Procedures 1 & Image Analysis 1 FINAL
1/224
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
225 Terms
AP stress studies
Which projections of the ankle are performed on a patient following an inversion or eversion injury?
AP and lateral
AP and both obliques
AP stress studies
AP, lateral, and both obliques
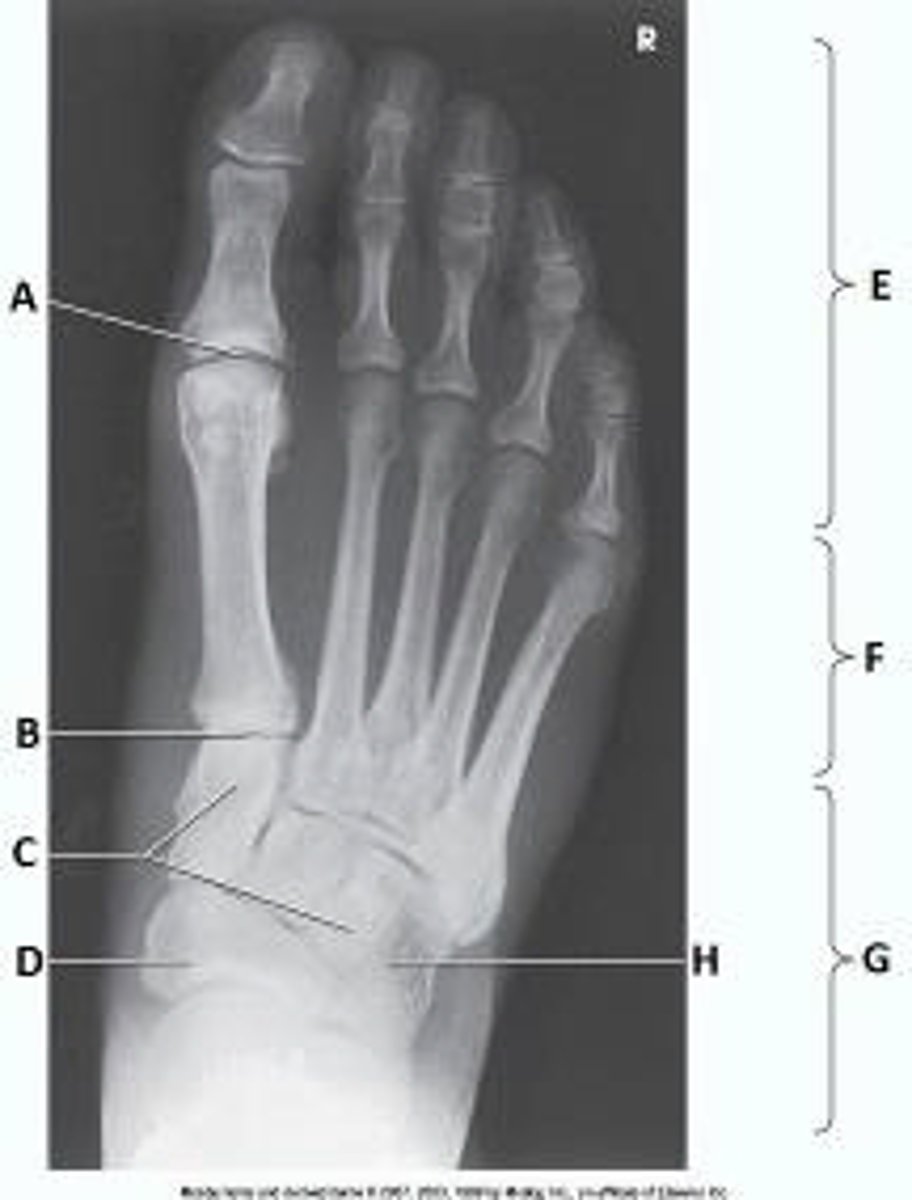
First metatarsophalangeal joint
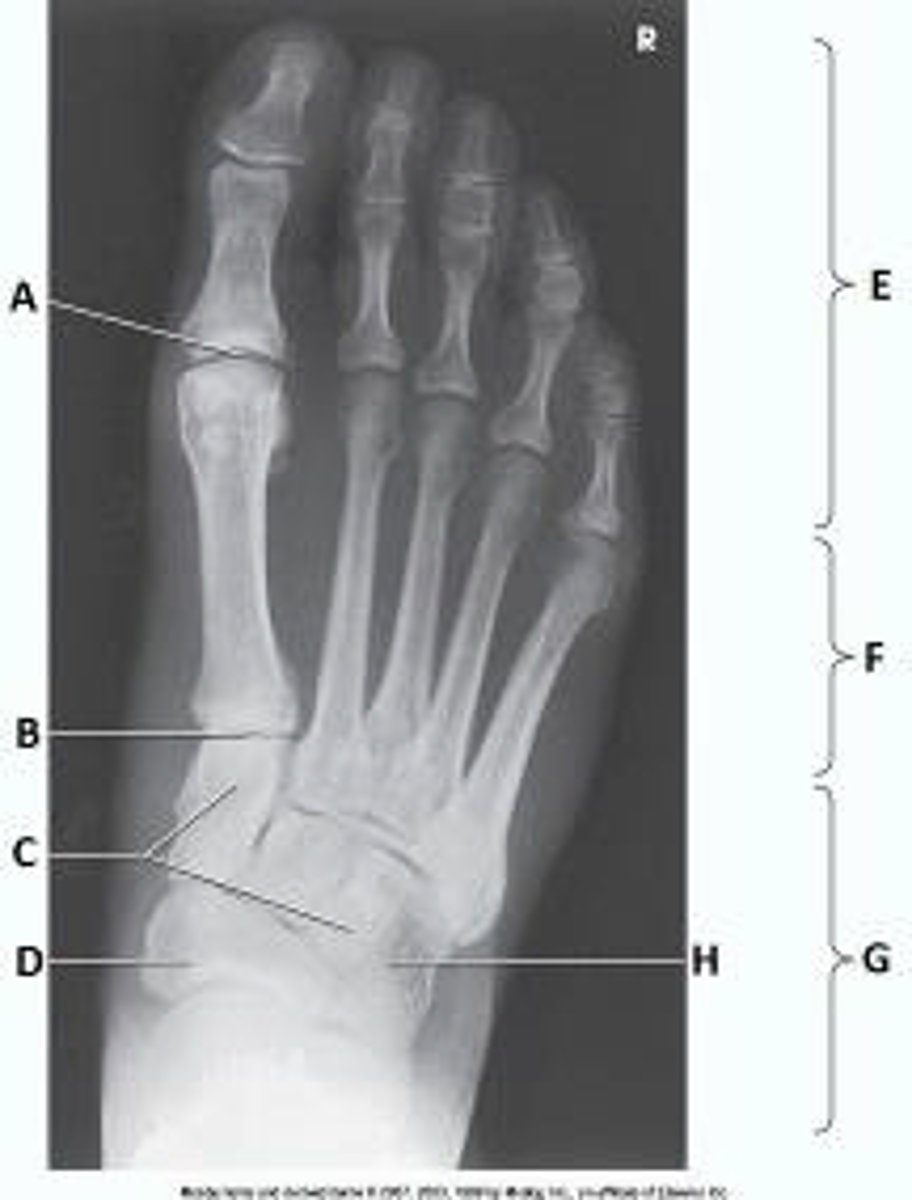
What anatomy is labeled as letter A in the image below?
First metatarsophalangeal joint
Proximal interphalangeal joint of first digit
Distal interphalangeal joint of first digit
Interphalangeal joint of first digit
1, 2, and 3
Which of the following will ensure that the knee is in proper position for a lateral projection?
1. Epicondyles perpendicular to the IR
2. Patella perpendicular to the IR
3. Leg flexed 20 to 30 degrees
full inspiration
To elevate the clavicle above the ribs and scapula for the AP axial projection, the phase of respiration should be:
full inspiration
full expiration
shallow breathing
suspended respiration
AP oblique knee with medial rotation
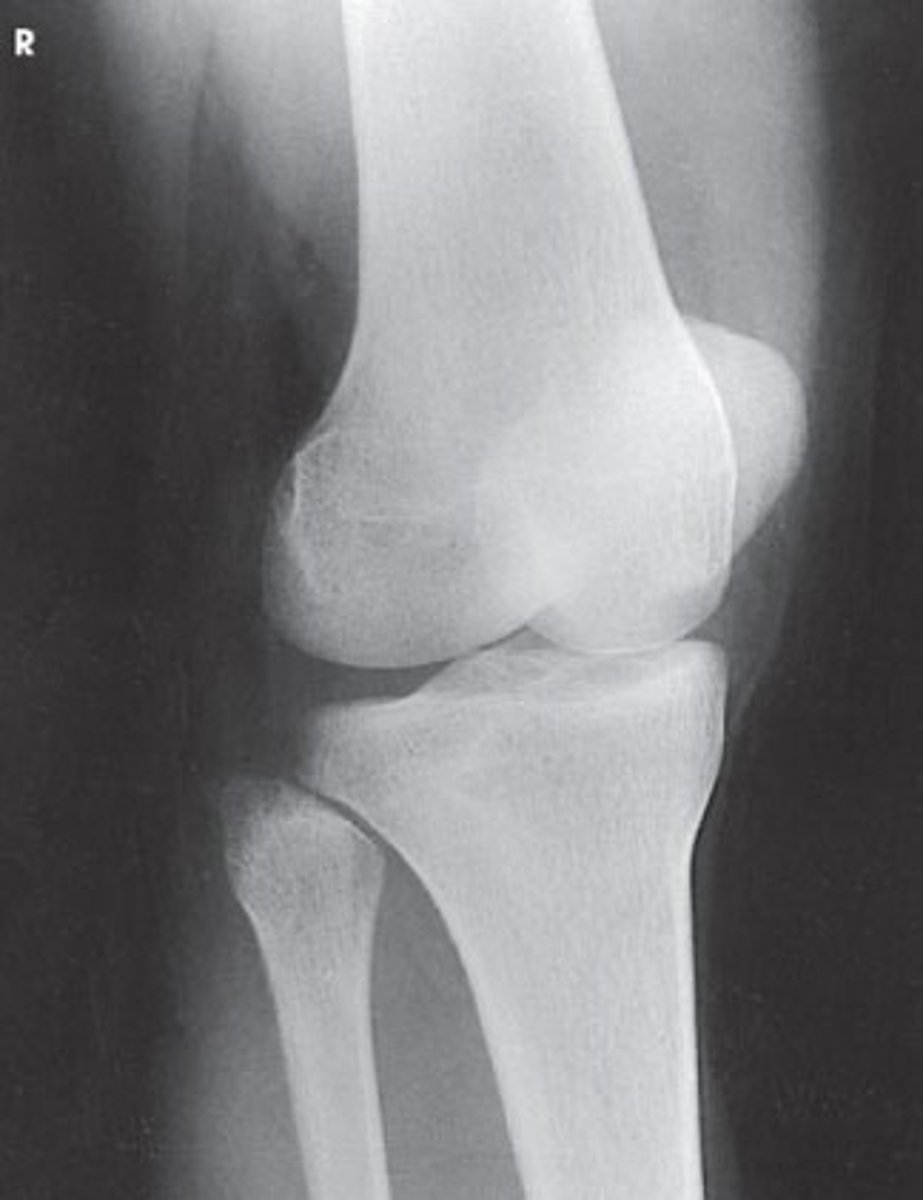
What projection is demonstrated in the image below?
AP oblique knee with medial rotation
AP knee
AP oblique knee with lateral rotation
PA knee
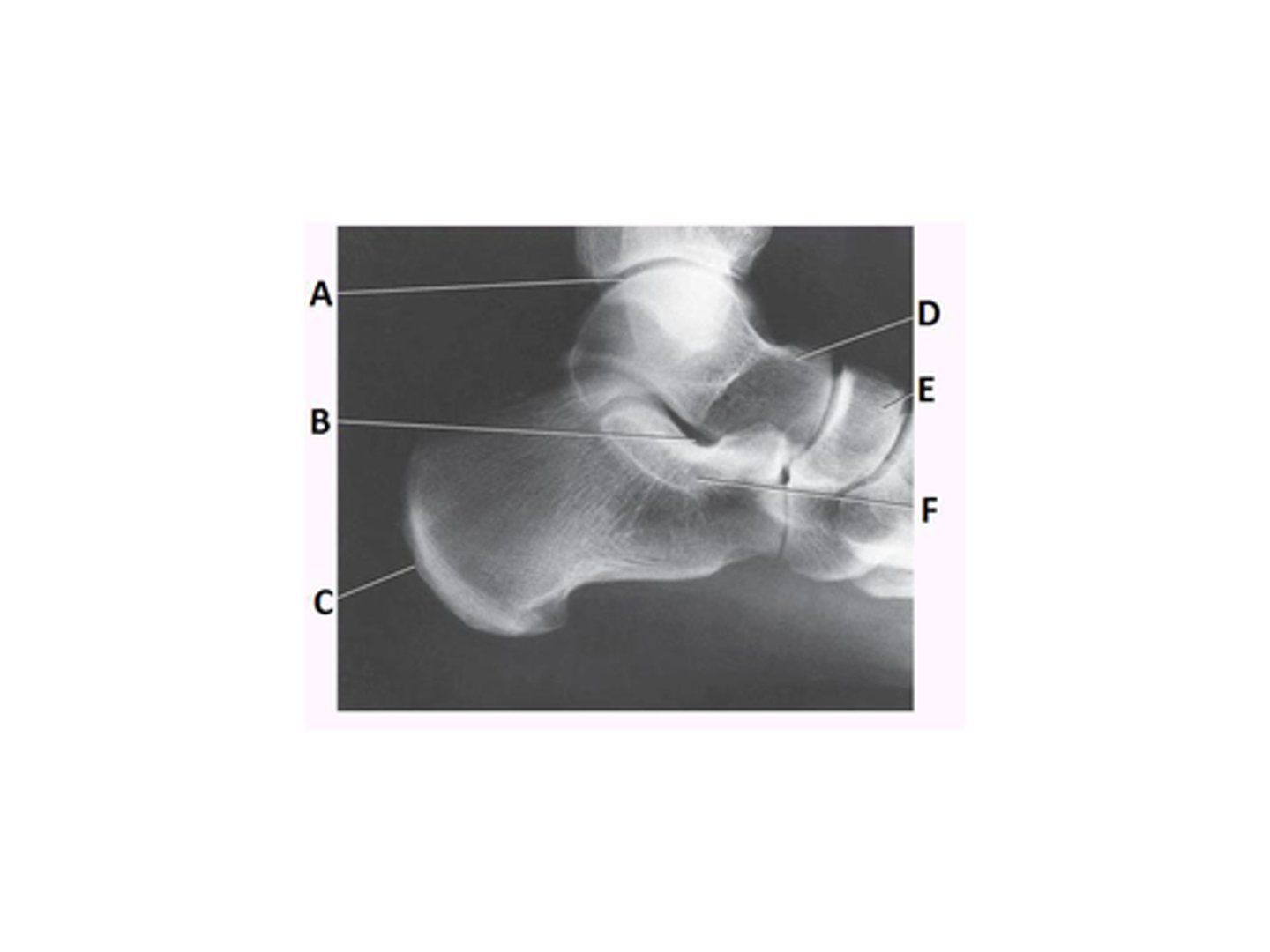
Mortise joint
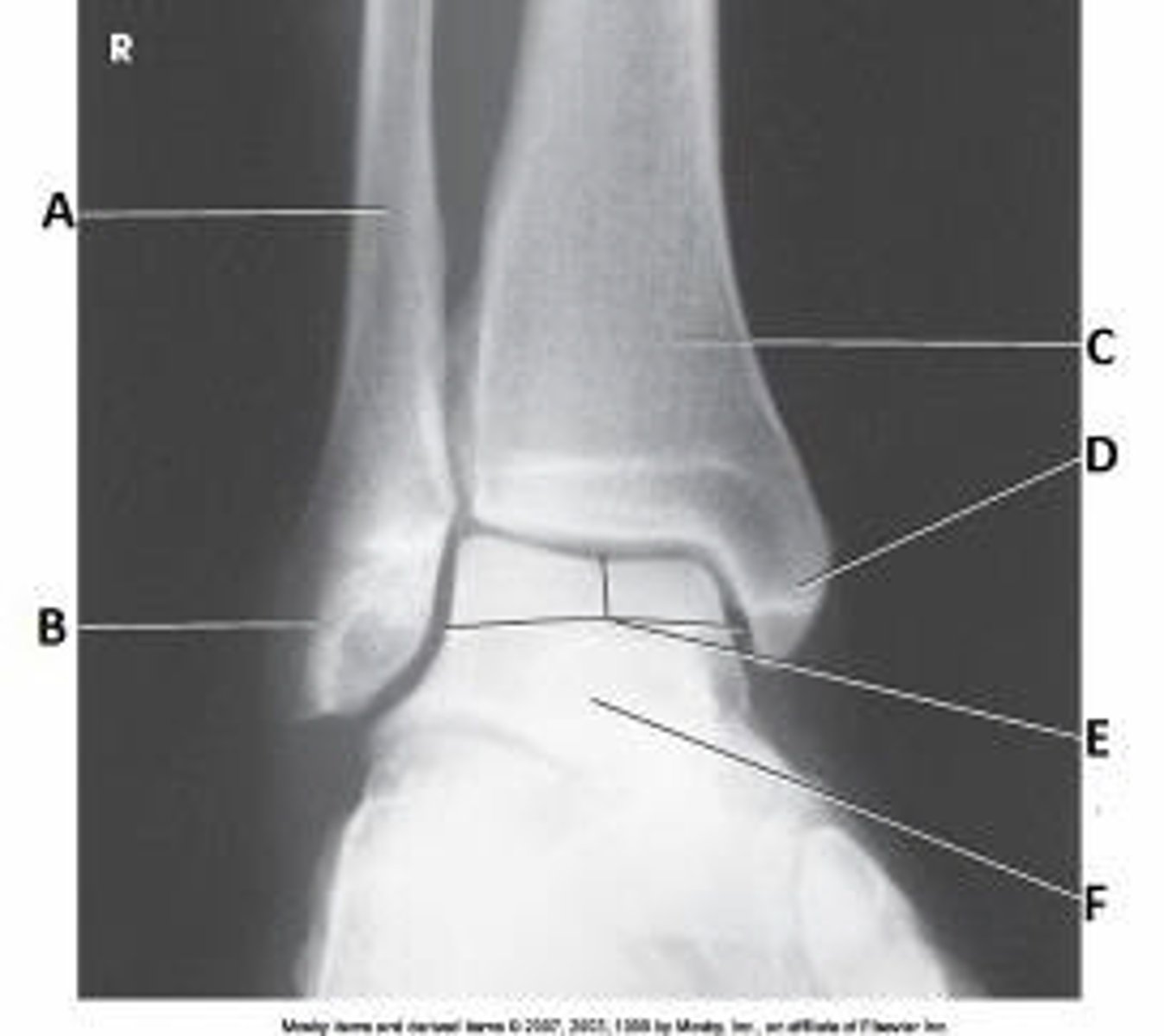
What anatomy is labeled as letter E in the image below?
Sinus tarsi
Tibiotalar joint
Mortise joint
Medial malleolus
Tibiotalar joint
What anatomy is labeled as letter A in the image below?
Tibiotalar joint
Tibiofibular joint
Sinus tarsi
Tibiocalcaneal joint
Perpendicular
What is the central-ray angle for an AP projection of the hip?
15 degrees
20 degrees
15 to 20 degrees
Perpendicular
sacroiliac joint
The ilia articulate with the sacrum posteriorly at the:
hip joint
pubic symphysis
sacroiliac joint
lumbar-5 and sacral-1 area
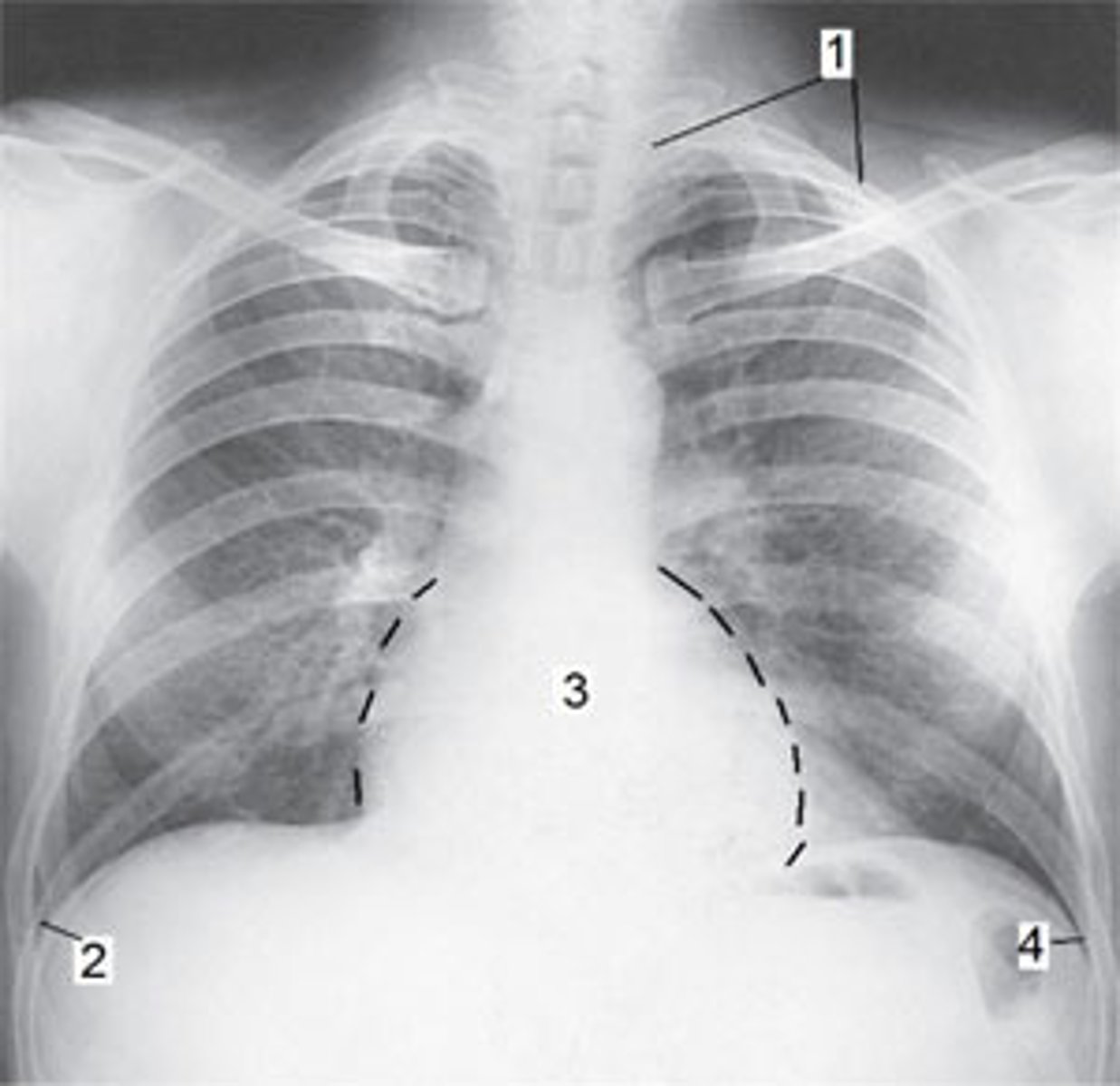
Apex of the left lung
Refer to the image below. Identify the anatomy marked as #1.
Heart
Left costophrenic angle
Right costophrenic angle
Apex of the left lung
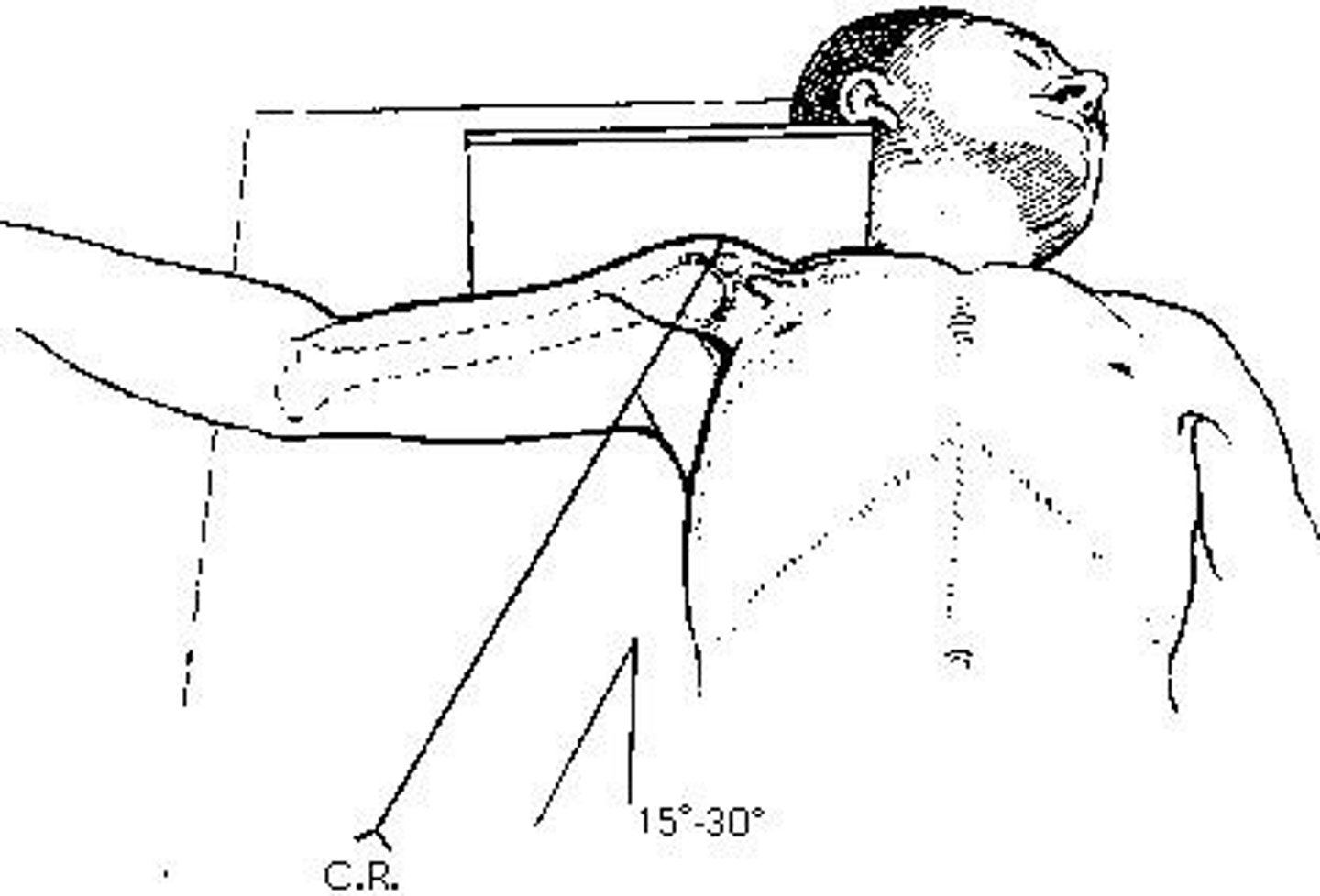
35 to 45 degrees toward the affected side
How many degrees is the body rotated for the AP oblique projection (Grashey method) of the shoulder joint?
20 degrees toward the affected side
20 degrees away from the affected side
35 to 45 degrees away from the affected side
35 to 45 degrees toward the affected side
Expiration
What is the respiration phase for an AP abdominal exam?
Inspiration
Expiration
Suspended respiration
Slow, deep breathing
inferosuperior axial (Lawrence)
The projection of the shoulder demonstrated in the figure above is the:
axiolateral
inferosuperior axial (Lawrence)
transthoracic lateral (Lawrence)
acromioclavicular (Pearson)
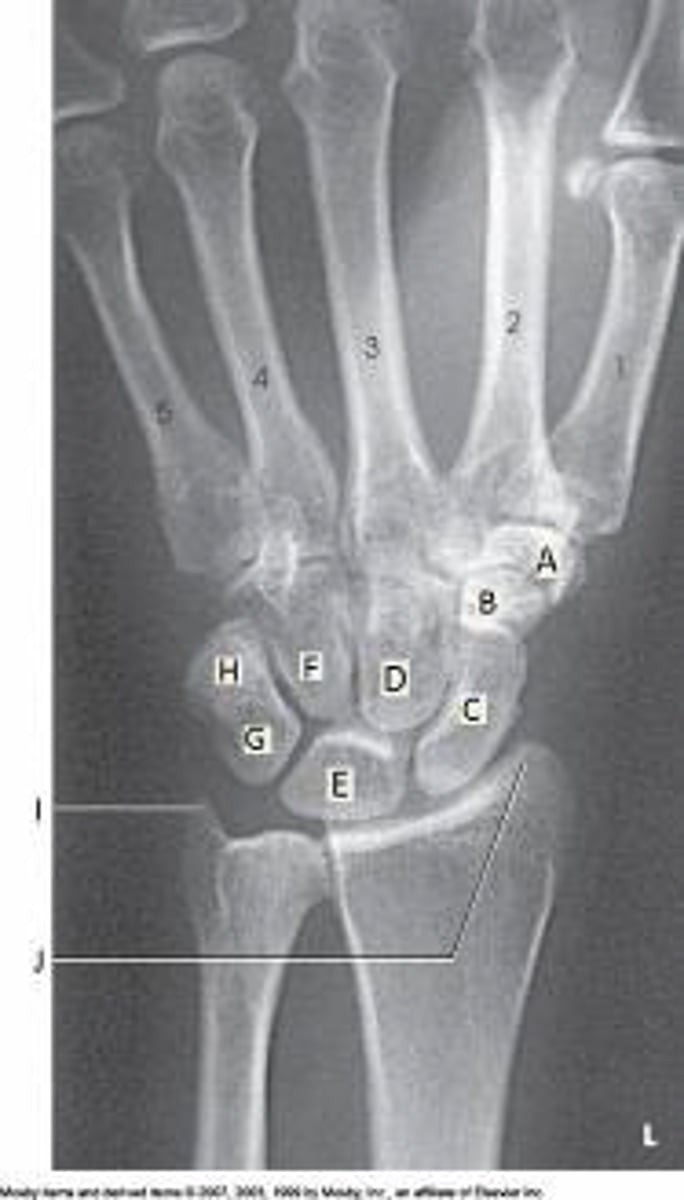
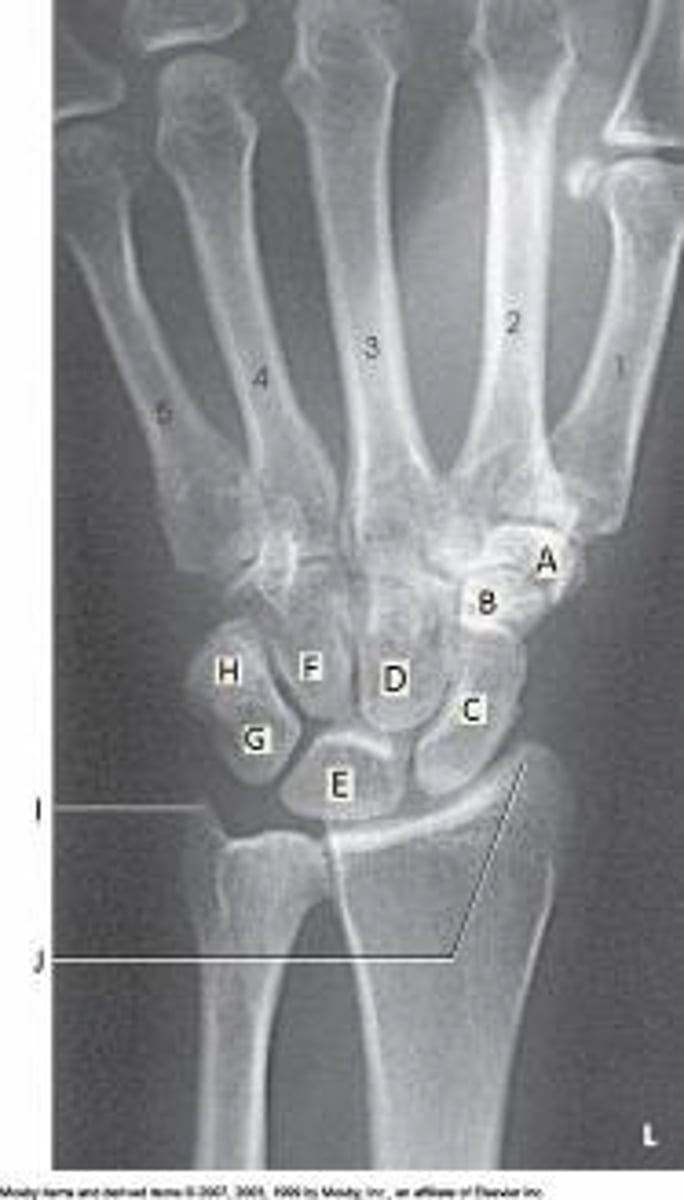
Lunate
Which bone is labeled as letter E in the figure above?
Capitate
Scaphoid
Triquetrum
Lunate
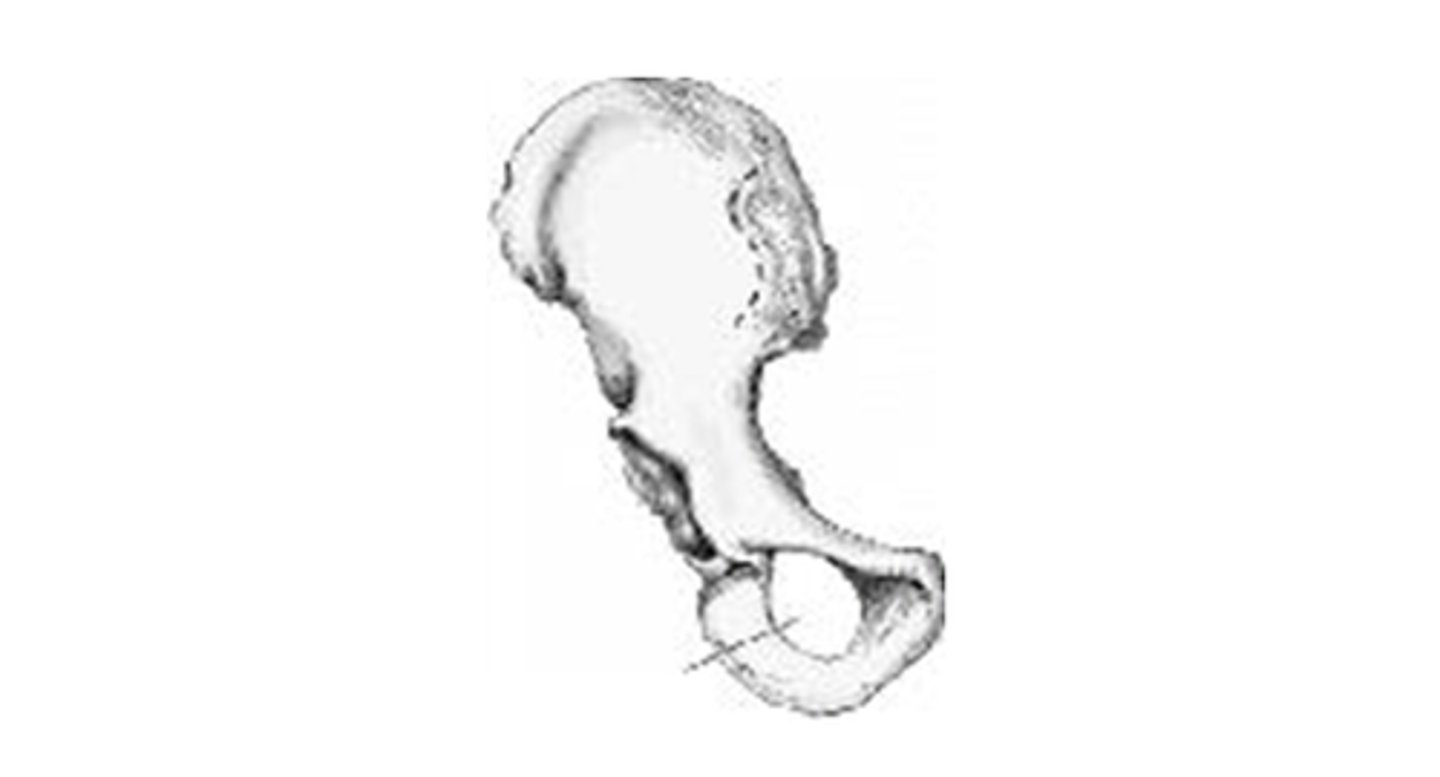
obturator foramen
The area of anatomy indicated on the figure above is the:
pubis
ischium
acetabulum
obturator foramen
ankle joint, midway between the malleoli
For an AP projection of the ankle, the central ray must enter the:
talus
subtalar joint
talofibular joint
ankle joint, midway between the malleoli
Bilateral AP weight-bearing
Which of the following projections of the knee best demonstrates the narrowing of a joint space?
AP
AP oblique
Lateral
Bilateral AP weight-bearing
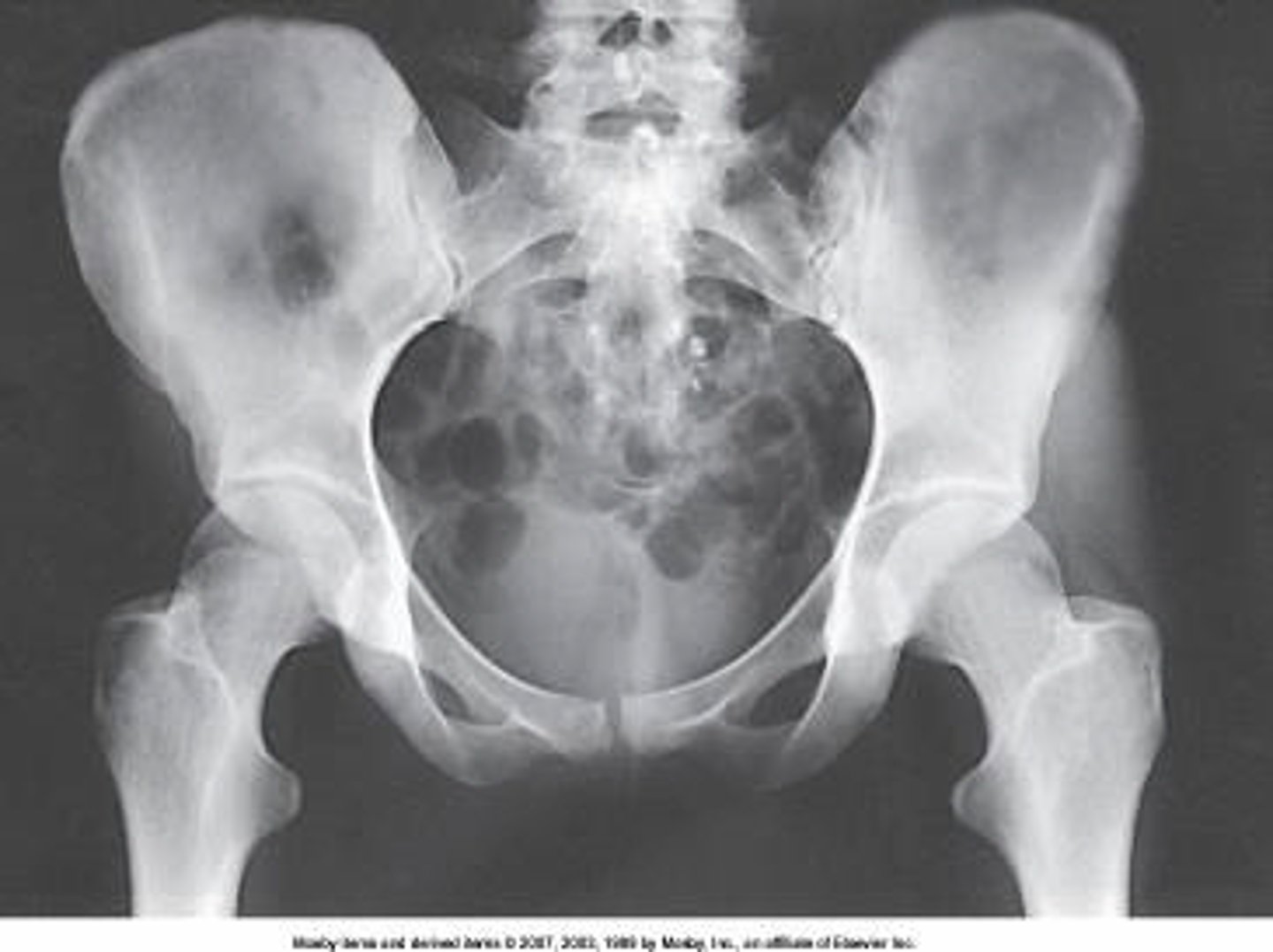
Greater trochanters
Which of the following will be shown "in profile" if the lower limbs are in correct position for an AP pelvis?
Lesser trochanters
Greater trochanters
Anterior superior iliac spines
Anterior inferior iliac spines
Adductor tubercle
Which anatomic part must be identified on lateral radiographs of the knee in order to identify over- or under-rotation?
Adductor tubercle
Lateral condyle
Medial condyle
An open patellofemoral joint space
0 degrees
The central ray for an AP oblique projection of the foot is:
0 degrees
5 degrees posteriorly
10 degrees posteriorly
15 degrees posteriorly
Back of hand against the thigh
Which position of the hand will place the humerus in internal rotation?
Prone
Supine
Palm against the thigh
Back of hand against the thigh
15 to 30
The central-ray angle for an AP axial projection of the clavicle when performed on a patient in the supine position is _____ degrees.
15
25
15 to 25
15 to 30
peritoneal cavity
The space between the two layers of peritoneum is called the:
pleural cavity
peritoneal cavity
diaphragm
abdominopelvic cavity
acromioclavicular articulations
The Pearson method is an AP projection of the:
shoulder joint
proximal humerus
scapulohumeral joint
acromioclavicular articulations
C
The scaphoid in the figure above is labeled as letter:
A
B
C
H
Abducted 90 degrees, forearm flexed
How is the arm positioned for an AP scapula?
Abducted 90 degrees, forearm flexed
Abducted 90 degrees, forearm extended
Adducted, lateral rotation
Adducted, medial rotation
Greater tubercle
Which of the following is prominently shown in profile on an AP projection of the shoulder with the humerus in external rotation?
Lesser tubercle
Greater tubercle
Scapulohumeral joint
Acromioclavicular joint
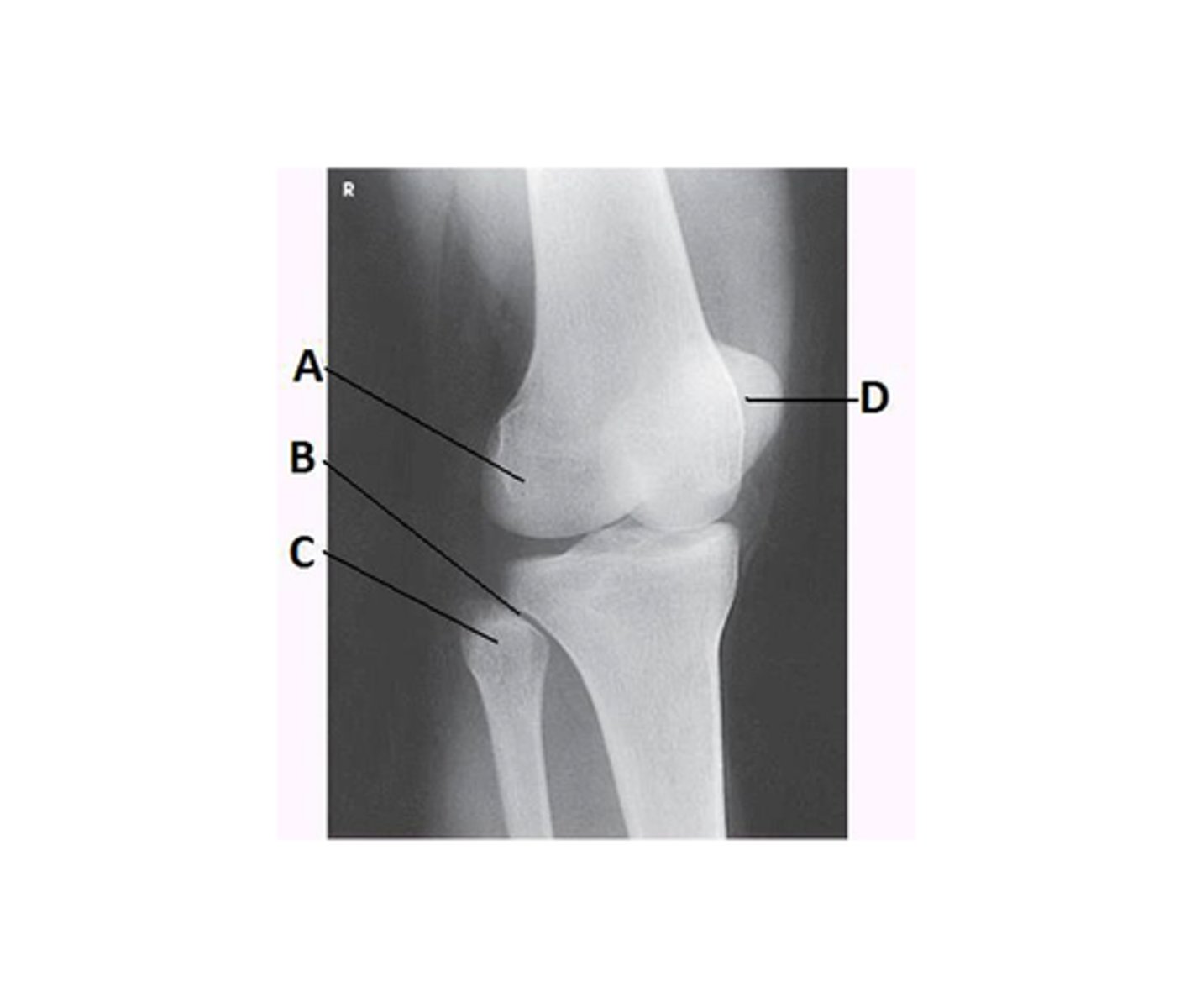
Capitulum
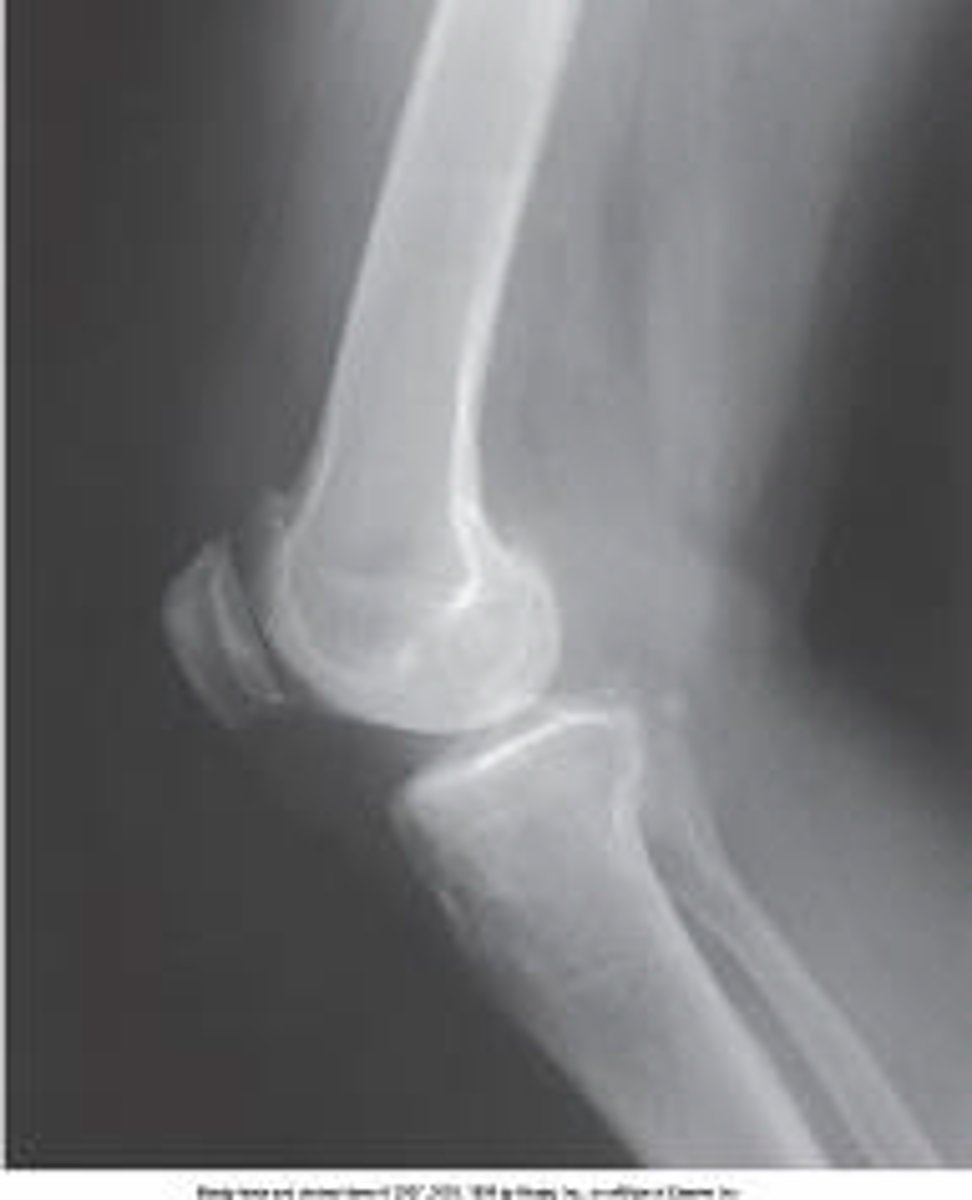
What anatomy is labeled as letter D in the image below?
Lateral epicondyle of the humerus
Medial epicondyle of the humerus
Capitulum
Trochlea
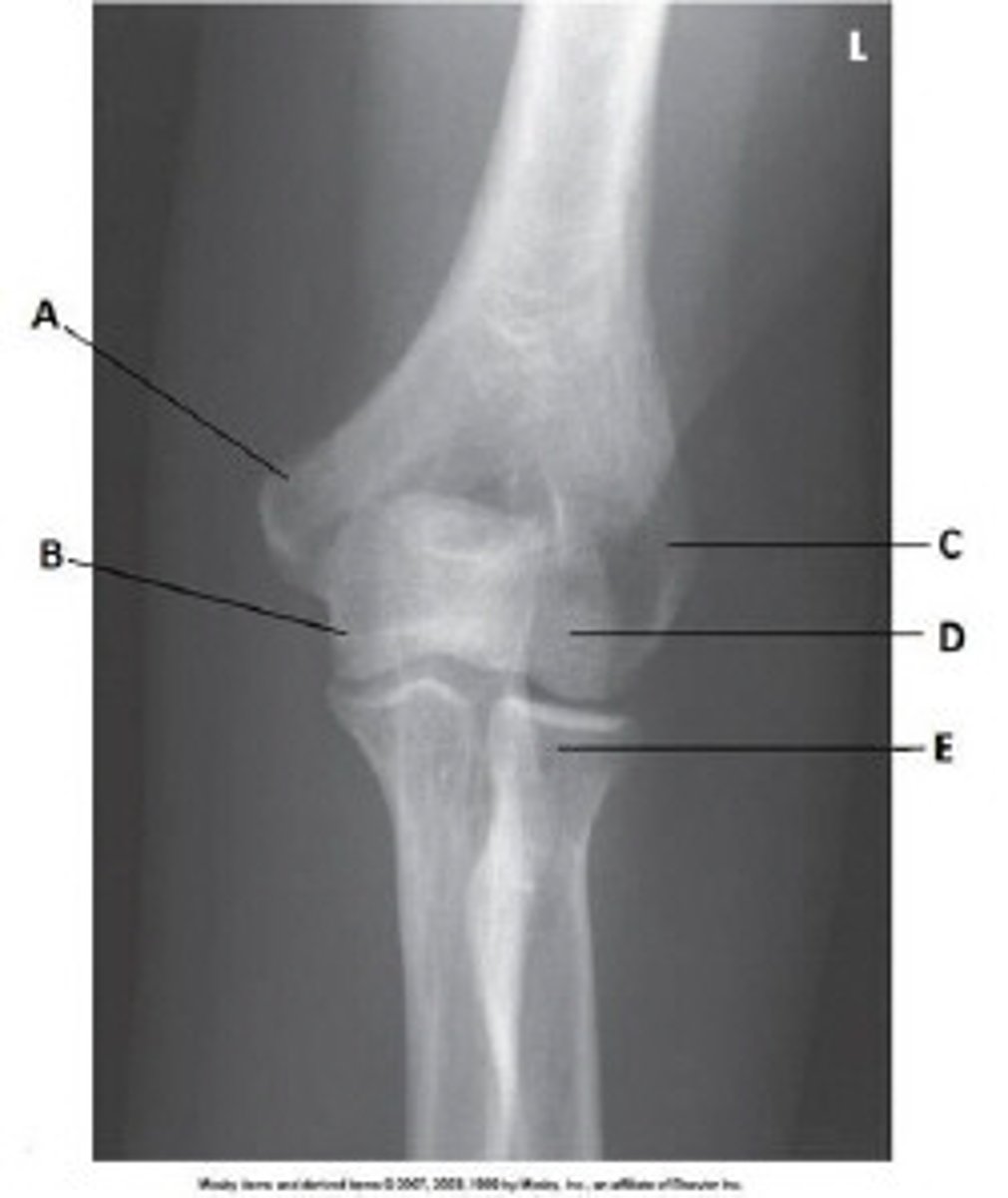
Coronoid process of ulna
What anatomy is labeled as letter B in the image below?
Capitulum
Lateral epicondyle of humerus
Trochlea
Coronoid process of ulna
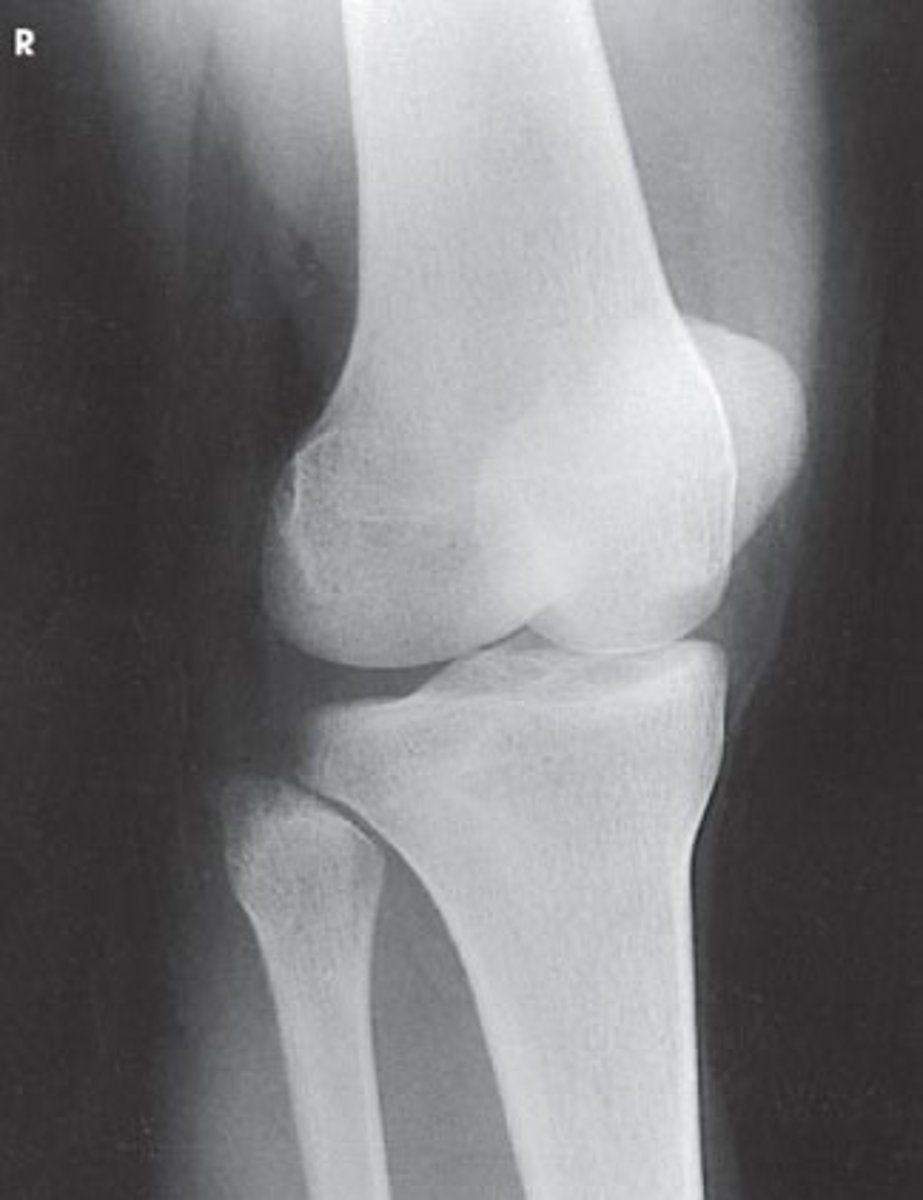
An AP of the knee and proximal leg
What is needed to complete the projection of the lower leg in the image below?
Nothing. This is a complete projection.
An AP of the knee and proximal leg
An AP of the ankle and distal leg
A lateral projection of the knee
ASIS
What anatomy is labeled as letter C in the image below?
Iliac crest
Ala of ilium
ASIS
AIIS
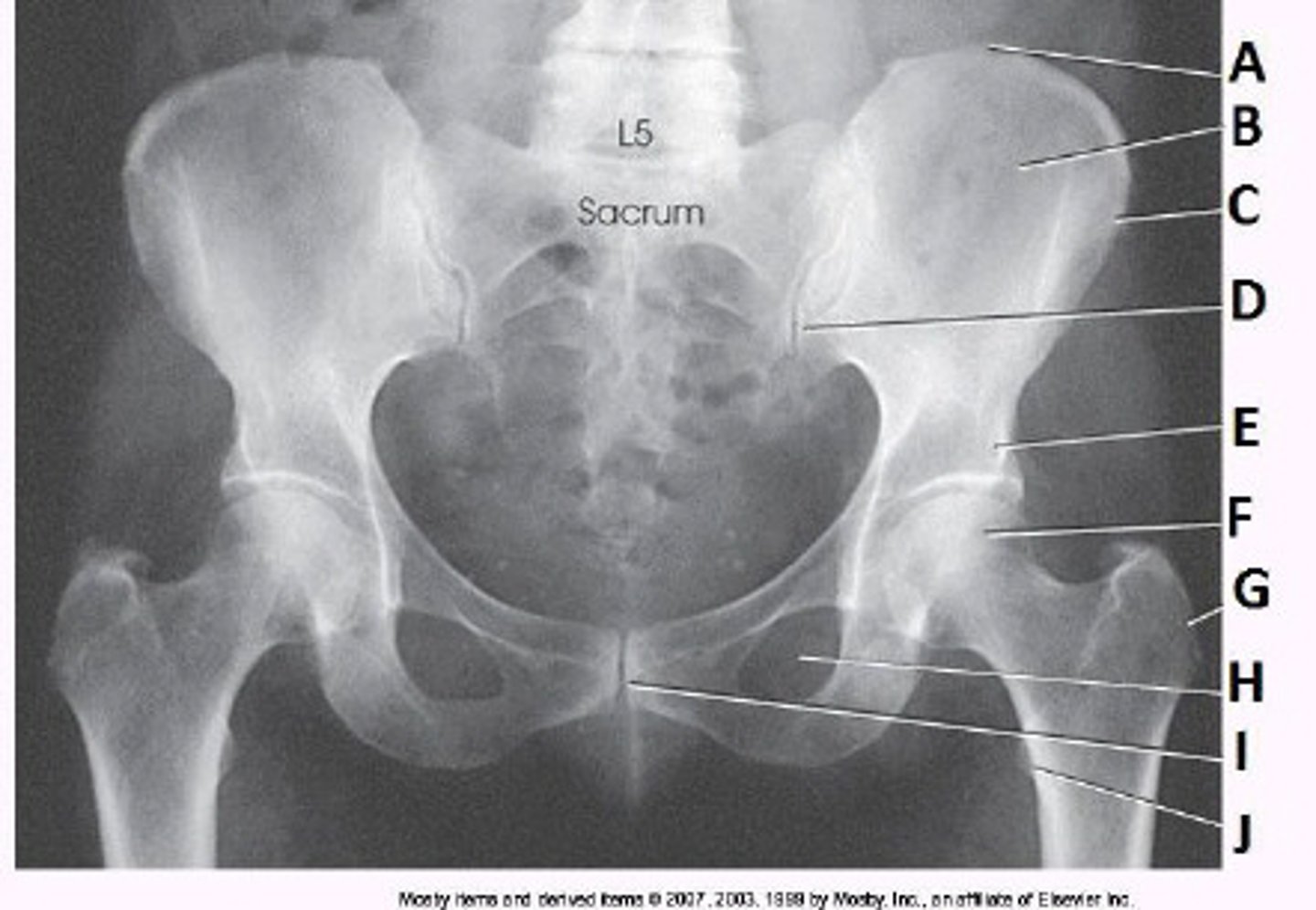
Acetabulum
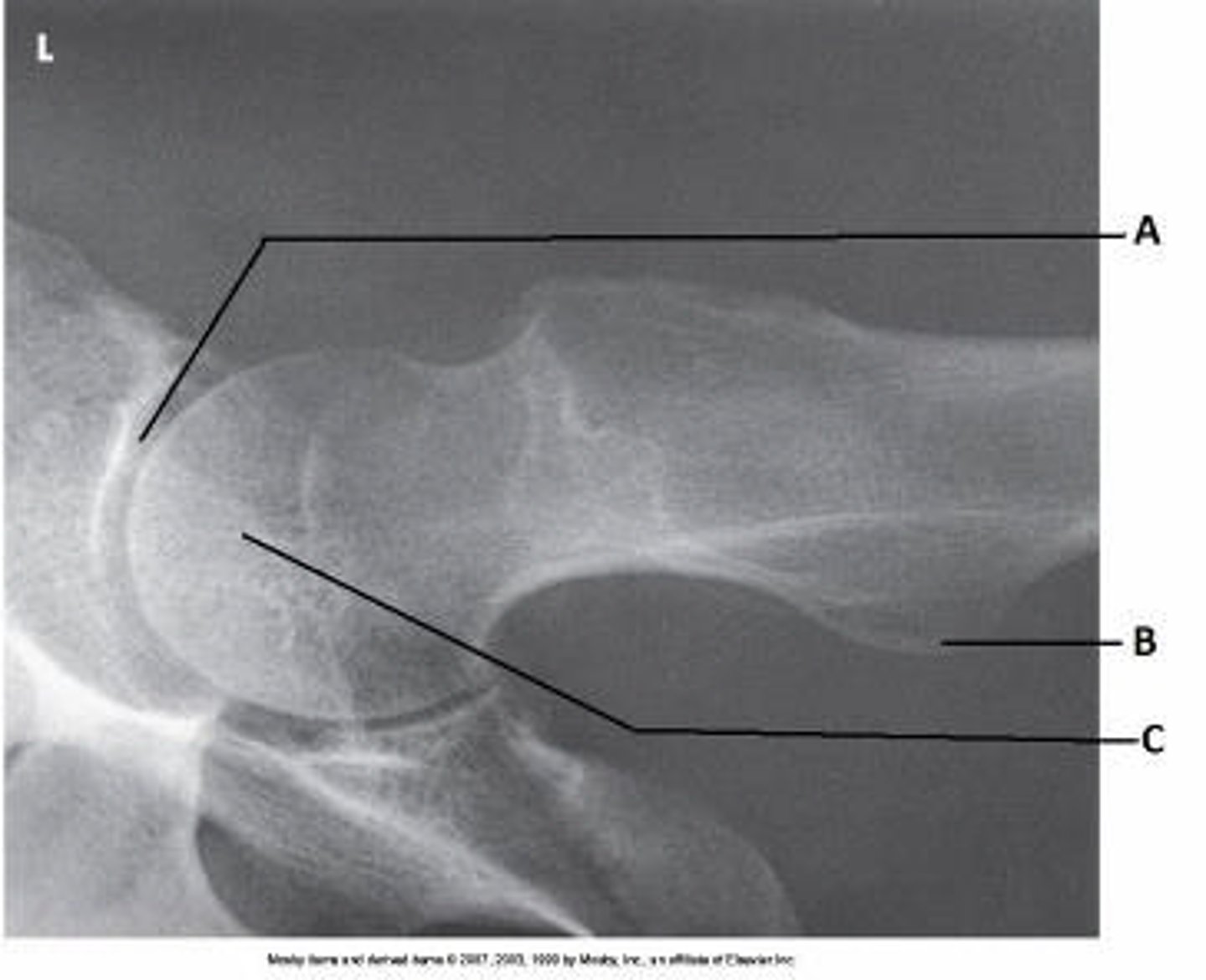
What anatomy is labeled as letter A in the image below?
Acetabulum
Femoral head
Femoral neck
Greater trochanter
1 inch distal to the medial malleolus
Where is the central ray directed for a lateral projection of the calcaneus?
1 inch distal to the medial malleolus
2 inches distal to the medial malleolus
1 inch posterior to the medial malleolus
2 inches posterior to the medial malleolus
Navicular
What anatomy is labeled as letter E in the image below?
Sinus tarsi
Sustentaculum tali
Navicular
Tibiotalar joint
30
For an AP oblique projection of the foot with medial rotation, the plantar surface of the foot should form an angle of _____ degrees.
15
30
45
60
45-degree medial rotation
What lower limb position is required to obtain the image below?
Anatomic position
45-degree medial rotation
45-degree lateral rotation
Tibial epicondyles perpendicular to IR
5 to 7 degrees cephalad
The central-ray angulation for a lateral projection of the knee is:
0 degrees
3 to 5 degrees cephalad
dependent upon the ASIS-to-tabletop measurement
5 to 7 degrees cephalad
Through the patellofemoral joint space
Where is the central ray directed for the tangential projection (Settegast method) of the patella?
Through the patellofemoral joint space
To the anterior aspect of the patella
At the level of the femoral condyles
To the apex of the patella
1 inch superior to the pubic symphysis
Where is the central ray directed for the AP oblique projection (modified Cleaves) of the femoral necks?
At the pubic symphysis
1 inch superior to the pubic symphysis
1 inch inferior to the pubic symphysis
2 inches superior to the pubic symphysis
The lower limbs were not internally rotated.
What positioning error is evident in the image below?
None. This image meets all evaluation criteria for this projection.
The lower limbs were not internally rotated.
The lower limbs were not externally rotated.
The knees were not flexed to reduce lordotic curve.
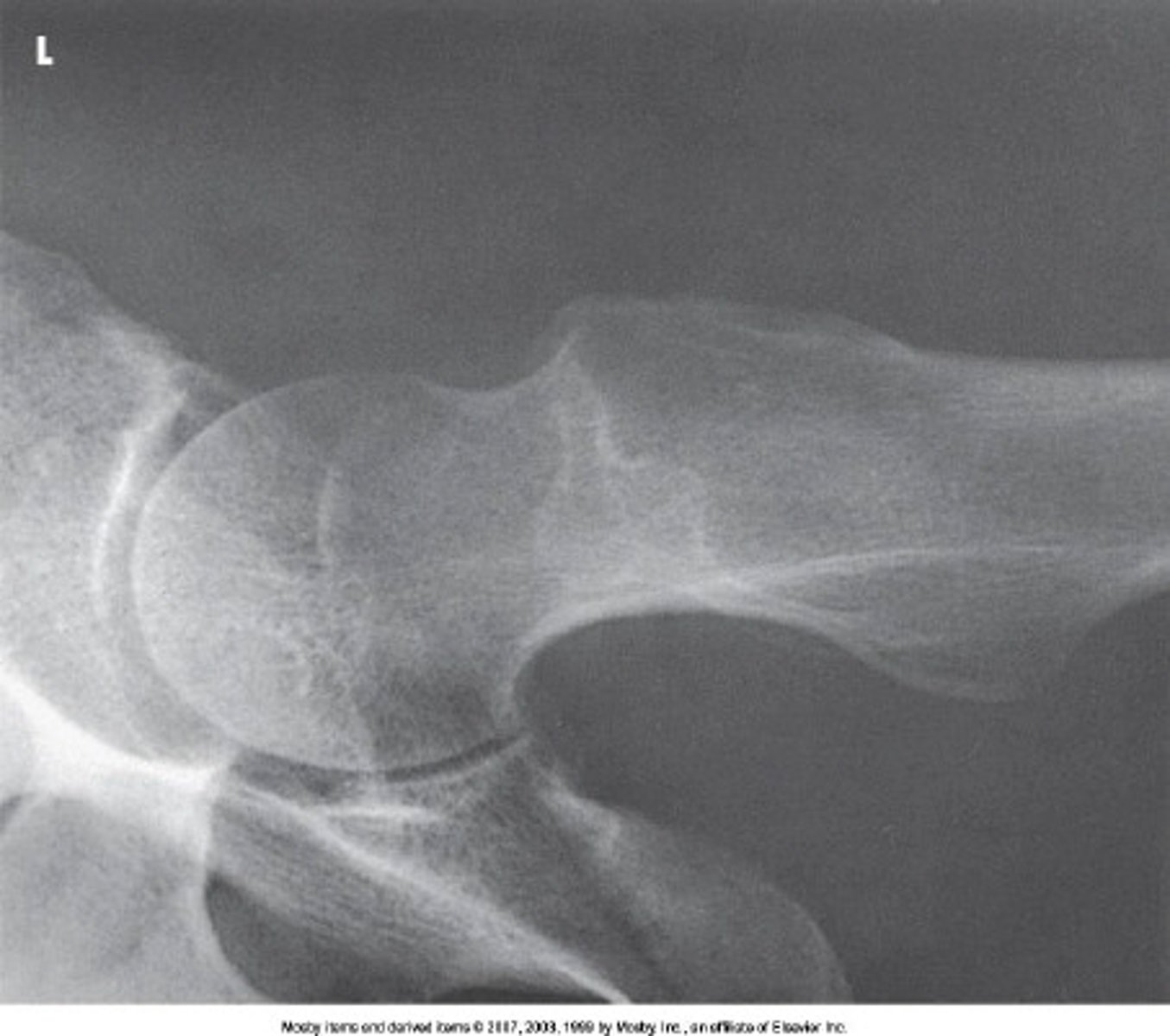
30 to 45
How many degrees are the lower leg and foot rotated for the AP oblique projection of the toes in medial rotation?
10 to 15
20 to 25
40 to 60
30 to 45
In dorsiflexion
To prevent lateral rotation, how should the foot be positioned for a lateral projection of the ankle?
In dorsiflexion
In plantar flexion
On a 10-degree angle wedge
On a 15-degree angle wedge
1 and 2
Which of the following describes the direction of the central ray for an axiolateral projection of the hip (Danelius-Miller)?
1. Perpendicular to the IR
2. Perpendicular to the long axis of the femoral neck
3. Perpendicular to the long axis of the femur
15
How many degrees of angulation are required to open the IP joint spaces of the toes on an AP projection?
0
10
15
20
Osgood-Schlatter disease
The incomplete separation or avulsion of the tibial tuberosity is known as:
osteosarcoma
osteomalacia
Paget's disease
Osgood-Schlatter disease
Navicular
Which tarsal bone lies directly anterior to the talus?
Cuboid
Navicular
Correct answer
Medial cuneiform
Lateral cuneiform
40 degrees
What is the central-ray angulation for the axial (plantodorsal) projection of the calcaneus?
25 degrees
30 degrees
35 degrees
40 degrees
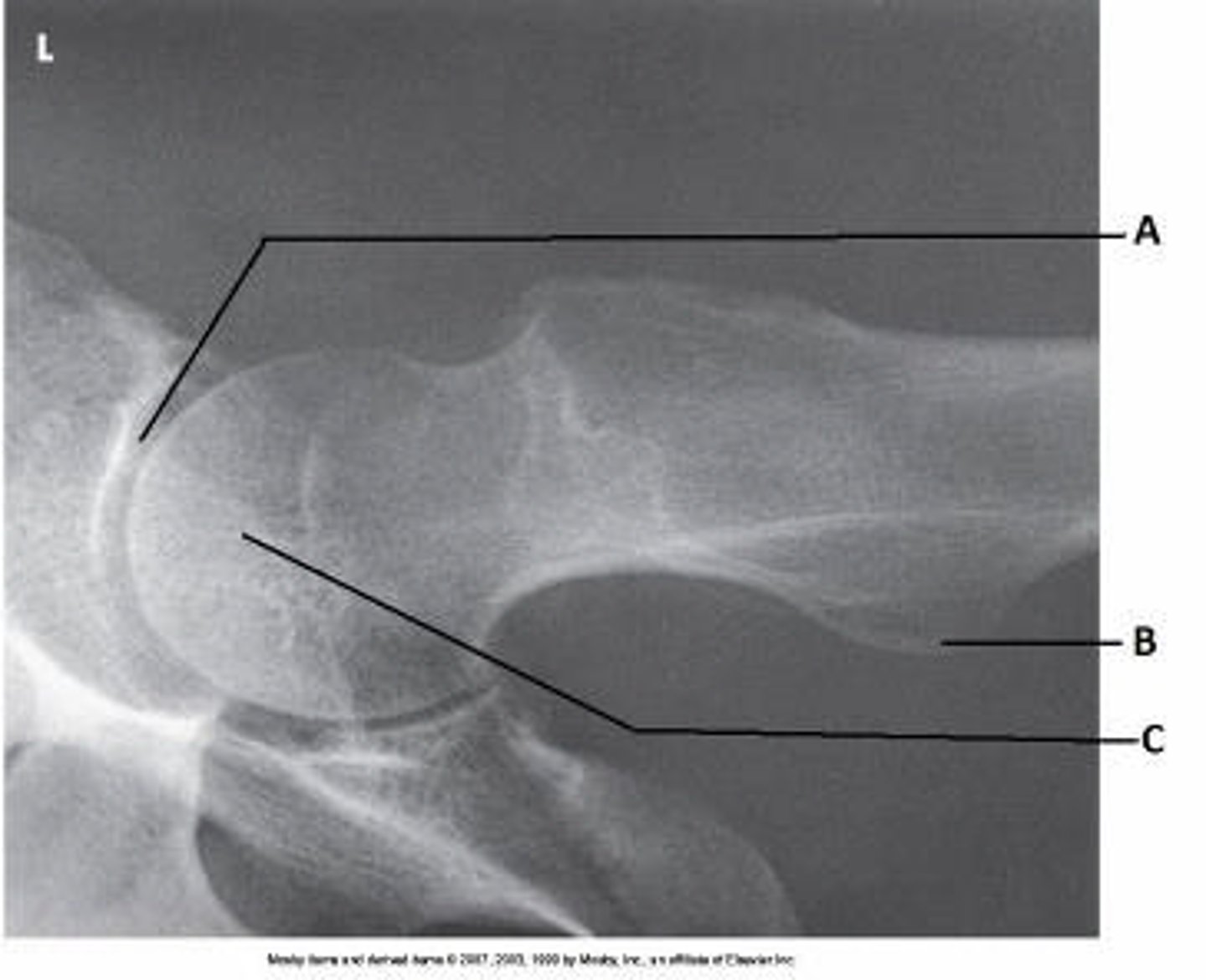
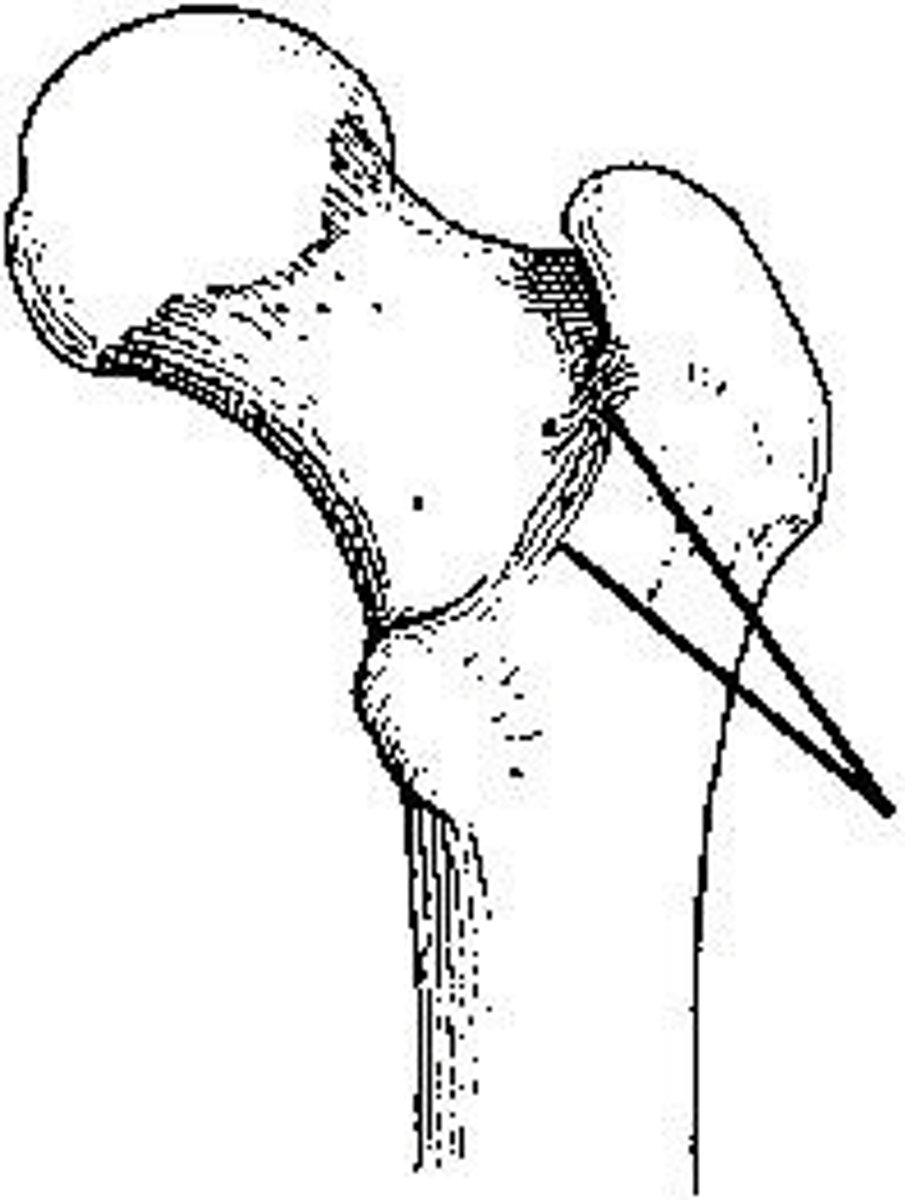
Axiolateral (Danelius-Miller)
What projection (method) is demonstrated in the image below?
AP oblique (modified Cleaves)
Mediolateral (Lauenstein)
Axiolateral (Danelius-Miller)
AP oblique (Judet)
1/2 inch below the patellar apex
Where is the IR centered for an AP projection of the knee?
1/2 inch above the patellar apex
1 inch above the patellar apex
1/2 inch below the patellar apex
1 inch below the patellar apex
Tibiofibular articulation
Which of the following is clearly demonstrated on an AP oblique projection of the knee in medial rotation?
Distal fibula
Tibiotalar articulation
Patellofemoral joint space
Tibiofibular articulation
femur
The strongest bone in the body is the:
femur
pelvis
skull
humerus
1, 2, and 3
The hip bone is composed of which of the following?
1. Ilium
2. Pubis
3. Ischium
Camp-Coventry (intercondylar fossa)
The patient position and central-ray method demonstrated in the figure above is the:
Holmblad (intercondylar fossa)
Camp-Coventry (intercondylar fossa)
Settegast (patellofemoral joint)
Hughston (patellofemoral joint)
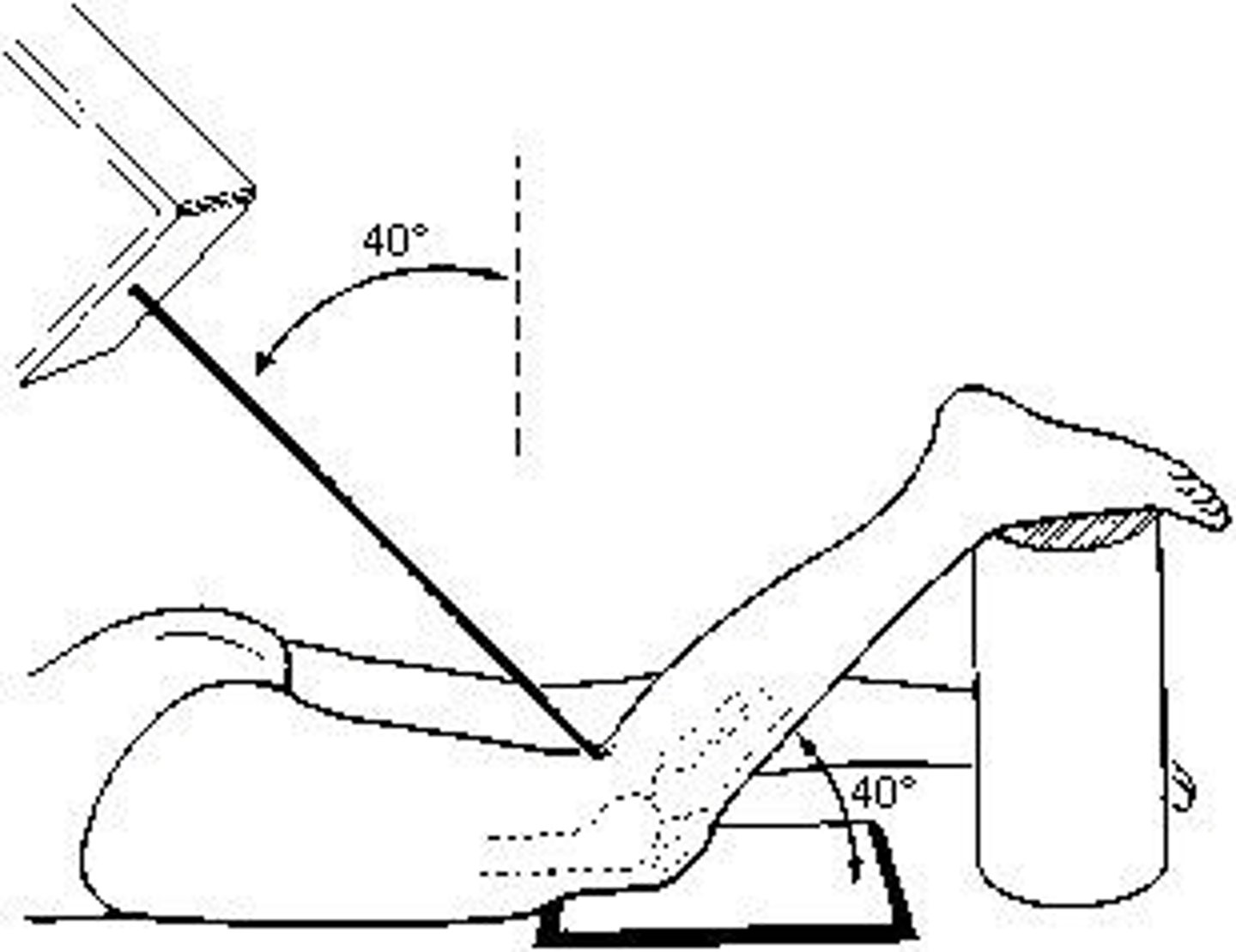
15 to 20
Unless contraindicated, the lower limb and leg should be internally rotated for an axiolateral projection of the hip (Danelius-Miller). How many degrees of rotation are required?
10
15
20
15 to 20
2 and 3
Which of the following best describes the female pelvis?
1. Heavy bones
2. Oval inlet
3. Wide outlet
Fibula
Which of the following bones does not bear body weight?
Tibia
Fibula
Navicular
Calcaneus
Plantodorsal axial calcaneus
What is the projection and anatomy of interest in the image below?
AP axial calcaneus
AP calcaneus
Plantodorsal axial calcaneus
Superoinferior axial calcaneus
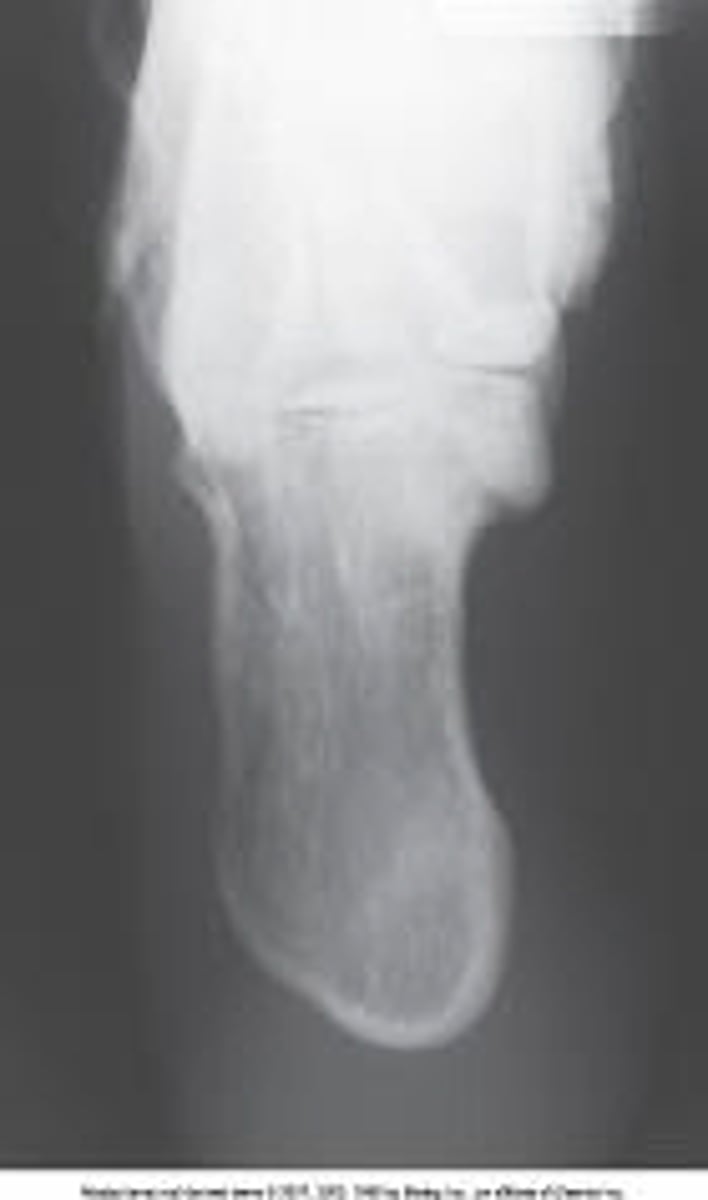
5 to 7 degrees cephalic
What is the central-ray direction needed to produce the image below?
Perpendicular
3 to 5 degrees cephalic
5 to 7 degrees cephalic
10 degrees cephalic
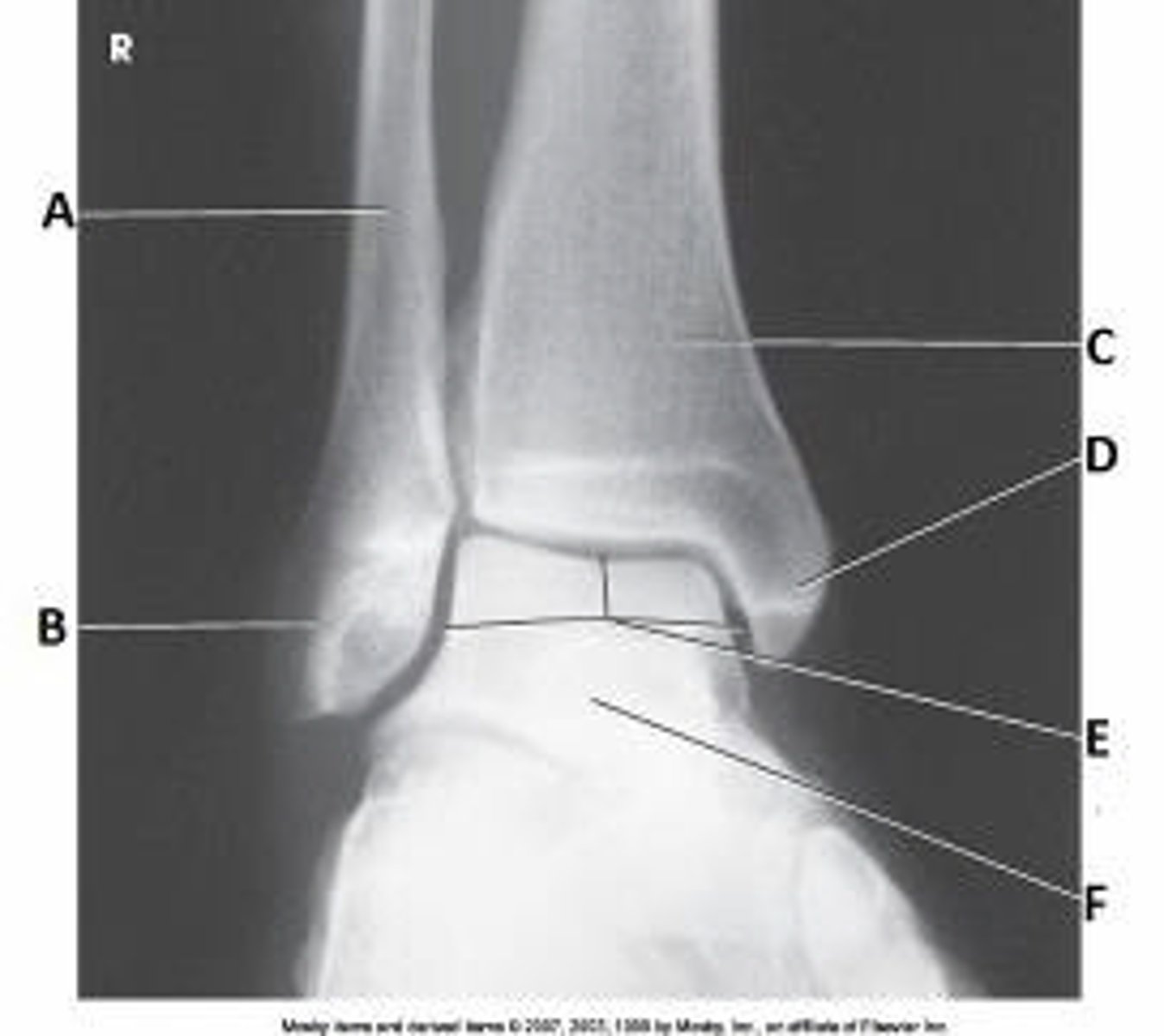
Lateral malleolus
What anatomy is labeled with the letter B in the image below?
Lateral malleolus
Medial malleolus
Talus
Tibiotalar joint
40
If the knee is flexed 40 degrees for the PA axial intercondylar fossa (Camp-Coventry) projection, the central ray will be angled _____ degrees.
0
40
50
40 to 50
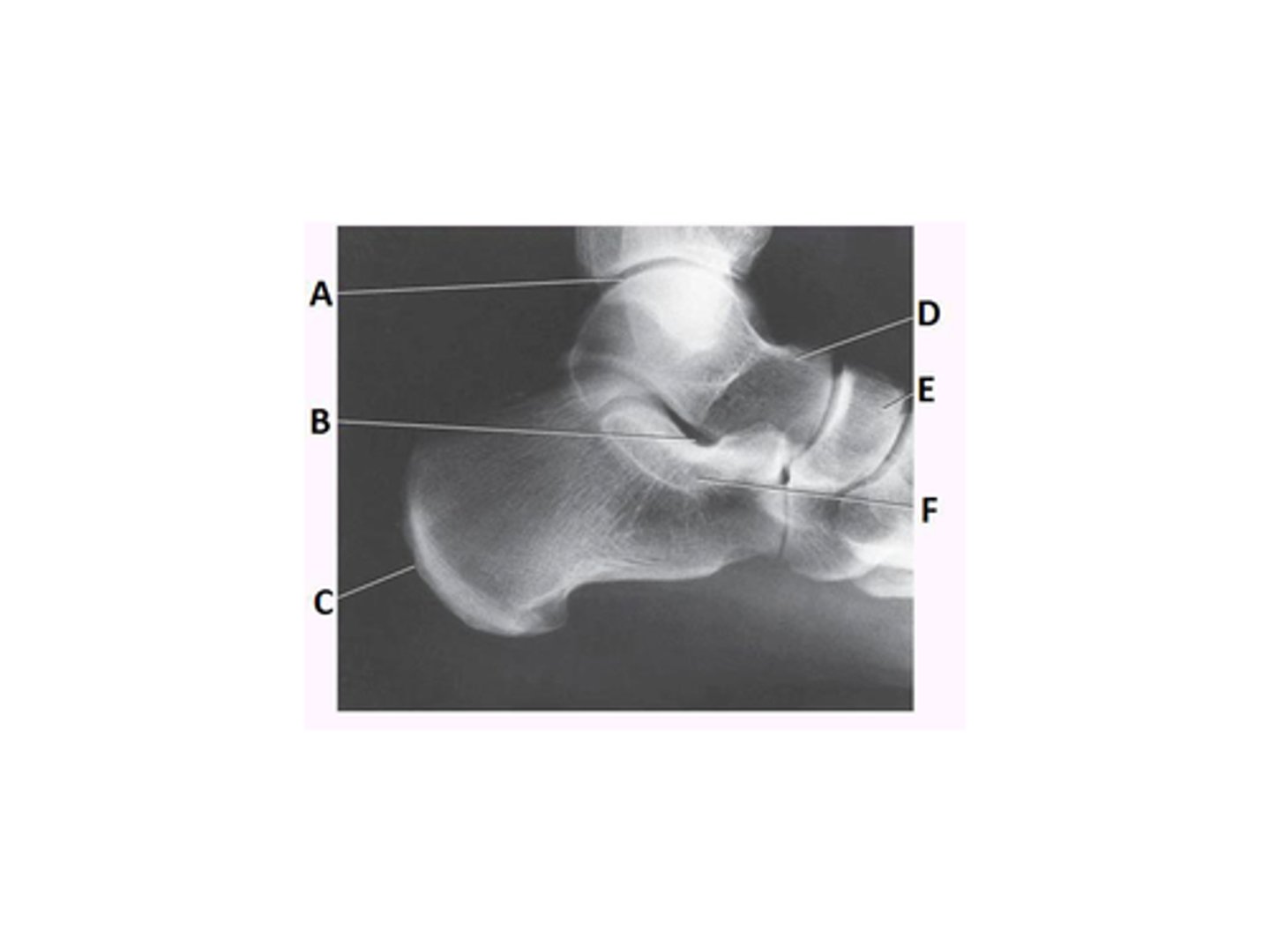
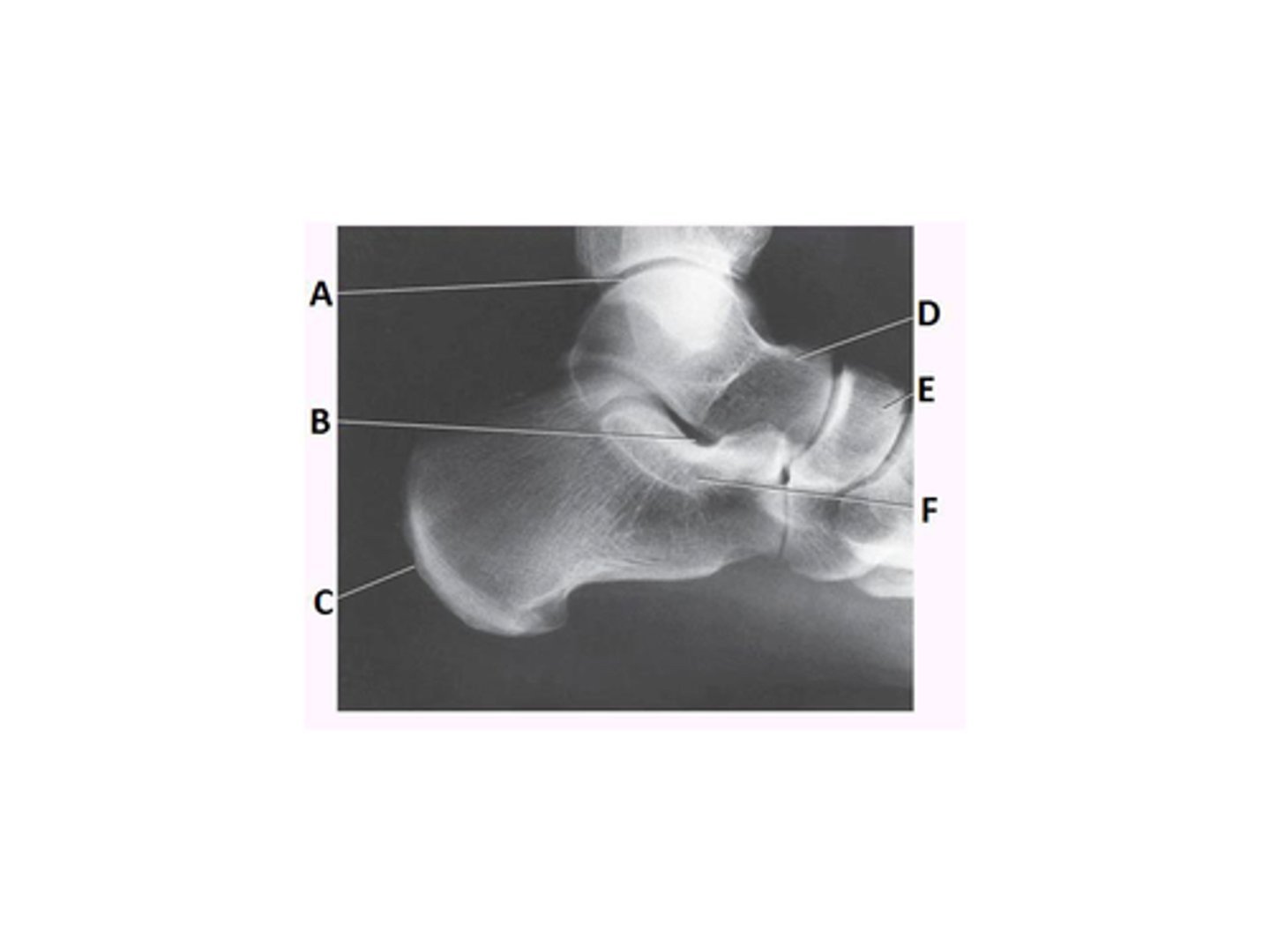
cuboid
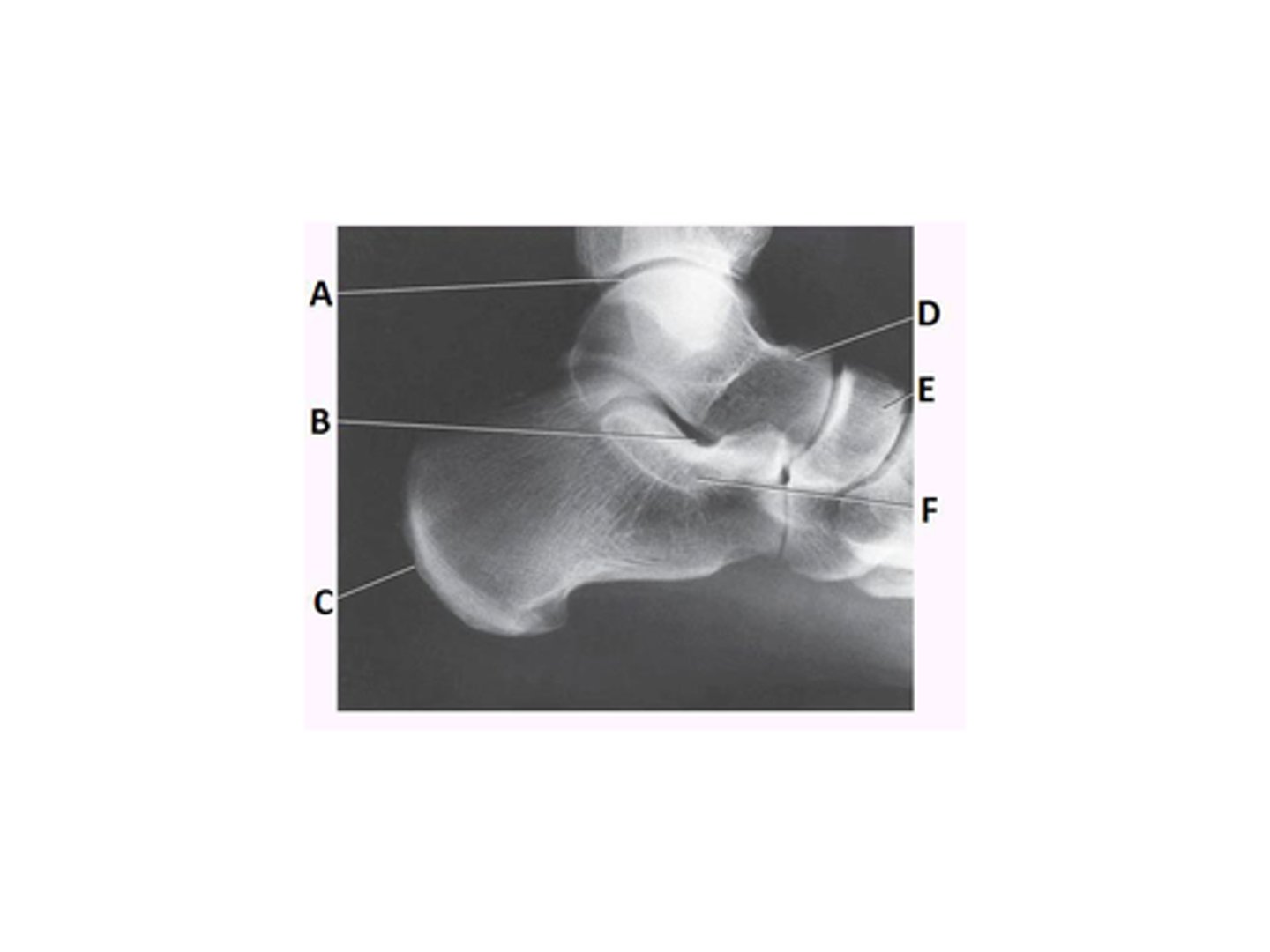
Letter H in the image below labels the:
navicular
cuboid
talus
lateral cuneiform
Modified Cleaves
Which of the following methods will demonstrate the femoral necks in the AP oblique projection?
Original Cleaves
Modified Cleaves
Danelius-Miller
Lauenstein, Hickey
0 degrees
The central-ray angle for an AP, bilateral weight-bearing knee is:
0 degrees
5 to 7 degrees cephalad
5 to 7 degrees caudad
dependent upon the ASIS-to-tabletop measurement
1, 2, and 3
Which of the following positions can be used to perform the tangential projection (Settegast method) of the patella?
1. Seated
2. Supine
3. Prone
Lauenstein, Hickey
Which of the following methods will demonstrate the hip in a lateral projection?
Cleaves
Modified Cleaves
Danelius-Miller
Lauenstein, Hickey
Midway between the ASIS and the pubic symphysis
Where is the IR centered for an AP pelvis?
Midway between the ASIS and the pubic symphysis
At the level of the ASIS
At the level of the pubic symphysis
2 inches below the iliac crest
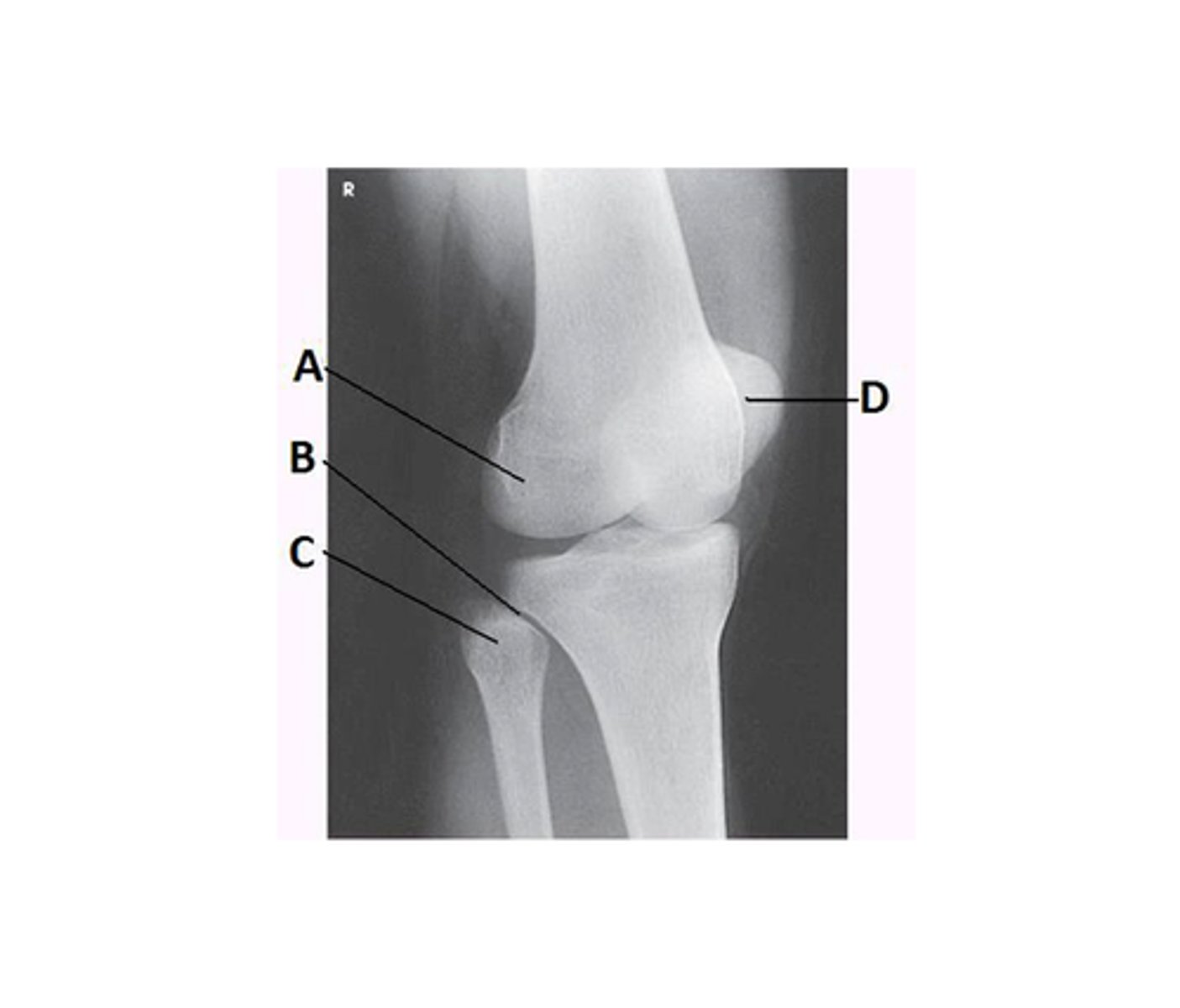
Proximal tibiofibular joint
What anatomy is labeled with the letter B in the image below?
Lateral femoral condyle
Lateral tibial condyle
Proximal tibiofibular joint
Tibial tuberosity
1 and 2
Which of the following describes the position of the IR for the axiolateral projection of the hip (Danelius-Miller)?
1. Parallel with the long axis of the femoral neck
2. Its upper border in the crease above the iliac crest
3. Perpendicular to the long axis of the femur
anterior superior
The part identified on the ilium shown in the figure above is the _____ iliac spine.
anterior superior
posterior superior
anterior inferior
posterior inferior
45
For an AP oblique projection of the knee, the limb is rotated _____ degrees.
25
30
45
30 to 40
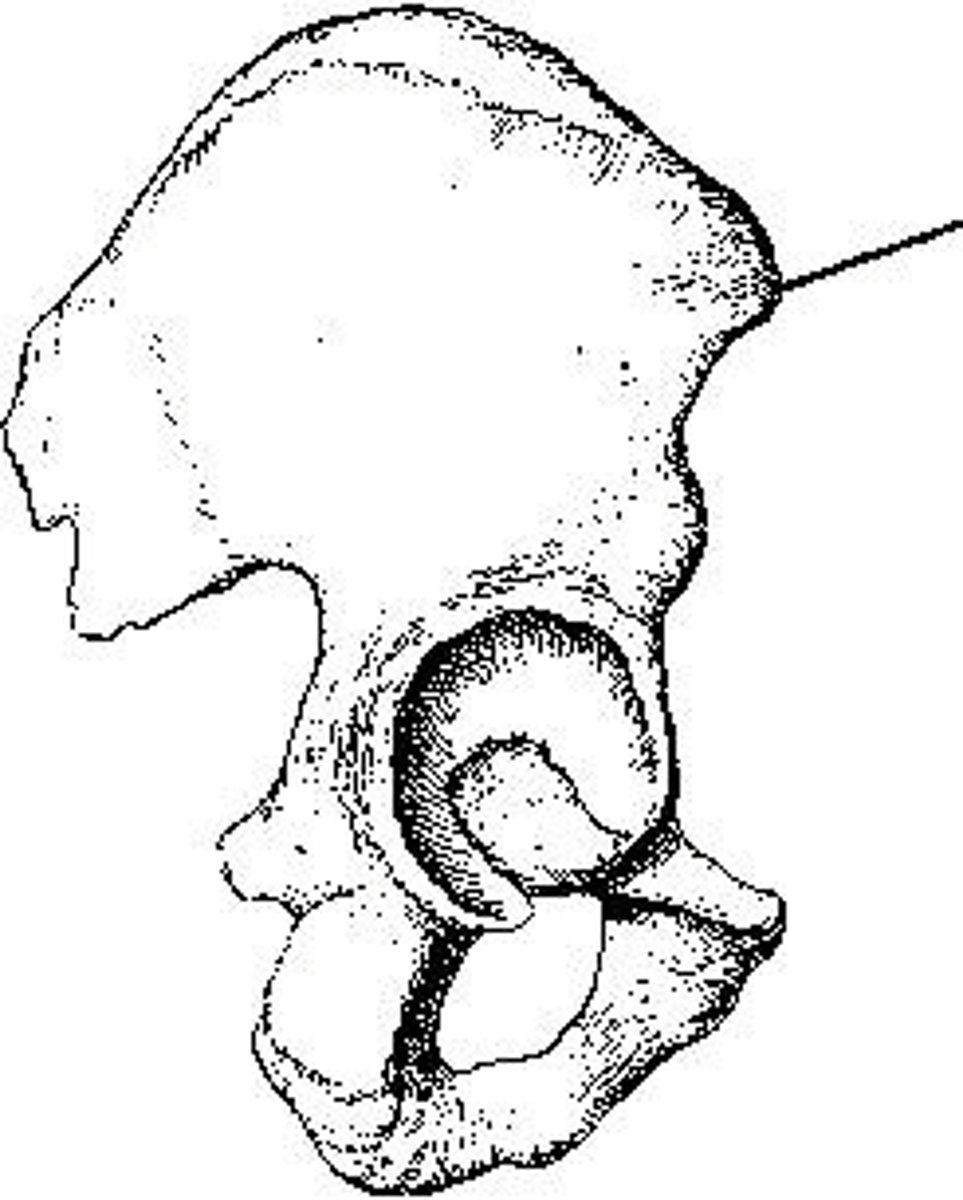
Lesser trochanter
What anatomy is labeled as letter B in the image below?
Acetabulum
Femoral head
Lesser trochanter
Iliac crest
tibial tuberosity
On the anterior surface of the tibia is a prominent process called the:
body
anterior border
tibial tuberosity
intercondylar eminence
intertrochanteric crest
The area identified on the bone shown in the figure above is the:
posterior inferior spine
lesser trochanter
greater trochanter
intertrochanteric crest
Talus
What anatomy is labeled as letter D in the image below?
Tibia
Fibula
Talus
Calcaneus
Prone
In which position is the patient placed for a PA projection of the patella?
Supine
Prone
Lateral
Upright
20 to 30 degrees
How much should the leg be flexed for a lateral projection of the knee?
10 degrees
45 degrees
10 to 20 degrees
20 to 30 degrees
Sinus tarsi
What anatomy is labeled as letter B in the image below?
Sinus tarsi
Sustentaculum tali
Navicular
Tibiotalar joint
third
For an AP projection of the toes, the central ray is directed to the _____ MTP joint.
first
second
third
fourth
AP oblique in medial rotation
Which of the following will clearly demonstrate the cuboid?
AP
Lateral
AP oblique in lateral rotation
AP oblique in medial rotation
Danelius-Miller
Which of the following methods demonstrate the hip in an axiolateral projection?
Chassard-Lapiné
Modified Cleaves
Danelius-Miller
Lauenstein, Hickey
15 to 20
To demonstrate the ankle mortise, the leg and foot should be rotated medially how many degrees?
10
25
45
15 to 20
AP oblique, medial rotation
Which projection of the foot will show the cuboid in profile?
AP
Lateral
AP oblique, lateral rotation
AP oblique, medial rotation
2; superior
The central ray for an AP pelvis is directed perpendicular to the center of the IR. The central-ray entrance point will be about _____ inches _____ to the pubic symphysis.
2; superior
3; superior
2; inferior
3; inferior
base of the third metatarsal
For a lateral projection of the foot, the central ray is directed to the:
head of the third metatarsal
base of the third metatarsal
tibiotalar joint
navicular
Anterior superior iliac spine
Which of the following is an important and frequently used radiographic positioning reference point?
Acetabulum
Ischial spine
Anterior superior iliac spine
Posterior superior iliac spine
intercondylar fossa
Posteriorly, the femoral condyles are separated by a deep depression called the:
Hide answer choices
popliteal surface
intercondylar eminence
patellar surface
intercondylar fossa
tibial plateaus
The two flat, superior surfaces of the tibia are called the:
tubercles
malleoli
condyles
tibial plateaus
15 to 20
The neck of the femur projects anteriorly at an approximate angle of _____ degrees.
15
20
15 to 20
20 to 25
Ankle mortise
Which of the following is not clearly demonstrated on an AP projection of the ankle?
Tibiotalar
Lateral malleoli
Ankle mortise
Tibiofibular overlapping
Lateral femoral condyle
What anatomy is labeled A in the image below?
Lateral tibial condyle
Patella
Lateral femoral condyle
Medial femoral condyle
90 degrees from the plane of the IR
For an axial projection of the calcaneus, the ankle should be dorsiflexed so the plantar surface of the foot is:
parallel with the central ray
perpendicular to the central ray
70 degrees from the plane of the IR
90 degrees from the plane of the IR
suspended respiration
The respiration phase for the axiolateral projection of the hip (Danelius-Miller) is:
inspiration
expiration
suspended respiration
shallow breathing
15 to 20 degrees
How many degrees should the feet and lower limbs be internally rotated for an AP pelvis radiograph?
5 to 10 degrees
15 to 20 degrees
20 to 30 degrees
25 to 30 degrees
45 degrees
For an AP projection of the shoulder with the arm in a neutral position, the epicondyles of the humerus should be _____ with the plane of the IR.
parallel
perpendicular
45 degrees
60 degrees
scapulohumeral
The articulation between the glenoid cavity and head of the humerus is called the _____ joint.
synovial
spheroidal
acromioclavicular
scapulohumeral
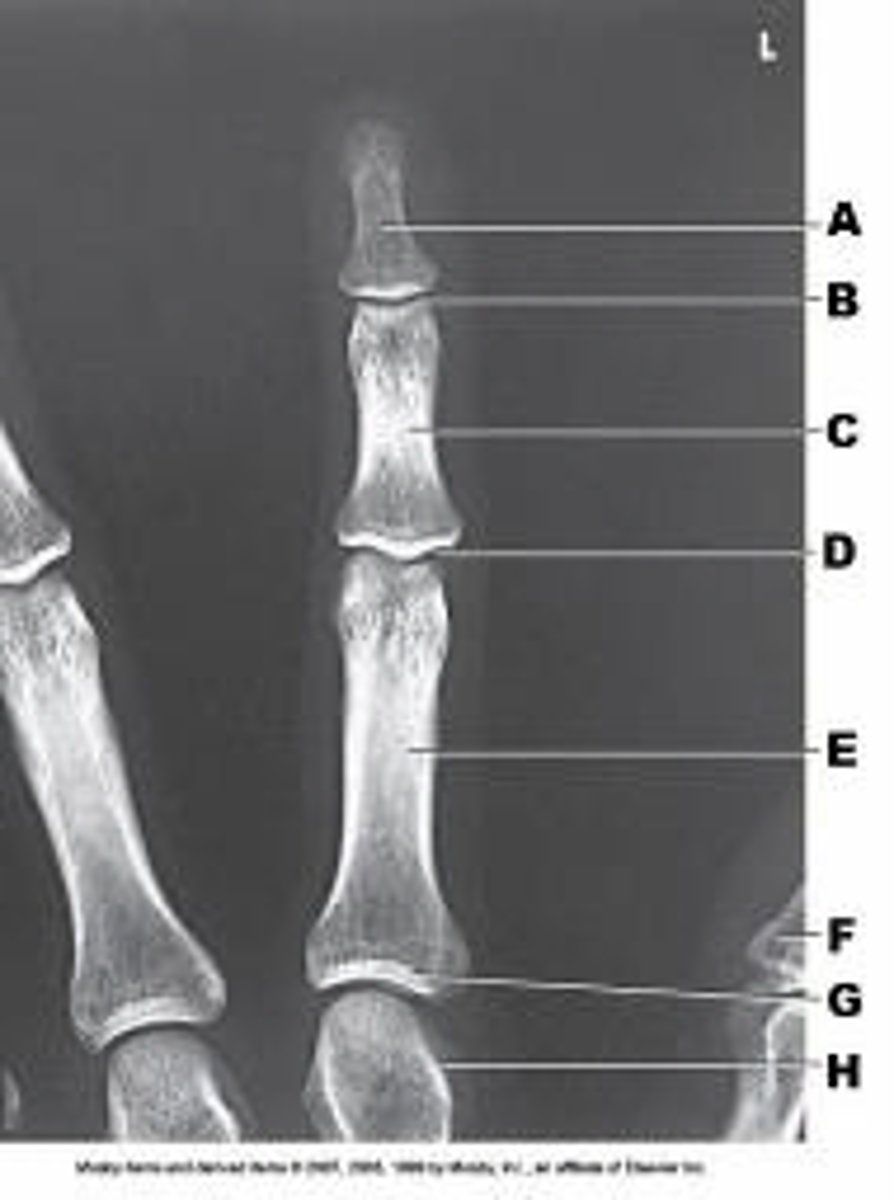
Proximal IP joint
What anatomy of the third digit is labeled as letter D in the figure above?
Distal IP joint
Proximal IP joint
Metacarpophalangeal joint
Carpometacarpal joint
1; coracoid process
For an AP projection of the shoulder, the central ray should enter _____ inch(es) inferior to the _____.
1; coracoid process
1; acromion
2; coracoid process
2; acromion
Supine
Which position of the hand will place the humerus in external rotation?
Prone
Supine
Palm against the thigh
Back of the hand against the thigh
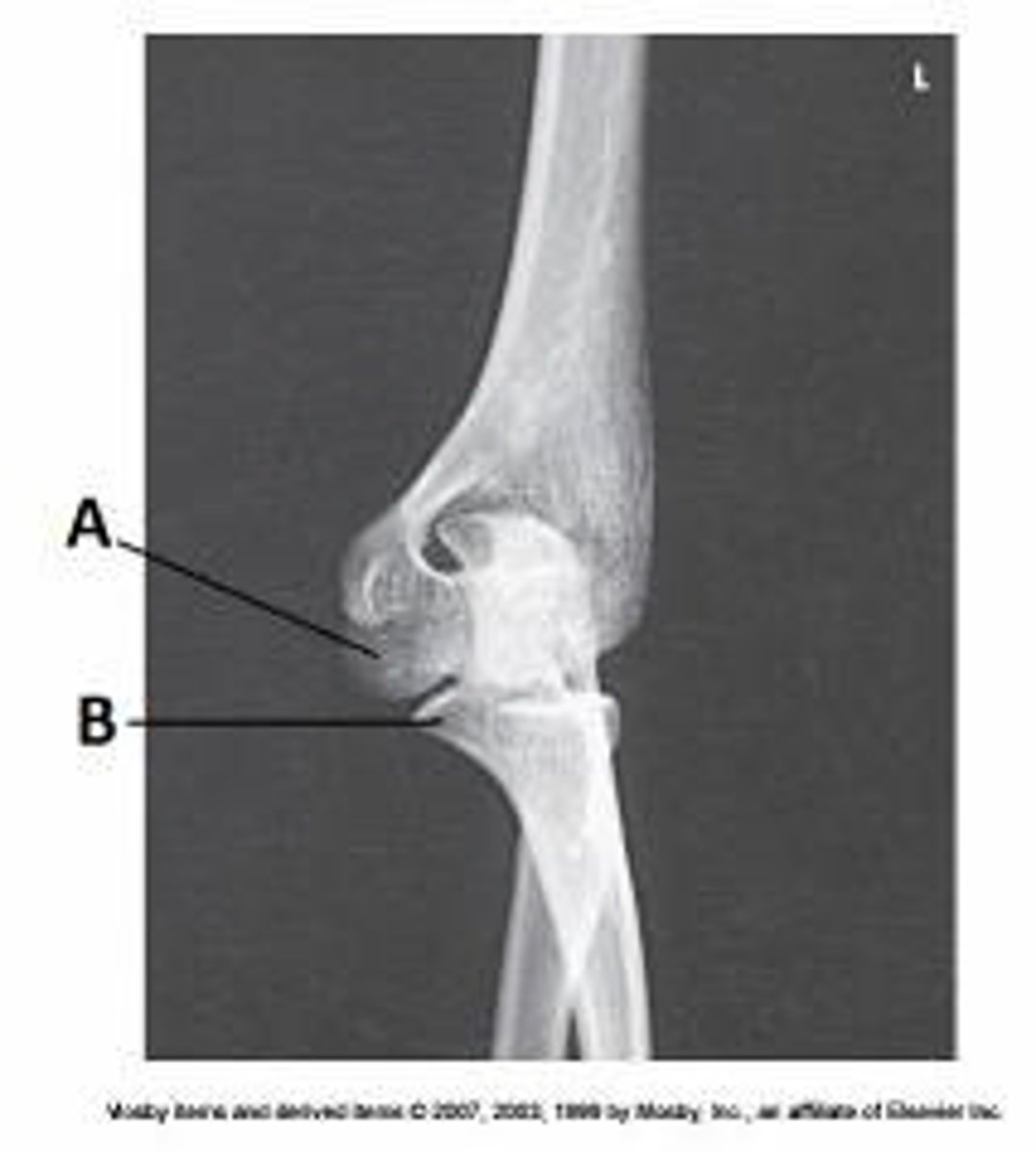
parallel to the IR
For the AP projection of the elbow, the humeral epicondyles are:
perpendicular to the IR.
parallel to the IR
superimposed over each other.
not clearly seen.
1, 2, and 3
Which of the following organs lie in the abdominal cavity?
1. Stomach
2. Gallbladder
3. Kidneys
1 and 2
1 and 3
2 and 3
1, 2, and 3