Microbiology 2314 Lab Exam Review
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
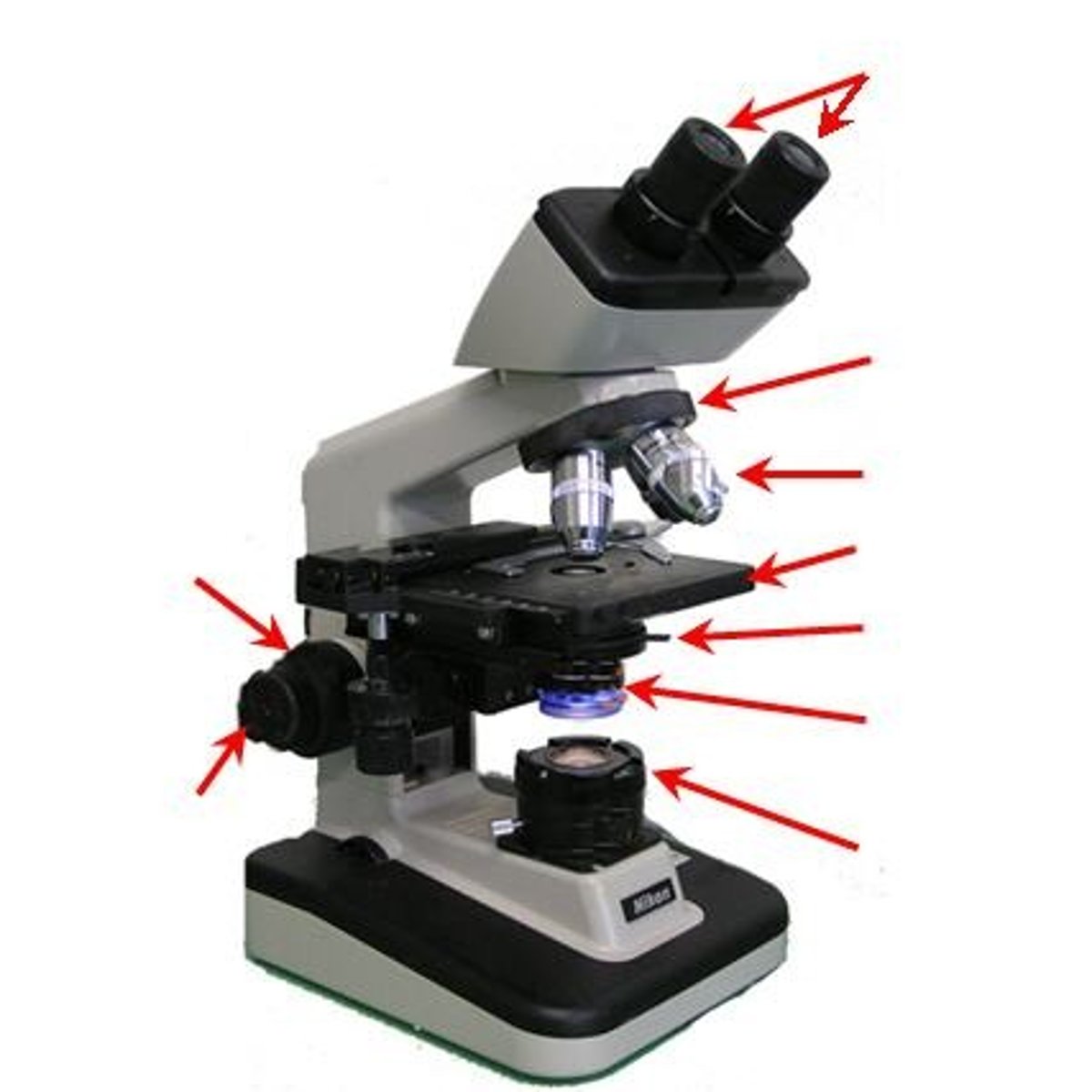
Parts of a microscope
Ocular lens, objective lenses, stage, stage clips, coarse adjustment knob, fine adjustment knob, diaphragm, condenser, light source, base, arm, nosepiece, mechanical stage
Resolving power
The ability of a microscope to distinguish two points as separate objects.
Parfocal
When a microscope stays in focus when changing objective lenses.
Equation to calculate scale of a drawing
(Size of drawing(mm) / actual size of (um)) = scale.
Ingredient that solidifies nutrient broth
Agar.
Autoclave conditions for sterilization
121°C, 15 psi, for 15-20 minutes.
Agar melting point
100°C.
Agar solidification point
40-45°C.
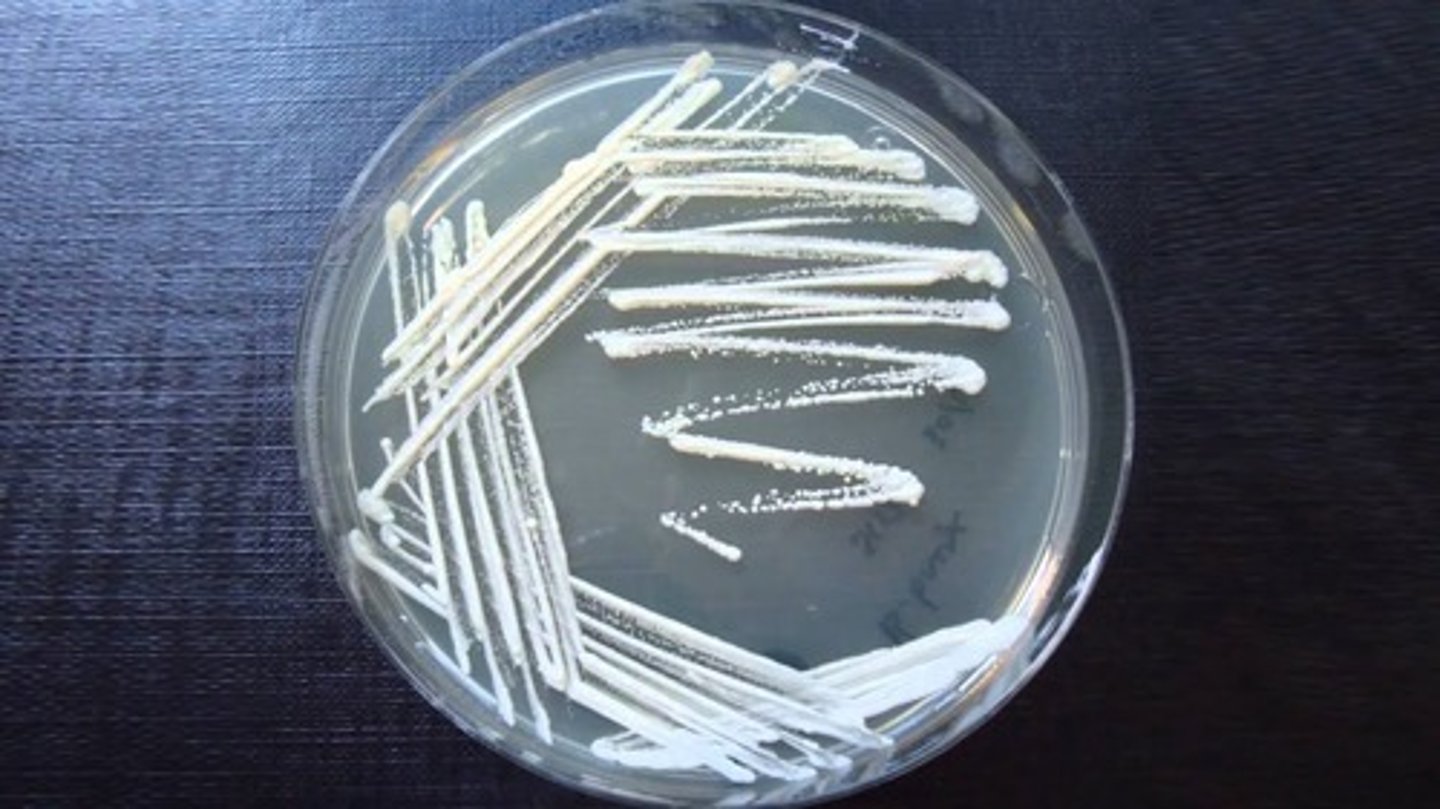
Pour plate vs. streak plate
Pour plate: Colonies grow within/on top of agar; Streak plate: Colonies grow only on the surface.
Why are plates incubated upside down?
To prevent condensation from dripping onto the agar.
Negative stain recognition
Background is stained, cells remain clear.
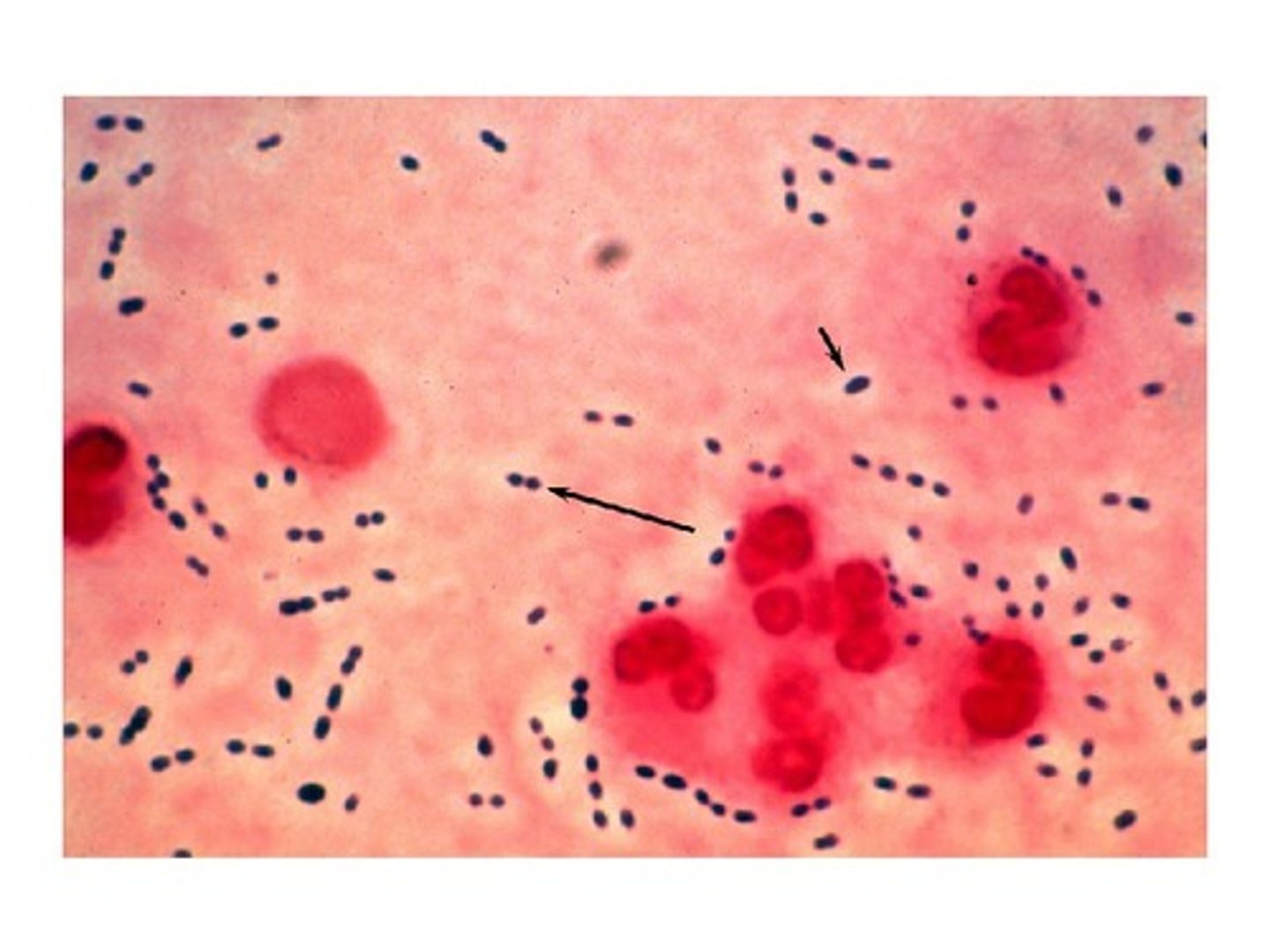
When would you use a negative stain?
To observe cell shape, size, and arrangement without heat fixing. ex. capsule
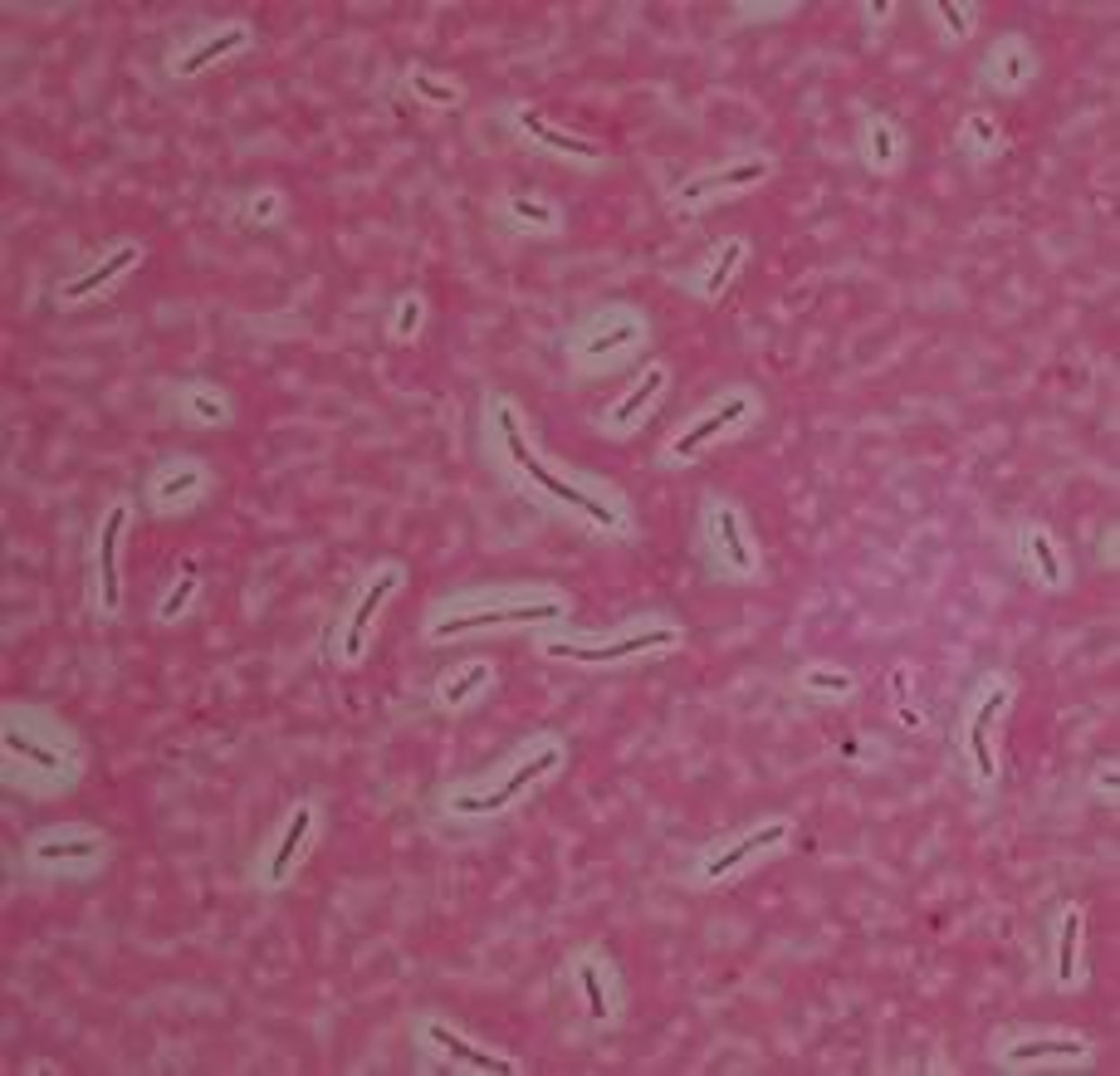
Dye used for negative stain? Is it acidic, neutral, or basic?
Nigrosin / Acidic
Basic dyes
Methylene blue, crystal violet, safranin (and basic fuchsin)
Cocci vs. rods
Cocci: Spherical; Rods: Cylindrical.
Simple stain
Uses a single dye to color cells for visualization.
Reason for heat-fixing slides
Kills bacteria and fixes them to the slide.
Capsule stain recognition
Clear halo around cells (capsule) with dark background.
Reagents used in capsule stain
Congo red + Maneval's stain.
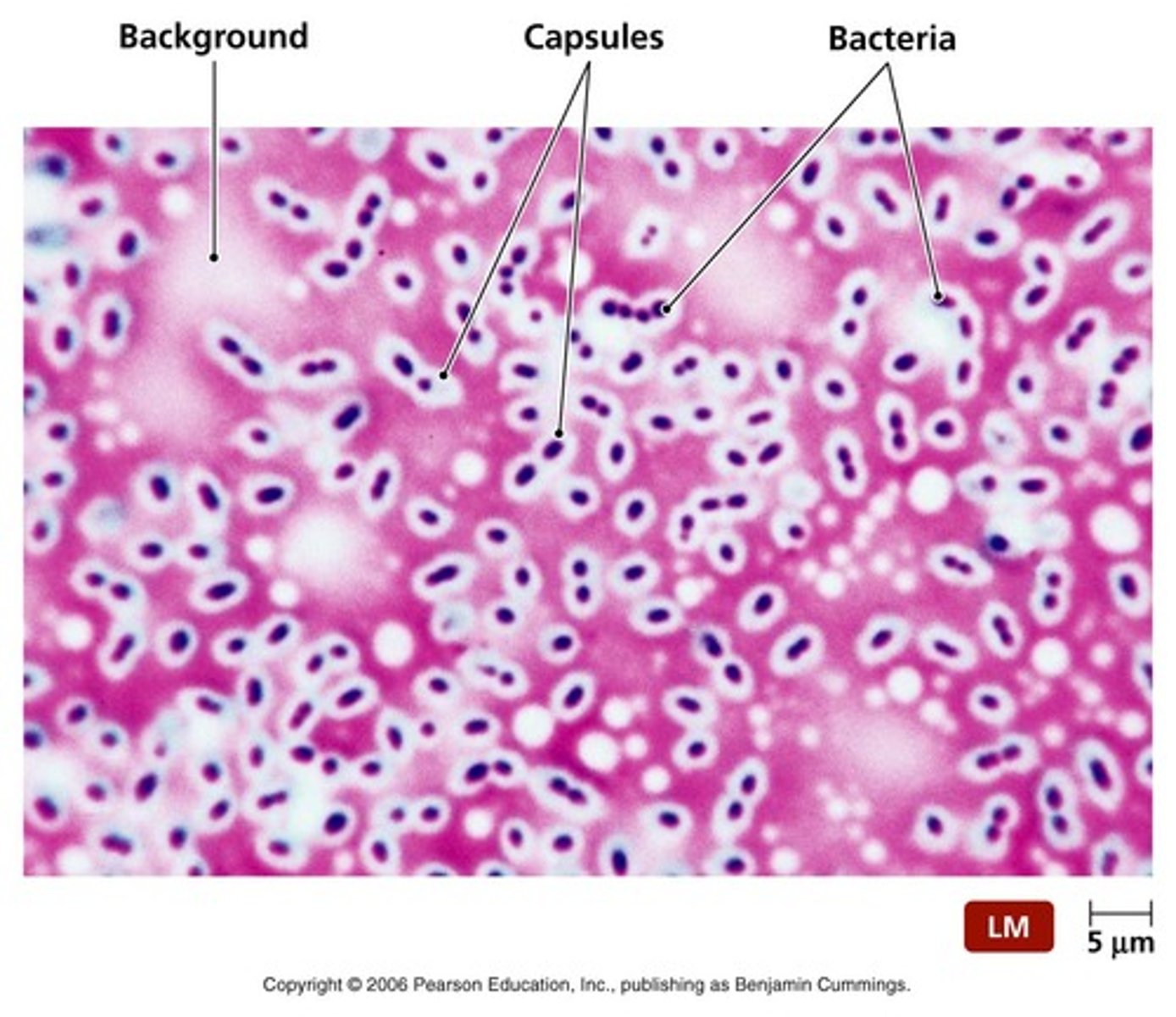
Molecules in a capsule
Polysaccharides or polypeptides.
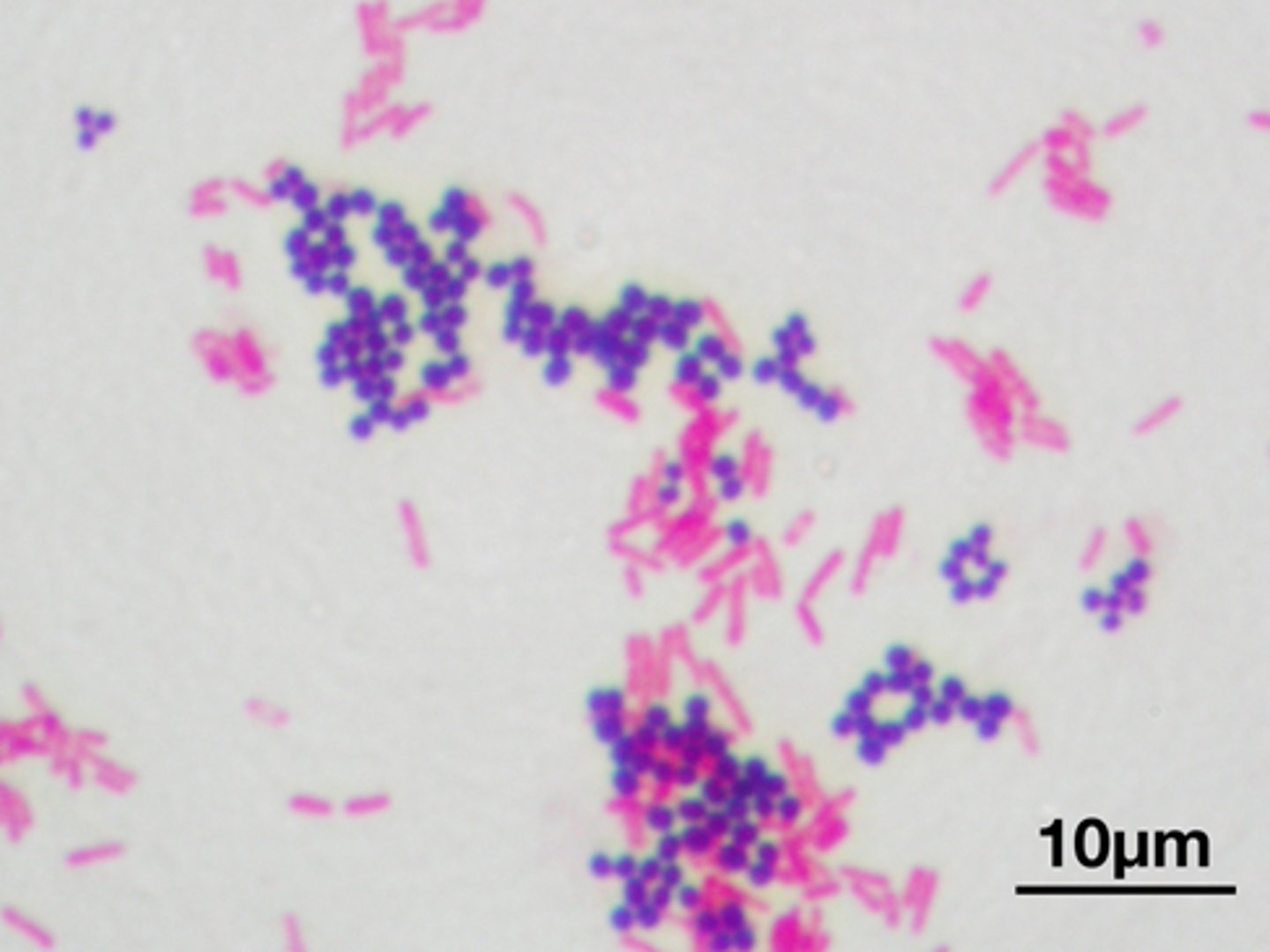
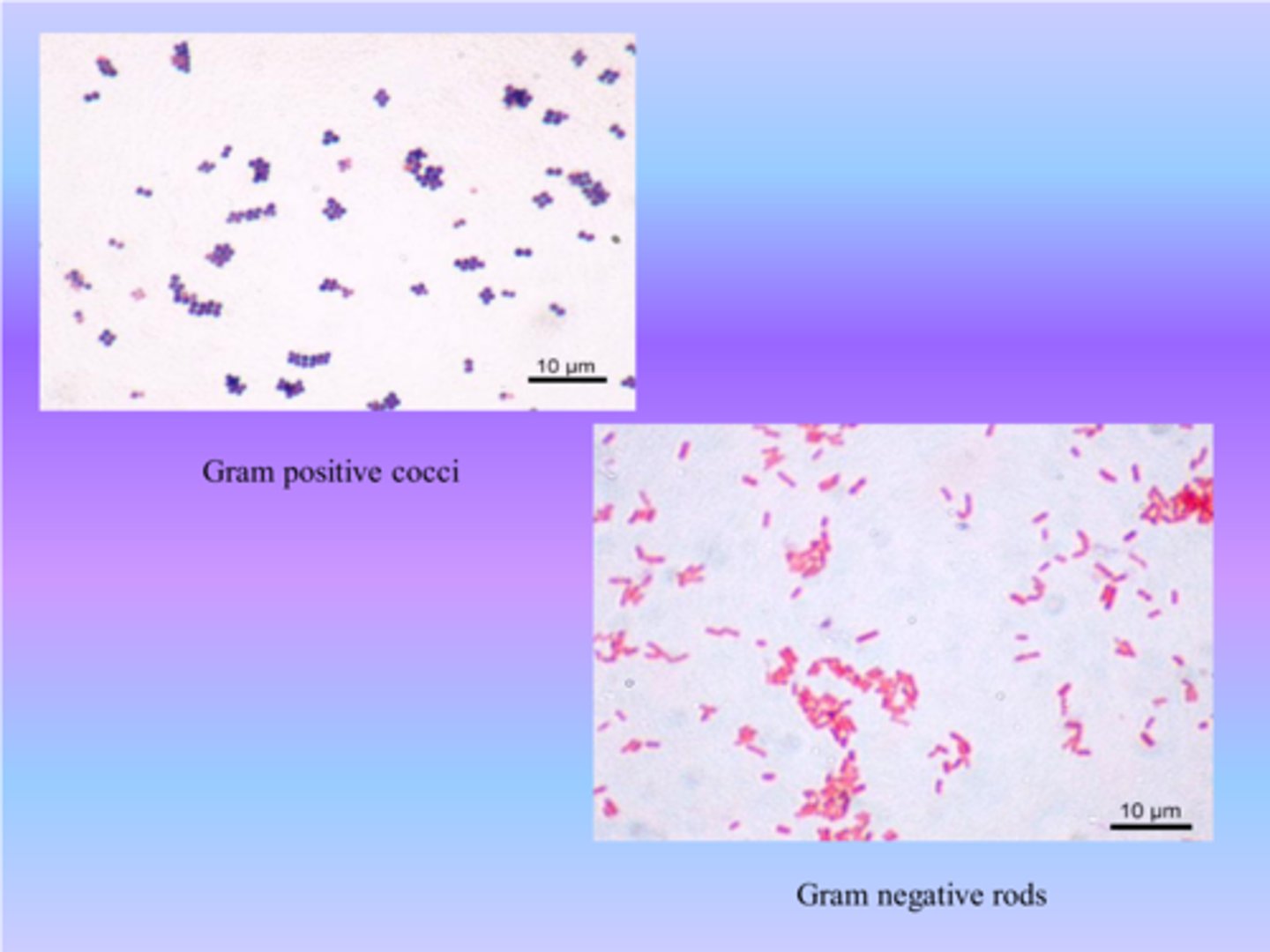
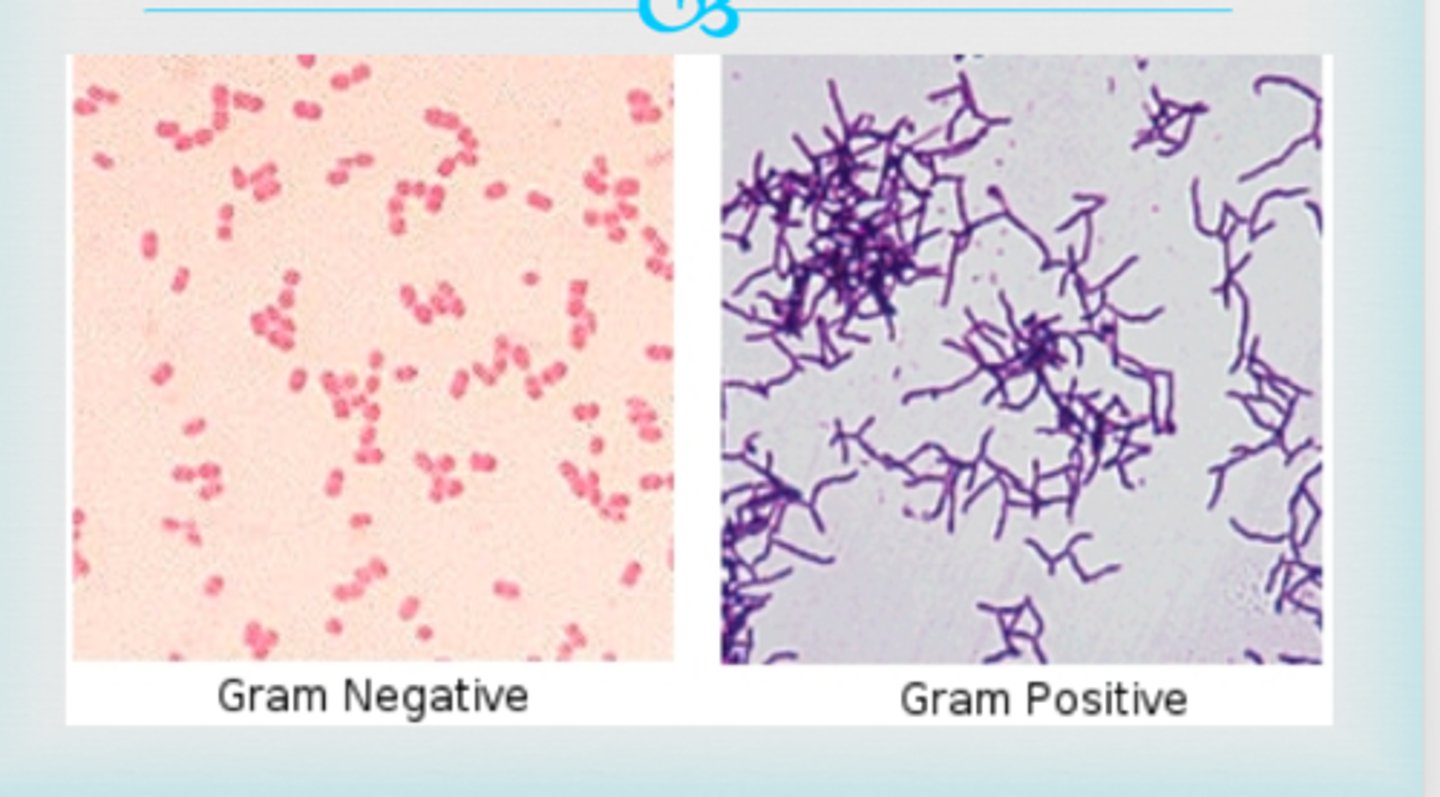
Gram-positive vs. gram-negative bacteria
Gram-positive: Purple; Gram-negative: Pink/red.
Dyes used in gram staining
Primary- Crystal violet Mordant- iodine, Decolorizer- ethanol, Counterstain- safranin.
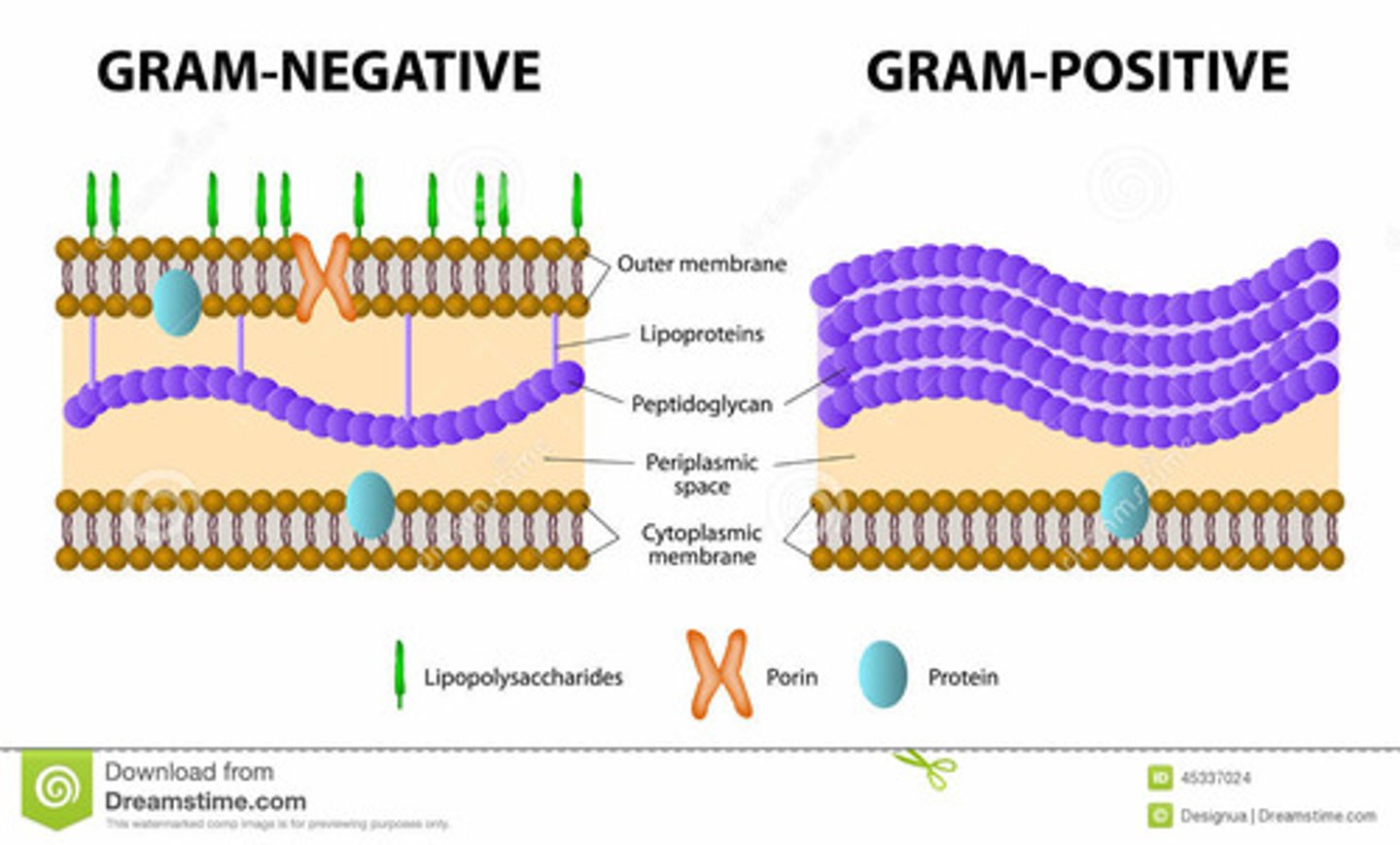
Differences in cell walls gram positive/negative
Gram+: Thick peptidoglycan, no outer membrane; Gram-: Thin peptidoglycan, outer membrane with LPS.
Examples of bacteria
Gram+: Bacillus subtilis; Gram-: Escherichia coli.
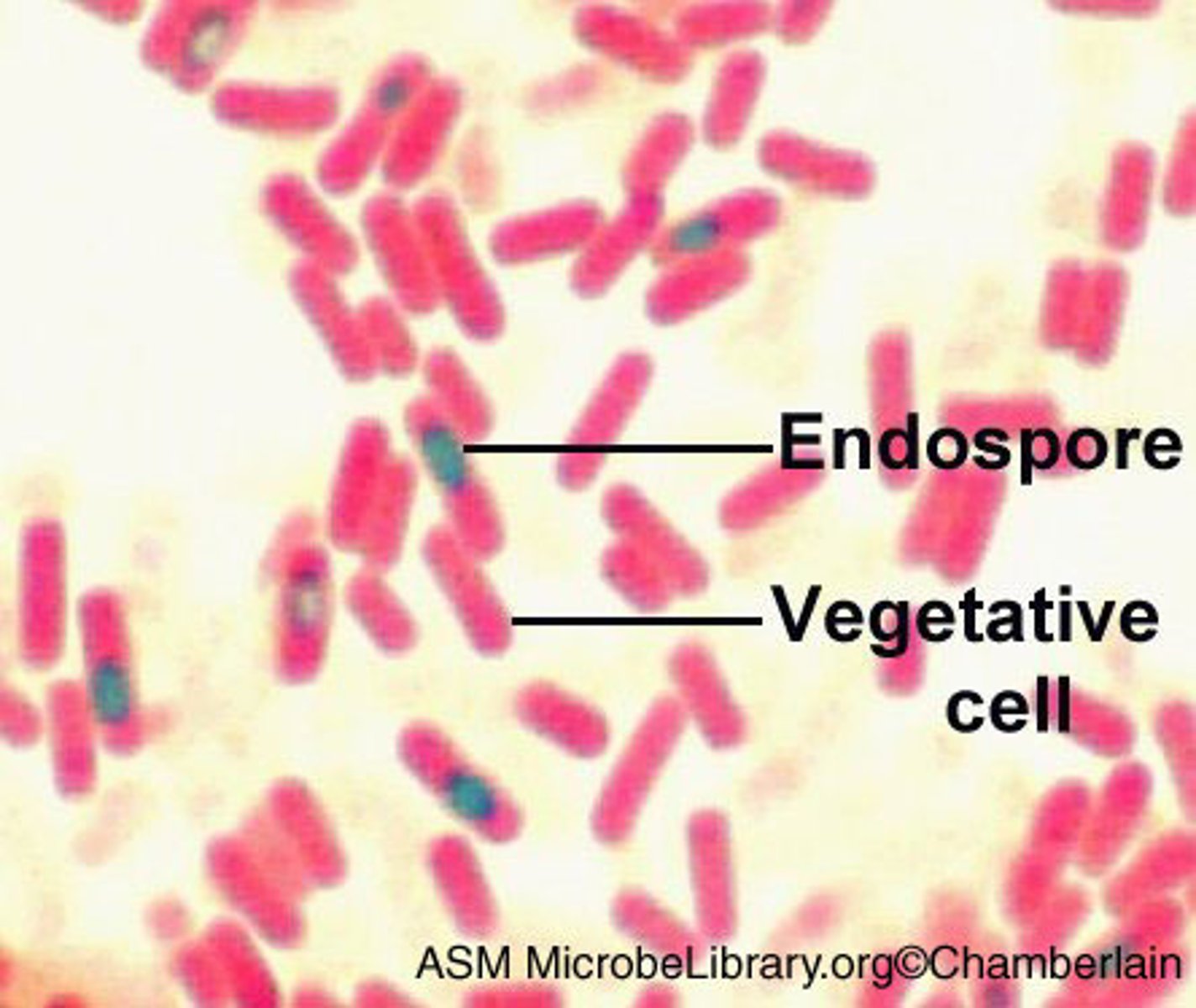
Spore recognition
Green ovals inside or outside red/pink cells.
Reagents in spore stain
Malachite green, heat, DI water, safranin.
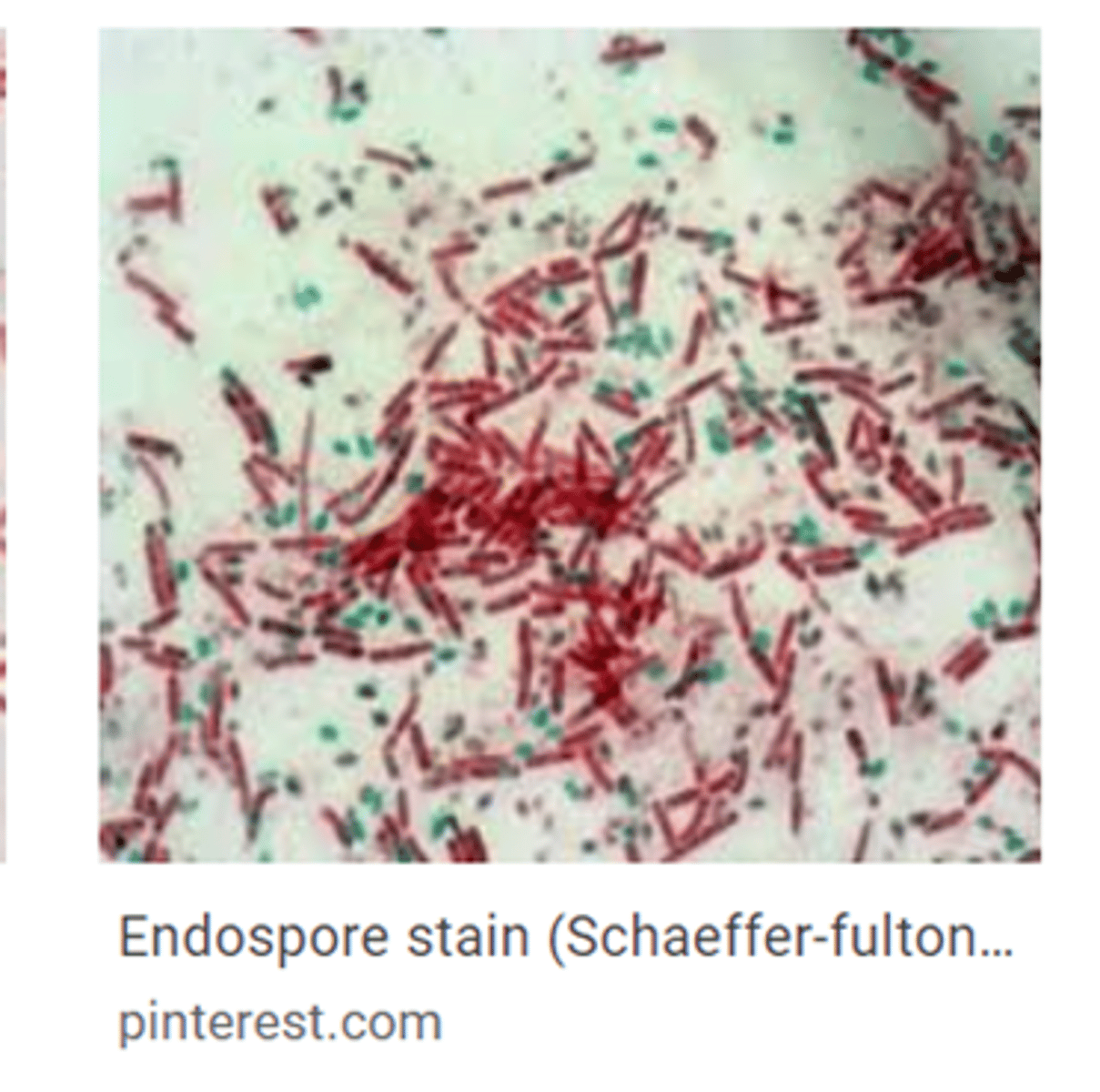
Purpose of spore formation
For survival in harsh conditions.
Spore-forming genus
Bacillus
Acid-fast bacterium characteristic
Mycolic acid.
Reagents in acid-fast stain
Carbol fuchsin, acid-alcohol, methylene blue.
Acid-fast bacteria recognition
Acid-fast: Red; Non-acid-fast: Blue.
Purpose of acid-fast stain
To identify bacteria with waxy cell walls, e.g., Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
What is the total magnification of the 4x objective?
40x
What is the magnification of the 10x objective?
100x
What is the magnification of the 40x objective?
400x
What is the magnification of the 100x objective?
1000x
What part of the microscope is shown? (eyepieces)
ocular lens
What part of the microscope is shown? (Under eye pieces)
Diopter Adjustment
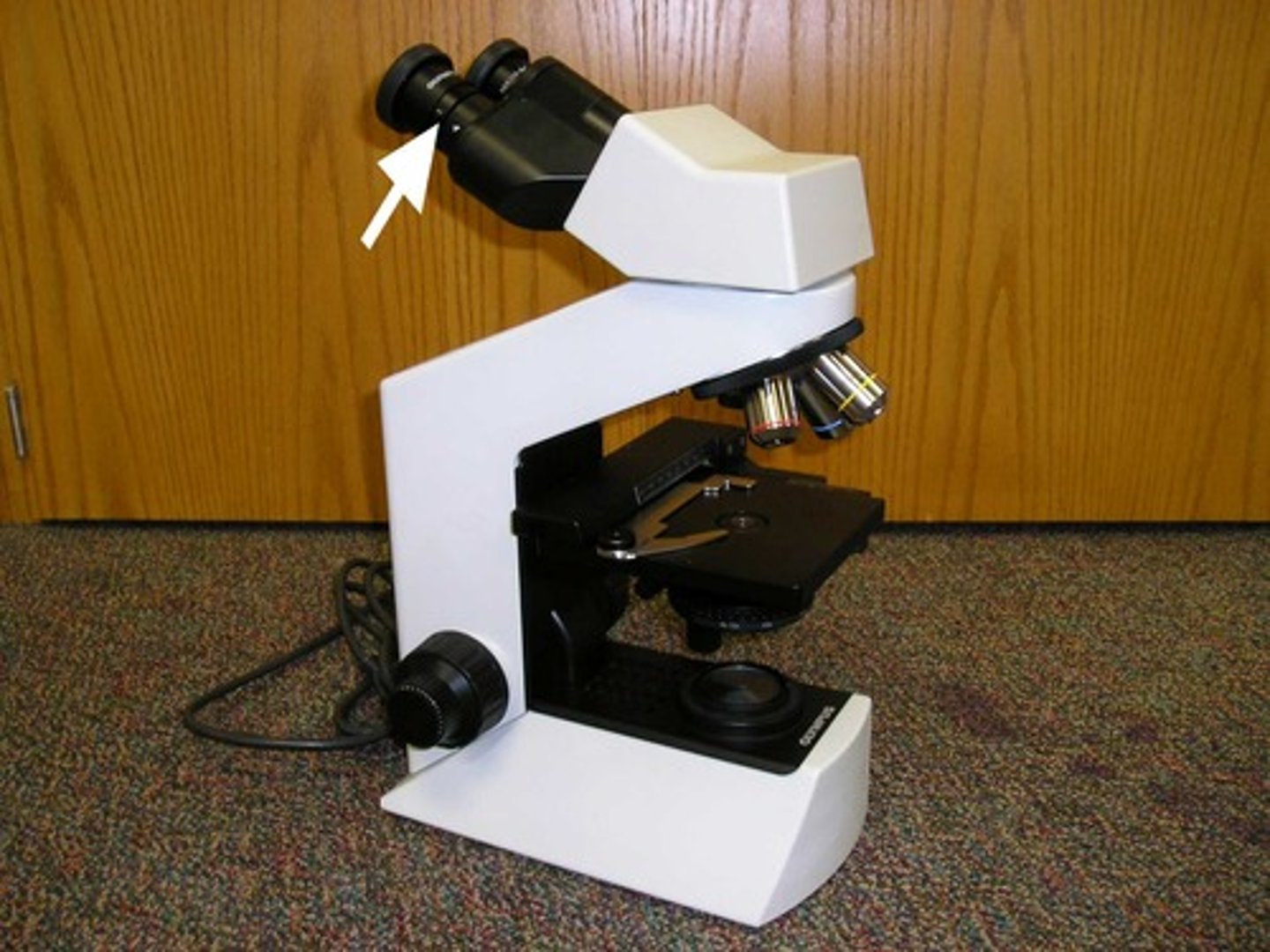
What part of the microscope is shown? (arch; major piece of body)
Arm
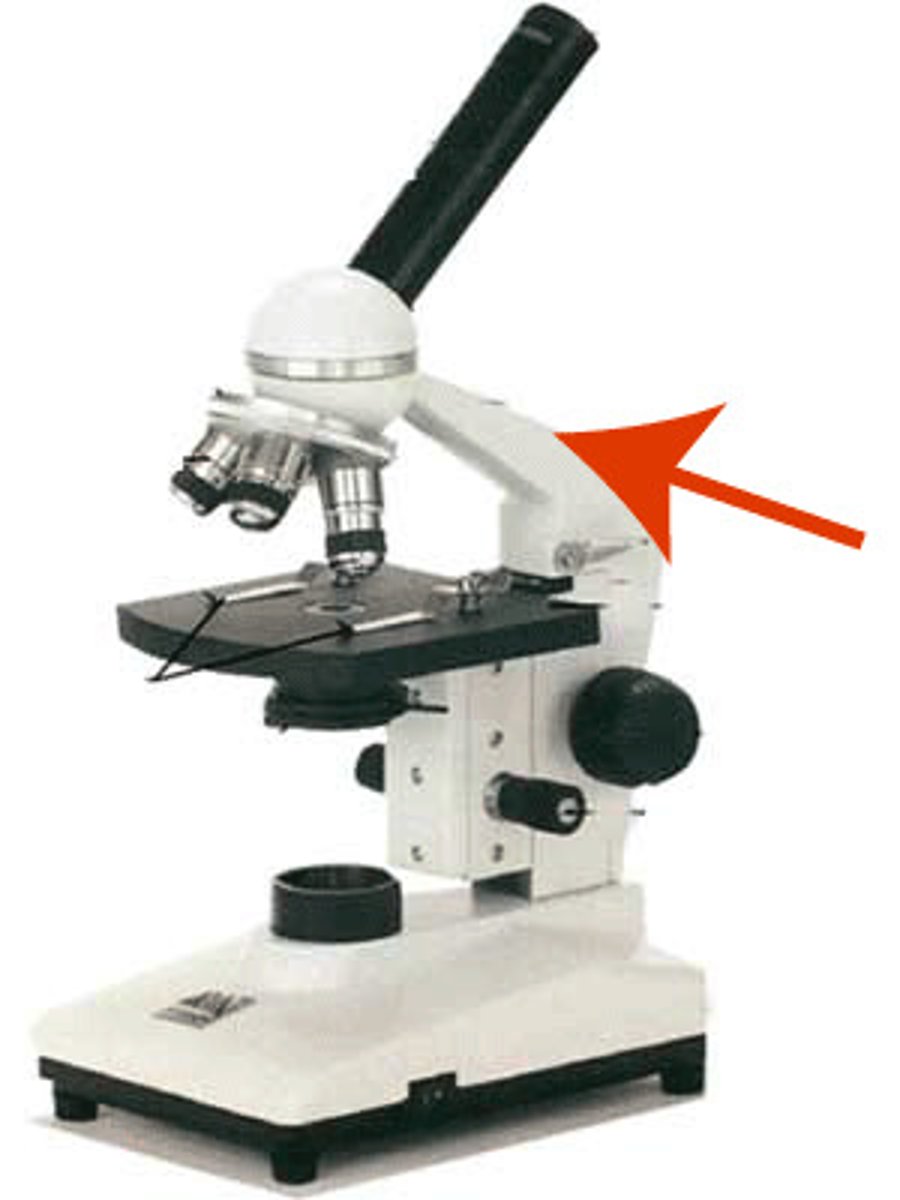
What part of the microscope is shown? (holds lenses)
Nose piece
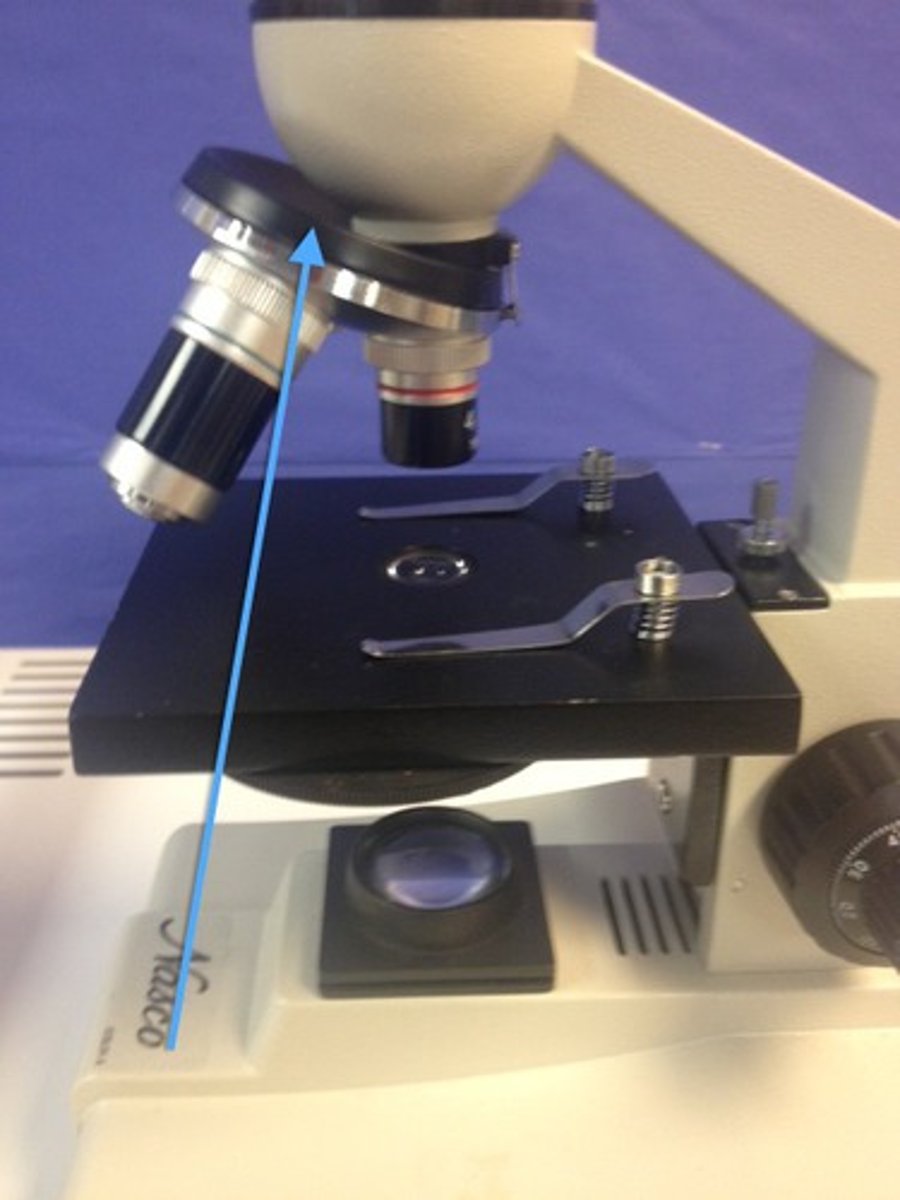

What part of the microscope is shown? (4 different kinds)
Objective lens
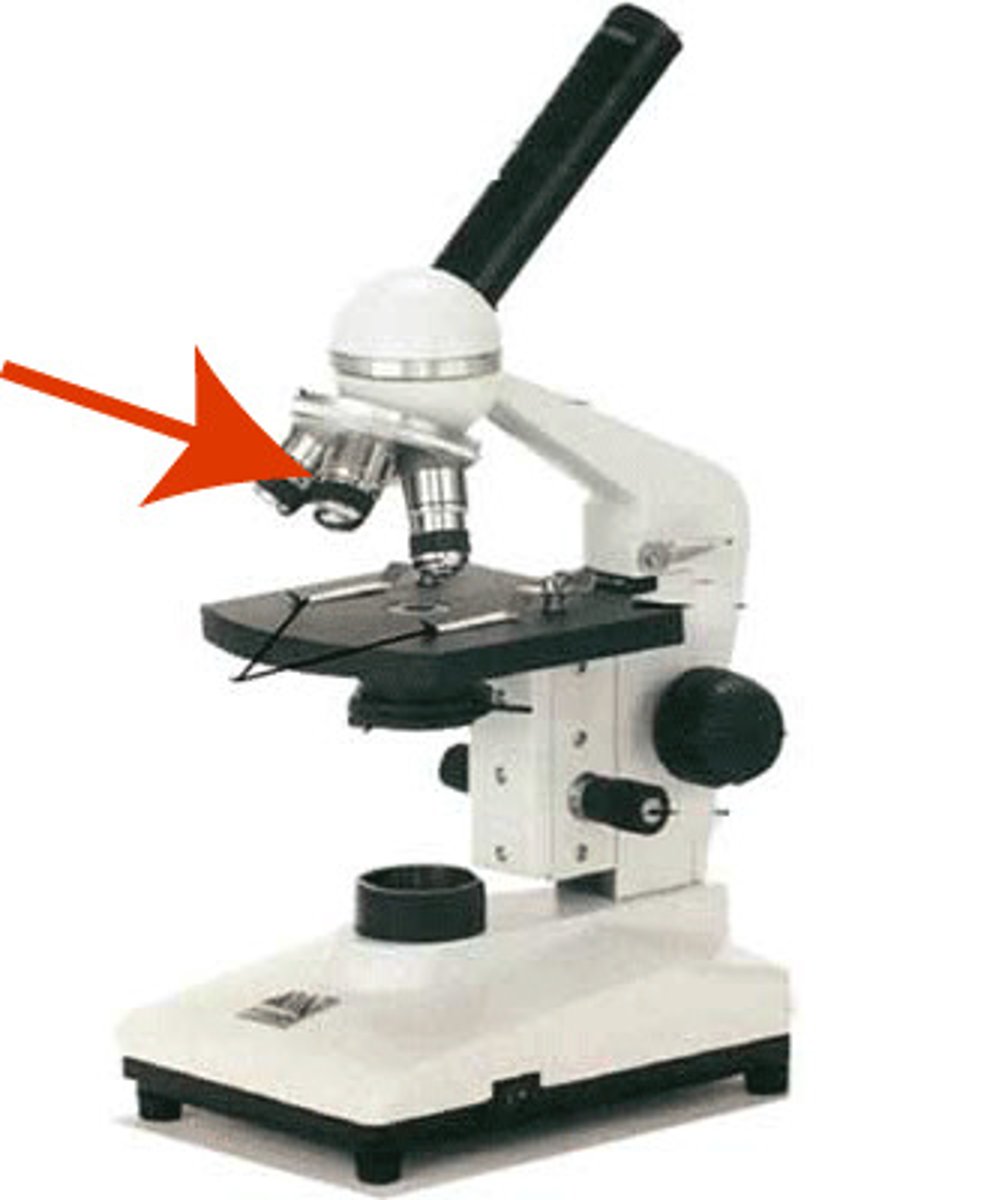

What part of the microscope is shown? (holds slide down)
Stage clip
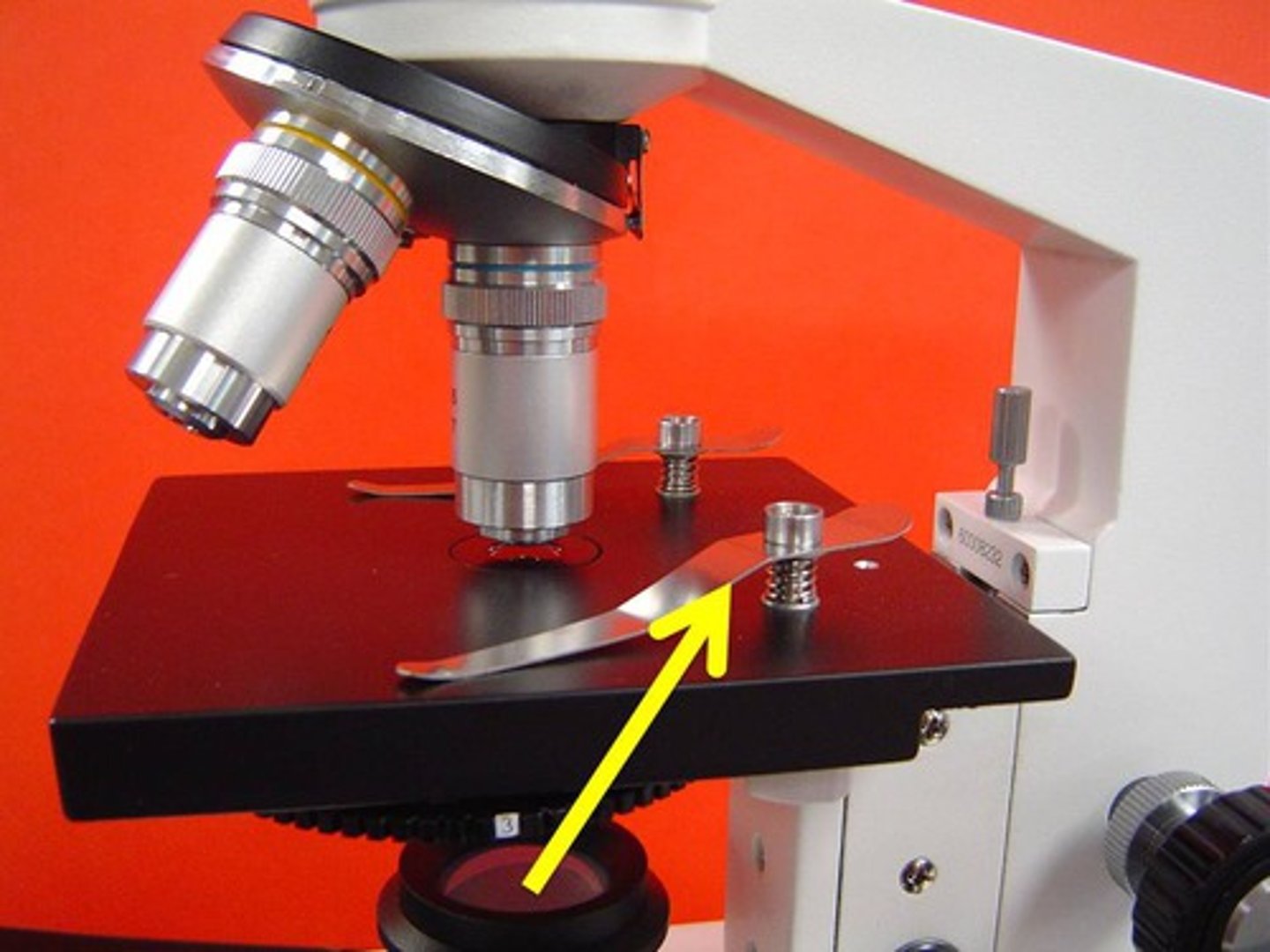

What part of the microscope is shown? (major portion where slide sits)
Stage
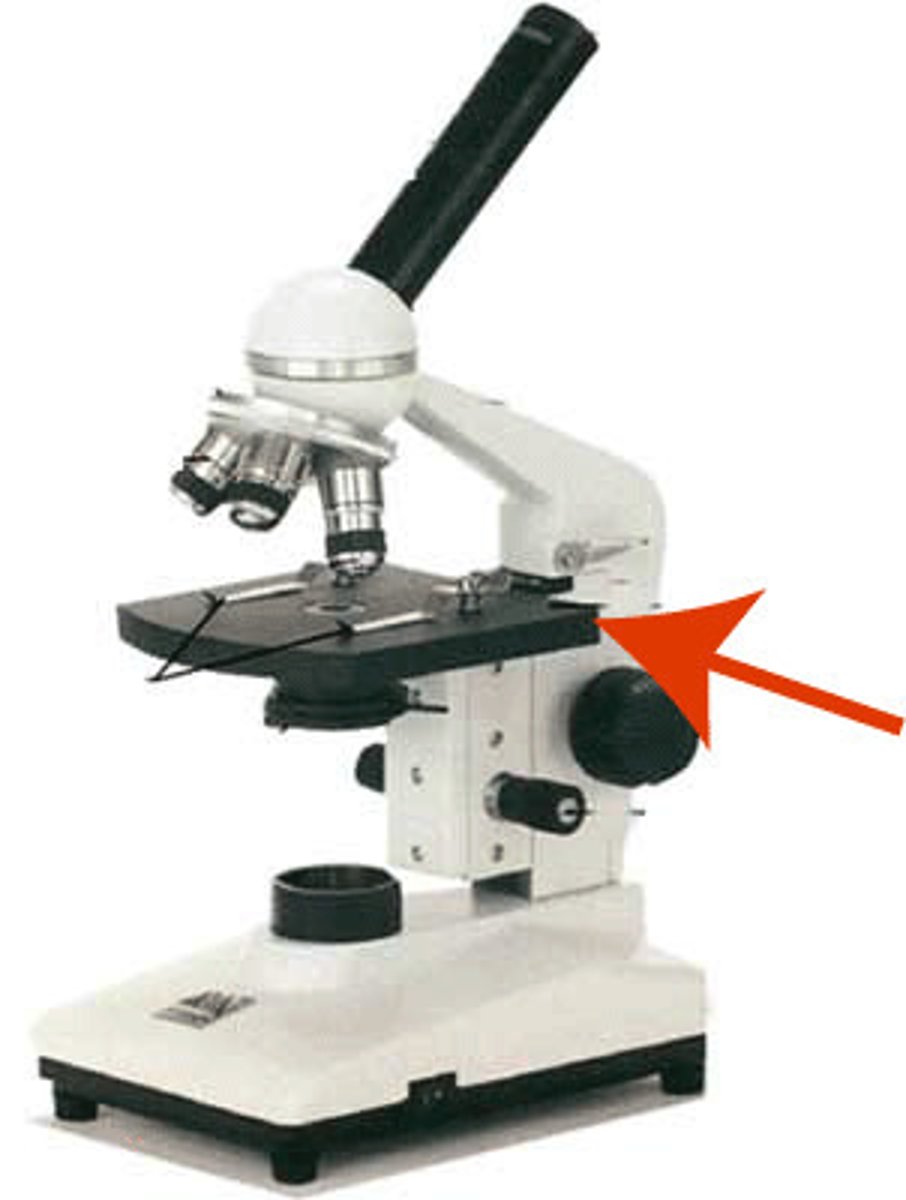
What part of the microscope is shown? (under stage)
Diaphragm
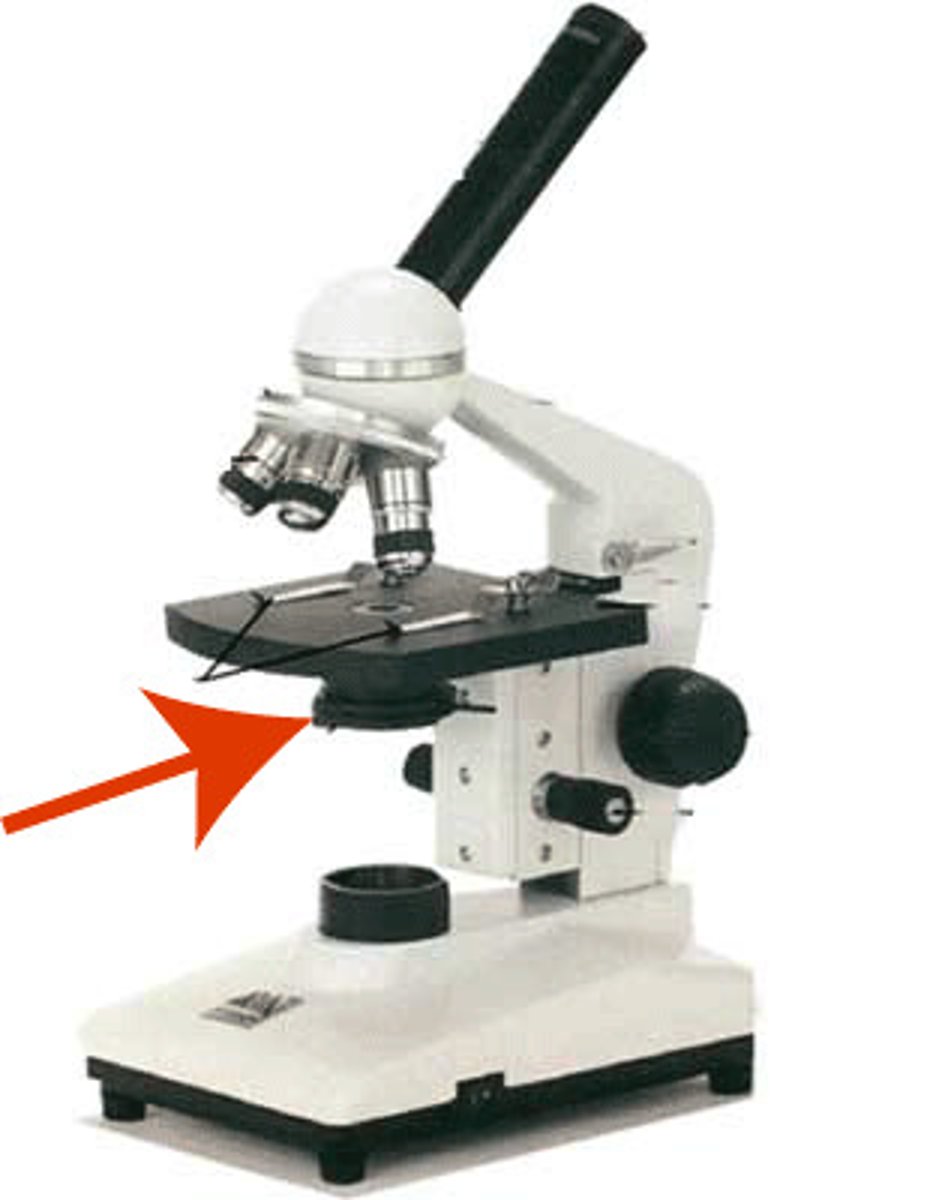
What part of the microscope is shown? (under diaphragm)
Condenser
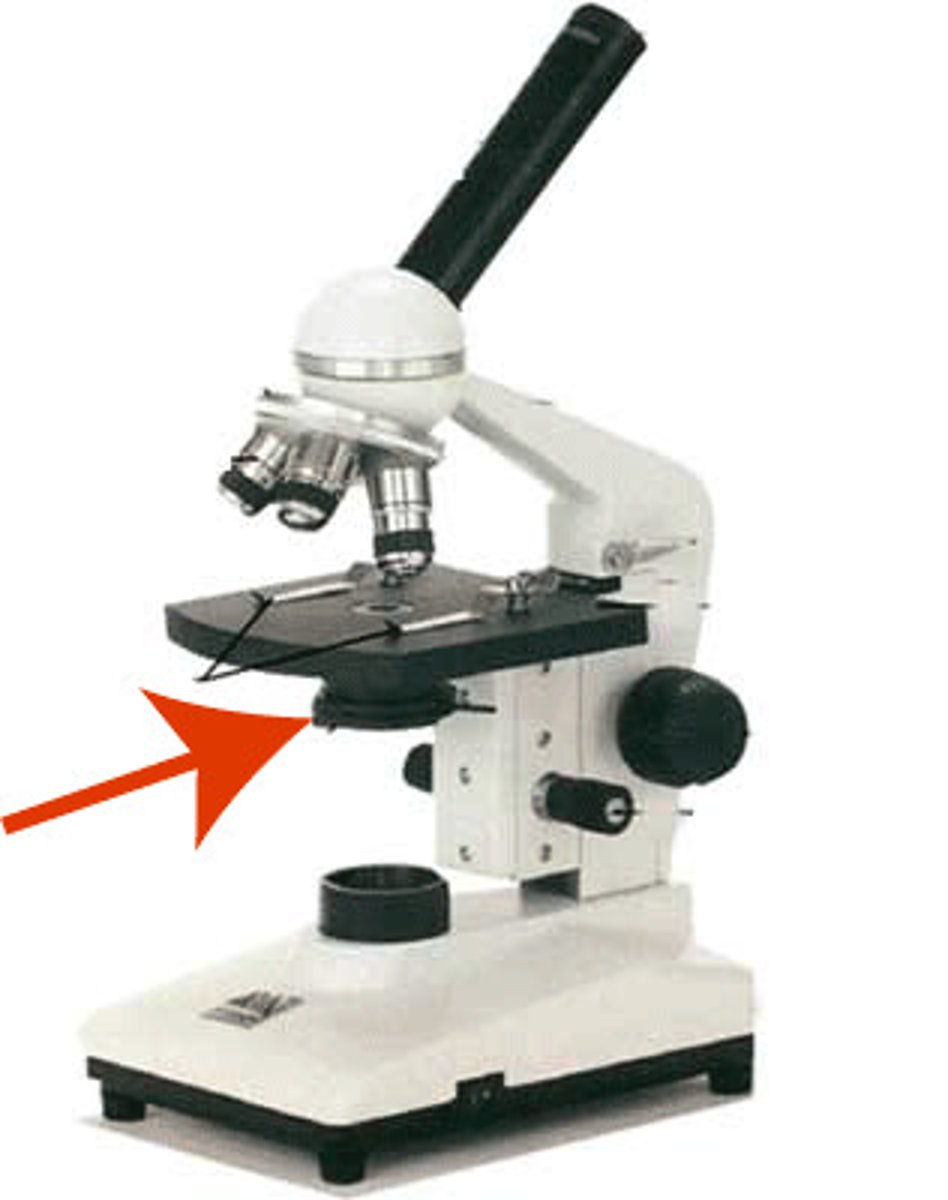
What part of the microscope is shown? (light source)
Illuminator
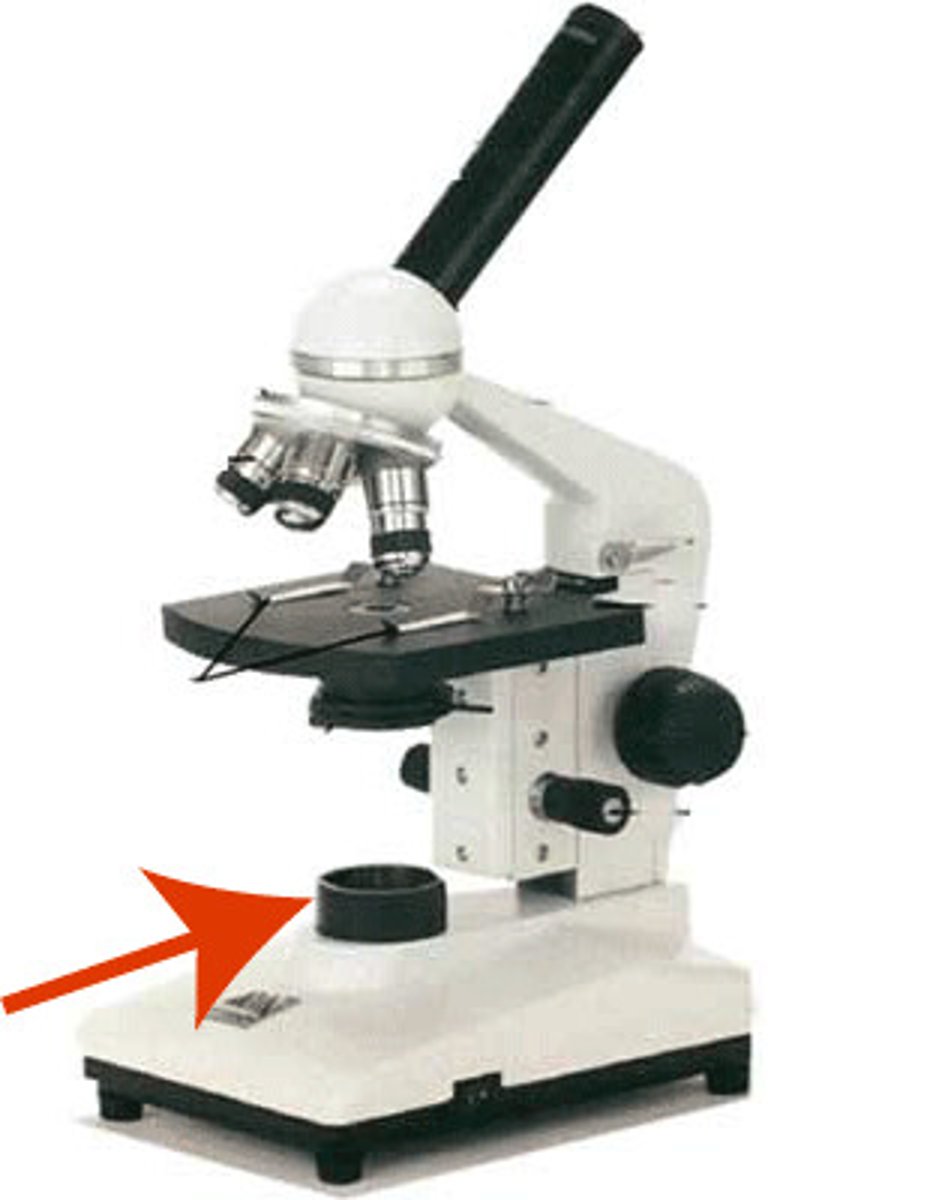

What part of the microscope is shown? (bottom)
Base

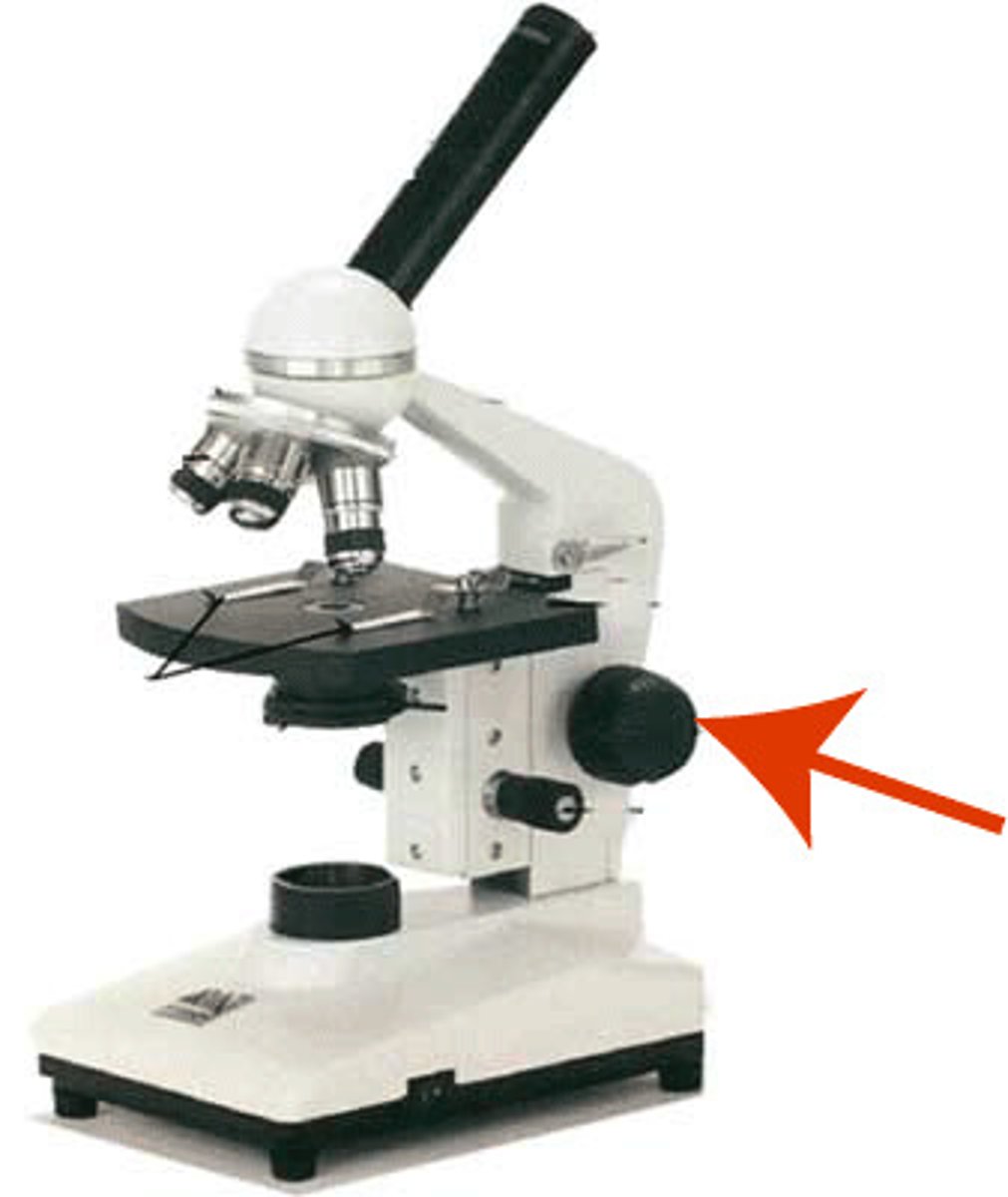
What part of the microscope is shown? (large focus)
Course adjustment knob

What part of the microscope is shown? (small focus)
Fine adjustment knob
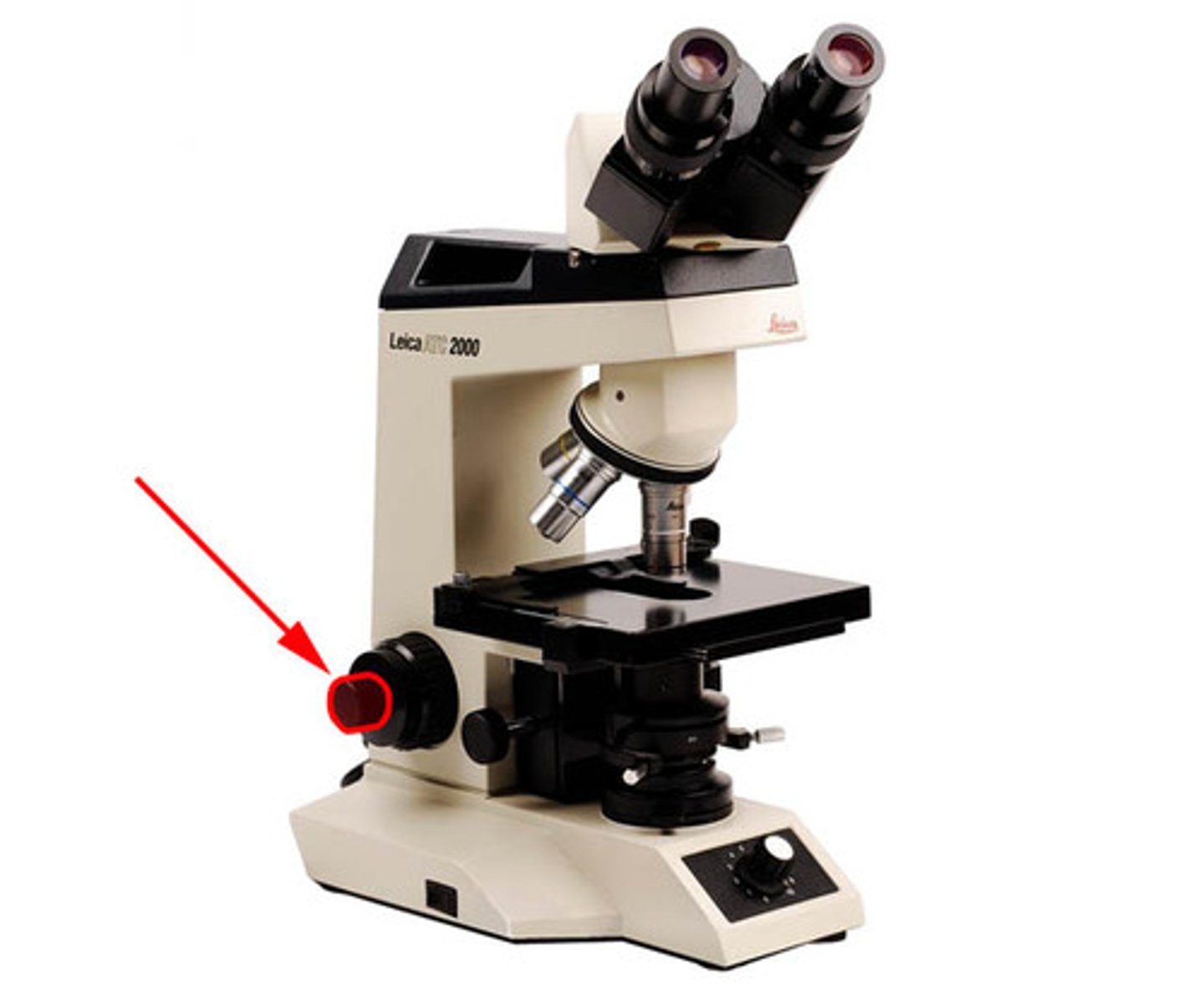
What part of the microscope is shown? (Controls light source)
Light switch
a. If viewed at under the 10x ocular lens, what is the size of the organism under the microscope in microns? (~5 micrometers) (multiply by 10 microns/division)
b. What is the size of the drawing in microns if drawn to be 12 mm?
c. If you draw the organism and it is 12 mm what is the scale of the object?
a. 5 micrometers x 10 microns/division = 50 microns
b. 12 mm x 1000 = 12000 microns
c. 12000 microns / 50 microns = x240
Agar is polysaccharide isolated from seaweed that is added to liquid media to make it harden.
a. What temp does it melt at?
b. What temp does it harden/cool at?
a. 100 degrees C
b. 45 degrees C
After the agar plates or slants cool and harden they need to be autoclaved to sterilize. What are the three conditions it should be at?
15 psi pressure, 15 minutes, 121 degrees C
Is this an example of a pour plate or a streak plate?
Pour plate
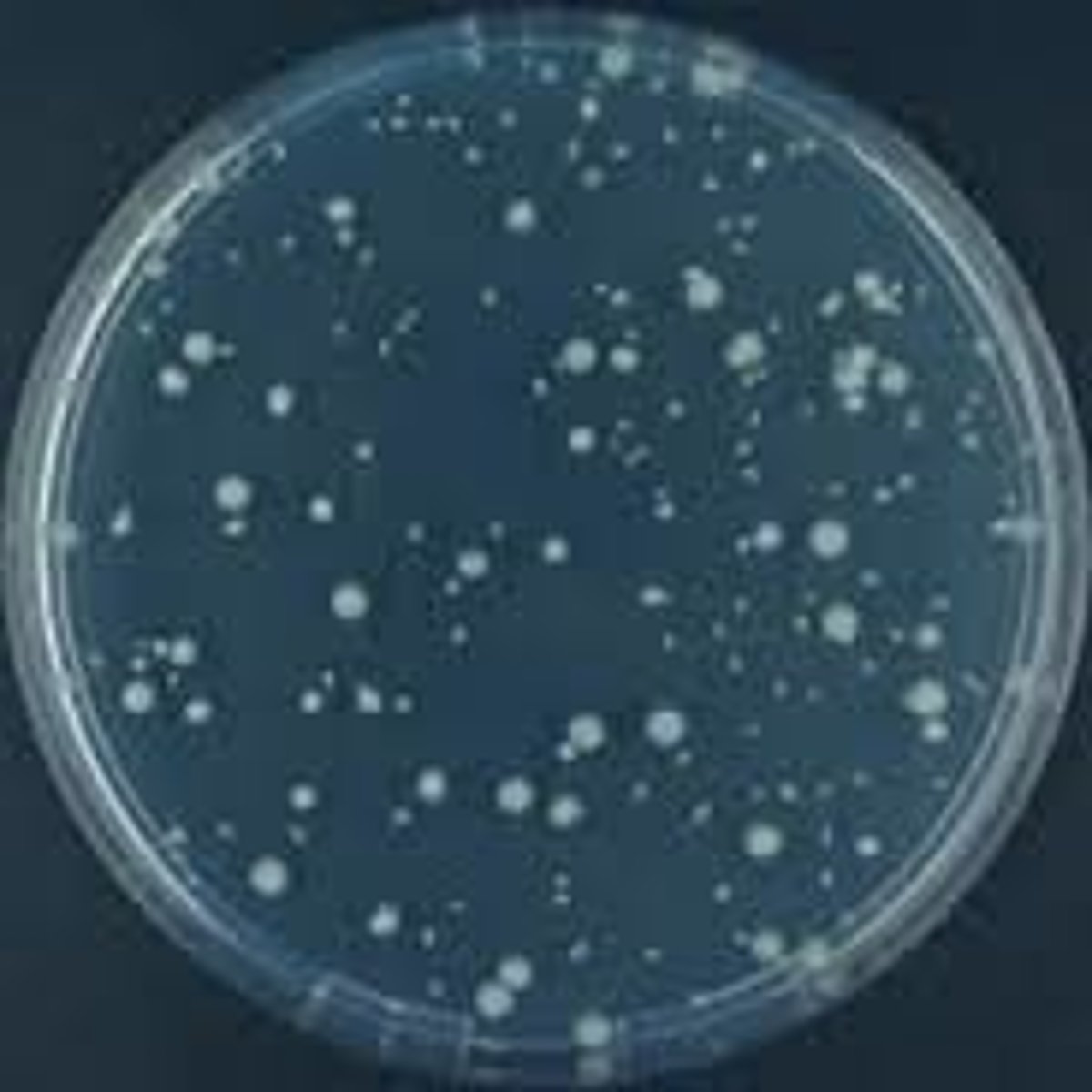
Is this an example of a pour plate or a streak plate?
Streak plate
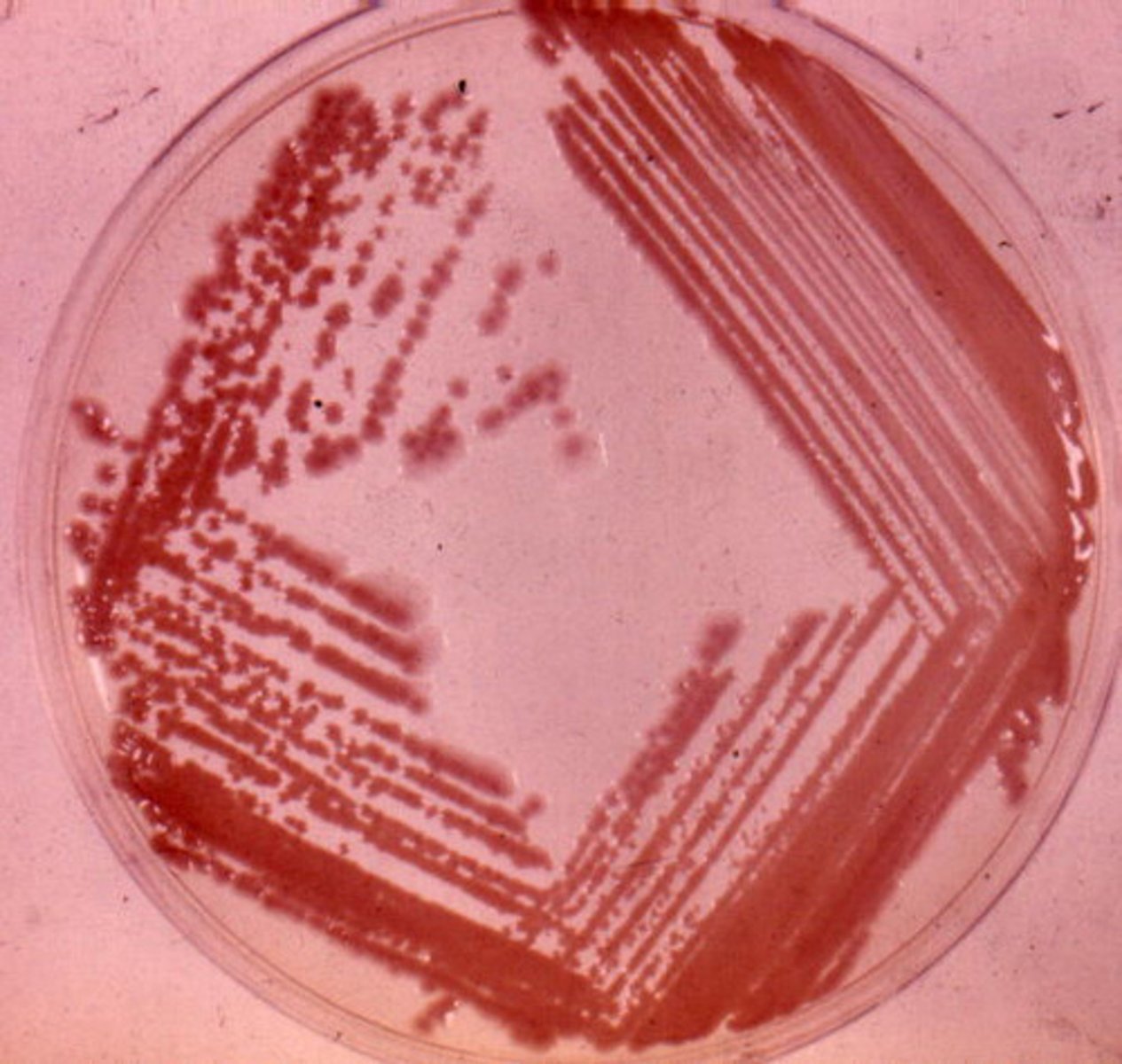
What is the primary dye in a Gram stain?
Crystal Violet
What is the mordant dye in a Gram stain?
Gram's Iodine
What is the decolorizer in a Gram stain?
Ethanol
What is the counterstain in a Gram stain?
Safranin
Name an acid-fast bacterium
Mycobacterium smegmatis
Steps of a Simple Stain
1. Take a drop of water and mix in a small amount of culture
2. Let dry and then heat fix by passing through flame 2-3 times
3. Add methylene blue and let sit for 1 minute
4. Rinse for 1 minute with DI water
5. Blot with blotting paper carefully to dry
What is the reagent used in a simple stain?
Methylene blue
What culture was used in the simple stain?
Enterococcus faecalis (cocci)
What is the purpose of flaming the loop before and after sampling culture?
To incinerate any contaminating organisms that may be present
What is the purpose of flaming the openings of tubes and containers?
To minimize the risk of contamination
What is the purpose of heat fixing the sample on the slide?
To fix the sample to the slide and to kill the bacteria
Gram Stain Procedure
1. Create a heat fixed sample of your organism
2. Cover the heat-fixed slide with crystal violet and let stand for 1 minute
3. Briefly wash off the stain with distilled water. Shake off excess water
4. Cover the slide with Gram's Iodine (mordant - helps the crystal violet bind to the cell wall) and leave for 1 minute
5. Wash off with DI water for 1 minute
6. Hold at a 45-degree angle and decolorize with EtOH (decolorizer) for 15 seconds
7. Rinse with DI water
8. Cover with slide with safranin (counterstain) for 1 minute
9. Wash with DI water and blot dry
What organisms were used in the Gram Stain, and which is + and which is -?
+ bacteria = Staphylococcus epidermidis
- bacteria = Pseudomonas Fluorescens
What reagents were used in the Gram Stain?
Crystal violet, Gram's iodine, Ethanol, Safranin
What are the features of a Gram-Negative bacterium?
Thin peptidoglycan layer, inner and outer membrane, periplasmic space
What are the features of a Gram-Positive bacterium?
Thick peptidoglycan layer, one membrane, teichoic acids
What is the purpose of a Negative Stain?
To study the morphology of the bacteria
Negative Stain Procedure
1. Put a drop of nigrosin on the slide
2. Use a sterile toothpick to take a sample from your oral cavity
3. Take another clean slide and hold at a 45-degree angle and use it to spread the nigrosin and sample across the slide
4. Air dry sample and nigrosin - DO NOT HEAT FIX!
5. Observe under 100x objective using oil
What organism and reagent was used in the Negative Stain?
Oral bacteria and nigrosin
Steps of an Endospore Stain
1. Cover smear with paper towel or bibulous paper and saturate with malachite green. Let sit for 7 minutes over a steaming water bath.
2. After slide is removed and cooled, wash with DI water
3. Cover with safranin for 30 seconds
4. Rinse with water
5. Blot with bibulous paper
What organism was used in the Endospore Stain?
Bacillus subtilis
What reagents were used in the Endospore Stain?
Malachite Green and Safranin
What is the purpose of an Endospore Stain?
Allows visualization of endospores and differentiation spores from vegetative cells
What are the results of an Endospore Stain?
Result is that the spores appear green and vegetative cells appear pink
Steps of a Capsule Stain
1. 1 drop of Congo red and 3 loopful of bacteria suspension. Air dry but don't heat fix
2. Stain with Maneval's stain for 5 minutes
3. Wash with water, air dry and observe
What are the reagents of a Capsule Stain?
Maneval's Stain (acidic) and Congo Red (basic)
What organism was used in the Capsule Stain?
Klebsiella pneumonia
Why does the capsule remain unstained in a Capsule Stain?
Capsule will remain unstained because its chemical composition repels stains and will appear as a clear halo- (Polysaccharides)
What is the purpose of an Acid Fast Stain?
Some Mycobacterium and Nocardia cell walls have mycolic acid (lipid that is composed of fatty acids and fatty alcohols that have hydrocarbon chains) and it stains acid-fast cells red by the carbolfuchsin which is a basic stain that attaches to the mycolic acid in mycobacterium
Steps of an Acid-Fast Stain
1. On a clean slide, use sterile technique to place 4 loopfuls of M. smegmatis on the slide
2. Collect a small amount of S. epidermis on the loop and use the loop to mix and smear the four spots together into a single smear
3. Air dry and heat fix
4. Cover slide with basic fuchsin for 5 minutes. Wash with water and shake off excess
5. Decolorize with acid-alcohol for 30 seconds. Rinse briefly with water
6. Counterstain with methylene blue for 30 seconds. Rinse briefly and shake off excess
7. Blot dry with bibulous paper and examine under oil immersion
What are the reagents of an Acid-Fast Stain?
Basic Carbolfuchsin (primary), Acid Alcohol (decolorizer), Methylene Blue (Counterstain)
What bacteria was used in the Acid-Fast Stain?
Acid-Fast = Mycobacterium smegmatis
Non-Acid-Fast = Staphylococcus epidermis
Enumeration Practice:
a. If there are 171 total cells in 6 of the blocks of 1ml samples, what is the number of cells per ml of cell suspension?
b. Using the diagram, pick the plate between 30 and 300. For this problem, the plate is 103 at 10^-6. Calculate and count the number of viable cells.
c. What is the percent viability of the yeast cells in this sample?
a. 171 / 6 = 28.5 x (4 x 10^6) = 1.14 x 10^8
b. Viable cells = 103 / (10^-6) = 103 x 10^6 = 1.03 x 10^8
c. ((1.03 x 10^8) / (1.14 x 10^8)) x 100 = 90%
Percent Viability Practice:
Direct Count yielded 3.5 x 10^8 cells
Plate Count yielded 4.5 x10^7 cells
What is the percent viability?
((4.5 x 10^7) / (3.5 x 10^8)) x 100 = 12.86%
Enumeration Practice:
a. If there are 36 total cells in 6 of the blocks of 1ml samples, what is the number of cells per ml of cell suspension?
b. Using the diagram, pick the plate between 30 and 300. For this problem, the plate is 276 at 10^-7. Calculate and count the number of viable cells.
c. What is the percent viability of the yeast cells in this sample?
a. 36 / 6 = 6 x (4 x 10^6) = 2.4 x 10^7
b. Viable cells = 276 / (10^-7) = 276 x 10^7 = 2.76 x 10^9
c. ((2.76 x 10^9) / (2.4 x 10^7)) x 100 = 11500%
*WONKY ON PURPOSE. JUST FOR PRACTICE