Topic 16: Redox & Equilibria
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Standard Electrode Potential definiton
The EMF of a half-cell compared with a standard hydrogen half cell, measured under standard conditions.
Standard Conditions:
298 K temperature
100 kPa pressure
higher pressure causes a more negative emf cause e- are produced
1.00 mol dm⁻³ ion concentration
higher concentration causes a more positive emf cause fewer e- are produced
Absolute Potential Difference definition
the potential difference between a metal and a solution of its ions
Standard Electrode Potential Values
more positive Eº value = more likely to get reduced equilibrium is to the right
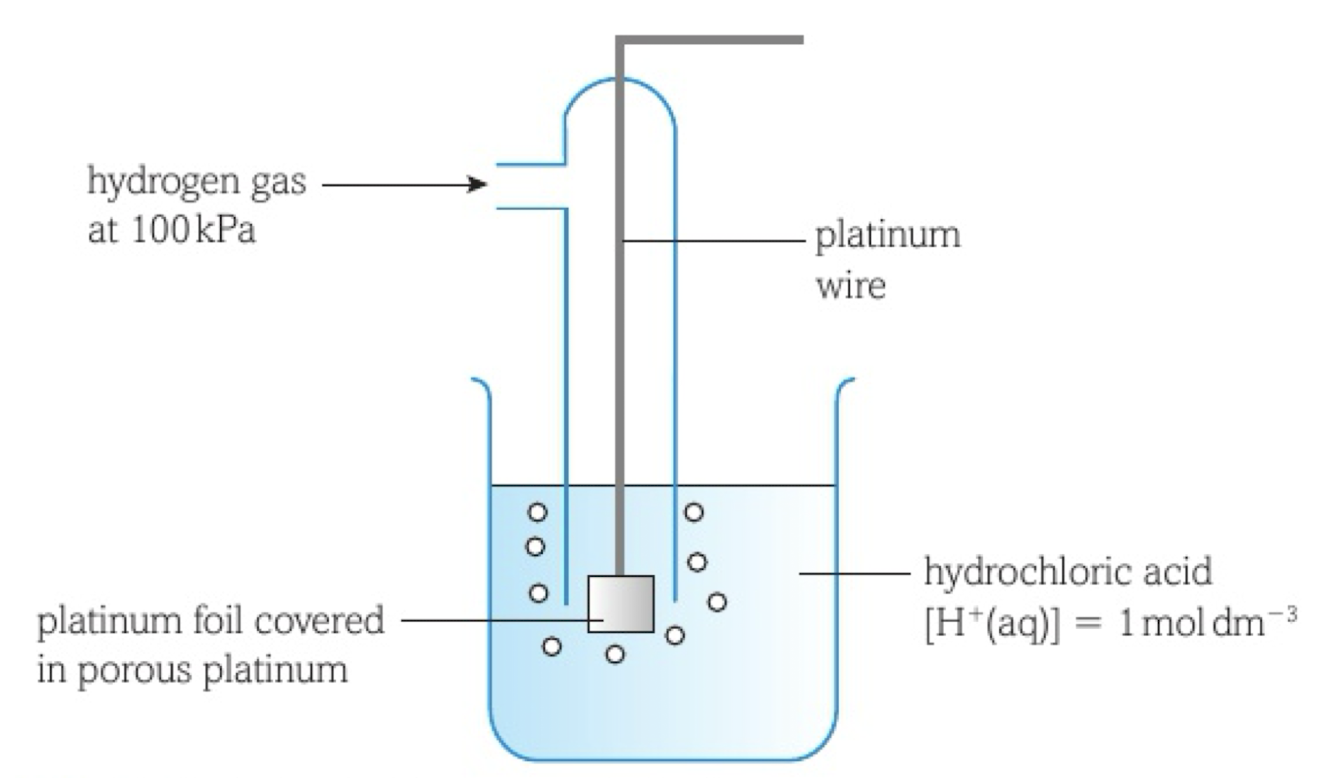
The Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE)
Platinum (unreactive) electrode coated with platinum black (inert, conducts electrons)
platinum foil on the bottom, covered in porous platinum (for a large surface area)
equilibrium between H+ ions and H gas
how to Measure the Standard Electrode Potentials
by conducting the standard hydrogen electrode (negative pole) , metal electrode and solution; via a circuit containing a high resistance voltmeter and a salt bridge.
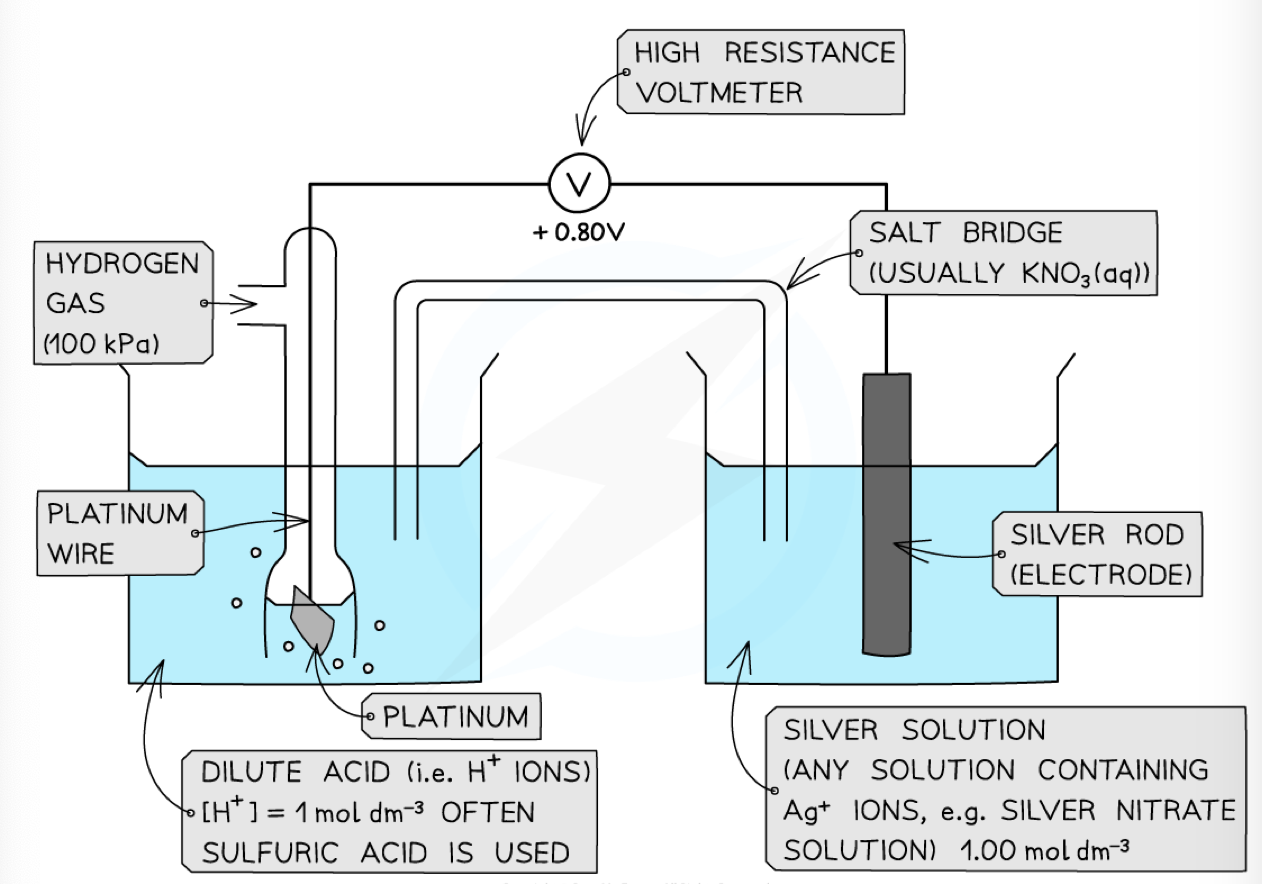
Writing Cell Diagrams
Anode (oxidation) || Cathode (reduction).
Reaction Feasibility
thermodynamically feasible if Eº cell > 0
a + Eº cell means the overall reaction is energetically favorable
but in practice, the value has to be more than 0.4
Electrochemical Series
more + Eº are stronger oxidizing agents
Relationship to Entropy & ln k
Eº cell ∝ΔSº
Eº cell ∝ln k
ΔG=-RT ln k
Acidic Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel Cells Electrolyte:
anode: H2 → 2H+ + 2e-
cathode: O2 + 4H+ + 4e- → 4OH-
Alkaline Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel Cells Electrolyte:
anode: 2H2 + 4OH- → 4H2O + 4e-
cathode: O2 + 2H2O + 4e- → 4OH-
advantages of Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel Cells
no harmful products
efficient
rechargeable
disadvantages of Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel Cells
hight costs
Hydrogen manufactured from fossil fuels
don’t work well in low temperatures
Potassium Manganate (VII) Titrations Equation
MnO4− + 8H+ + 5Fe2+ →. Mn2+ + 5Fe3+ +. 4H2O
reagent, condition and color change of KMn reaction
Mn (VII) gets reduced to 2+
Fe gets oxidized to 3+
purple → colorless
Iodine-Thiosulfate Titration Equation
2S2O3(aq) 2- + I2 (aq) → 2I- (aq) + S4O6 (aq) 2-