Kinetics - Chemistry Physical
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Collision Theory
particles need to collide with energy < or = activating energy
In right orientation to react successfully
More frequent and successful collision = faster rate of reaction
What 4 factors affect rate of reaction
4 factors that affect rate of reaction are
Change in concentration/pressure
Change in Temperature
Change in Surface Area
Addition of Catalyst
what 3 things happen when there’s an increase in concentration/pressure
collision frequency increases
Collision energy stays the same
Activation energy stays the same
NO CHANGE IN MAXWELL BOTZMAN DISTRIBUTION
What 3 things happen when there’s increase in temperature
increase in number of molecules with activation energy
More frequency of collisions
More successful collisions
increase in most probable energy
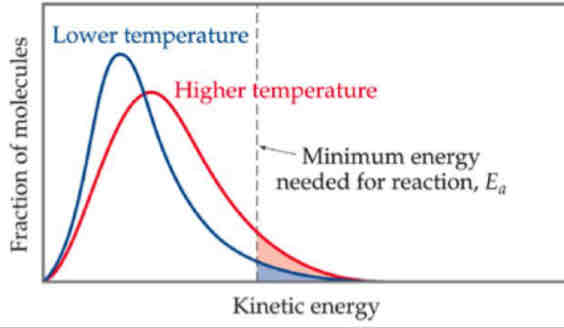
What 3 things happen when surface area increases
collision frequency increases
Collision energy stays the same
Activation energy stays the same
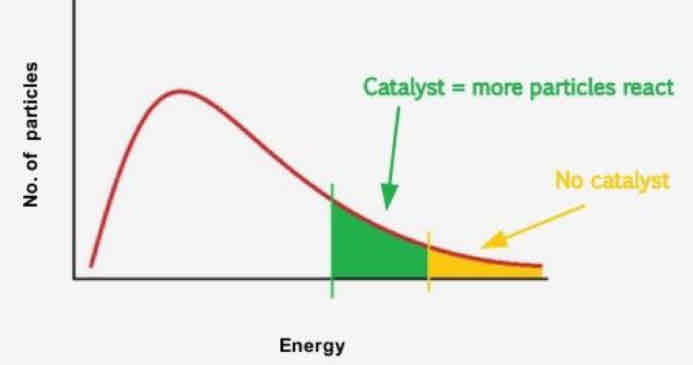
What 3 things happen when catalyst is added
Provides an alternative route
collision Frequency stays the same
Collision Energy stays the same
Activation energy decreases
NO CHANGE IN SHAPE OF MAXWELL BOLTZMANN
Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution
all molecules in a substance don’t have the same amount of energy they are distributed in a pattern called Maxwell
Total area under curve represents number of molecules, therefore must remain constant
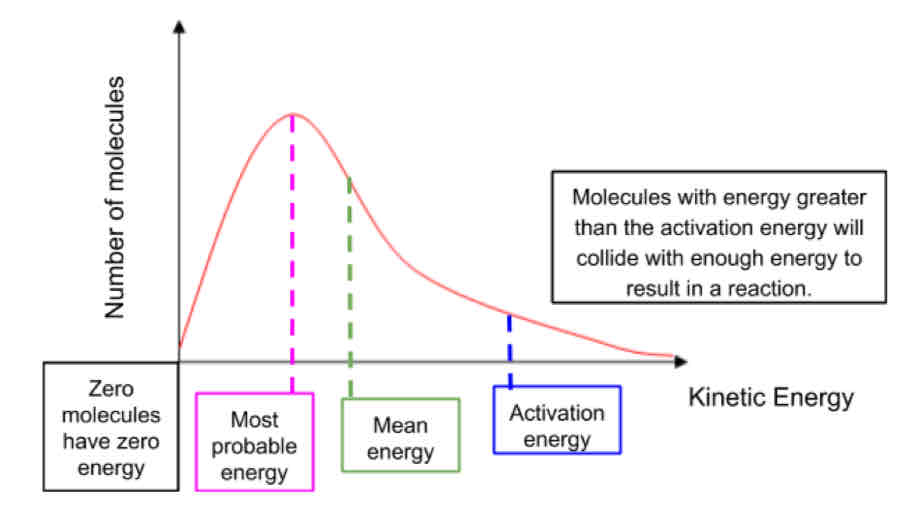
Explain process that causes some molecules to have very low energies
collisions
Cause molecules to slow down or loose energy
What is activation energy?
Minimum energy required for a reaction to occur
What is the Form of Rate Equation
Rate = k[A]^m [B]^m
![<p>Rate = k[A]^m [B]^m</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1aef8801-6265-488c-a7b2-8f72a42a2f66.jpg)
What is the orders of reaction
Order of reaction is the power of concentration term in rate of reaction.
if reactant is doubled and rate stays same - 0
If reactant doubles and rate doubles - 1
If reactant doubles rate quadruples - 2
Why is initial rates of reaction used to determine these orders rather than rates of reaction at different times during experiment
Concentrations are known
What is the overall order
it is the sum of the reactants orders
What Units of Rate constant
concentration - mol/dm3
Rate - mol dm^-3 S^-1
K depends on orders of reactants
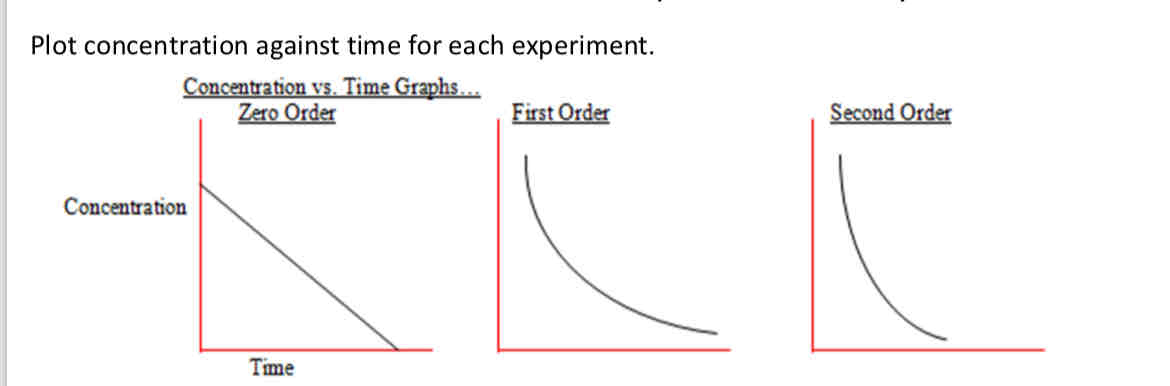
What do the graphs look like for concentration against time
zero order - downwards straight line
First order - downwards curve
Second order - steeper than first order
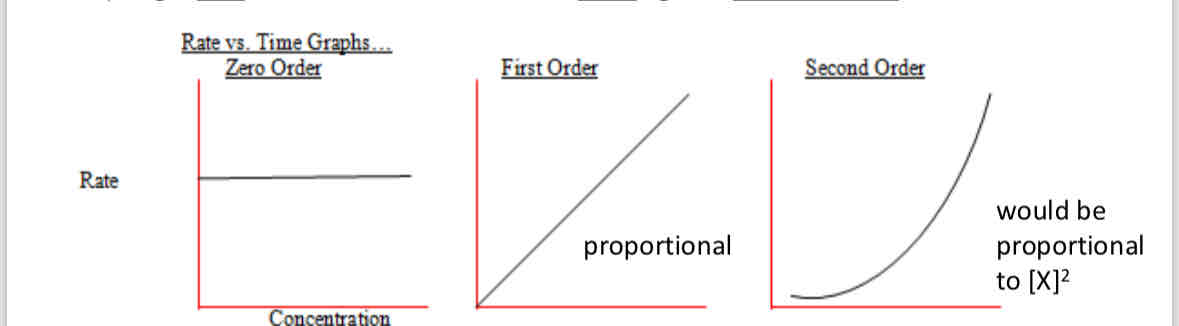
What do the graphs for Rate against concentration look like
zero - straight horizontal line (y is constant)
First order - x=y
Second - upwards curve y=x²
What is the Reaction Mechanism
Reaction mechanism is the series of steps that make up the overall reaction
What is the rate determining step
Rate determining step is the slowest step in the reaction mechanism
How do we find the rate determining Step
Series if rate experiments are done to derive rate equation
If reactant appears in rate equation it’s involved in rate determining step
Order tells you number of molecules involved
How do you know a substance is a catalyst
Appears in rate equation
Not in reaction equation
A mixture of 2dm3 of hydrogen 1 dm3 oxygen is at RTP. What happens
a) No reaction to form water because molecules do not collide with sufficient energy
b) molecules do not collide with sufficient energy
C) mean velocity of H is less than O
D) partial pressure of each gas is same
a) No reaction to form water because molecules do not collide with sufficient energy
Choose correct statement : if distribution curve of molecular energies is an ideal gas at a given temperature
A) no molecules with 0 energy
B) curve is symmetrical about maximum
C) changing temp as no effect on position of maximum
D) most molecules have mean energy
A) no molecules with 0 energy
Addition of catalyst to an equilibrium mixture choose correct answer :
A) activation energy for reverse action increases
B) equilibrium constant for forward reaction increases
C) Rate of reverse reaction increases
D) enthalpy change for forward reaction decreases
C) Rate of reverse reaction increases
In a given temperature the average kinetic energy for molecules in gas is??
Constant
Which statement is correct for the distribution curve of molecular energies in a gas?A. The curve is symmetrical about the maximum.
B. There are always some molecules with zero energy.
C. The position of the maximum of the curve is not dependent on the temperature.
D. The mean energy of the molecules is greater than the most probable energy of the molecules.
D) mean energy of molecules is greater than most probable energy
When using larger conical flask how is the time affected
Time will increase

Collision theory In endothermic reaction
as concentration increases amount of heat given out increases
More Successful Collisions
Increases rate of reaction
Why it's important to clean the exposed magnesium ribbon before reacting it with hydrochloric acid
it’s coated with MgO
The corrosion product will react not Mg
Two differences between the reactions of magnesium with hot water and steam
reaction is faster with steam
MgO produce with water Mg(OH)2 with steam
Bubbling with water and bright white light with steam
Rate of reaction
Measured change in concentration of a substance in unit time
When is it possible to use 1/T to find rate of reaction
When measured change is fixed or constant
In a typical procedure, a mixture of 1.00 g of propanone, 5.00 g of ethane-1,2-diol and 0.100 g of benzenesulphonic acid, C6H5SO3H, is heated under reflux in an inert solvent. Benzenesulphonic acid is a strong acid.When the concentration of benzenesulphonic acid is doubled, the rate of the reaction doubles. It can be deduced that:A. the reaction is first order overall.
B. the reaction is third order overall.
C. the reaction is acid-catalysed.
D. units for the rate constant, k, are mol-2dm6s-1.
C. Reaction is acid catalysed
( not enough informations about the other reactant orders for it to be A/B)
The rate equation for the hydrogenation of ethene (C₂H₄(g) + H₂(g) → C₂H₆(g)) is Rate = k[C₂H₄][H₂]. At a fixed temperature, the reaction mixture is compressed to triple the original pressure. What is the factor by which the rate of reaction changes?
9
What is the rate Equation where Conc of propane is 100x that of iodine and hydrochloric acid if iodine is order 0
K[H+]. The concentration change of propane is negligible as its constant so has a constant effect on rate and therefore is also order 0
A general equation for a reaction is shown.
A(aq)+B(aq)+C(aq)→D(aq)+E(aq)
In aqueous solution, A, B, C and D are all colourless but E is dark blue.
A reagent (X) is available that reacts rapidly with E. This means that, if a small amount of X
is included in the initial reaction mixture, it will react with any E produced until all of the X
has been used up.
Explain, giving brief experimental details, how you could use a series of experiments to
determine the order of this reaction with respect to A. In each experiment you should obtain
a measure of the initial rate of reaction
Stage 1: Preparation1a. Measure known volumes of reagents.
1b. Measure a known amount of reagent X or use a colorimeter.
1c. Combine reagents in separate containers (up to two reagents and X can be mixed together, but X should not be added last)Stage 2: Procedure2a. Start a timer when mixing reagents (unless only two reagents are mixed)
2b. Record the time for a color change (blue), colorimeter reading, or disappearing cross.
2c. Use the same concentration of B and C, the same total volume, and the same amount of X.
2d. Maintain a constant temperature (using a water bath, if necessary)
2e. Repeat the experiment with different concentrations of A (this can be achieved by varying the volume of A while keeping the total volume constant)Stage 3: Use of Results3a. Calculate the rate as 1/time.
3b. Plot 1/time against the concentration/volume of A, or plot log(1/time) against log(concentration/volume of A)
3c. Interpret the graph to determine the order of the reaction (the shape of the graph, the gradient of the log plot, or the ratio of changes in concentration and rate can be used to determine the order)
What does it mean by term order of reaction with respect to A
Power of concentration term
Why Doubling temperature has a much greater effect on rate of reaction than doubling concentration
Reaction occurs when energy is greater or equal to activation energy
When doubling temperature many more particles reach activation energy or more
But when doubling concentration of E it only doubles the number of particles with this concentration
In arhaenius graphs
Gradient = -Ea/R