Bio Vocab chp 6-22
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
cellular metabolism
all the chemical processes occurring within the cell
mitochondria
where the processes of cellular respiration take place
matrix
the fluid-like substance that occupies the space enclosed by the inner membrane of the mitochondria
cellular respiration
the aerobic harvesting of energy from food molecules, in other words, the energy-releasing chemical breakdown of food molecules and the storage of potential energy in the form of ATP
breathing
the process your body uses to exchange gases (O2 and CO2) between your blood and the outside air, this occurs in tiny sacs called alveoli in the lungs
alveoli
tiny dead-end sacs within the vertebrate lungs that act as sites for gas exchange between the blood and lungs
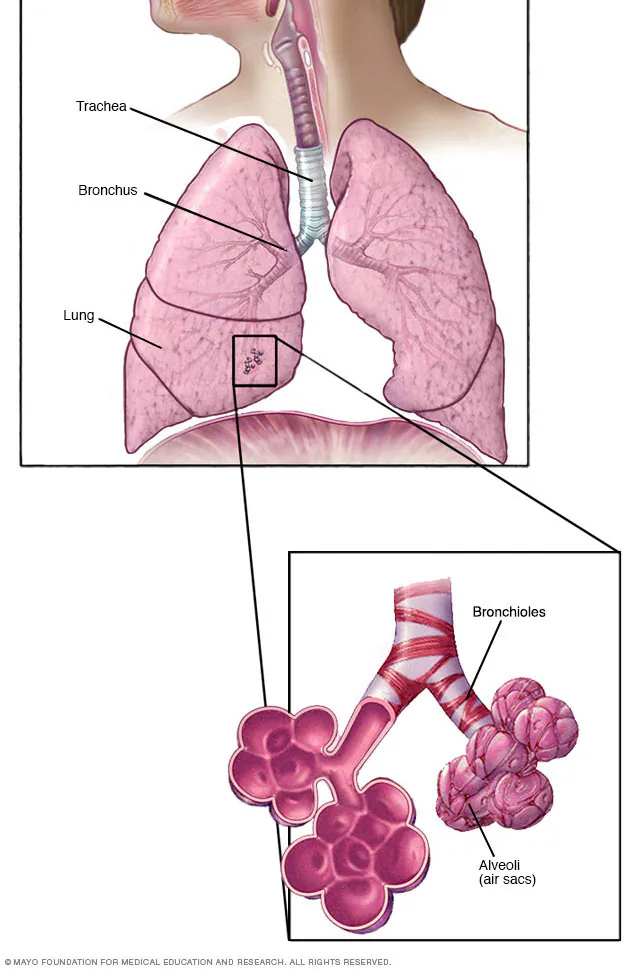
diaphragm
the sheet of muscle separating the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity in mammals
surfactants
specialized secretions that keep alveoli from sticking shut due to the surface tension created by their moist surfaces
hemoglobin
a molecule consisting of 4 polypeptides and is responsible for carrying oxygen in the blood
oxygen
the gas used by cells during cellular respiration, also a by-product of photosynthesis
carbon dioxide
the gas released as a by-product of cellular respiration, also used to build sugar molecules in photosynthesis
glucose
a simple carbohydrate produced in photosynthesis and consumed in cellular respiration
adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
the source of energy for most cellular work and is the product of cellular respirationadeno
adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
when ATP is used in cellular work and a chemical reaction breaks the bonds between a phosphate group, releasing potential energy that allows a cell to preform work
NAD+ (oxidized) / NADH (reduced)
a coenzyme that readily accepts or gives up electrons and a H+ ion. It acts as a carrier molecule during cellular respiration
coenzyme
a small, organic substance that unites with a given protein to form an active enzyme complex, allowing the enzyme to preform its function
calorie
the energy needed to raise 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius
kilocalorie
(1000 calories) the amount of energy needed to raise 1000 grams of water by 1 degree Celsius
chemical work
the building of molecules within a cell, like building a protein from individual amino acids
transport work
pumping of a solute across a cellular membrane
mechanical work
movement of an object, ex. muscle contractiona
aerobic
processes involving oxygen a
anaerobic
processes (such as fermentation) that do not involve oxygen