Understanding DNA Structure and Function in Biochemistry
1/445
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
446 Terms
Nucleotide
Building block of DNA and RNA.
Nucleoside
Five-carbon sugar bonded to a nitrogenous base.
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, genetic material in cells.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid, involved in protein synthesis.
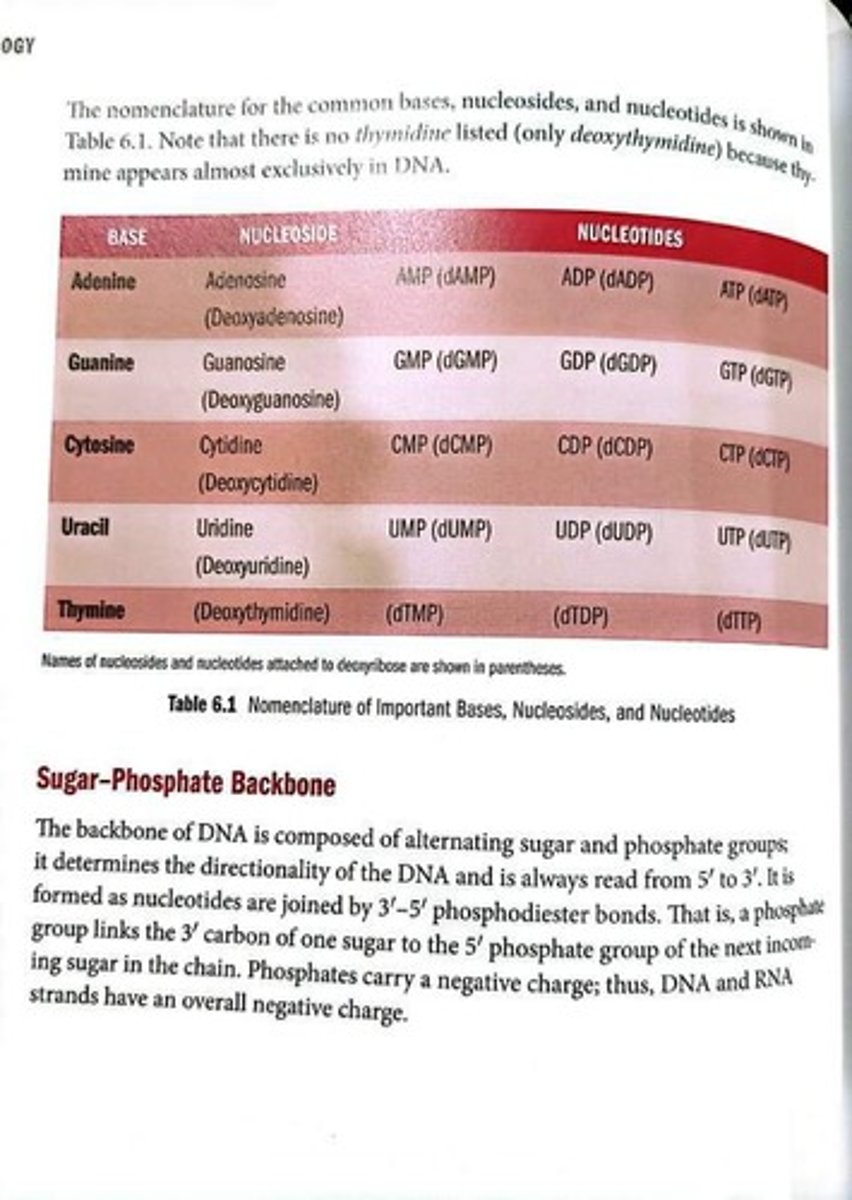
Deoxyribose
Sugar in DNA, lacks an -OH at C-2.
Ribose
Sugar in RNA, has an -OH at C-2.
Phosphodiester bond
Links nucleotides via sugar and phosphate groups.
Antiparallel strands
DNA strands run in opposite directions.
5' end
End of DNA with phosphate group attached.
3' end
End of DNA with free -OH group.
High-energy bonds
Bonds in ATP due to phosphate repulsion.
Adenosine
Nucleoside formed from adenine and ribose.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Nucleotide with three phosphate groups.
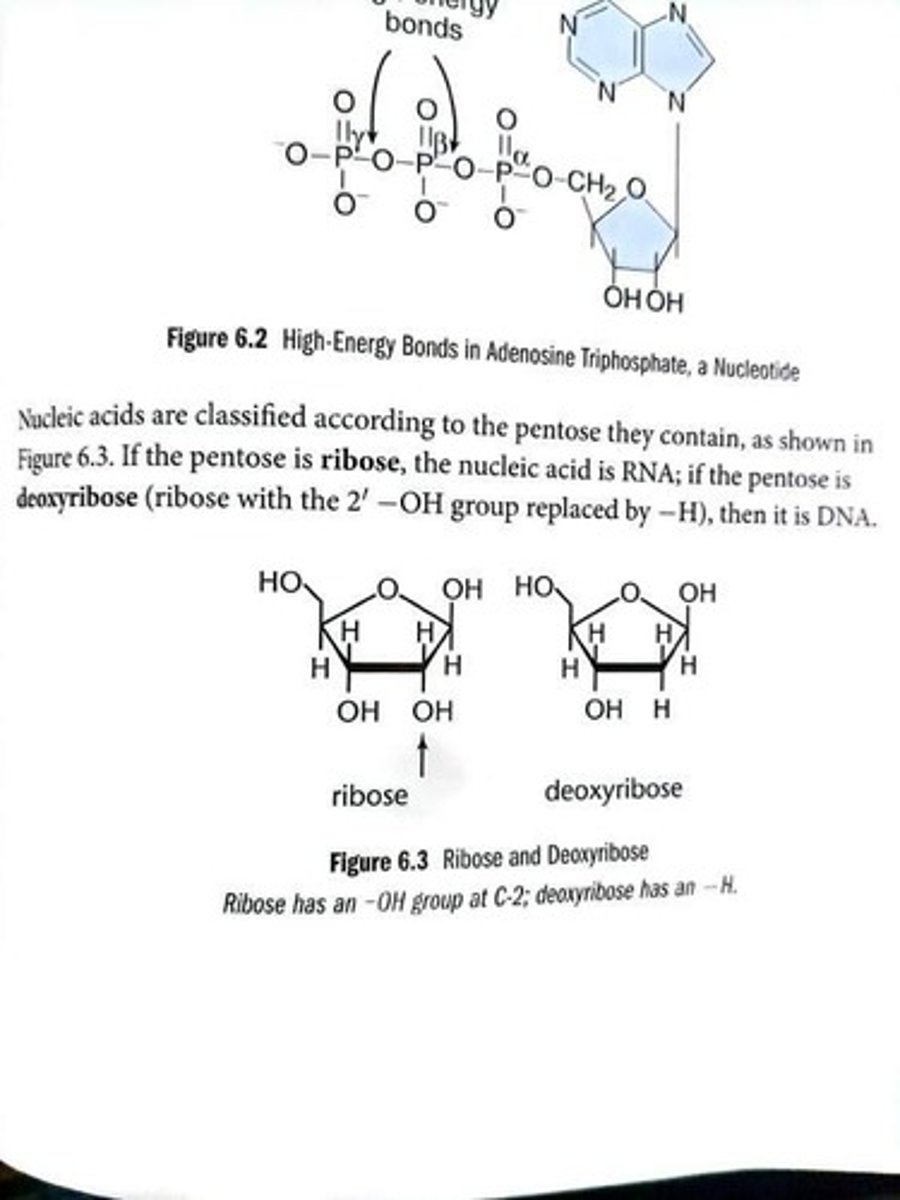
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
Nucleotide with two phosphate groups.
Guanosine
Nucleoside formed from guanine and ribose.
Cytidine
Nucleoside formed from cytosine and ribose.
Thymidine
Nucleoside formed from thymine and deoxyribose.
Uridine
Nucleoside formed from uracil and ribose.
Nucleotide nomenclature
Naming based on number of phosphate groups.
Chromosomes
Structures containing DNA in the nucleus.
Mitochondrial DNA
DNA found in mitochondria, distinct from nuclear DNA.
Chloroplast DNA
DNA found in chloroplasts, involved in photosynthesis.
Negative charge of DNA
Result of phosphate groups in the backbone.
Nucleic Acid Strand
Sequence of nucleotides forming DNA or RNA.
Double-Stranded DNA
DNA structure consisting of two polynucleotide strands.
Single-Stranded RNA
RNA structure consisting of a single polynucleotide strand.
Purines
Nitrogenous bases with two ring structures.
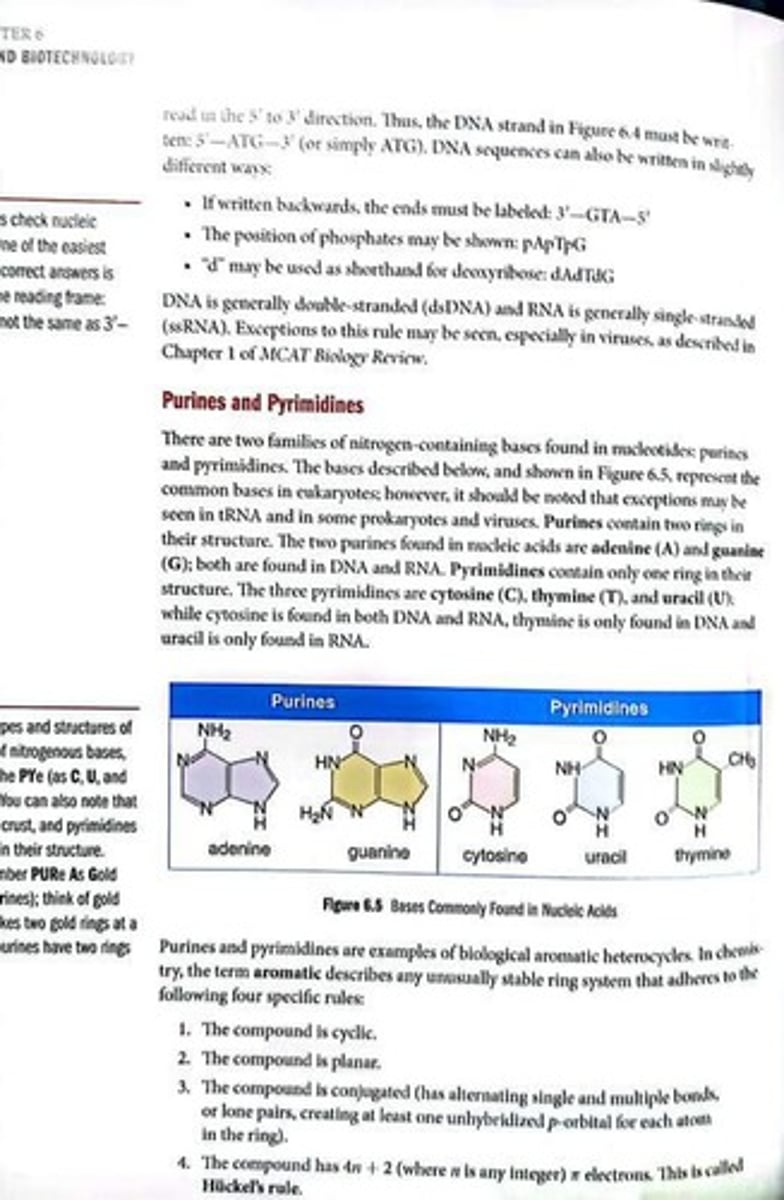
Pyrimidines
Nitrogenous bases with one ring structure.
Adenine (A)
Purine found in both DNA and RNA.
Guanine (G)
Purine found in both DNA and RNA.
Cytosine (C)
Pyrimidine found in both DNA and RNA.
Thymine (T)
Pyrimidine found only in DNA.
Uracil (U)
Pyrimidine found only in RNA.
Aromatic Compounds
Stable ring structures following specific rules.
Delocalized Electrons
Electrons that can move across a molecule.
Heterocycles
Ring structures containing different elements, like nitrogen.
Watson-Crick Model
Three-dimensional structure of DNA proposed in 1953.
Base Pairing
Specific pairing of nucleotides in DNA structure.
Polynucleotide Chains
Long sequences of nucleotides linked together.
X-ray Crystallography
Technique used to determine DNA structure.
Rosalind Franklin
Scientist whose work aided DNA structure discovery.
Biological Aromatic Heterocycles
Compounds with stable rings containing different elements.
Stability of Nucleic Acids
Exceptional stability due to aromatic ring structures.
Sugar-phosphate backbone
Outer structure of DNA helix, supports stability.
Complementary base-pairing
Specific pairing of adenine with thymine, guanine with cytosine.
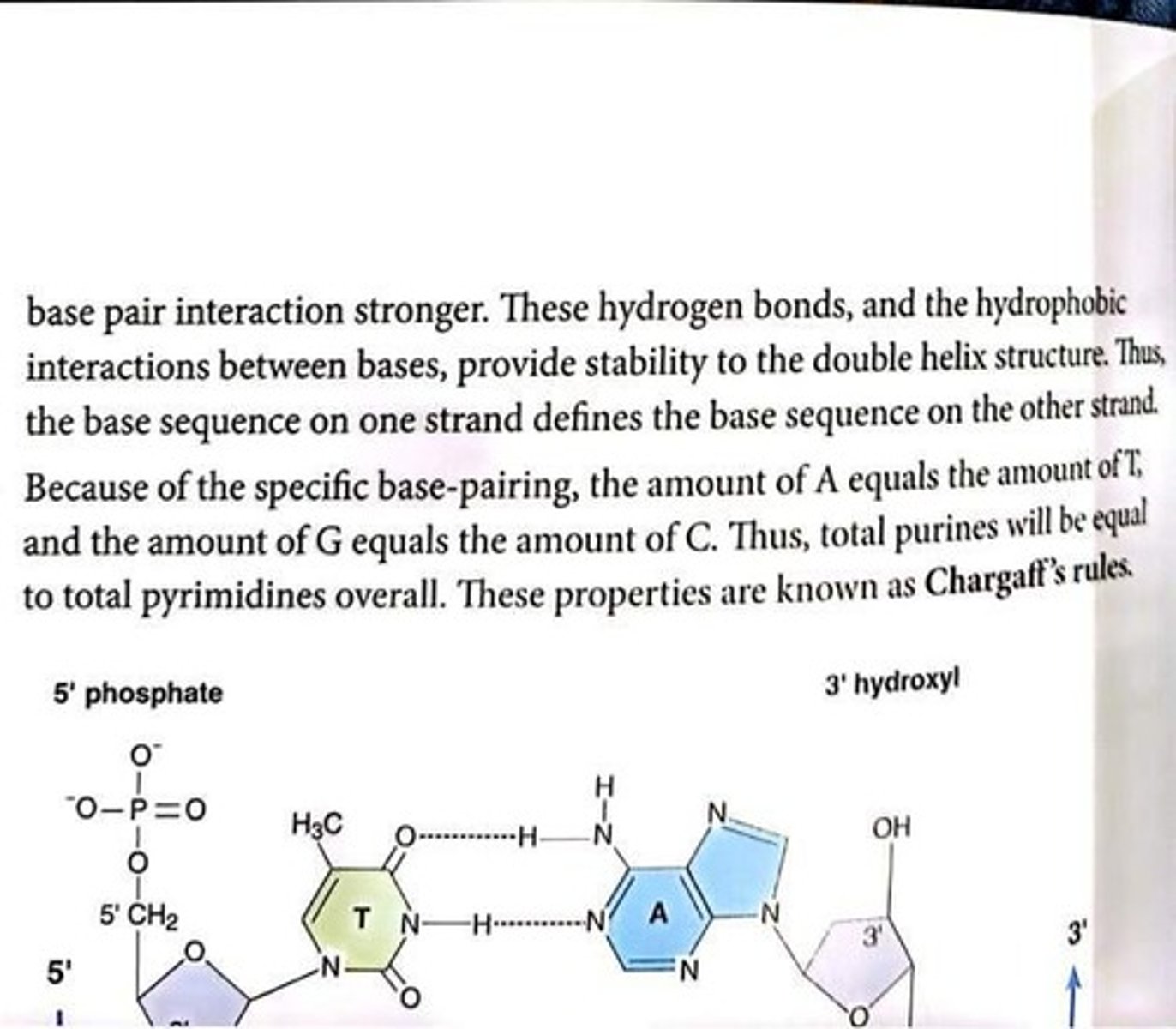
Hydrogen bonds
Weak interactions stabilizing base pairs in DNA.
Chargaff's rules
A=T and G=C; purines equal pyrimidines.
B-DNA
Right-handed double helix with 3.4 nm turn.

Z-DNA
Left-handed helix with zigzag appearance, 4.6 nm turn.
Denaturation
Separation of DNA strands by disrupting hydrogen bonds.

Reannealing
Process of complementary DNA strands pairing again.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Technique amplifying DNA sequences through denaturation and reannealing.
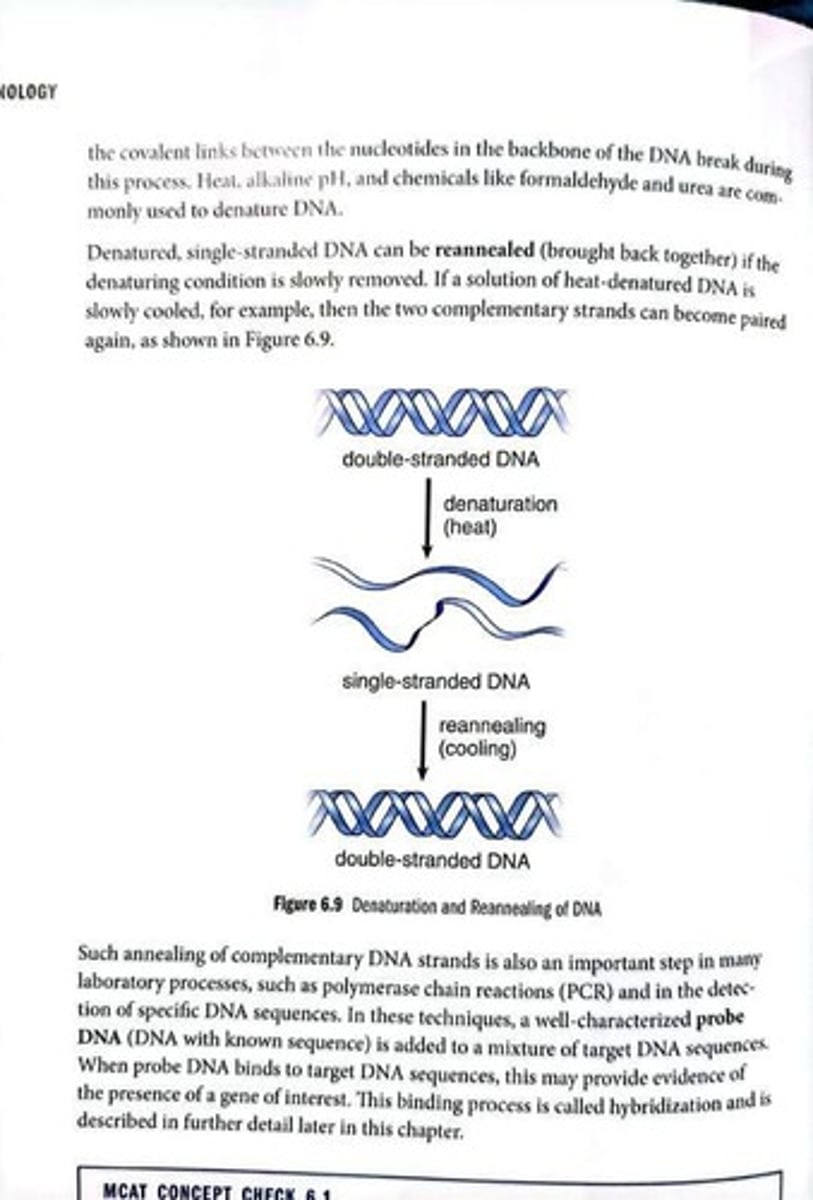
Hybridization
Binding of probe DNA to target DNA sequences.
Histones
Basic proteins around which DNA is wound to form chromatin.

Chromatin
Complex of DNA and histone proteins in eukaryotic cells.
Euchromatin
Less condensed form of chromatin, accessible for transcription.
Heterochromatin
Tightly packed form of chromatin, less transcriptionally active.
Telomeres
Protective caps at the ends of chromosomes.
Centromeres
Region where sister chromatids are joined.
Major grooves
Spaces between DNA strands, often protein binding sites.
Minor grooves
Smaller spaces between DNA strands, less accessible.
GC-content
Percentage of guanine and cytosine in DNA, affects stability.
Histone
Protein that organizes DNA into nucleosomes.
Nucleosome
DNA wrapped around a histone core.
Telomere
Repeating DNA sequence at chromosome ends.
Telomerase
Enzyme that extends telomeres during replication.
Centromere
Region of DNA at chromosome center.
Replication Fork
Y-shaped structure during DNA replication.
Origins of Replication
Sites where DNA unwinds for replication.
Replisome
Protein complex facilitating DNA replication.
S Phase
Cell cycle phase for DNA replication.
Transcription
Process of synthesizing RNA from DNA.
Microtubules
Cytoskeletal structures separating chromatids during anaphase.
DNA Replication
Process of copying DNA for cell division.

Animal Studies
Research indicating telomere shortening relates to aging.
Beads on a String
Visual representation of nucleosomes under microscopy.
DNA Blueprint
Genetic information guiding organism's functions.
Highly Repetitive Sequences
DNA segments found in heterochromatin.
Transcriptionally Active
DNA regions involved in gene expression.
Sister Chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome.

Cell Division
Process where a cell divides into two.
Replication Forks
Points where DNA strands separate during replication.
Eukaryotic Replication
Slower process with multiple origins of replication.
Prokaryotic Replication
Faster process with a single origin of replication.
Helicase
Enzyme that unwinds DNA strands for replication.
Single-Stranded DNA-Binding Proteins
Proteins that stabilize unwound DNA strands.
Positive Supercoiling
Torsional strain caused by DNA unwinding.
Negative Supercoiling
Introduced by topoisomerases to relieve torsional stress.
Semiconservative Replication
Each new DNA molecule retains one parental strand.
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands from templates.
Antiparallel Orientation
Strands run in opposite directions in DNA double helix.
Leading Strand
Continuously synthesized strand in the same direction as fork.

Lagging Strand
Discontinuously synthesized strand opposite to replication fork.
Okazaki Fragments
Short DNA segments synthesized on the lagging strand.
RNA Primer
Short RNA strand required to initiate DNA synthesis.

Nucleases
Enzymes that degrade unprotected DNA strands.
Topoisomerases
Enzymes that relieve torsional strain in DNA.
Template Strand
Parental DNA strand used for synthesis of new strand.
Hydrogen Bonding
Attraction between bases that stabilizes DNA structure.
Replication Process
Series of steps to duplicate DNA molecules.