Hon Biology - Cell Transport
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/28
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1
New cards
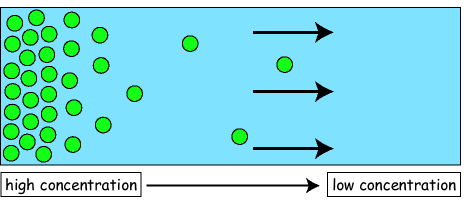
Diffusion
Movement of particles or molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration without a transport protein
2
New cards
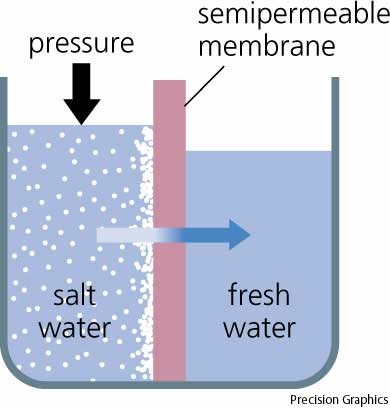
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
3
New cards
Selectively pemeable membrane
A membrane that allows certain materials to pass through, but not others
4
New cards
Equilibrium
The condition that exists in system when there is a relatively equal distribution of a particular molecule
5
New cards
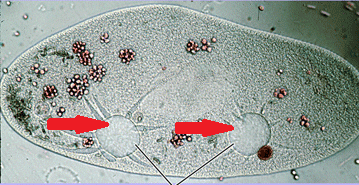
Cell Membrane
regulates and controls what enters or leaves the cell
6
New cards
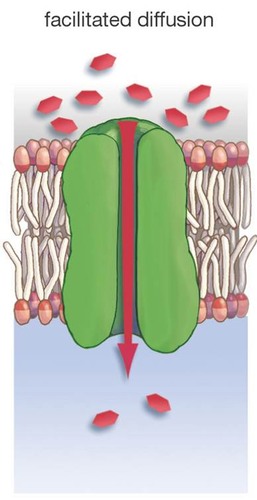
Facilitated Diffusion
Use of carrier PROTEINS for diffusion, does not require energy for a molecule to travel across the membrane
Moves molecules from high to low solute concentration
Moves molecules from high to low solute concentration
7
New cards
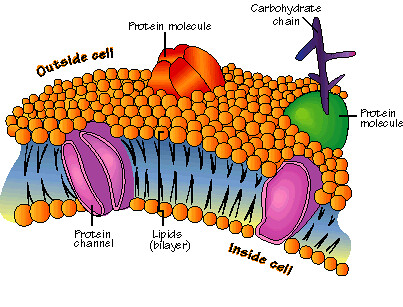
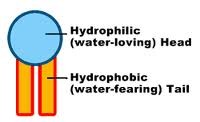
Phospholipid
molecule that makes up cell membranes. It has a hydrophilic "head" and two hydrophobic "tails".
8
New cards
Hydrophobic
water hating. substances that will not mix with water.
9
New cards
Transport Protein
Proteins within the cell membrane that function to move substances into or out of the cell.
10
New cards
Passive Transport
molecules move with the concentration gradient from high to low concentration NO energy required.
11
New cards
phagocytosis
"Cell eating" a type of endocytosis in which large particulate substances or small organisms are taken up by a cell. It's carried out by some protists and by certain immune cells of animals.
12
New cards
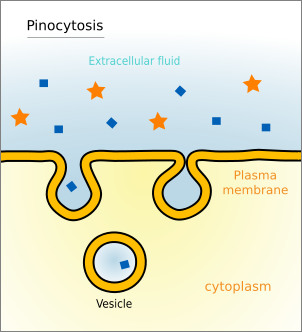
pinocytosis
Cellular "drinking"; a type of endocytosis in which the cell takes fluid and dissolved solutes into small membranous vesicles.
13
New cards
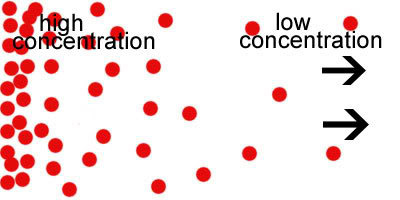
concentration gradient
a region along which the density of a chemical substance increases or decreases.
14
New cards
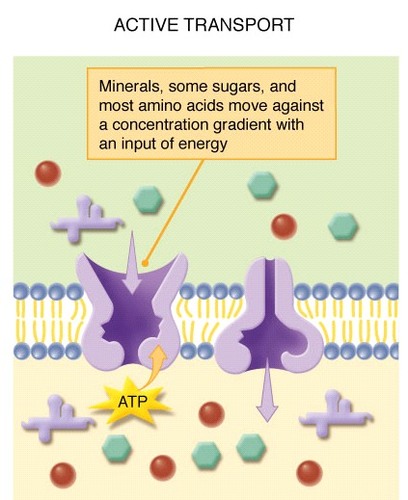
active transport
the movement of a substance across a cell membrane against its concentration gradient, through specific transport proteins and requiring ATP
15
New cards
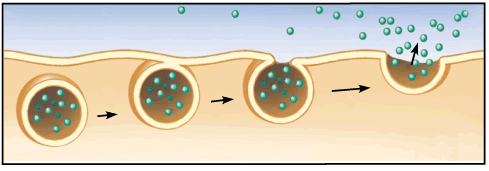
exocytosis
the secretion of molecules by the fusion of vesicles containing them with the plasma membrane.
16
New cards
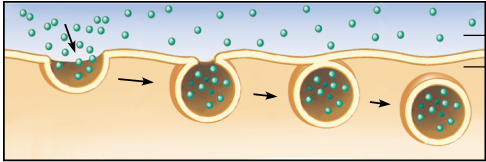
endocytosis
cellular uptake of molecules & particles by the formation of vesicles from the plasma membrane.
17
New cards
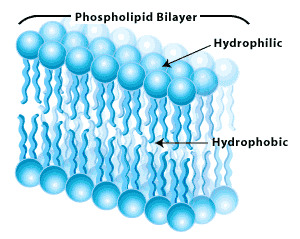
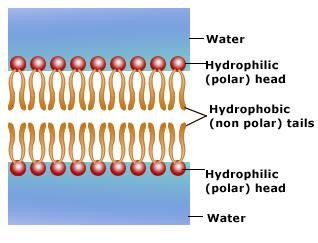
phospholipid bilayer
a double layer of phospholipid molecules that form membranes in cells
18
New cards
hydrophobic
the tail of a phospholipid molecule that is repelled by water
19
New cards
hydrophilic
the head of a phospholipid molecule that is attracted to water
20
New cards
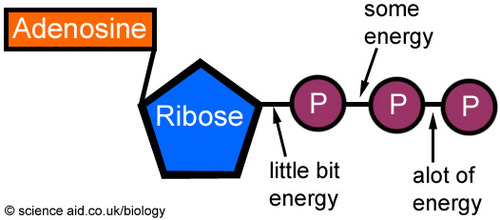
ATP
the molecule that provides energy for cellular processes by breaking a bond
21
New cards
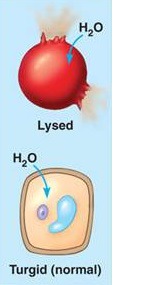
hypotonic solution
contains less solute concentration than the cell; water will tend to enter the cell and swell it
22
New cards
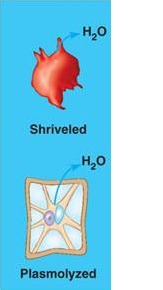
hypertonic solution
when a cell is placed in a solution and the concentration of the solute outside of the cell is higher than it is inside
23
New cards
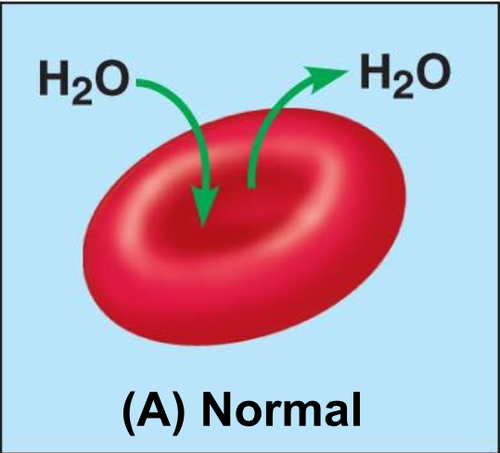
isotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is essentially equal to that of the cell which resides in the solution
24
New cards
solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
25
New cards
solvent
In a solution, the substance in which the solute dissolves.
26
New cards
Homeostasis
The maintenance of internal conditions of an organism
27
New cards
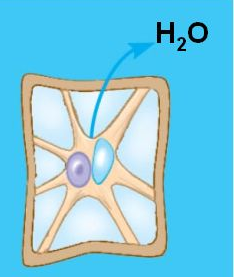
Plasmolysis
The shrinking of a cell due to water diffusing out
28
New cards
Cytolysis
The swelling an rupturing a of cell due to water diffusing into the cell

29
New cards
contractile vacuole
saclike organelles that expand to collect excess water and contract to squeeze the water out of the cell