RP 7: Investigation into simple harmonic motion using a mass–spring system and a simple pendulum.
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is the method to investigate how the time period of a mass-spring system varies with the mass attached? (7)
- Set up a clamp stand and suspend a spring vertically from it.
- Attach a 50 g mass holder to the spring and allow the system to come to rest.
- Pull the mass vertically downwards a few centimetres and release it.
- Start a stopwatch when the mass passes a fixed fiducial marker and time 10 complete oscillations.
- Divide the time by 10 to find the time period (T) for that mass.
- Add 50 g at a time up to a total of 500 g, and repeat the procedure.
- Repeat each measurement at least twice and calculate the mean time period for each mass.
What equipment is needed to investigate the variation of the time period of a spring with mass? (7)
- Spring.
- 50 g masses with 50
g mass holder.
- Stand and clamp.
- Pin.
- Blue tack (fiducial marker).
- Metre ruler.
- Stopwatch.
What does a setup to investigate how the time period of a mass-spring system varies with the mass attached look like? (3)
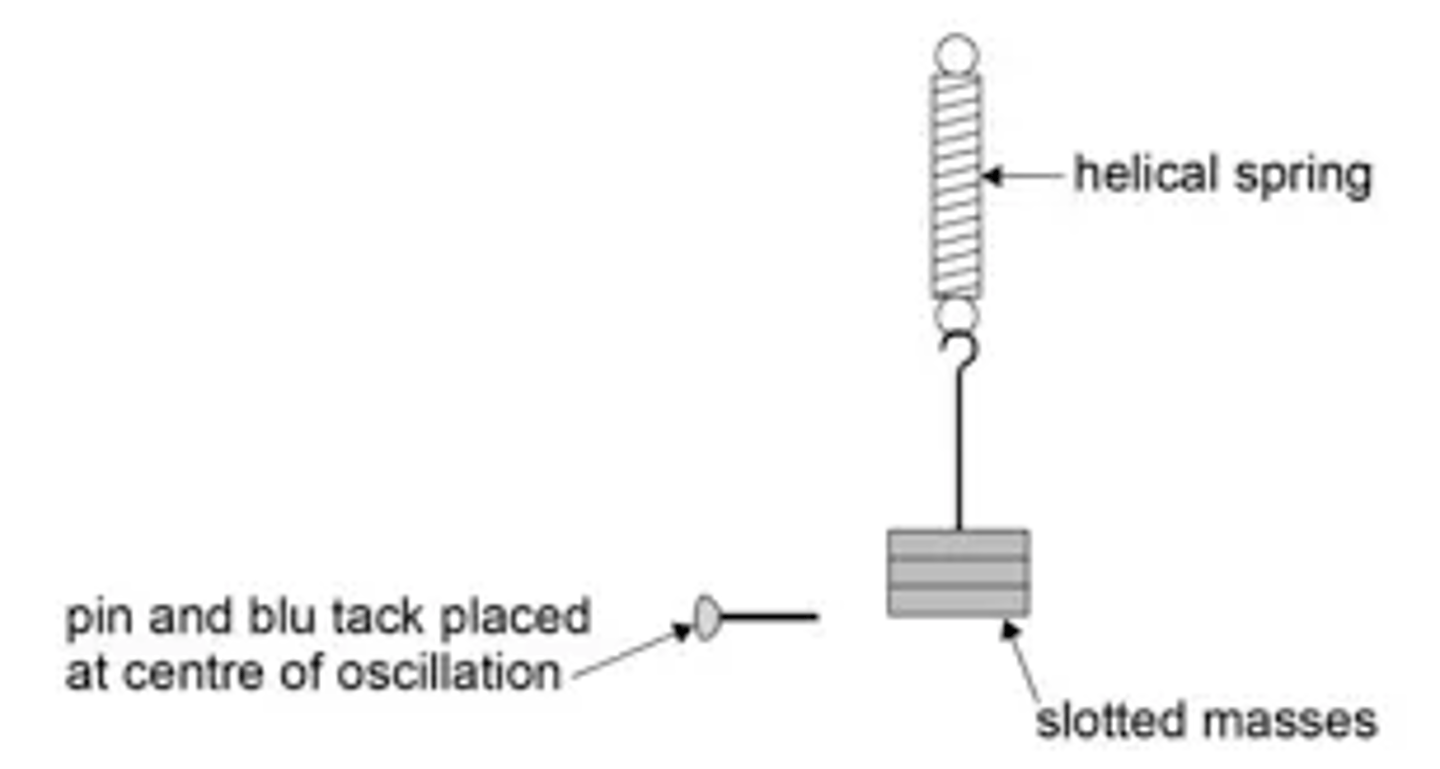
What is the independent variable in the mass-spring experiment? (1)
The independent variable is the mass added to the spring.
What is the dependent variable in the mass-spring experiment? (1)
The dependent variable is the time period of oscillation of the spring-mass system.
What are the controlled variables in the mass-spring experiment? (3)
- The controlled variables include the spring used.
- Another controlled variable is the amplitude of oscillation.
- Another controlled variable is the environment (e.g. air currents, surface).
What graph is plotted to determine the spring constant? (1)
Plot a graph of T² against m using the results from the experiment.
What does the graph plotted to determine the spring constant look like? (3)
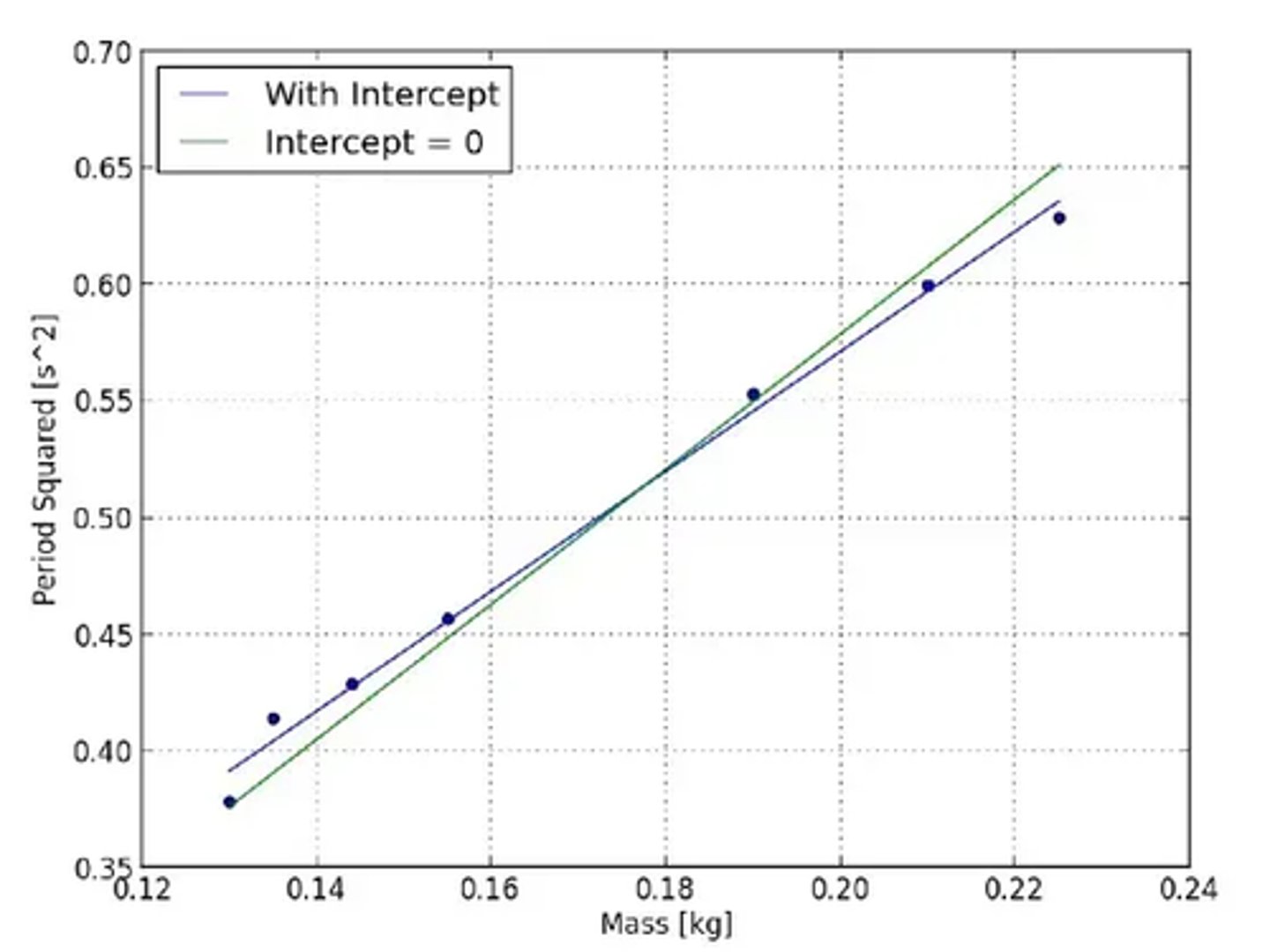
How is the gradient of the mass-spring graph used to find the spring constant? (1)
The gradient of the line will be equal to 4π² divided by the spring constant (k).
What formula is used to find the spring constant from the graph? (1)
Calculate the spring constant using the formula
k = 4π² ÷ gradient.
What is one safety precaution for the mass-spring system experiment? (1)
Only pull the spring down by a few centimetres to reduce the risk of heavy masses falling off and causing injury.
How can reaction time uncertainty be reduced in the spring experiment? (1)
Use a fiducial marker at the centre of oscillation to reduce reaction time uncertainty when starting and stopping the stopwatch.
How can percentage uncertainty in period measurement be reduced? (2)
- Time a larger number of oscillations for each mass, such as 10.
- This reduces the percentage uncertainty in the time period measurement.
What is the method used to determine how the period of a simple pendulum varies with its length? (7)
- Set up a pendulum using a string and bob suspended from a clamp stand..
- Adjust the length so the distance from the point of suspension to the centre of mass of the bob is 1.500 m.
- Pull the bob to one side with a small angle (less than 15°) and release it.
- Start the stopwatch as the bob passes a fiducial marker (the bottom of the marker should be level with the bottom of the bob) and time 10 complete oscillations.
- Divide the time by 10 to obtain the time period (T) for that length.
- Reduce the length by 0.100 m each time down to 0.500 m and repeat.
- Repeat each measurement at least twice and record the mean T for each length.
What equipment is required to investigate the variation of the time period of a simple pendulum with length? (7)
- Pendulum bob with 2 m string.
- Stand and clamp.
- Pin.
- Blue tack (fiducial marker).
- Metre ruler.
- Stopwatch.
- Two wooden blocks.
What does the setup to determine how the period of a simple pendulum varies with its length look like? (3)
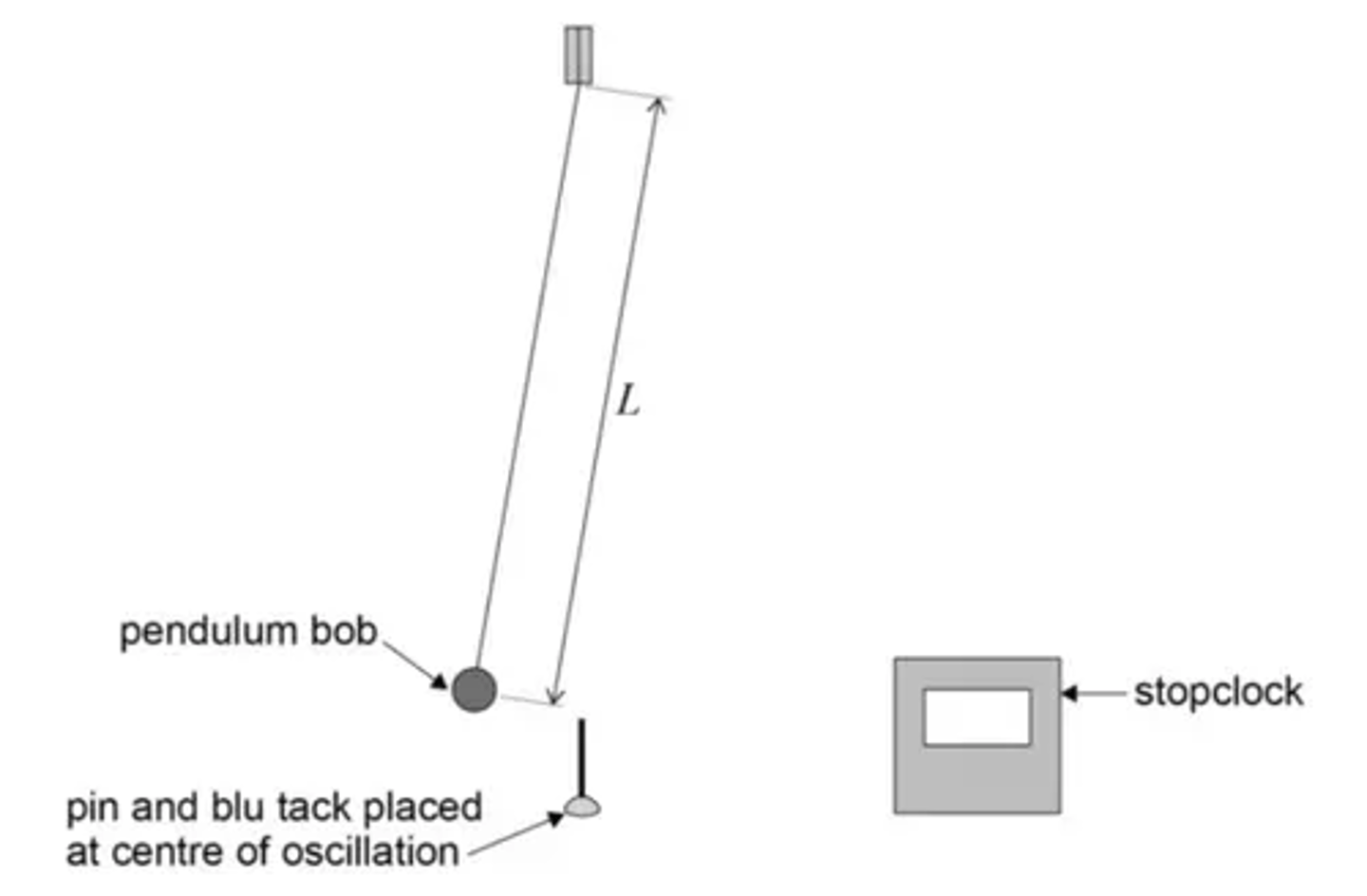
What is the independent variable in the simple pendulum experiment? (1)
The independent variable is the length of the pendulum (from the pivot to the centre of mass of the bob).
What is the dependent variable in the simple pendulum experiment? (1)
The dependent variable is the time period of one oscillation.
What are the controlled variables in the simple pendulum experiment? (3)
- The controlled variables include the angle of displacement (kept under 15°).
- Another controlled variable is the bob mass.
- Another controlled variable is the method of timing.
What graph is plotted to determine g in the pendulum experiment? (1)
Plot a graph of T² against L.
What does a graph plotted to determine g in the pendulum experiment look like? (3)
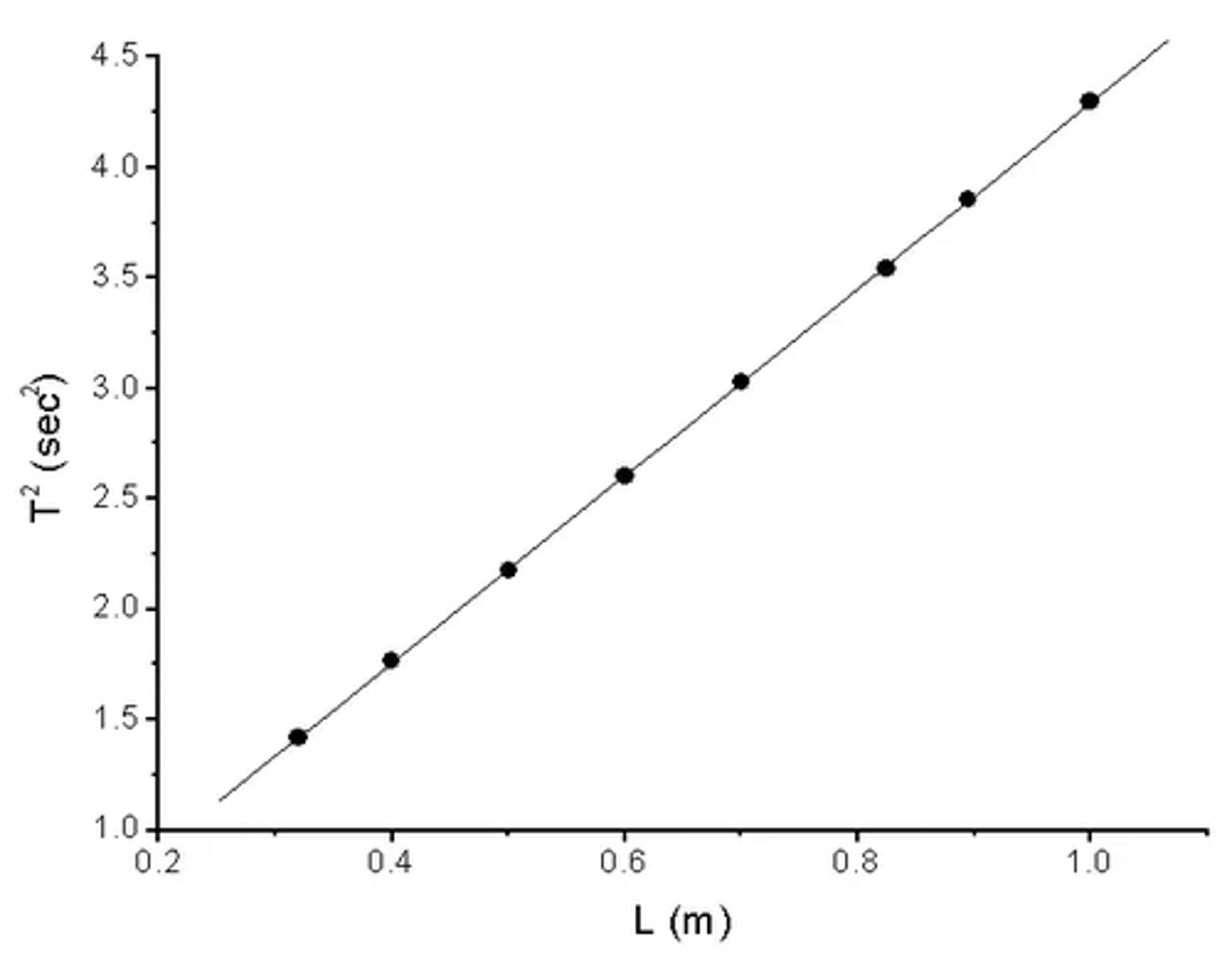
How is the gradient of the graph plotted to determine g in the pendulum experiment used to find g? (1)
The gradient of the line is equal to 4π² divided by g.
What equation is used to find g from the graph? (1)
Use the equation g = 4π² ÷ gradient to calculate the gravitational field strength.
What condition must be met for the pendulum formula to be valid? (2)
- The angle between the string and the vertical must be less than about 15°.
- This is so that the motion approximates simple harmonic motion.
How can uncertainty in timing be reduced in the pendulum experiment? (2)
- Time a greater number of oscillations, such as 10.
- This reduces percentage uncertainty in the period.
How can reaction time error be reduced in the pendulum experiment? (1)
Use a fiducial marker at the equilibrium position to reduce reaction time error when starting and stopping the stopwatch.