth rate is calculated over a specific time interval Δt.
What does the term 'autocatalytic growth' imply?
It implies that growth accelerates as the population increases, leading to rapid population increases.
What is the role of immigration in population growth?
Immigration contributes to population increase by adding new individuals to the population.
What is the role of emigration in population growth?
Emigration contributes to population decrease by removing individuals from the population.
How does demographic stochasticity differ from environmental stochasticity?
Demographic stochasticity refers to random variations in population processes, while environmental stochasticity refers to random changes in environmental conditions affecting populations.
What is the formula for calculating population growth over a time interval?
N(t + Δt) - N(t) = (b - d)N(t)Δt.
What is the significance of a closed system in basic population growth models?
A closed system assumes no movement in or out of the population, simplifying growth calculations.
What is the relationship between instantaneous birth and death rates and population size?
The birth and death rates are expressed as per capita rates, meaning they depend on the number of individuals in the population.
What is the effect of a high intrinsic rate of increase (r) on population growth?
A high intrinsic rate of increase leads to rapid population growth.
What is the implication of the phrase 'Babies having babies having babies'?
It illustrates the concept of autocatalytic growth where population increases rapidly as individuals reproduce.
What does the term 'demographic balance' refer to in population studies?
Demographic balance refers to the equilibrium between births, deaths, immigration, and emigration in a population.
What is the intrinsic growth rate (r) of Paramecium caudatum?
1.59 individuals per day.
What is the doubling time for the T phage virus?
3.3 minutes.
What is the doubling time for Escherichia coli?
17 minutes.
What is the intrinsic growth rate (r) of Rattus norvegicus (Brown rat)?
0.0148 individuals per day.
What is the intrinsic growth rate (r) of Bos taurus (Domestic cow)?
0.001 individuals per day.
What is the intrinsic growth rate (r) of Homo sapiens (Humans)?
0.000042 individuals per day.
What does the exponential growth model predict about population size?
It predicts future population size based on initial size (N0) and intrinsic growth rate (r).
What is the formula for population size at time t in the continuous growth model?
Nt = N0 * e^(rt) where N0 is the initial population size, e is the base of natural logarithm, r is the intrinsic growth rate, and t is time.
What are the assumptions of the exponential growth model?
1. No immigration or emigration. 2. Constant birth and death rates. 3. No age or size structure. 4. Continuous growth with no time lags.
What is the difference between discrete and continuous growth models?
Discrete models predict population size at specific time steps, while continuous models predict population size continuously over time.
What is the formula for predicting population size in a discrete growth model?
Nt+1 = λNt, where λ is the finite rate of increase.
What is demographic stochasticity?
Random variation in birth and death rates that occur in a population year to year.
What is environmental stochasticity?
Random fluctuations in the environment, such as changes in climate, fires, floods, and hurricanes.
What is the formula for calculating the rate of increase in population size (λ) across multiple time steps?
λ = (Nt/N0)^(1/t).
What is the equation for geometric growth in a discrete model?
Nt = λ^t * N0.
What is the equation for exponential growth in a continuous model?
dN/dt = rN.
What is the intrinsic growth rate (r) of Avicennia marina (Mangrove)?
0.00055 individuals per day.
What is the intrinsic growth rate (r) of Nothofagus fusca (Southern beech)?
0.000075 individuals per day.
What is the intrinsic growth rate (r) of Tribolium castaneum (Flour beetle)?
0.101 individuals per day.
What is the expected population size of forest herbs after 8 years if the initial size is 100 and r is 0.05?
Approximately 149.2 individuals.
What is the significance of George Box's quote, 'All models are wrong, but some are useful'?
It highlights that while models simplify reality and may not be entirely accurate, they can still provide valuable insights.
What is the main purpose of ecological models?
To understand and navigate complex ecological systems.
What is the expected population size of a species with an intrinsic growth rate of 0.34 after 2 days if starting with 100 individuals?
Approximately 100 e^(0.34 2) individuals.
What is Exponential Population Growth?
A type of growth that is density independent, observed when organisms colonize a new habitat with plentiful resources.

What are some scenarios where Pure Exponential Growth occurs?
It occurs during recovery after a disaster or when there is no competition.
How can researchers calculate the growth rate of a population?
By combining data on survivorship and fecundity.
What is the Net Reproductive Rate?
It is the growth rate per generation, calculated using generation time.
What does generation time refer to?
The average time between a mother's first offspring and her daughter's first offspring.
Who was Thomas Robert Malthus and what did he argue?
Malthus argued that food supply could never keep pace with human population growth, leading to inevitable human suffering and famine.
What are 'Positive Checks' according to Malthus?
Factors that shorten human life and increase death rates, such as unhealthy labor, extreme poverty, diseases, war, and famine.
What are 'Preventative Checks'?
Factors that reduce birth rates, such as marrying later and having children later in life.
What impact did technological advancements have on population growth?
They contributed to population growth through improvements in sanitation, medical care, agricultural practices, and contraceptives.
What is the trend in human population doubling time from 1802 to 2020?
Doubling time has decreased from 127 years in 1802 to 48 years in 2020.
What is the difference between density dependent and density independent growth?
Density dependent growth is a function of population size, while density independent growth has a constant rate regardless of population size.
What is Positive Feedback in population growth?
It refers to an instantaneous growth rate that increases as population density increases.
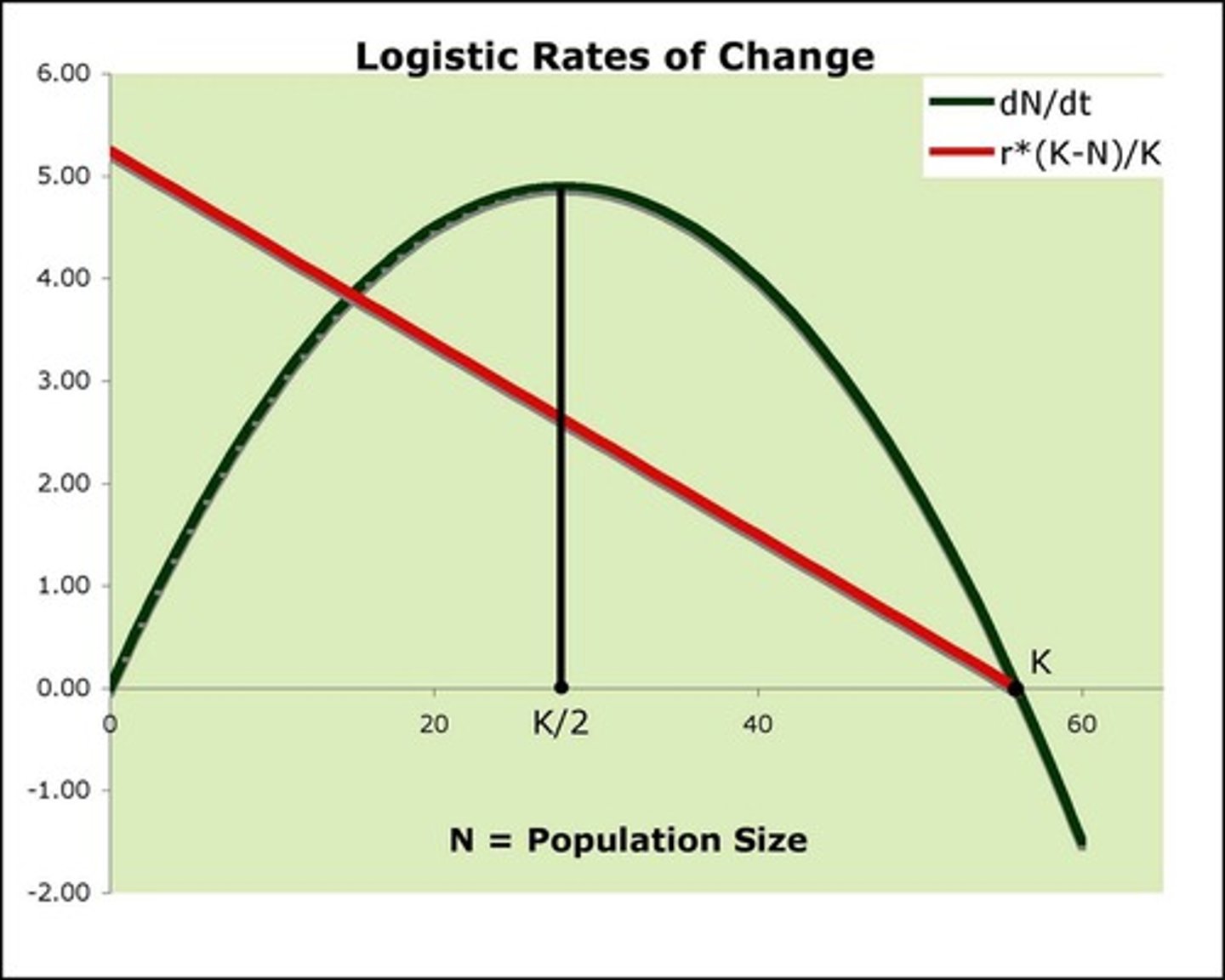
What happens to population growth as N approaches K?
Population growth slows down, and when N equals K, growth is zero.
What are the assumptions of logistic growth?
Linear density-dependence and constant carrying capacity (K), both of which can be false.
What are Allee effects?
Positive density-dependence effects that occur at small population sizes.
What modifications can be made to density dependent growth models?
Modifications can include effects of carrying capacity, time lags, age structure, and environmental or demographic stochasticity.
What is the Ideal Free Distribution?
A concept where species distribute themselves across habitats to maximize per capita benefits.
What are the assumptions of the Ideal Free Distribution?
(1) Fitness declines as population density increases, (2) organisms are free to move, (3) they can estimate habitat fitness, and (4) they aim to maximize fitness.
How do organisms behave in variable habitats according to the Ideal Free Distribution?
They shift to maximize per capita benefit.
What is an example of a species exhibiting density dependent growth?
Paramecium caudatum and Balanus balanoides (barnacle) populations.
What is the significance of carrying capacity (K) in population growth models?
It represents the maximum population size that an environment can sustain.
What does demographic stochasticity refer to?
Variation in the sequence of births and deaths within a population.
What is environmental stochasticity?
Variation in birth and death rates due to environmental factors.