Lecture 10: Visceral Innervation of the Head
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
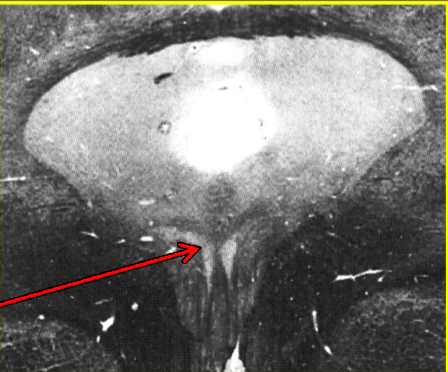
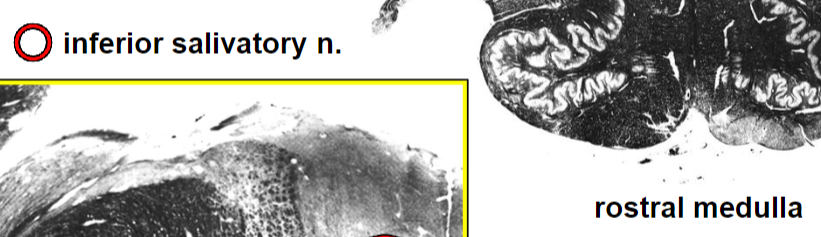
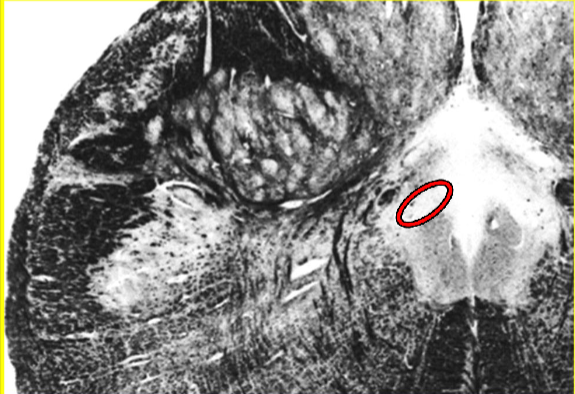
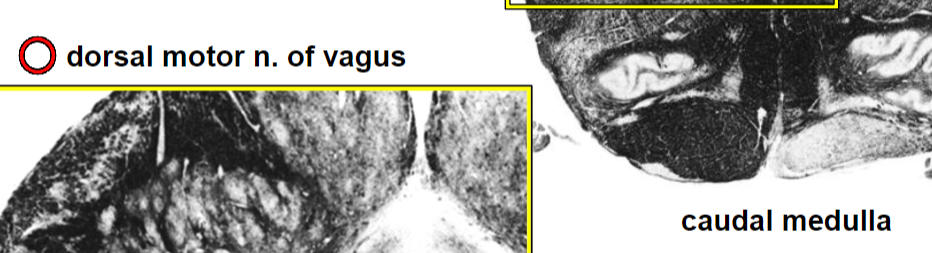
Brainstem VE (parasympathetic) cranial nerve nuclei

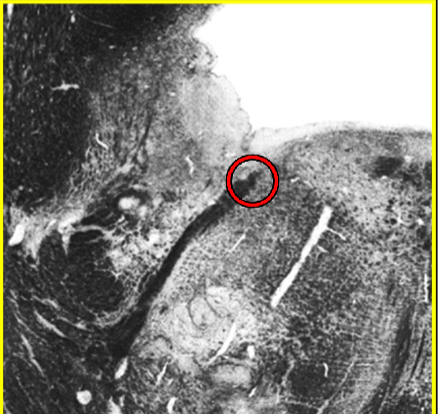
Brainstem VE (parasympathetic) cranial nerve nuclei
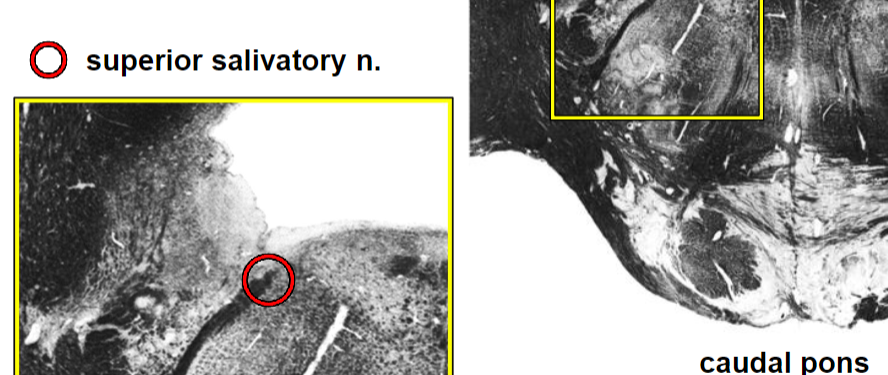
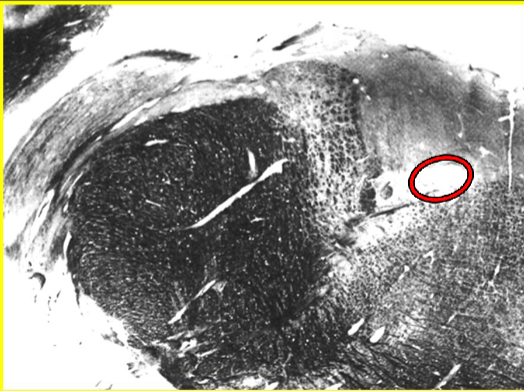
Brainstem VE (parasympathetic) cranial nerve nuclei
Mydriasis
Pupils that are fixed and dilated
Oculomotor nerves are compressed, often as a result of intracranial hemorrhaging
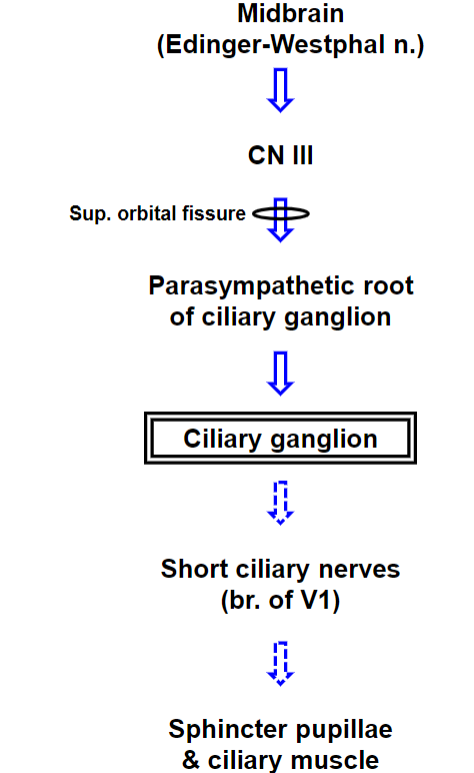
Parasympathetic Autonomic Innervation of the Eye
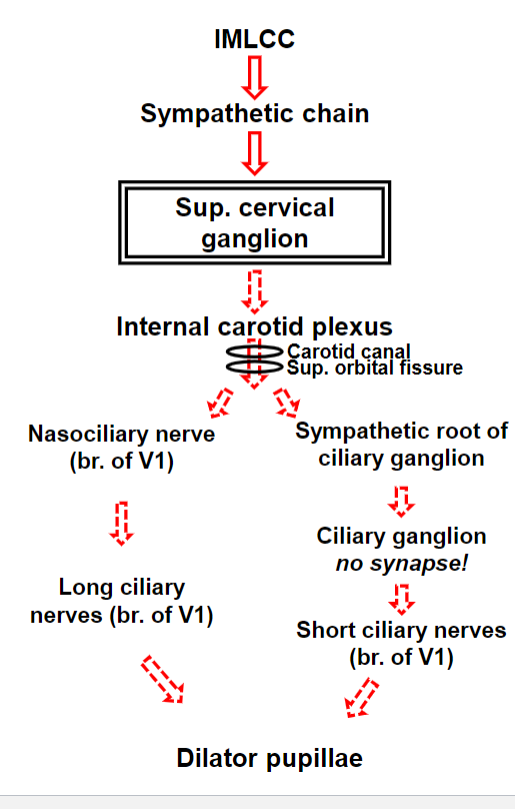
Sympathetic Autonomic Innervation of the Eye
Autonomic Innervation of the Parotid Gland

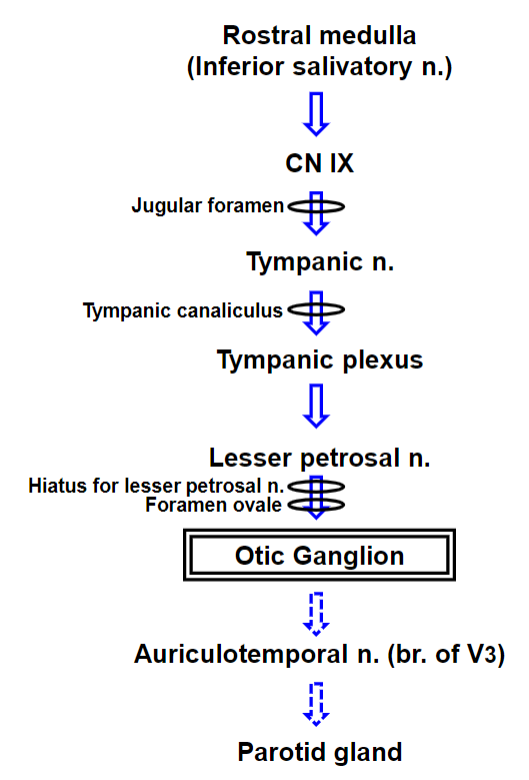
Parasympathetic Autonomic Innervation of the Parotid Gland
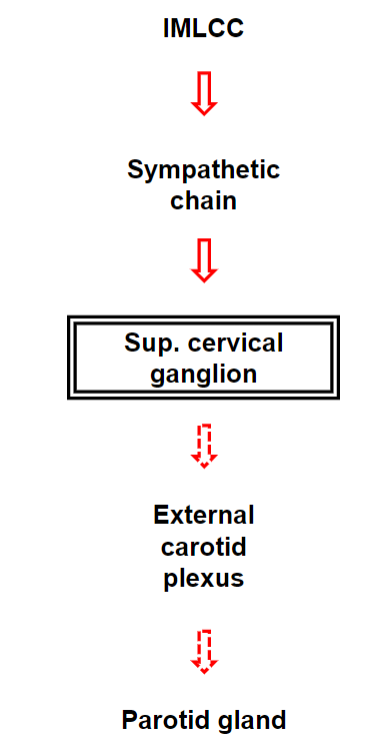
Sympathetic Autonomic Innervation of the Parotid Gland
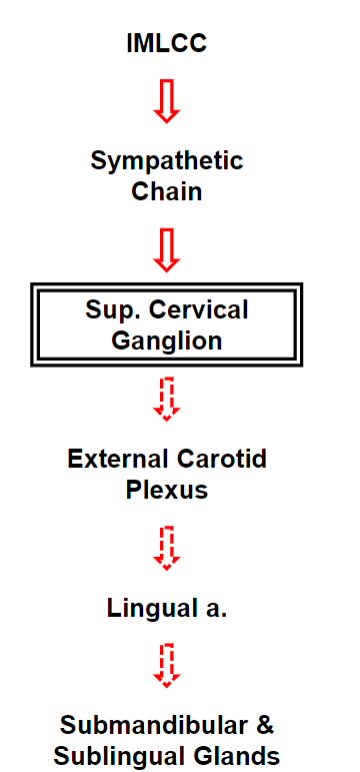
Autonomic Innervation of the Submandibular & Sublingual Glands

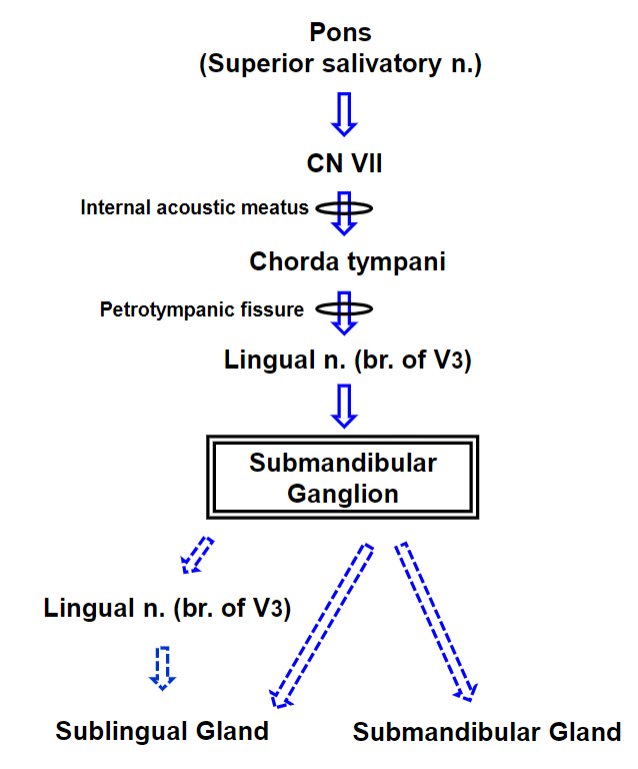
Parasympathetic Autonomic Innervation of the Submandibular & Sublingual Glands
Sympathetic Autonomic Innervation of the Submandibular & Sublingual Glands
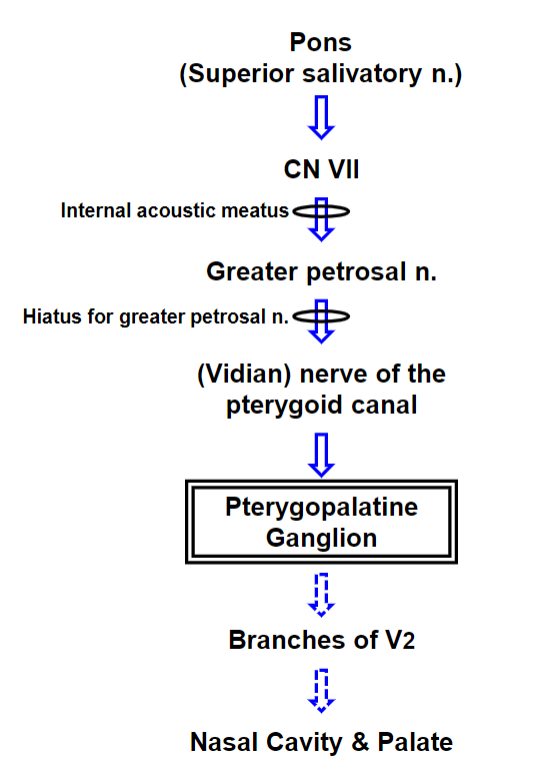
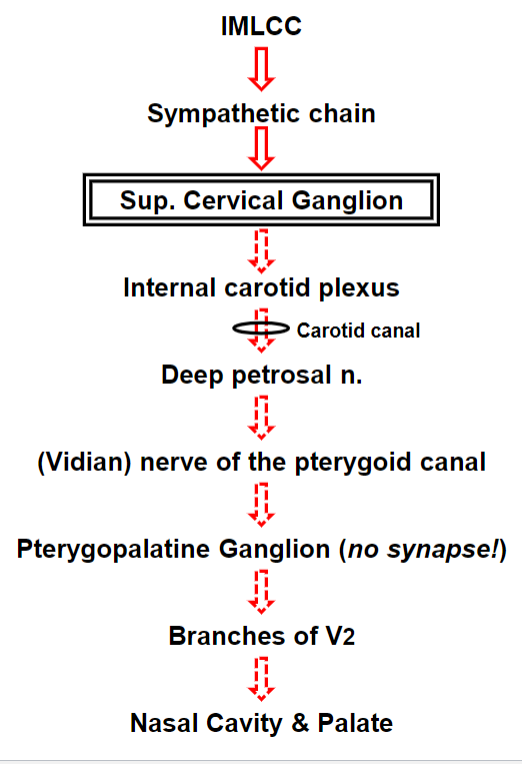
Autonomic Innervation of the Mucosa of the
Nasal Cavity and Palate

Parasympathetic Autonomic Innervation of the Mucosa of the Nasal Cavity and Palate
Sympathetic Autonomic Innervation of the Mucosa of the Nasal Cavity and Palate
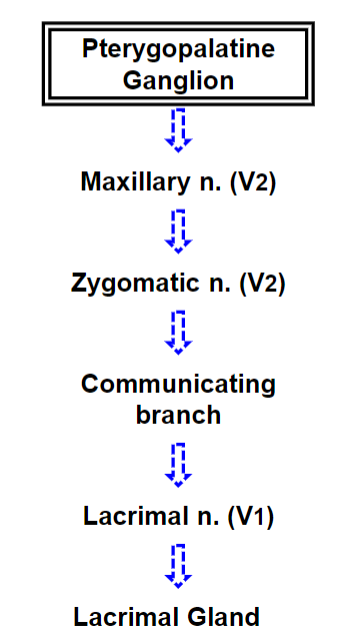
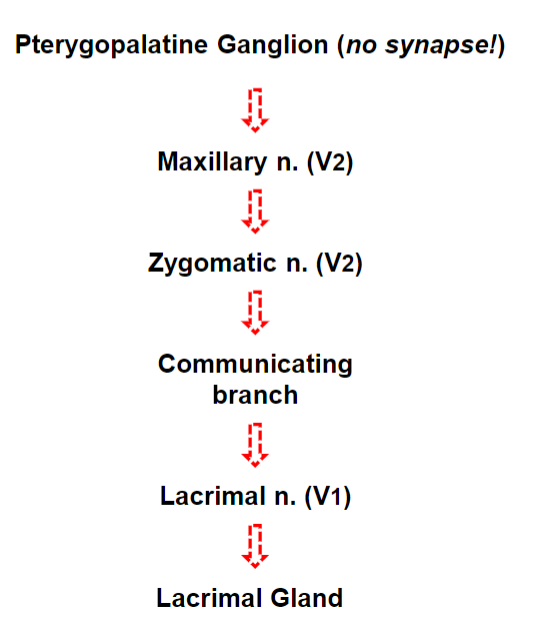
Parasympathetic Autonomic Innervation of the Lacrimal Gland
Sympathetic Autonomic Innervation of the Lacrimal Gland
Bell palsy
Disorder of CN VII: idiopathic form thought to be viral infection or autoimmune disorder
Ipsilateral facial paralysis
Ipsilateral hyperacusis (hypersensitivity to sound due to denervation of stapedius muscle)
Ipsilateral loss of lacrimation and loss of taste from anterior 2/3 of tongue on affected side
Horner syndrome
Interruption of the sympathetic pathway to the head
Signs/symptoms (ipsilateral)
Ptosis (drooping eyelid)
Miosis (constricted pupil)
Anhidrosis (lack of sweating)
Flushing of face (loss of vascular tone)
Interruption of the sympathetic pathway to the head can occur at multiple locations:
Hypothalamospinal tract
Spinal cord
Sympathetic chain
Superior cervical ganglion
Internal carotid plexus