Psychology 10,11& 12 Study Guide b
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
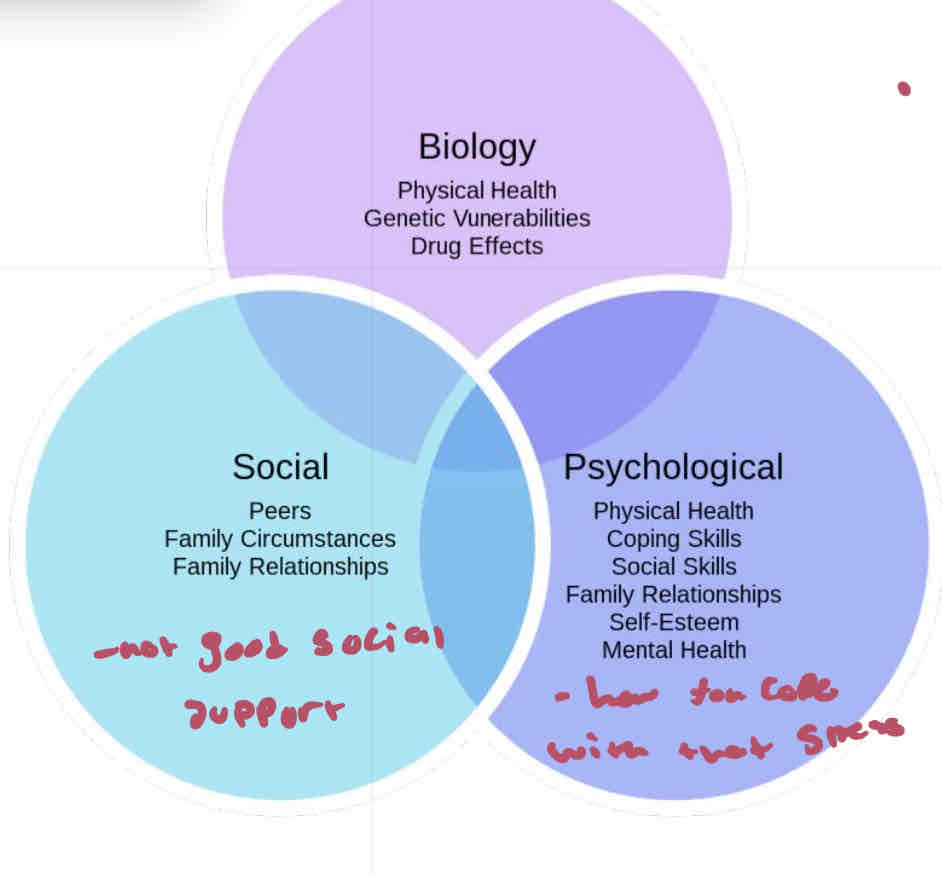
Biopsychosocial Model
How stress effects / how to cope
Helps understand the interplay of health
Every person is different with coping , understanding how people respond to stress
Biology
physical health
Genetic Vulnerabilities
Drug Effects
Social
peers
Family circumstances
Family relationships
No good social support
Psychological
physical health
Coping skills
Social skills
Family relationships
Self esteem
Mental health
How you cope with that stress
What is stress
A type of response that typically involves and unpleasant state
Uncertainty
Lack of control
Concerns other will evaluate or treat us negatively
Situations with levels of uncertainties
How much control we have over that situation
Social concern , other evaluate or treat vs negatively, social base ( NOT UNIVERSAL)
Distress
Involves negative events ; lost loved one , stuck in traffic , passing exam
Eustress
Positive event, marriage , preparing for college , new job
Major life events : Dailey hassle , Major , castrophic
40% might get divorced
Stimulus - 1960,viwed as significant life events
Dailey hassle - Monday- day to day events
Major - personalized
Catastrophic events: wars,tornadoes
Daily Hassles
Mundane strains and annoyances associated with routine activities in everyday life
daily stressors , minor occur more frequently
Routinely paying bills , long hour , kids
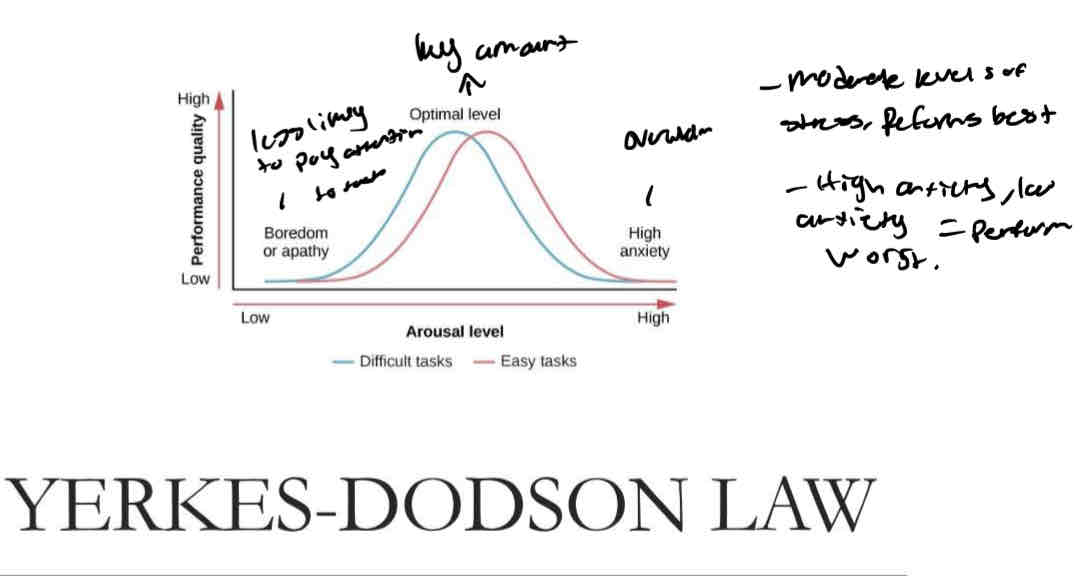
YERKES-DODSON LAW
( Boredom of Apathy) - low/ less likely to pay attention
(Optimal level )- key amount ,moderate levels of stress , performs best
( High anxiety) - overworked , high anxiety levels , perform worst
Occupational Stress: Job burnout
Job Burnout: a general sense of emotional exhaustion and cynicism in relations to ones job
exhaustion
Depersonalization
Diminished personal accomplishment
Compassion fatigue
High effort / Low reward
High effort : constant time pressure , lot of responsibility , pressure to work overtime
Low Reward: job security , promotion prospects , unforced job change
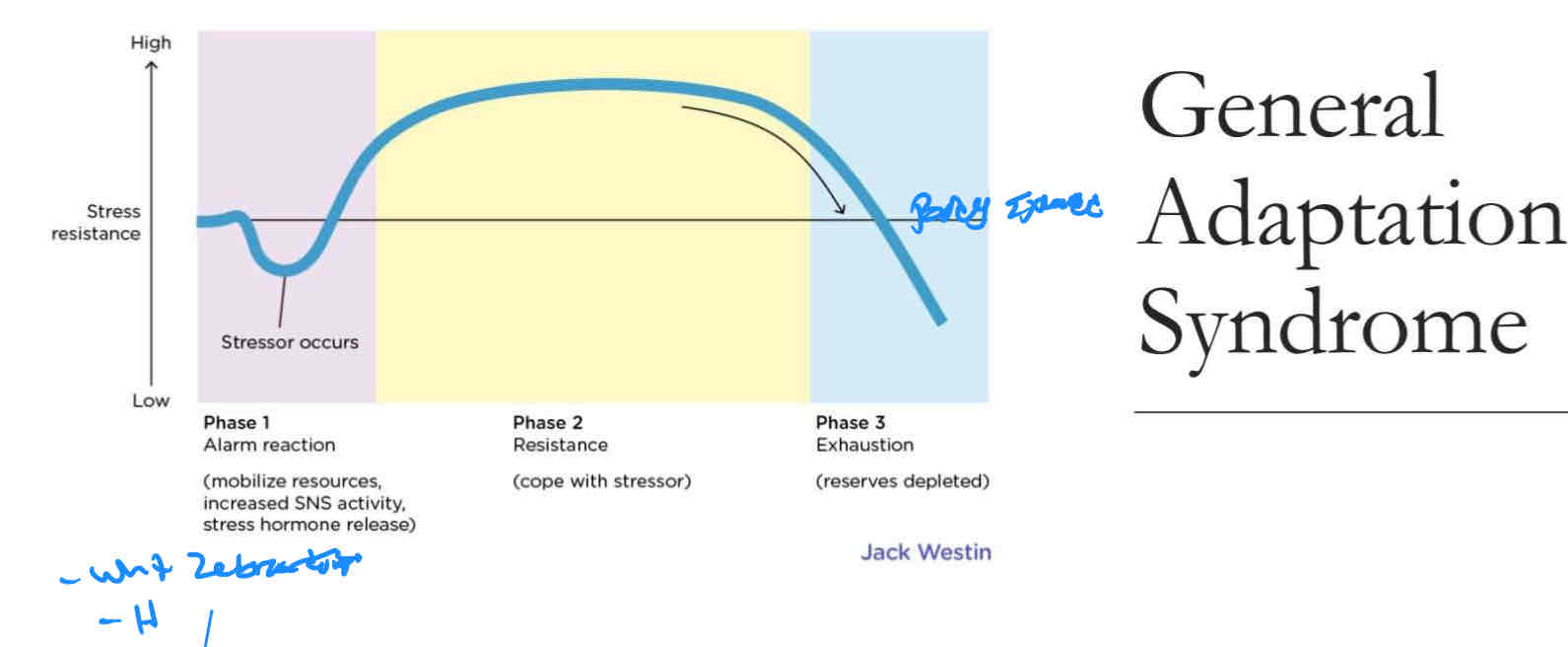
General Adaptation Syndrome:
Alarm,Resistance,Exhaustion
Alarm phase : the body mobilizes the sympathetic nervous system to meet an immediate threat.( fight or flight, infections ,illness)
Resistance Phase : The body attempts to resist or cope with a stressor that cannot be avoided.
Exhaustion Phase: Persistent stress depletes the body of energy , thereby increasing vulnerability to physical problems and illness.
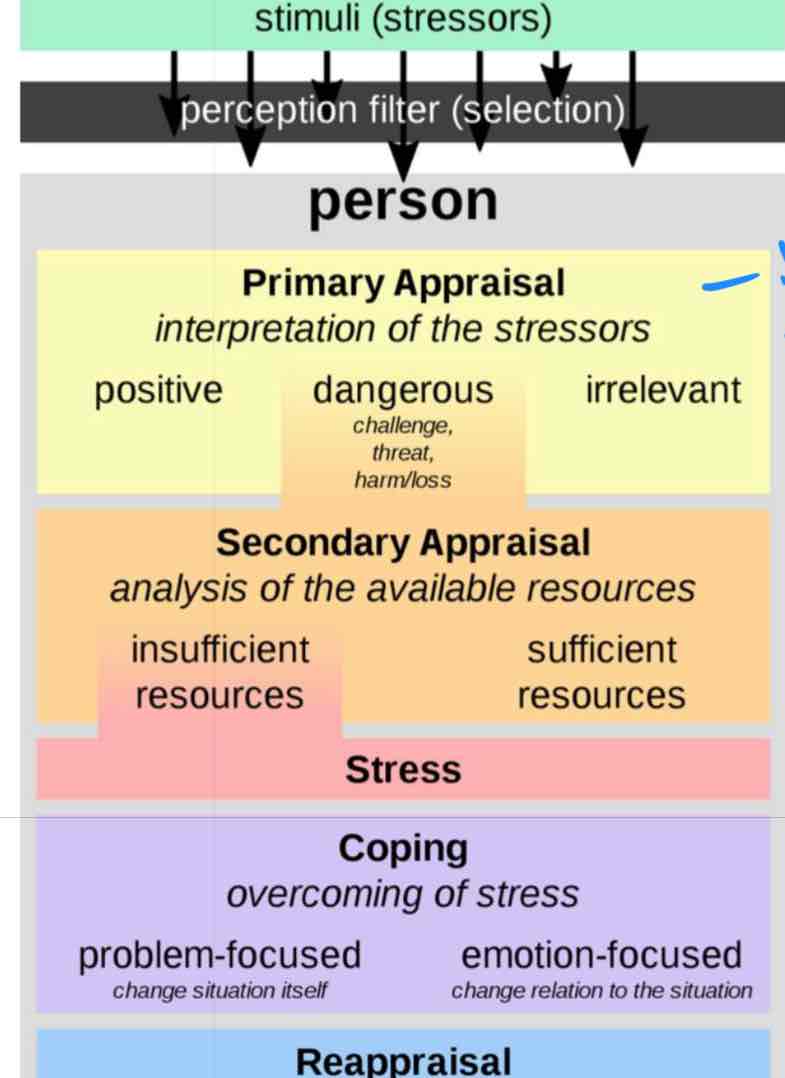
Stress Appraisal Theory ( Richard Lazarus)
Environment- stimuli stressors
Perception filter (selection )
Person :
Primary Appraisal : Your interpretation of the stressors : positive, dangerous , irrelevant
Secondary Appraisal: analysis of the available resources ; insufficient resources , sufficient resources
Stress:
Coping: overcoming stress;
problem focused- change situation itself
emotion focused - change relation to the situation
Reappraisal- pacing and learning , ongoing constant evaluating stressor
Sam Axis
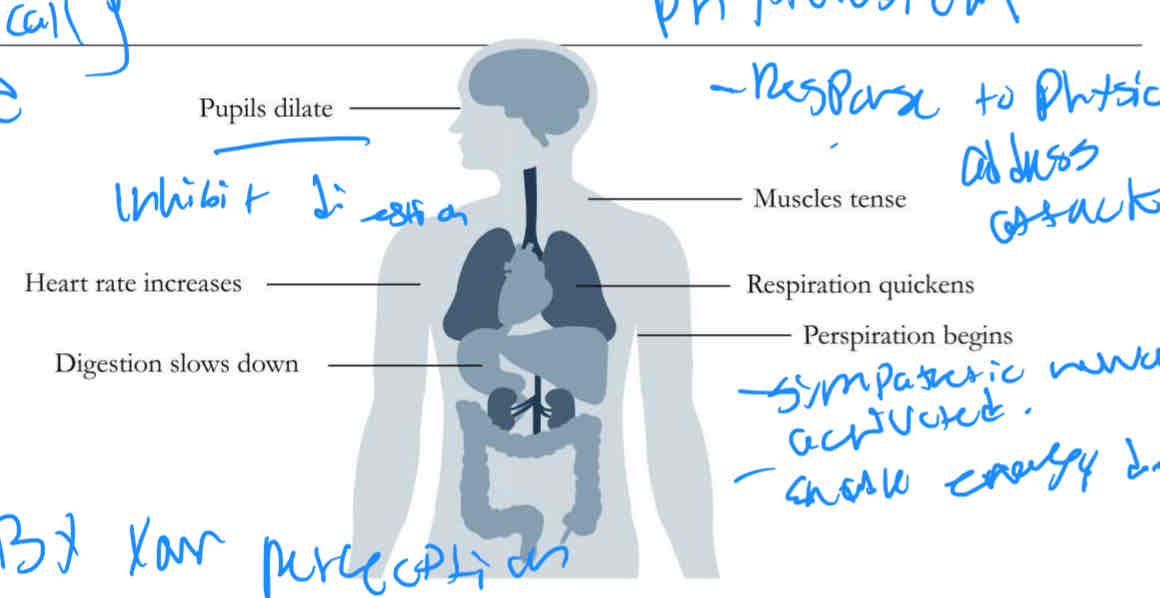
A Nerodoctrine stress response system
pupils dilate
Heart rate increase
Digestion slows down
Muscle tense
Respiration quickness
Perspiration begins
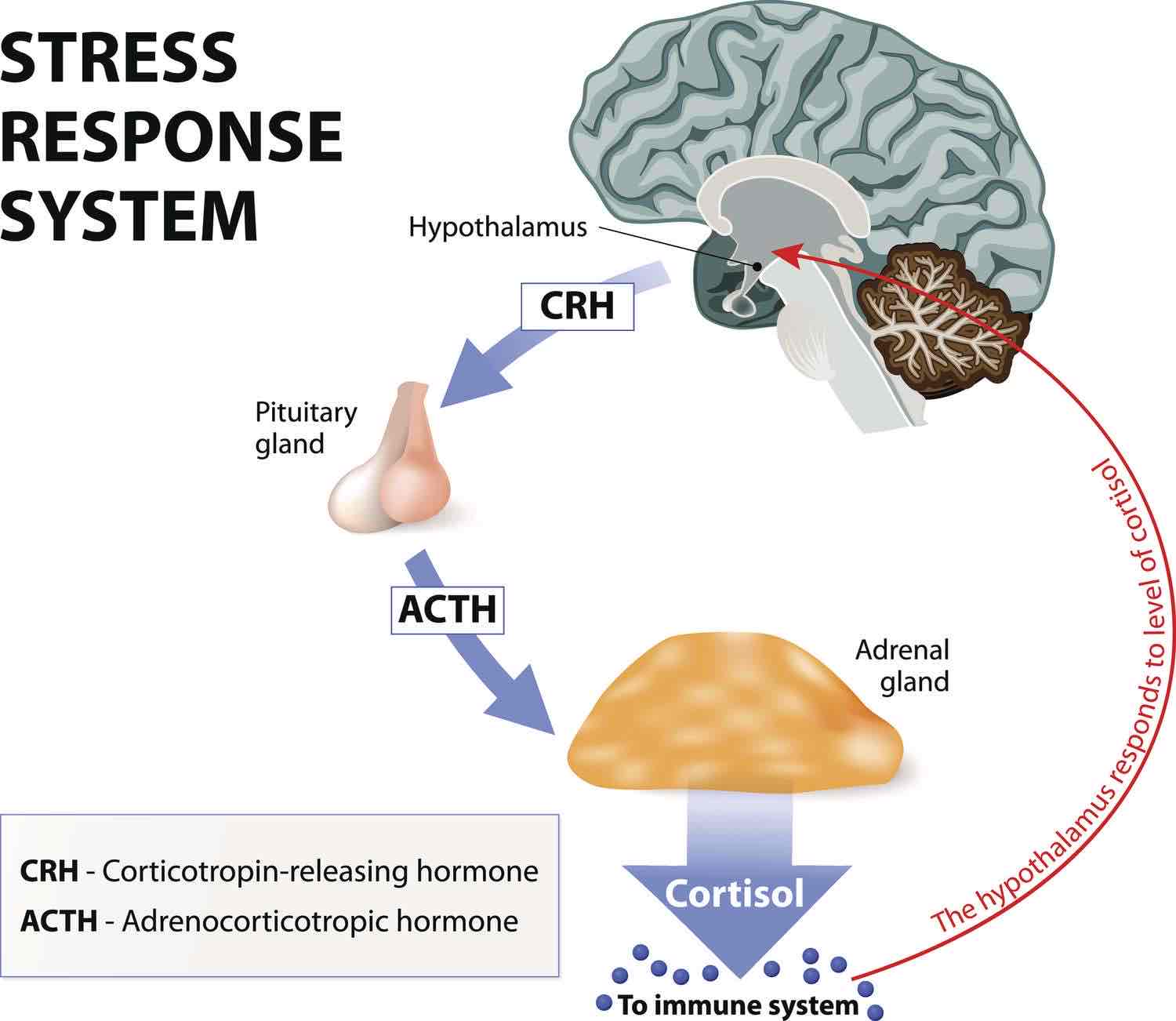
HPA Axis
Central nervous system and the endocrine system adjusting the balance of the hormones in response to stress, hypothalamus stimulating the pituitary gland releases hormones in response to stress.
Challenge reactivity
Heart rate increase
Blood vessel expand
Enhanced performance
Threat reactivity
Heart rate increases
Blood vessels constrict
Inhibited performance
How women and men respond to stress ?
Both release oxytocin
Men: testosterone , inhibits release of oxytocin , fight or flight
Women: estrogen , regulates effects of oxytocin , tend and befriend , protect
Effects of Stress ?
Allostatic Loaded : the sustained activation of many physiological system in response to frequent or chronic stressors
Ex; someone who experienced repeated exposure to stressful life events
Psychoneuroimmunology
stress disrupts the communication between the brain and the body which weakens the immune system
Stress causes damage at the cellular level ?
effects on telomeres
Antigens= five, bacteria, cancer cells
Chemical - Brian - immune system , how to respond
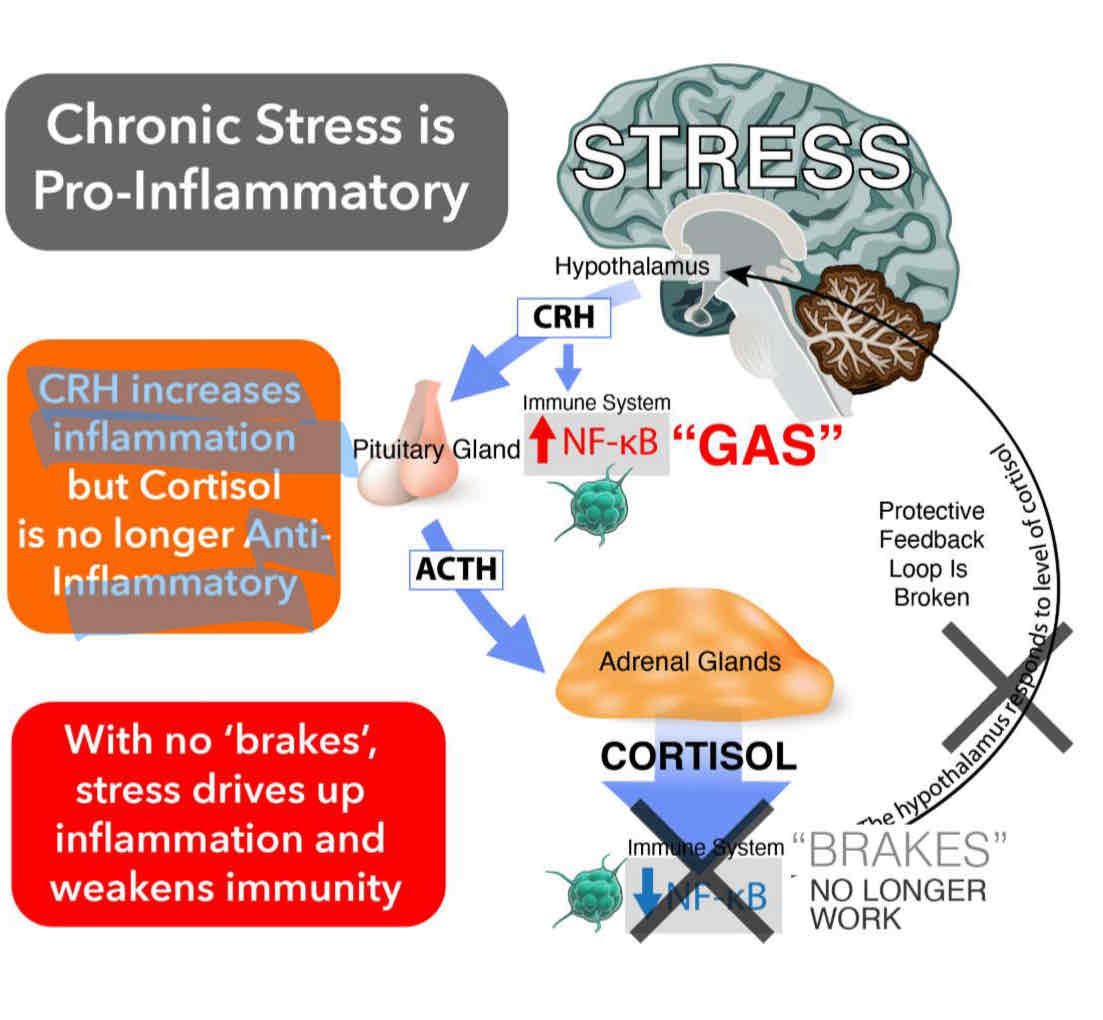
The effects of chronic stress on the immune system ?
Cortisol suppresses the immune system effectiveness
reduces white blood cell count
Lack of control over inflammation response
CRH increases inflammation but cortisol is no longer Anti inflammatory
Difficult for the body to recover form illness
CRH released
Cortisol- inflammation , can’t keep body safe from infection
According to Stress Appraisal Theory, which type of appraisal is more likely to result in a positive response to stress?
Challenge Appraisal
- alarm
- resistance
-exhaustion
Alarm-stress hormones and adrenaline start to increase
Resistance -irritability, frustration, and concentration issues appear
Exhaustion -depression, fatigue, and anxiety attacks may occur
Realistic vs Unrealistic Optimism
Realistic Optimism: ability to balance out negative and positive things in situations, circumstance and people, more likely to take care of themselves.
Unrealistic optimism : good things will just happen, there is nothing to worry about everything will be great ,they predict a personal future outcome will be more favorable than the suggest relevant objective standards.
Different types of Genes x environment interactions
Diathesis- Stress Model : stress environment
Differential Sensitivities: more likely to be affected positive by a warm environment
Hypothesis:
Epigenetic’s: Based on what you go through and you dealt with it , adds to dna stress response influence child stress response
Problem vs emotional focused coping
P: attempting to manage or alter the stressor
Ex; alter the stress, test coming up, breaking down how well you studied
E: attempting to reduce the negative emotions associated with the stress
Ex;how you respond emotionally to an event , alters how you deal with that event managing emotional respond … self blaming , drugs , yoga , prayer
Piaget Theory of cognitive development:
Sensorimotor:0-2, understands the world through touch , movement , listening , sucking on things , looking
Preoperational : 2-7 , children learn to use language and are able to represent, symbolize and think about their environment
Formal Operational: 11,being able to manipulate the world in your Mind, formulate hypothesis and test them to arrive at an answer to a problem , scientific reasoning
Concrete Operational:7-11, a child is cable of performing a variety of mental operations and thoughts using concrete concepts , logical thinking
Theory of Mind
The ability to understand another’s mental state
Develop around age4
How children understand their perspectives vs other perspectives
Sally Anne ; removing toy out of the box experiment
False Belief Task
A type of task in which children must infer that another person does not posses knowledge that they possess..
SALLY ANNE ; removing toy out of box , seeing if the other person realizes it
Challenges to Piaget
Children should assume that the spaces has more but the children chose the shorter one when properly motivated with candy versus marbles
3 yr old chose the row with more candy even though it was shorter
Mary Ainsworth Strange Situation is used for ?
kid cries when mom leaves and left with caregiver , kid does not cry when mom leaves
push - pull
Observe attachment in children ( secure , anxious ,avoidant )
Different Attachment Styles
Secure : cries when caregiver leaves, comforted by caregivers return , comfortable in unknown situation
Avoidant : may cry when care giver leaves, avoids caregiver upon return
Ambivalent : cries when caregiver leaves , shows push- pull behavior when caregiver returns
Romanian orphanages taught us about neglect :
poor living conditions , no intellectual stimulation , schedule of being fed and bathed but apart from that were in cribs all day
If attachments do not form the consequences will be severe
Deprivation have long term effect on social , cognitive and intellectual development
No interactions
Brain develops
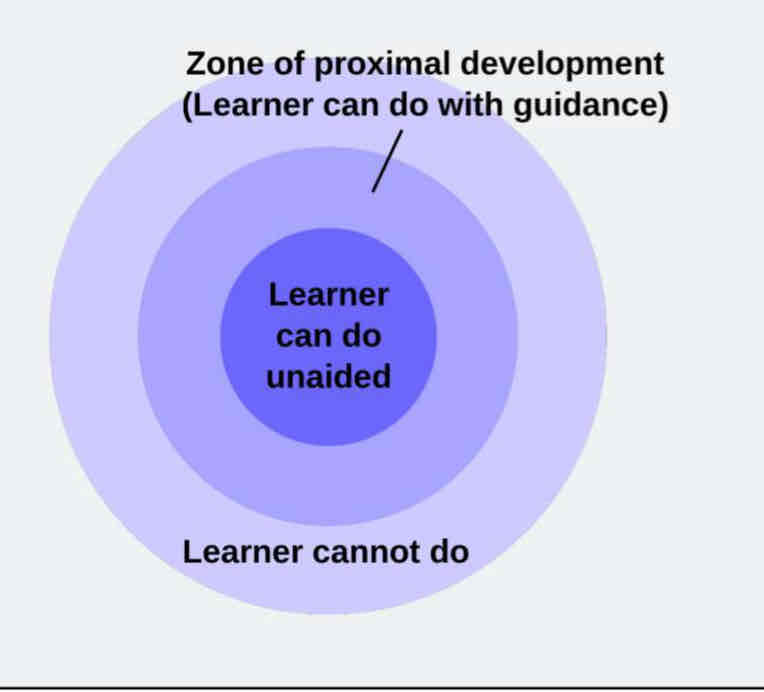
Vygotskys approach to learning
parents scaffold or support child as they to do things by themselves .
Parenting styles
Authoritative - high warmth , moderate control - moderate
Authoritarian - low warmth , high control -really bad
Permissive - high warm , low control - mean girl parents , wanna be BFF low income
Uninvolved - low warmth , low control - very indifferent to children’s needs and wants
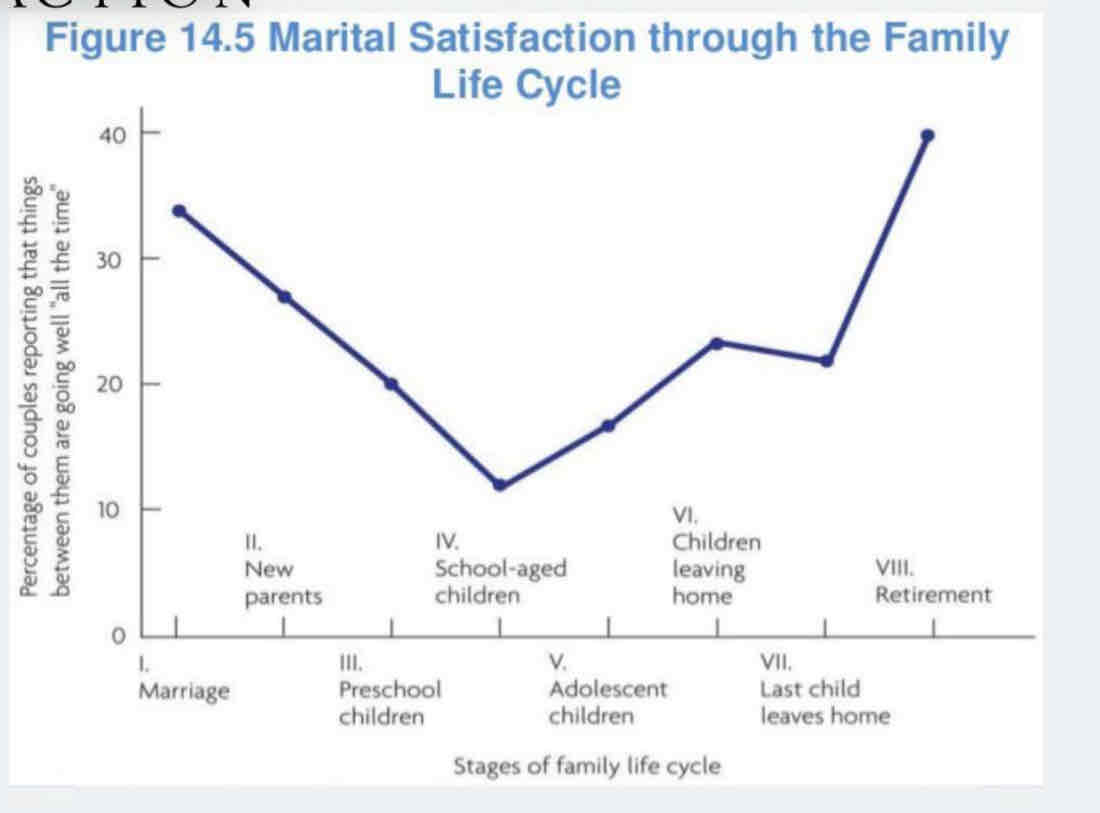
Marital satisfaction changes with age :
Parents may decrease well being and marital satisfaction - marriage , life stimulation , kids
Psychodynamic approach ( Freud )
Id: pleasure principle , a basic level of personality everything pleasure avoided painful
superego : seat of moral conscious, right vs Wrong
Ego: reality principle , trying to satisfy both pleasure while making sure all rational thoughts , problem solving, compensate
Defense mechanisms:
Displacement : shift interiors of emotions from 1 object to another . Dad yelling at child for be in upset at work but puts it on the child
Projection : projecting qualities or insecurities onto someone else . Closeted homophobe or something
Repression : can take any type of trauma and push it down into your unconciousness , least supported
Denial : Refusing to admit the source of your anxiety , denial
Trait Theory
Cardinal : dominant trait , direct a person step and stable across all situations
Central : general dispositions , everyone has it , how you normally reason to a typical situation , typical behavior
Secondary : relevant in certain contexts , only show up in certain instances , situations , presenting information of a class.
Trait Theory
Shapes how a person interprets the world and can lead people to behave in a similar ways across different situations.
Functionally equivalent situations
Cue a similar response that cue a similar response form a person .
Looks exactly the same but different behaviors , allows you to be an introvert
Lexical hypothesis
Reflected in the language used to describe ours or others personality traits
identifying central traits
Openness to experience : down to earth , try new things ,
Conscientiousness: disorganized , weak, organized, self disciplines
Extroversion : quiet solitudes , trusting , helpful
Agreeableness , trusting, helpful ,suspicious ,
Neuroticism: calm , emotionally put together , self satisfied ,worried , insecure , pity party
Behavioral inhibiton System
Psychological mechanisms that control how people act
Behavioral Approach system
Motivational system that is part of the reinforcement sensitivity theory , goal - striving approach to rewards
Measuring personality
Self reports : popular , measure or test that asks an individual about their own behaviors , attitudes beliefs or symptoms
Projective tests: personality test that involves responding to ambiguous images words , or scenes
Rorschach inkblot Test: a person is asked to tell what he or she sees in and thinks about ink blots of varying designs and colors. The weird butterfly picture
Themeatic apperception test :uses pictures to help asses a persons personality , describing ambigious scenes to learn more about a person emotions motivation and personality.
Informant reports : family members reports on others, used to avoid biases from relying solely on self reports
Behavior tests : acessing personality , determine how well a person is doing in her everyday life and whether they exhibit specific problem behaviors .room=warm or cold , neat freak , messy
Agreeableness and Conscientiousness
Get older they both increase
Neuroticism and extroversion (vitality )
Least agreement , go down , dominance
Self- concept
Understanding of who you think you are
Cocktail party effect
If you are in a crowded area , but when someone yells your name you hear it in that old room .
Working self - concept
The immediate experience of the sealed , traits stand out
Self esteem
The evaluations of one’s characteristic
Global self esteem
Overall self esteem
Domain specific self esteem
Self esteem regarding a specific area
Reflected appraisal
Self esteem is base on how other views you , someone important ignores or calls you stupid which decreases your self esteem
Self serving biases
Characteristics ways of processing information to maintain a positive attitude towards the self
Self serving attributions
All positive to self , neg to outsiders of self
A over average effect
Not attainable
Idiosyncratic trait
Getting away with murder , murder = being smarter,
Overestimating our contributions
Overestimate your contributions vs how much you actually are contributing
The dark triad
Negative personality traits
Narcissism , psychopathy , cohesion over people
The light triad
All things positive
Humanism - valuing dignity and worth of each individual
Kantiianism - treating people as ends up unto themselves, not mere means
Faith in humanity - believing in the fundamental goodness of humans
High self esteem
Can be secure or fragile , view things positively
High fragile
Disturbed , constantly seeking validation , linked to violence and narcissism