CFA Level 1: Derivatives
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Derivative (L1)
A security that derives its value from an underlying asset, index, or rate.
Underlying (L1)
The asset, index, or rate on which a derivative's value is based. It can include stocks, bonds, commodities, or market indices.
Exchange Traded Derivatives (L1)
Derivatives with standardized contracts, (pre-written, pre-approved legal agreements with fixed terms used for common transactions, allowing little to no negotiation.)
More liquid, more transparent, and lower cost.
More efficient clearing & settlement.
Central Clearing: Collateral deposits, mark to market, clearinghouse takes the other side of each trade; minimize counter party risk.
OTC Derivatives (L1)
Derivatives with customizable contracts (pre-written, pre-approved legal agreements with fixed terms used for common transactions, allowing little to no negotiation.)
Less liquid and transparent, and higher trading costs.
Required to have central clearing party & collateral deposit: reduces counterparty risk, similar to exchange-traded derivatives.
Systemic risk is the most concerning risk
Forward Commitments (L1)
Agreements made today for a future transaction at a predetermined price.
Future, Forward contracts, and swaps are examples.
Contingent Claims (L1)
a derivative whose payoff and value are entirely dependent upon the occurrence of a specific future event.
Certain conditions are met and satisfied by one party.
Examples: Options & credit derivatives.
Central Clearing (L1)
A process where a central counterparty (clearinghouse) interposes itself between two parties of a transaction, becoming the buyer to every seller and the seller to every buyer. It involves:
Collateral deposits: Participants provide margin to cover potential losses.
Mark-to-market: Daily revaluation of positions and adjustment of collateral to reflect current market prices.
Clearinghouse roles: The clearinghouse guarantees the performance of contractual obligations, significantly minimizing counterparty risk for participants.
Novation (L1)
The process where a clearinghouse replaces the original bilateral contract between two parties with two new contracts:
One between the first party and the clearinghouse, and another between the second party and the clearinghouse.
This effectively makes the clearinghouse the counterparty to both original parties, centralizing risk and facilitating clearing and settlement.
Clearinghouse (L1)
A central financial institution that acts as an intermediary (central counterparty) in financial markets, especially for derivatives and exchange-traded contracts. It becomes the "buyer to every seller" and the "seller to every buyer," guaranteeing the fulfillment of contractual obligations. Its main responsibilities include:
- Mitigating Counterparty Risk: By interposing itself between parties, it minimizes the risk that one party defaults on its obligations.
- Standardizing Clearing and Settlement: It ensures uniform procedures for trade processing.
- Managing Collateral: It requires participants to post margin (collateral deposits) and performs daily mark-to-market valuations to cover potential losses.
Forward Contracts (L2)
A customized contract where a price agreement is set for a commodity/security, with the settlement deferred and set in the future.
Spot Market (L2)
A price agreement & transaction occurring at the same time. Also known as the spot price, represented as (St).
At expiration the settlement price = spot price.
Converged from future prices over time to contract expiration.
Forward Contract Seller (L2)
Seeks to benefit from price depreciation.
Contract Specifies (L2)
A futures characteristic that focuses on quality & quantity of good, delivery time, place & manner of delivery.
Option Seller for American Option (L2)
Can only be exercised any time before expiration.
Option Seller for European Option (L2)
Can only be exercised only at expiration.
Option Seller (L2)
Also known as the writer, or short position. Incurs an obligation to perform if owner decides to buy or sell (exercise).
American options are worth at least as much as otherwise-identical European options.
Put Option (L2)
Right to sell at strike price (exercise) .
Call Option (L2)
Right to buy at a strike price (exercise).
Swap Contract (L2)
For a fake loan, each party makes periodic payments based on a interest rate, or on the performance of index, bond, portfolio, or commodity.
Features custom instruments, equal to a series of forwards.
Payments are typically netted, may or may not require margin, and multiple settlement dates.
Fixed Rate Peyer (L2)
An interest rate swap participate, that receives a net payment on the swap for any interest period for which the market reference rate exceeds the fixed rate.
Floating Rate Payer (L2)
An interest rate swap participate, makes a payment each interest period based on a market reference rate.
Fixed & Floating Rate Payer (L2)
An interest rate swap participate, may face a positive or a negative mar to market over the life of an interest rate swap contract.
Settlement Price (L2)
Average of trades during closing period, used to calculate margin.
Option Buyer (L2)
Also known as the owner, or long position.
Pays a premium to purchase the right to exercise an option at a future date.
Exchange Specifies (L2)
A futures characteristic that focuses on the minimum price fluctuation (tick), on daily price limit.
Long buys & short sells the future.
Margin in collateral not a loan.
Margin posted & market to market daily.
Clearinghouse golds the other side of each trade.
Futures Contract (L2)
A standardized forward contract due to being exchange traded.
Forward contract Purchaser (L2)
Buyer of a contract, specifically a derivative contract, seeks to benefit if spot price (St) exceeds thr forward price F0(T) . Also known as the long party.
Risk Transfer (L3)
The ability to buy or sell a derivative today eliminates the timing mismatch between an economic decision.
Cash Flow Hedge (L3)
A derivative designated as absorbing the variable cash flow of a floating rate asset or liability.
Hedge Accounting (L3)
Gains or losses on derivative offset the effects of changing asset & liability values.
Operational Advantage (L3)
Future margin requirements are quite low vs cost of a cash market purchase.
Price Discovery Function (L3)
Investors track an equity index future prices to gauge sentiment before the market opens.
Transparency (L3)
A type of derivative risk in which portfolio & risk exposures is not understood by investors.
Basic Risk (L3)
A type of derivative risk in which underlying mismatch with hedged risk, or mismatch of expiration data & date hedged transaction.
Systemic Risk (L3)
A type of derivative risk in which excessive speculations may have negative impact on financial markets and institution.
Net Investment Hedge (L3)
A derivative designated as offsetting the foreign exchange risk of the equity of a foreign operation.
Net Value Hedge (L3)
Hedging the value of a foreign subsidiaries’ equity in a parent subsidiaries’ balance sheet with currency forward.
Futures Contract (L6)
A standardized, legally binding agreements or sell a specific asset at a fixed price at a future date.
No Arbitrage Future’s Price with exclusion of cost and benefits of holding asset (L6)
Equal to the No arbitrage Forward Price
F0= Forward/Future Price r(f) = risk free interest rate
T = Time to maturity S0= Spot Price
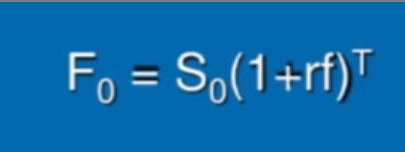
Constant Interest Rates along with Future/Forward Contract Prices (L6)
Futures and forward prices would be the same.
No Arbitrage Future’s Price with cost and benefits of holding asset (L6)
F0= Forward/Future Price r(f) = risk free interest rate
T = Time to maturity S0= Spot Price
PV0(Ben) = Benefits of Holding Asset at present value
PV(Cost) = Costs of Holding Asset at present value

Future Contract Price at Post-Initiation (L6)
Price resets to the settlement price + value returns to 0 daily, as mark to market gains and losses are settled.
Has daily mark to market cash flow.
The Settlement Price as a result becomes the new futures price.
Forward Contract Price at Post-Initiation (L6)
The prices does not change, and the value changes as the asset price changes due to no market to market cash flows.
Forward Convexity Bias (L6)
Has value to an investor, specifically to a short party in a FRA.
Difference in payoffs is small for short-rated FRAs, but significant for long-dated FRAs.
Convexity of Forward Payoffs (L6)
Gain from an interest rate decrease is larger than the loss from an interest rate increase.
Short Party → Receives Fixed Payoffs
Long Party → Pays Fixed Payoffs.
STIR (Short Term Interest Rate) Future (L6)
Exchanged traded version of a FRA, standardized and liquid.
Implied forward rate (Forward MRR) computed the same way as an FRA.
Calculated as
100 - (100 * Implied Forward Rate)
Put Call Parity for European Option (L9)
Both the protective put and the fiduciary call have the same payoffs at expiration, so must have same values before expiry to prevent arbitrage.
Fiduciary Call = Protective Put
Expressed as: S + P = C + X / (1+Rf) ^T
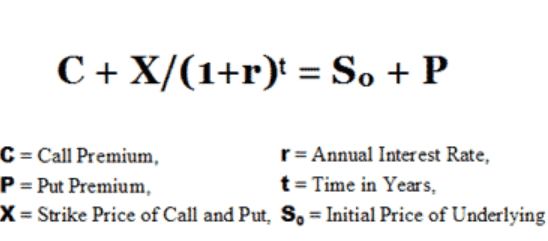
Protected Put (L9)
A protection to the investment in the event of a downside.
Synthetics (L9)
Synthetically creating a financial instrument instead of buying a call in open markets.
Put Call Parity for Long Position (L9)
C0 + PV(X) = P0 +S0
C0 = Call Option
PV(X) = Risk Free Bond
S0 = Stock price (current)
P0 = Put Option
Put Call Parity for Call in Long Position (L9)
Call (C0) = P0 + S0 - PV(x)
Put Call Parity for Put in Long Position (L9)
Put (P0) = C0 + PV(X) - S0
Put Call Parity for Stock Current Price in Long Position (L9)
Stock Current Price (S0) = C0 +PV(X) - P(0)
Put Call Parity for Risk Free Bond in Long Position (L9)
Risk Free Bond (PV(x)) = P0 + S0 -C0
Put Call Parity for Call in Short Position (L9)
Call (-C0)= -P0 - S0 + PV(X)
Put Call Parity for Put in Short Position (L9)
Put(-P0) = -C0 - PV(X) +S0
Put Call Parity for Stock Current Price in Short Position (L9)
Stock Current Price (-S0) = -C0-PV(X)+P0
Put Call Parity for Risk Free Bond in Short Position (L9)
Risk Free Bond(-PV(X))= -P0 - S0 + C0
Firm Value Assumption (L9)
Firms debt is financed through 0 coupon bond (ZCD) , no coupon payment is made thus no coupon payment before bond maturity.
Firm Value (L9)
Sum of equity value and debt.