Lab 3 Cnidaria and Ctenophora - EVERYTHING
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
In which tissue layer are the cnidocytes located?
epidermis
Why are cnidocytes located where they are located?
A) Because they are used for digestion of prey, they must be located in the innermost tissue layer.
B) Because they contain toxins, they must be located in the innermost tissue layer.
C) Because they are used for defense and prey capture, they must be located in the outermost tissue layer.
C) Because they are used for defense and prey capture, they must be located in the outermost tissue layer.
The nematocyst is an _____ inside the _____. When the small trigger on the [cell] is stimulated, an increase in _____ pressure within the cell causes the _____ to violently discharge, exploding out of the cell and releasing a long, hollow, threadlike _____.
The nematocyst is an organelle inside the cnidocyte. When the small trigger on the [cell] is stimulated, an increase in osmotic pressure within the cell causes the nematocyst to violently discharge, exploding out of the cell and releasing a long, hollow, threadlike filament.
Does Hydra reproduce sexually? Asexually? Or both?
Both
Sexually through the production of eggs and sperm (gonads are visible on some individuals)
Asexually through budding.
- Obelia occurs as a _____ polyp where Hydra occurs as a _____ polyp.
- Obelia has _____ polyps (gonangia), Hydra does not.
- _____ is more sessile (Hint: Obelia or Hydra?)
- Obelia occurs as a colonial polyp where Hydra occurs as a solitary polyp.
- Obelia has reproductive polyps (gonangia), Hydra does not.
- Obelia is more sessile
Which of the following is a similarity between the scyphozoan medusa and the hydrozoans medusa bud of Obelia?
A) Both are radially symmetrical with tentacles surrounding the mouth
B) Scyphozoan medusa are generally the same size as hydrozoan medusa with similar number of tentacles.
C) Hydrozoan medusae possess a velum, but lack the oral arms that scyphozoan jellyfish possess.
A) Both are radially symmetrical with tentacles surrounding the mouth
Which of these are characteristics that can help distinguish between hydrozoan and scyphozoan medusae?
A) In scyphozoans, the medusa stage is typically large and free-living, with the polyp stage small.
B) Hydrozoan medusae generally have a muscular shelf, or velum, projecting inward from the margin of the bell.
C) Schyphozoa medusae generally also have a muscular shelf, or velum, but it's projecting outward forming the arms.
B) Hydrozoan medusae generally have a muscular shelf, or velum, projecting inward from the margin of the bell.
Velum is NOT found in scyphozoan.
What is the structural equivalent of the chambers of leuconoid sponges in the Scyphozoa?
A) thick layer of mesoglea
B ) a branched gastrovascular cavity
C) a very large number of tentacles
D) asexual reproduction in the polyp stage
B ) a branched gastrovascular cavity
Cassiopeia sp., commonly known as the "mangrove jellyfish" or "upside-down jellyfish"
Could you think of a biological reason why they are usually found upside down?
This behavior provides sunlight to micro-algae living the tissue (endosymbionts known as zooxanthellae, similar to those occurring in corals) which provide nutrients to the host.
Match the structure with its correct function.
d, b, a, c

Which of these is a characteristic that differentiates fire corals and true corals?
A)Fire corals are hydrozoans but have no cnidocytes, whereas true corals are anthozoans and have cnidocytes
B) Fire corals are hydrozoans that have cnidocytes relatively visible to the naked eye, whereas the cnidocytes of anthozoan corals are not visible to the naked eye
C)Fire corals and true corals are both corals from the Class Anthozoa, they are just different orders.
B) Fire corals are hydrozoans that have cnidocytes relatively visible to the naked eye, whereas the cnidocytes of anthozoan corals are not visible to the naked eye
Which of the following is a characteristic of corals (anthozoans) that is also found in Porifera?
A) neurons
B) gastrovascular cavity
C) filter-feeding
D) nematocysts
C) filter-feeding
The sea pansy is a collection of polyps with different forms and functions. They're found in shallow waters on soft sandy bottoms, and can detach easily, are bioluminescent, and predated on by tiger nudibranchs.
What would be the selective advantage of being bioluminescent?
Sea pansies are bioluminescent when they are touched or attacked by a predator.
(Protection and reproduction)
Select from the list which are similarities between Cnidaria and Ctenophora?
A) Both are marine
B) Both are diploblastic, with mesoglea
C) Both have bilateral symmetry
A) Both are marine
Both are marine, diploblastic, radial symmetry, and a branching gastrovascular cavity
Which are differences between the Cnidaria and the Ctenophora?
A) Ctenophores have cnidocytes like cnidarians
B) Ctenophores have eight "comb rows" of fused cilia along the sides of the animal used for movement, these are not present in cnidarians.
C) Many cnidarians are completely sessile or with a life cycle that it's sessile, all ctenophores are also sessile
B) Ctenophores have eight "comb rows" of fused cilia along the sides of the animal used for movement, these are not present in cnidarians.
Ctenophores have colloblasts, cnidarians have cnidocytes.
Ctenophores have no alternation of generations and some think they have a complete gut.
Many cnidarians are completely sessile or with a life cycle that it's sessile.
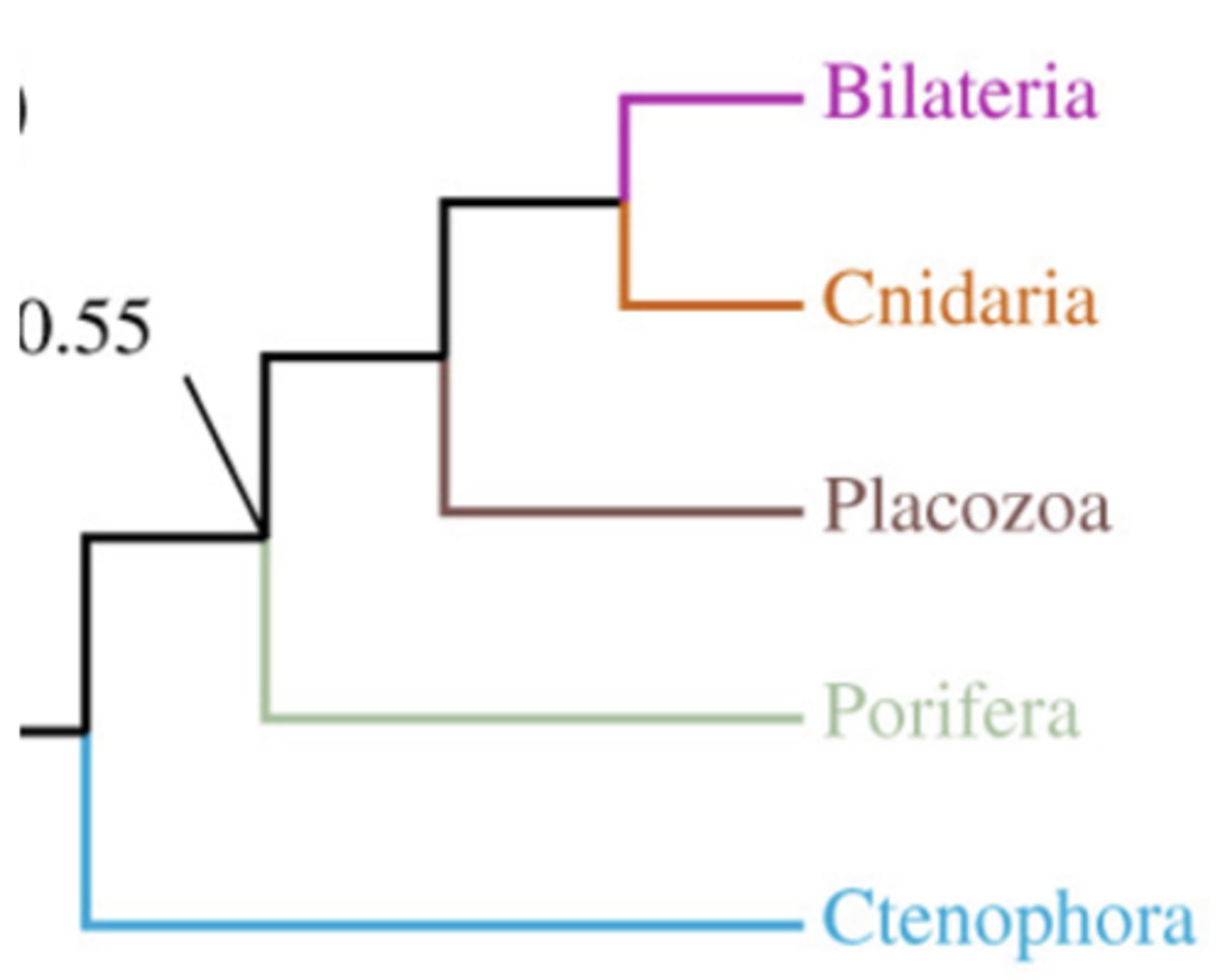
If the phylogeny shown here is correct, what is the implication for the evolution of the diploblastic body (tissue level of organization) in animals?
A) The diploblastic body evolved independently (separately) in Ctenophores and Cnidarians
B) An ancestor of the Porifera had a more complex body but it was lost
C) Either of the other two answers could be correct.
C) Either of the other two answers could be correct.
What specialized cells in cnidarians aid in capturing and subduing prey?
cnidocytes
What structure(s) would help you determine whether a polyp of Obelia is a hydranth (feeding polyp) or a gonangium (reproductive polyp)?
A) Presence of tentacles
B) GVC
C) Manubrium
A) Presence of tentacles
Hydranths have tentacles, whereas gonangia do not.
1. How many embryonic layers does the organism shown have?
2. What are the layers called?
3. What is the name having a body derived from only two embryonic cell layers called?
1. Two embryonic layers
2. Endoderm and ectoderm
3. Diploblastic

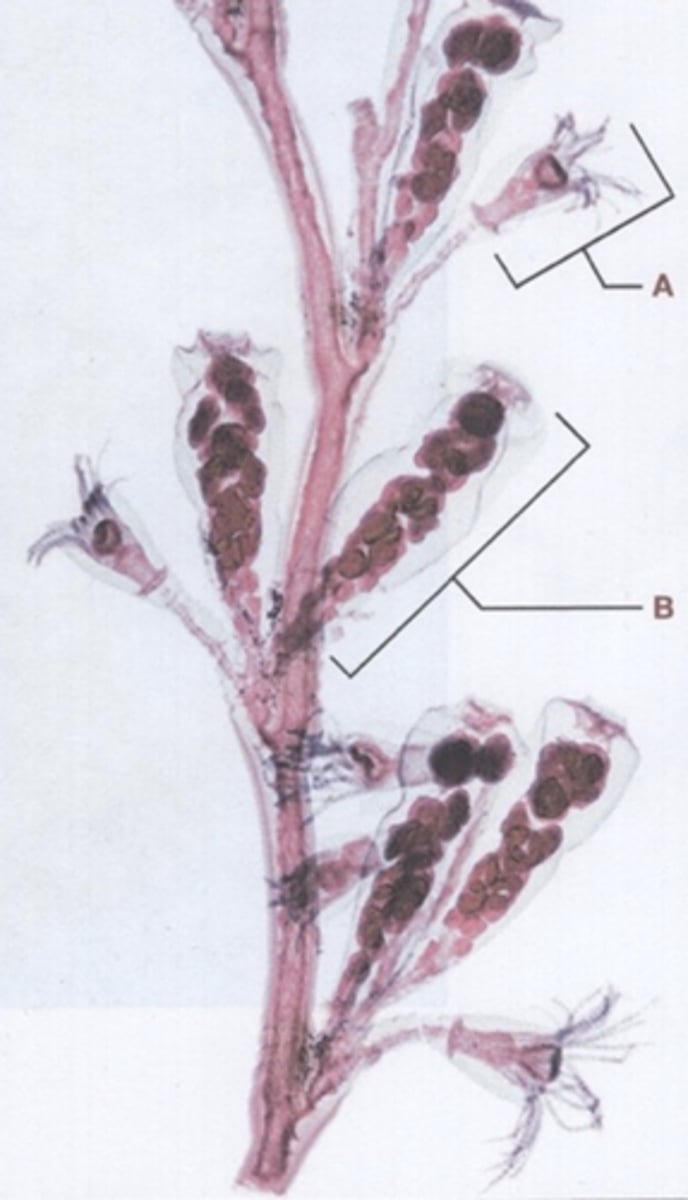
1. What is the specific name of the structure indicate by line A?
2. What is the function of the structure indicated by line A?
3. What is the specific name of the structure indicated by line B?
4. What is the function of the structure indicated by line B?
1. Hydranth (gastrozooid)
2. Feeding
3. Gonangium (gonozooid)
4. Reproduction
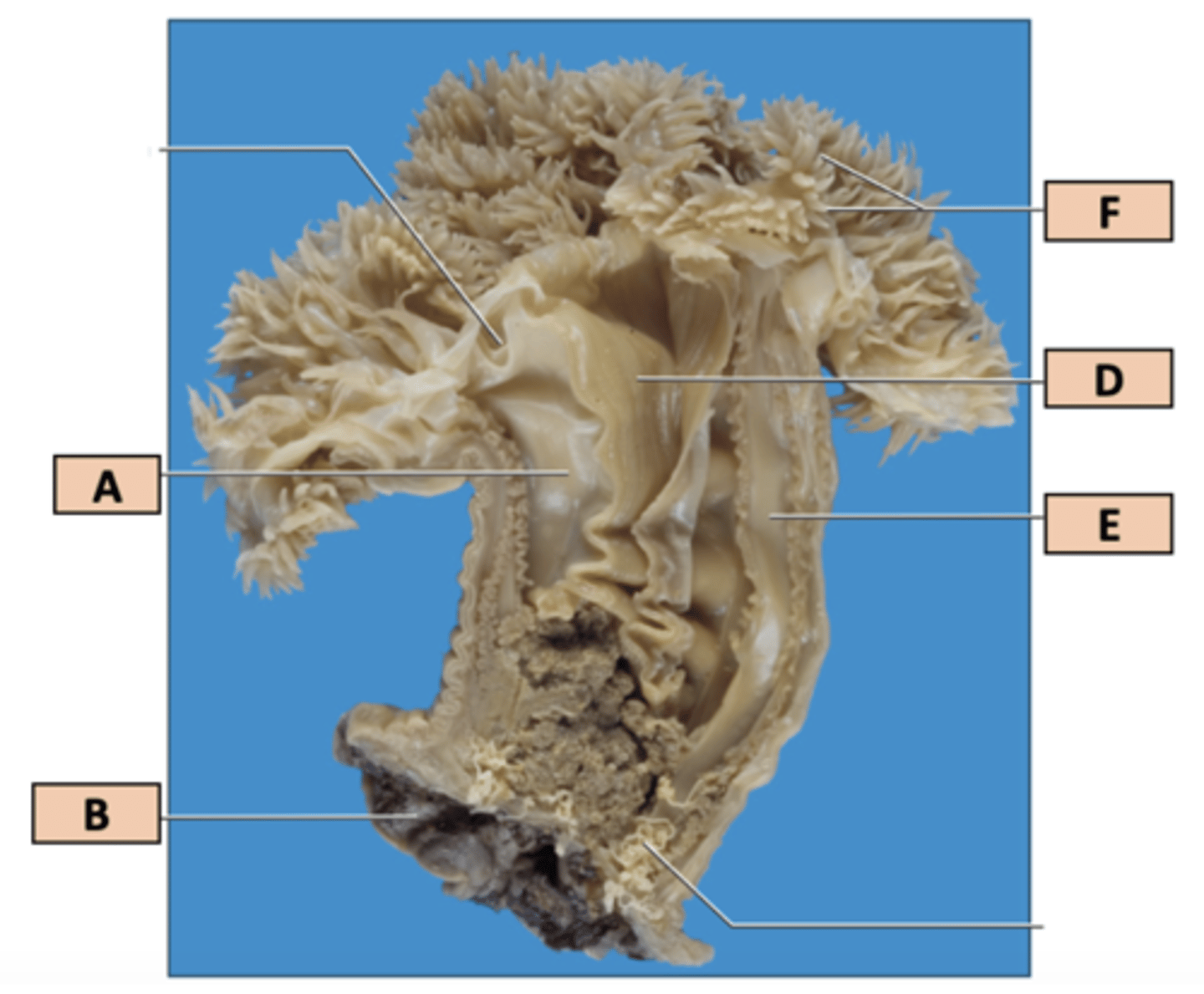
Match the structures below with the corresponding letter pointing at them in the image
1. _____ and _____ septa
2. _____ tentacles
3. _____ pedal disc
4. Identify the space indicated by line D _____
5. What modification do sea anemones possess to increase their digestive surface area?
1. A, E
2. F
3. B
4. Pharynx
5. Septa
What Phylum do these animals belong in?
Phylum Cnidaria

Phylum Cnidaria Characteristics

What type of symmetry do cnidarians have?
radial symmetry
- no head, front, back
- oral and aboral surfaces
What type of organization (cell, tissue, etc.) cnidarians have?
tissue level (no organs)
What does it mean when an organism is diploblastic (like those in Phylum Cnidaria and Phylum Ctenophora)?
They have two true tissue layers (epidermis and endodermis/gastrodermis)
Ectoderm is the same as...
Epidermis
Endoderm is the same as...
Gastrodermis
What type of skeleton do cnidarians have?
Hydrostatic skeleton (fluid held under pressure in a closed body)
Muscles within the hydrostatic skeleton contract which creates pressure and moves the fluid-filled body
Do cnidarians have an incomplete or complete gut?
Incomplete gut
- Rely on passive prey capture
- Extracellular and intracellular digestion
True or False?
Cnidarians have a gastrovascular cavity (GVC).
True
- Saclike and has only one opening which serves as both mouth and anus.
- Functions as a
Extracellular digestion
type of digestion in which food is broken down outside the cells in a digestive system and then absorbed
intracellular digestion
type of digestion in which food is digested inside specialized cells that pass nutrients to other cells by diffusion
True or False?
Cnidarians have a mesoglea.
True
Mesoglea- non-cellular middle layer that provide support. between the two tissue layers
- Not a tissue layer!
- Jelly-like substance
- Provides support for the body
- Hydrostatic skeleton
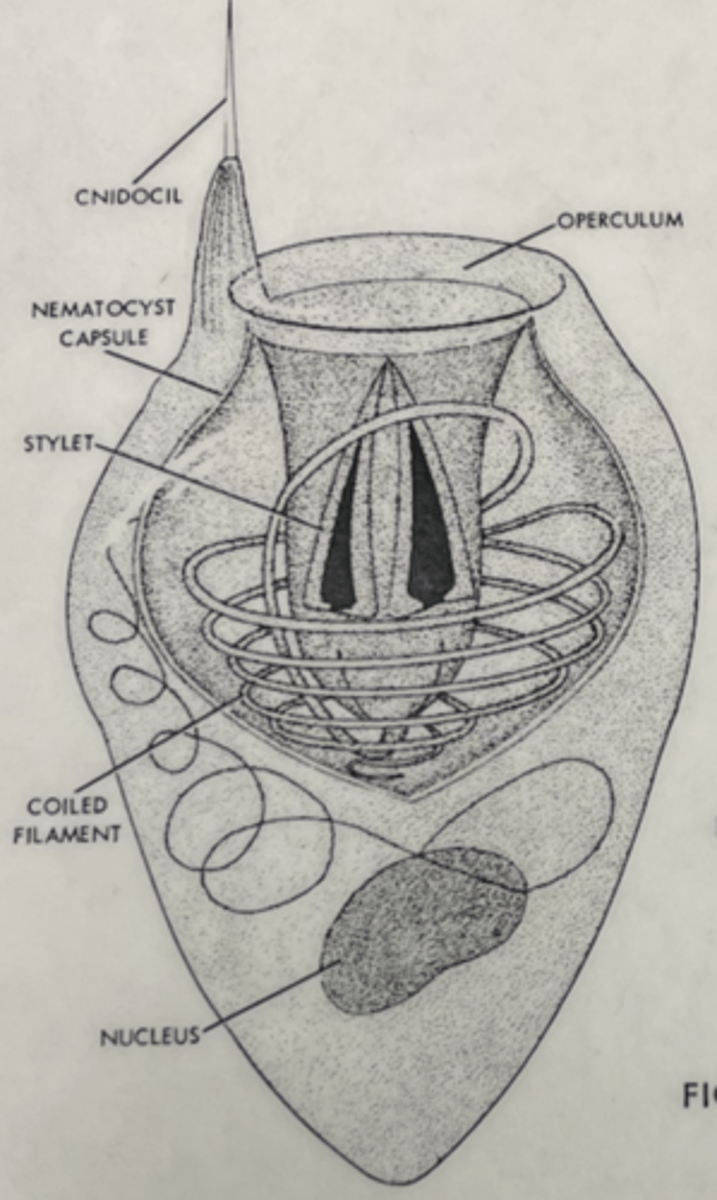
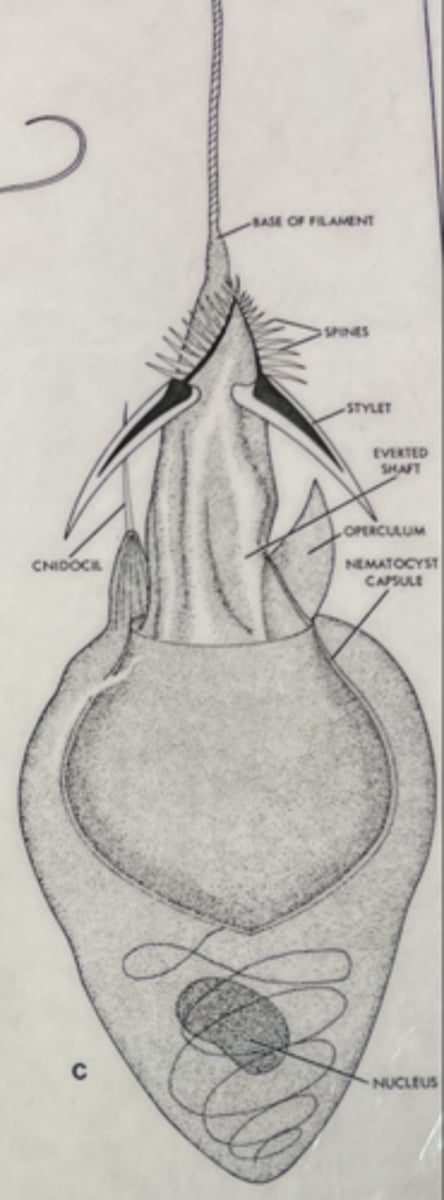
What are the stinging cells of cnidarians called?
Cnidocytes
- Each contains a stinging capsule/organelle (nematocyst)
-- Either penetrate, fasten/coil, or adhere; some inject toxins
- Hundreds of thousands may line exterior surface
- Used for both prey capture and predator deterrent
Cnidocytes
A specialized cell, containing cnidocyst, which is involved in capturing the prey in cnidarians
Cnidocyte
A specialized organelle inside a cnidocyte, consisting of an ejectable thread the causes a sting
- Like mini-harpoons that can be ejected and used for anchorage, defense, and prey capture
Nematocyst
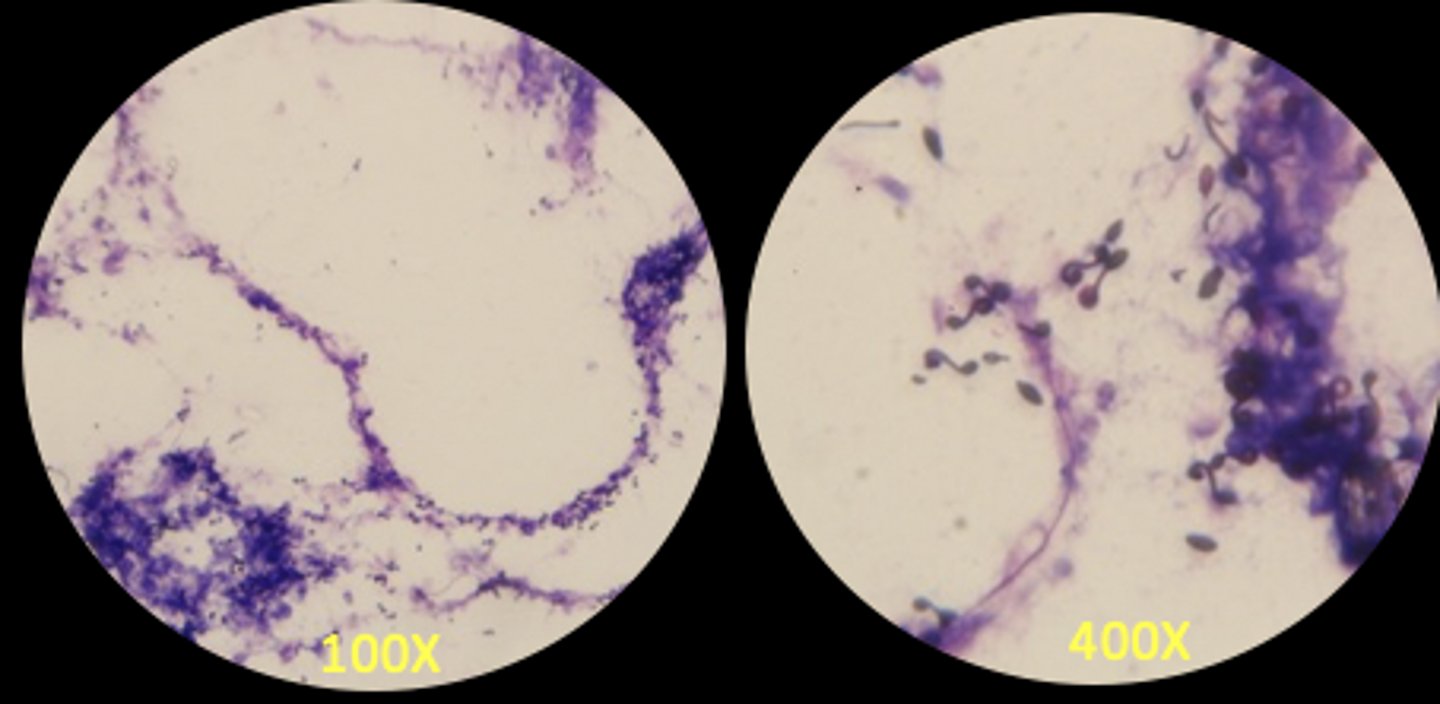
What is this a picture of?
Discharged nematocyst
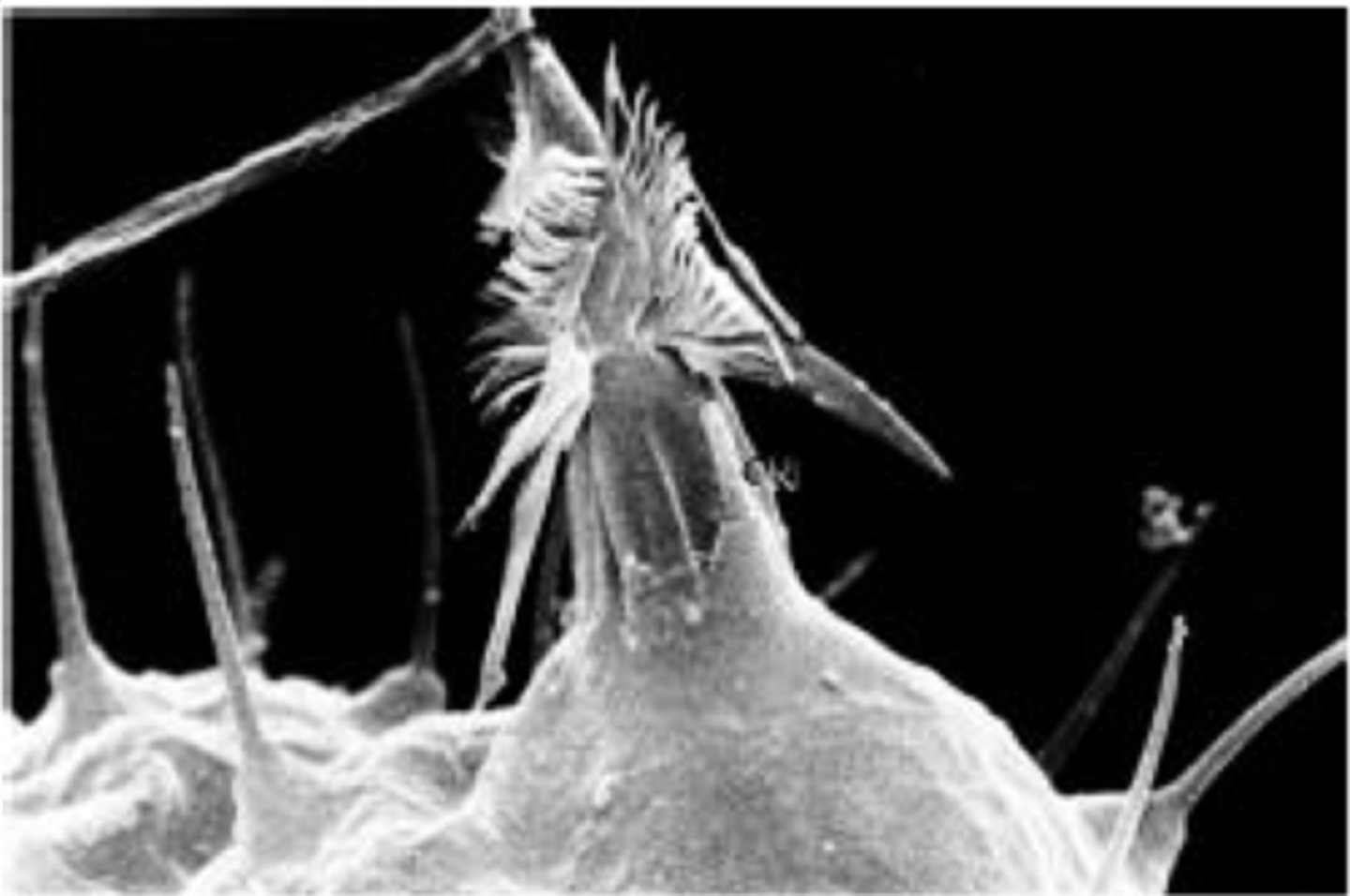

What is this a picture of?
Undischarged nematocyst
What is this a picture of?
Discharged nematocyst
What is this a picture of?
Cnidocyte
What are the names of the two body forms that occur in the life cycle of a cnidarian?
Polyp and Medusa
Is the polyp form of a cnidarian sessile or motile?
Sessile
Is the medusa form of a cnidarian sessile or motile?
Motile
What type of larvae do cnidarians have?
Planula larvae
In other words, their larvae is ciliated and motile.
What are the four classes of cnidarians?
Hydrozoa, Scyphozoa, Cubozoa, Anthozoa
What are the representative animals of the Phylum Cnidaria Class Hydrozoa?
Hydra, Obelia, Fire Coral, Portuguese man-of-war
- Polyp is dominant stage
- Most colonial
- Produce a medusa stage
- Velum ring and no oral arms (Exception is genus Hydra)
- Medusa have very little mesoglea (looks like plastic bags)
- Display sexual (medusae) and asexual (polyps) reproduction
Phylum Cnidaria Class Hydrozoa Characteristics
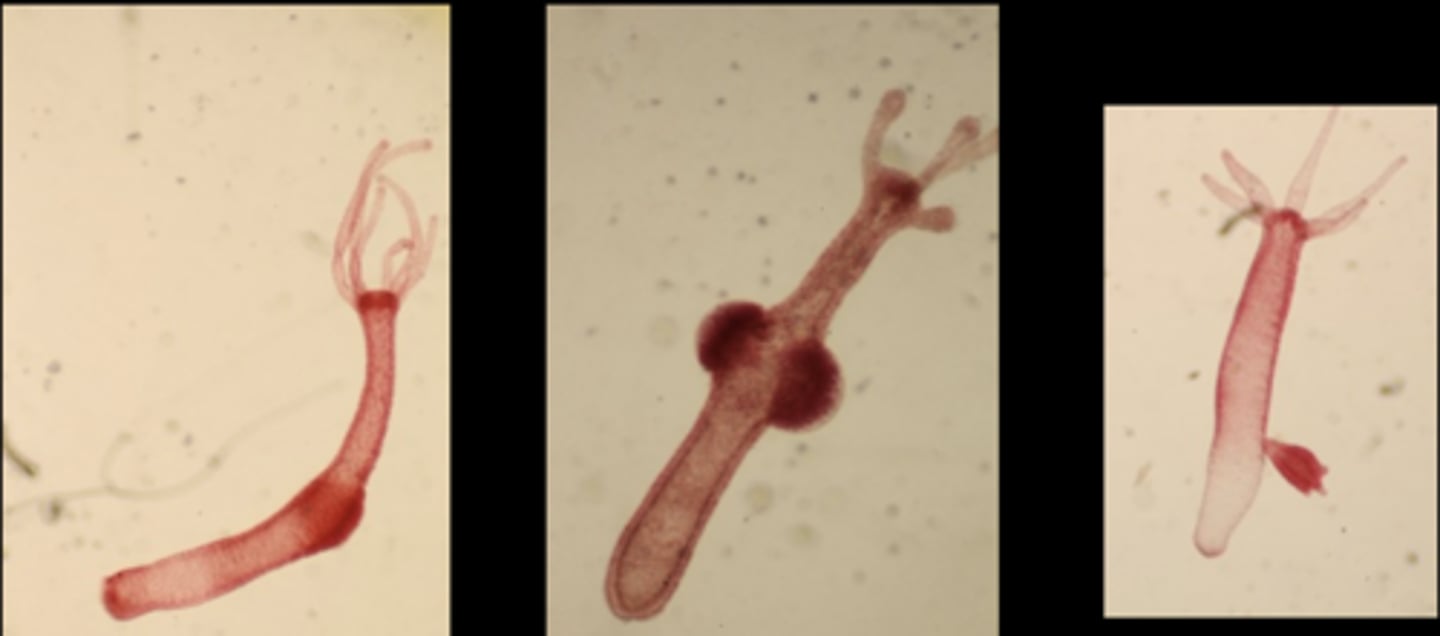
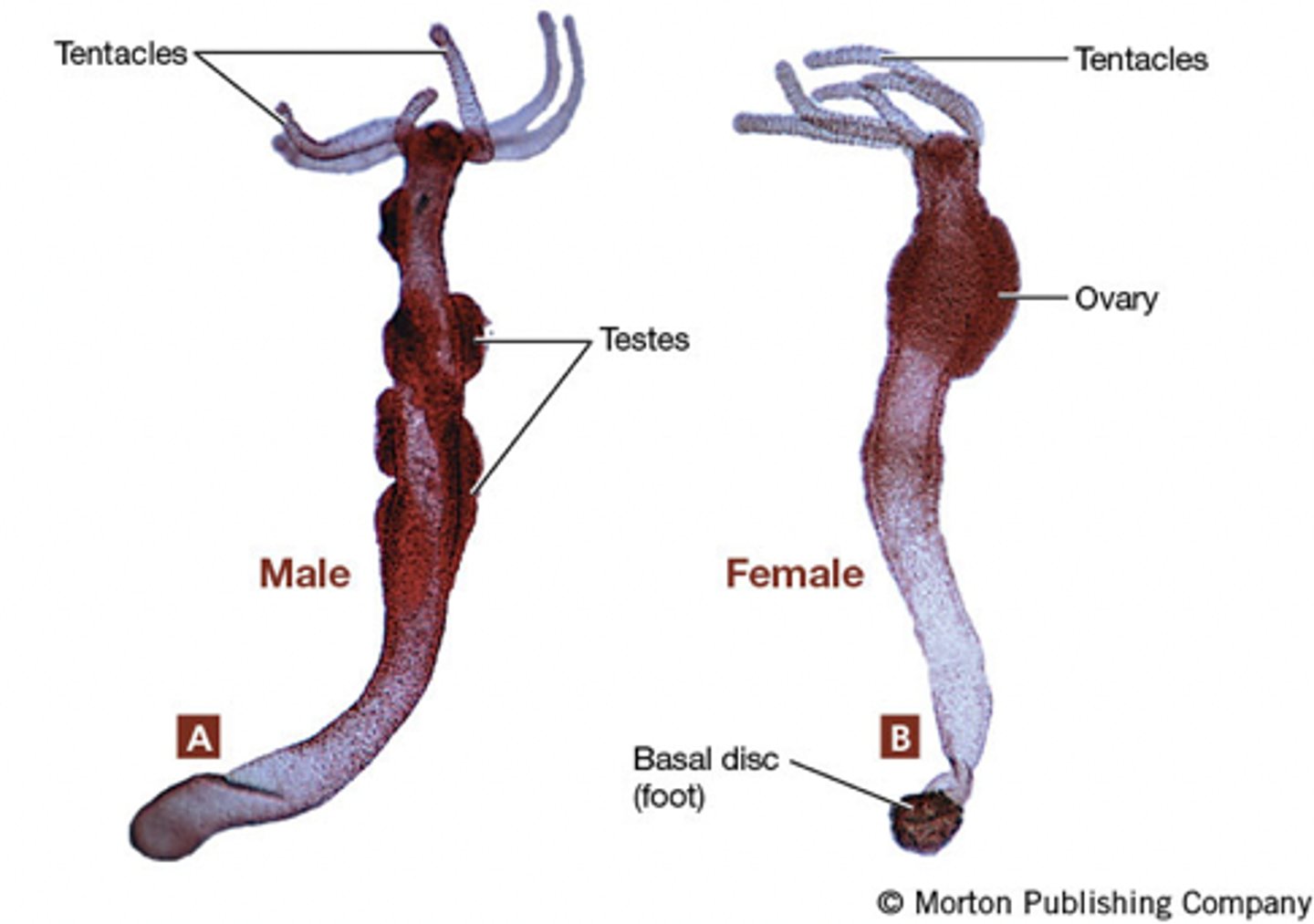
What class do these two organisms belong in?
Class Hydrozoa
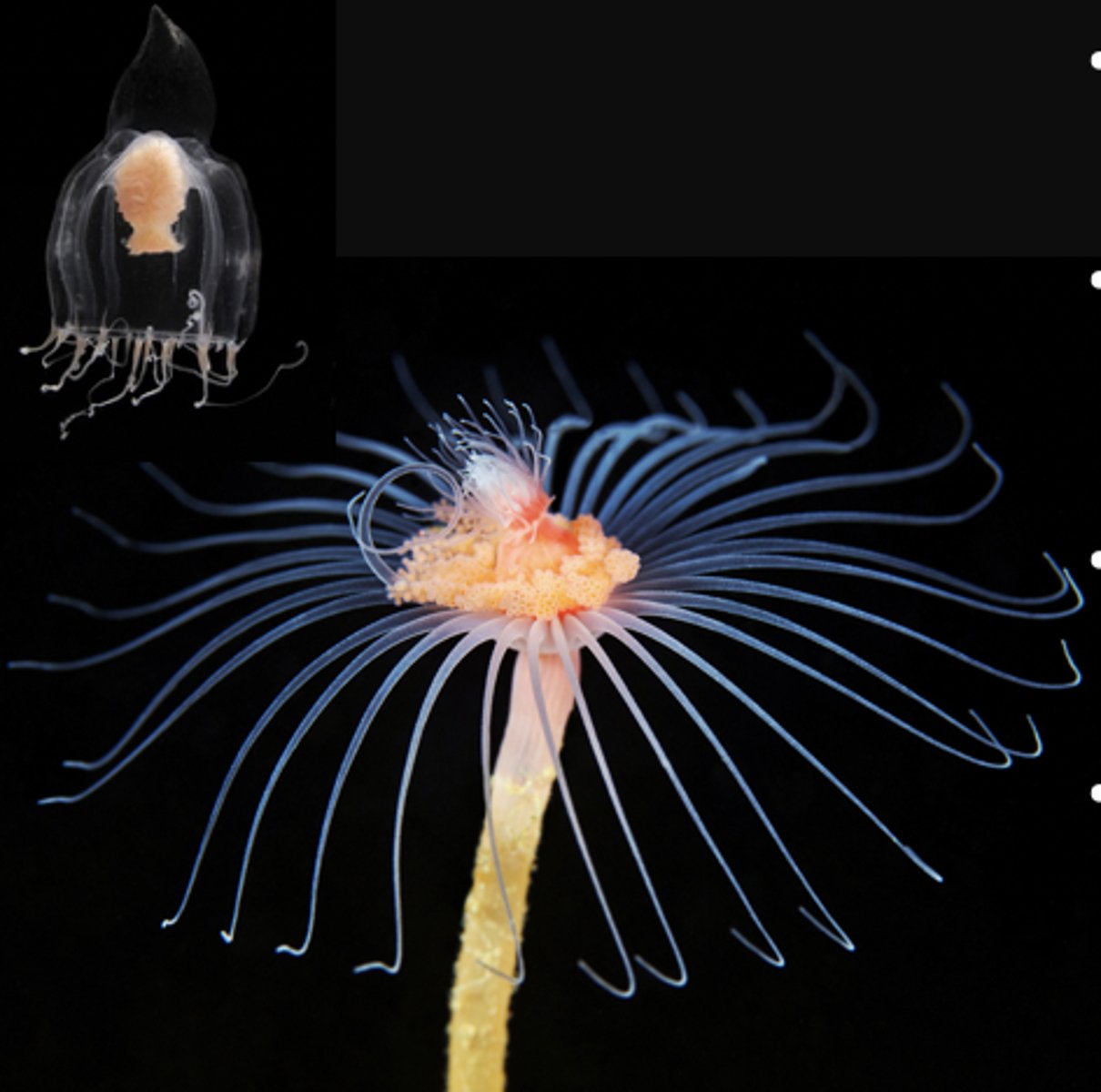

- Exist as individual polyp
- Freshwater
- Can reproduce sexually or sexually within same individual
Hydra littoralis
What is the phylum, class, and genus of this organism?
Phylum: cnidaria
Class: hydrozoa
Genus: hydra
What phylum, class, and genus does this organism belong in?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Hydrozoa
Genus: Hydra
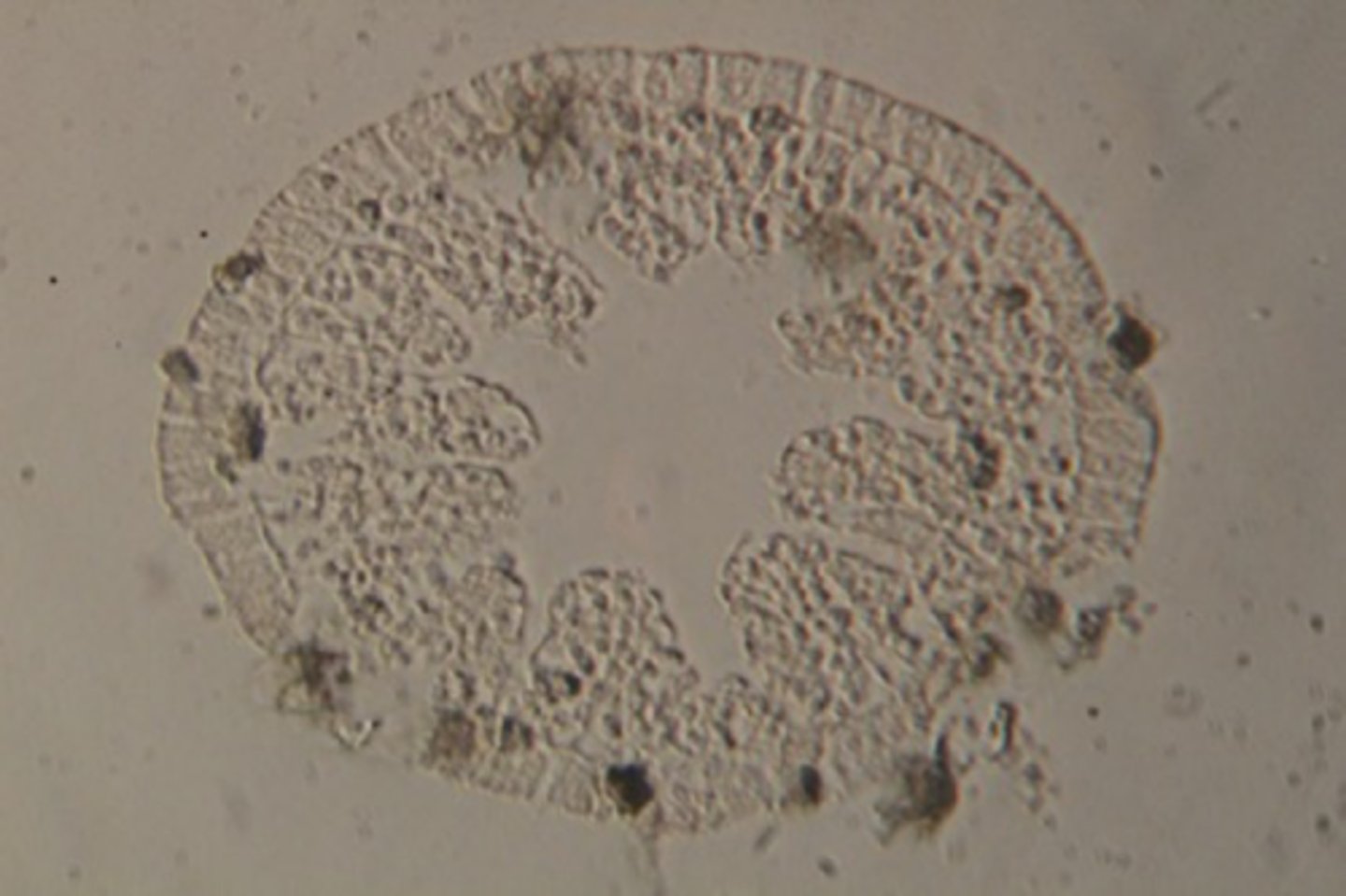
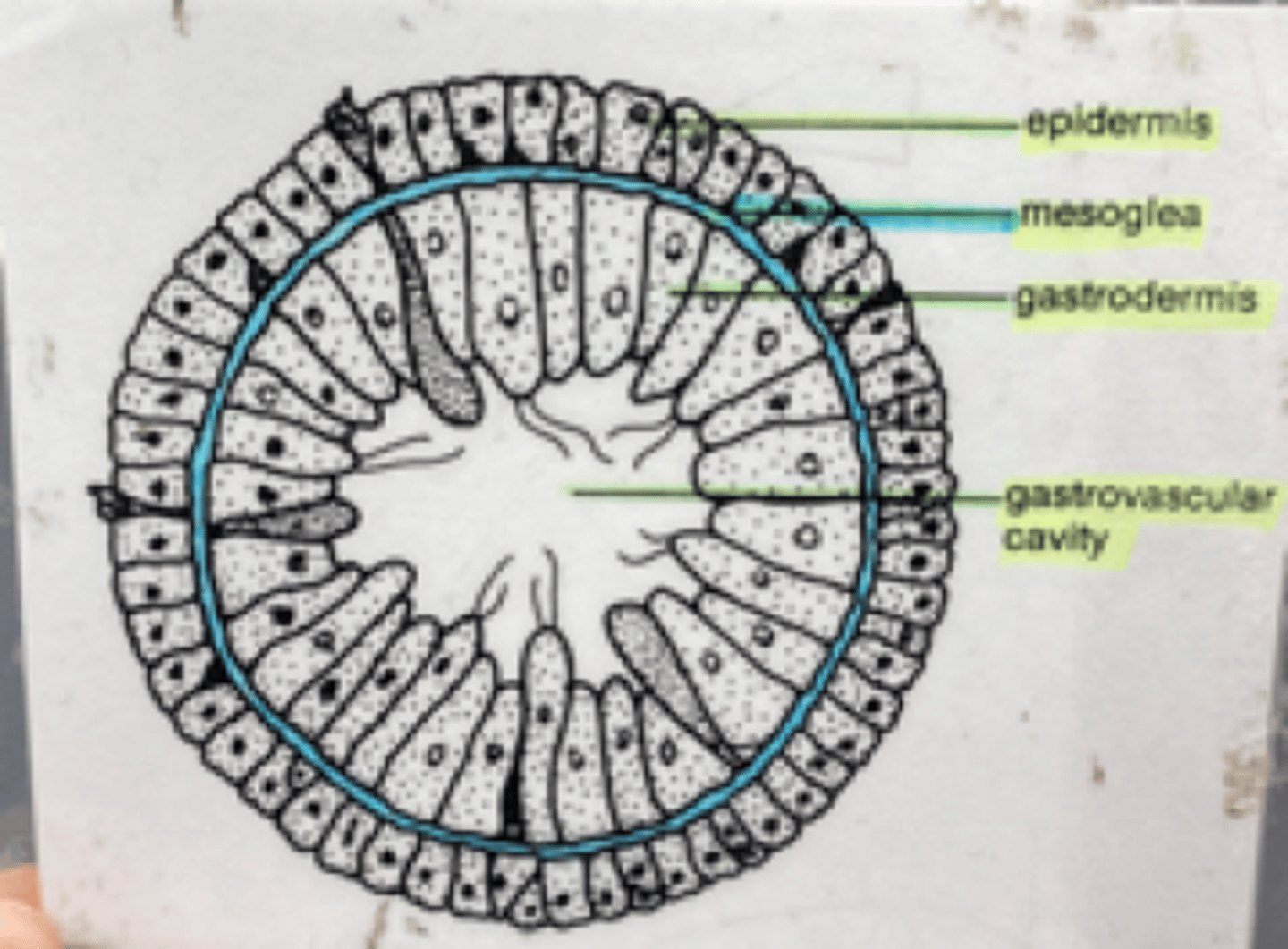
Hydra c.s. (cross-section)
What phylum, class, and genus does this organism belong in?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Hydrozoa
Genus: Hydra
Hydra l.s. (longitudinal section)
These photos are taking in succession moving down the slide to capture entire hydra l.s.
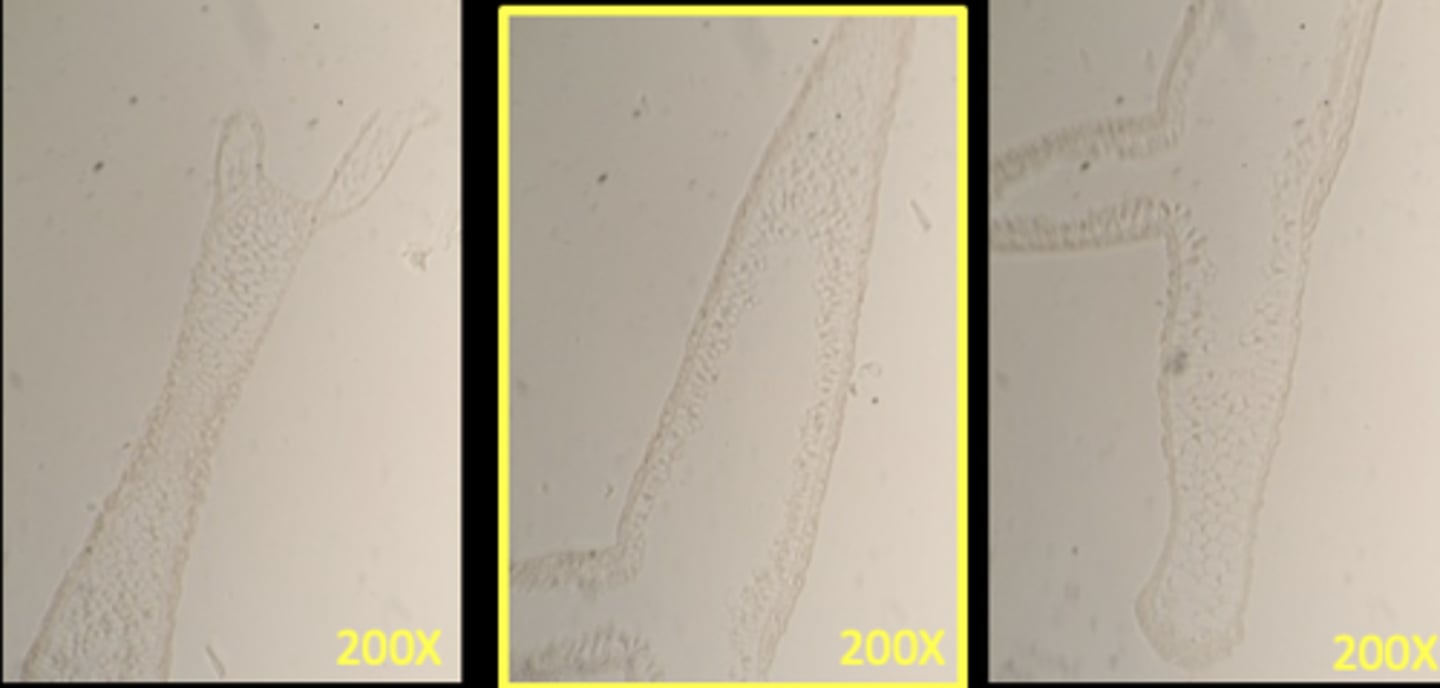
What is this picture showing?
pay attention to labels
Cross-section of Phylum: Cnidaria Class: Hydrozoa Genus: Hydra
Reproduction Cycle of Cnidarians in Class Hydrozoa
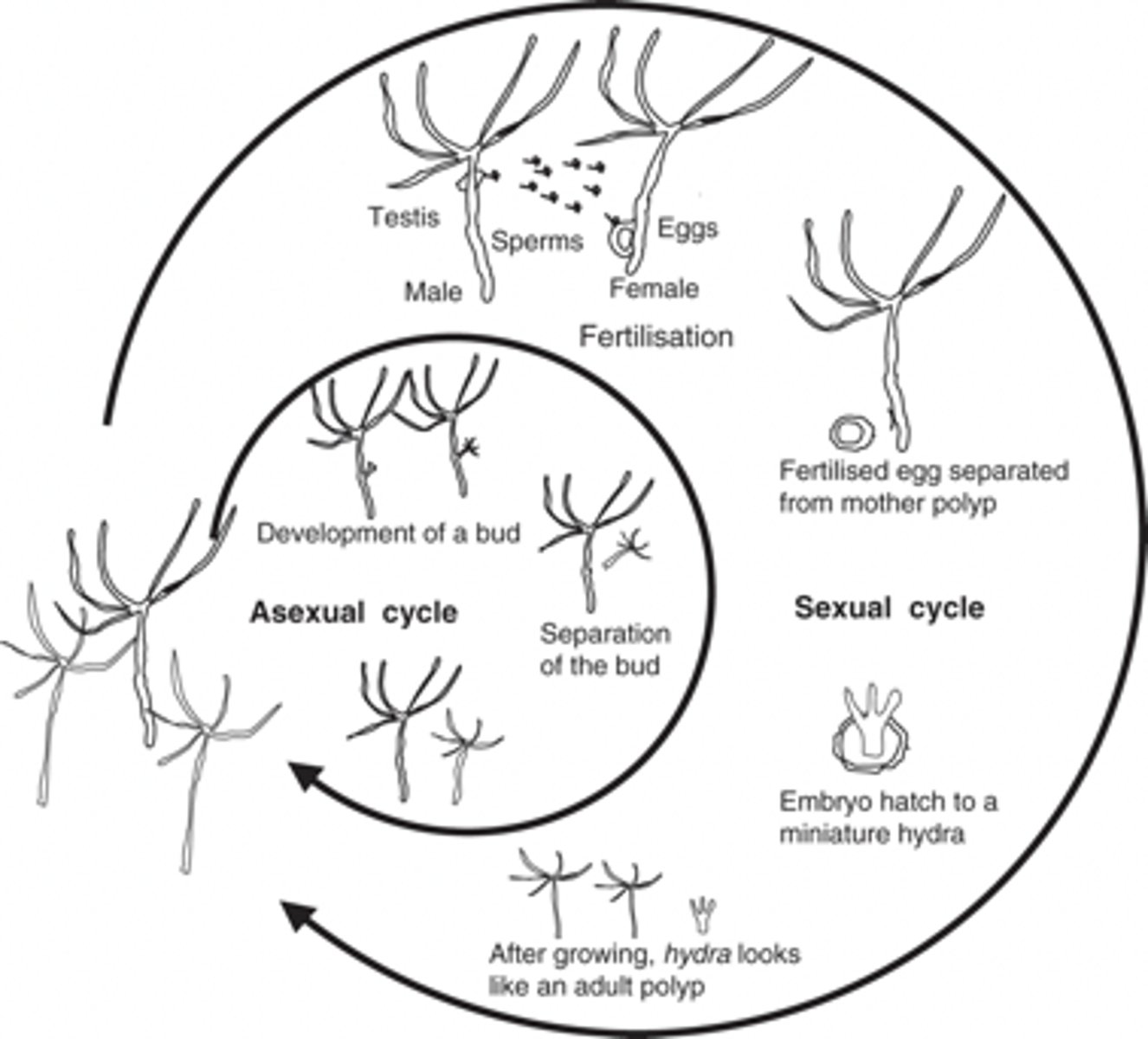
Sexual Reproduction of Cnidarians in Class Hydrozoa
pay attention to labels
Asexual Reproduction of Cnidarians in Class Hydrozoa
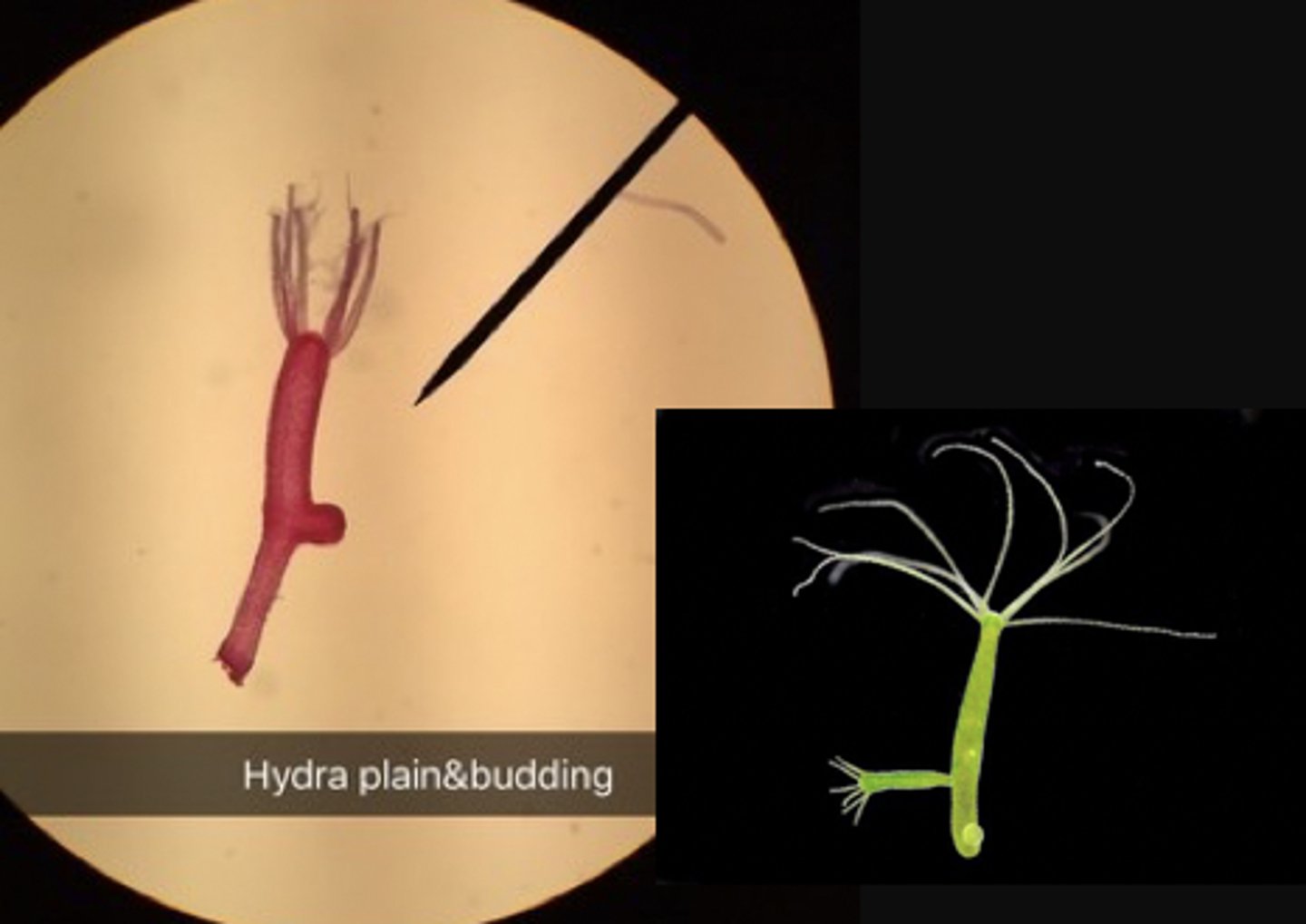
What is the phylum, class, genus, and body form of this organism?
pay attention to labels
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Hydrozoa
Genus: Obelia
Body Form: Polyp
Obelia is an example of a polymorphic colony
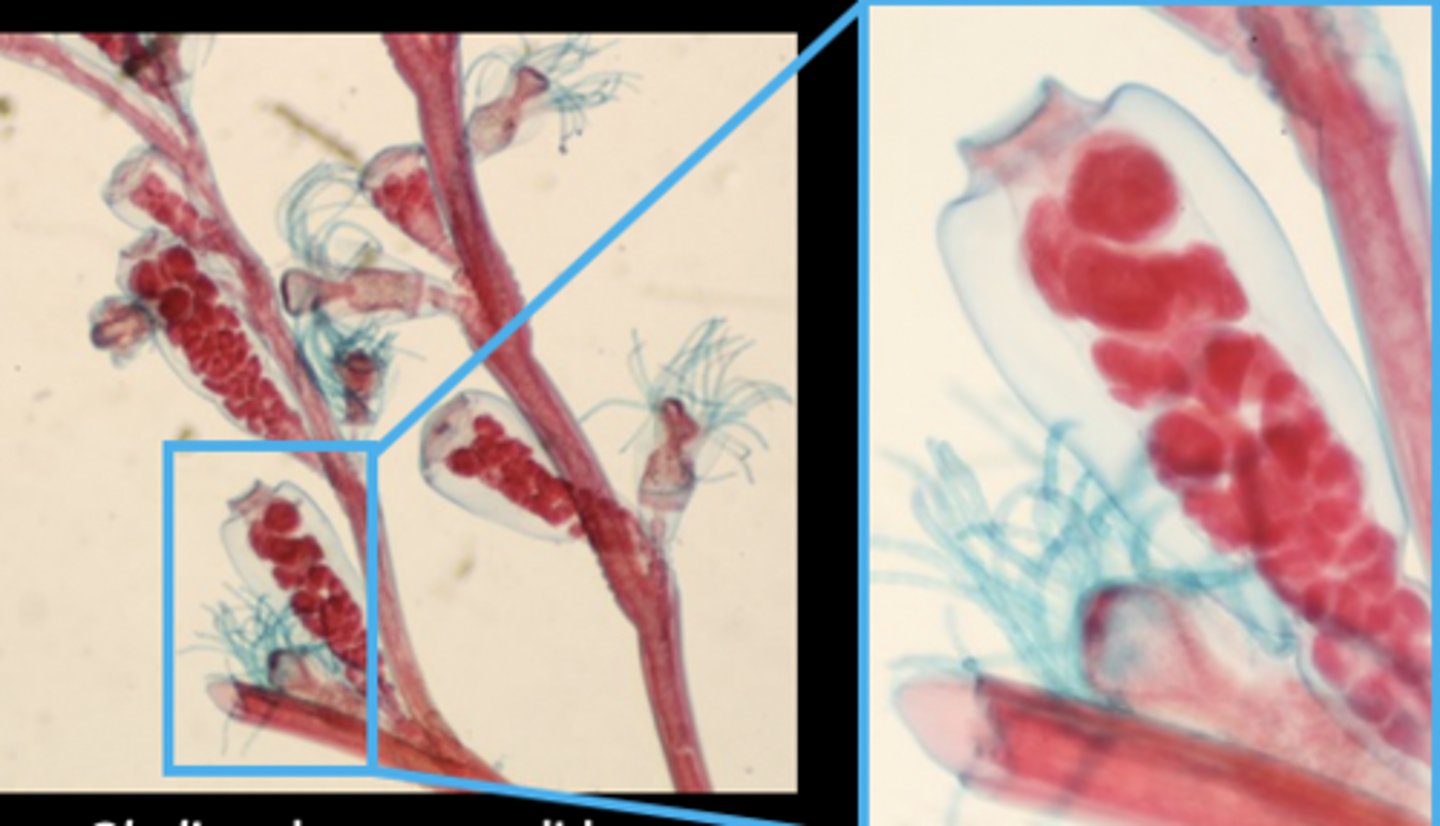
What is the phylum, class, genus, and body form of this organism?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Hydrozoa
Genus: Obelia
Body Form: Polyp
Obelia is an example of a polymorphic polyp colony
True or False?
Obelia is an example of a polymorphic polyp colony
True
What does polymorphism mean?
having more than one form
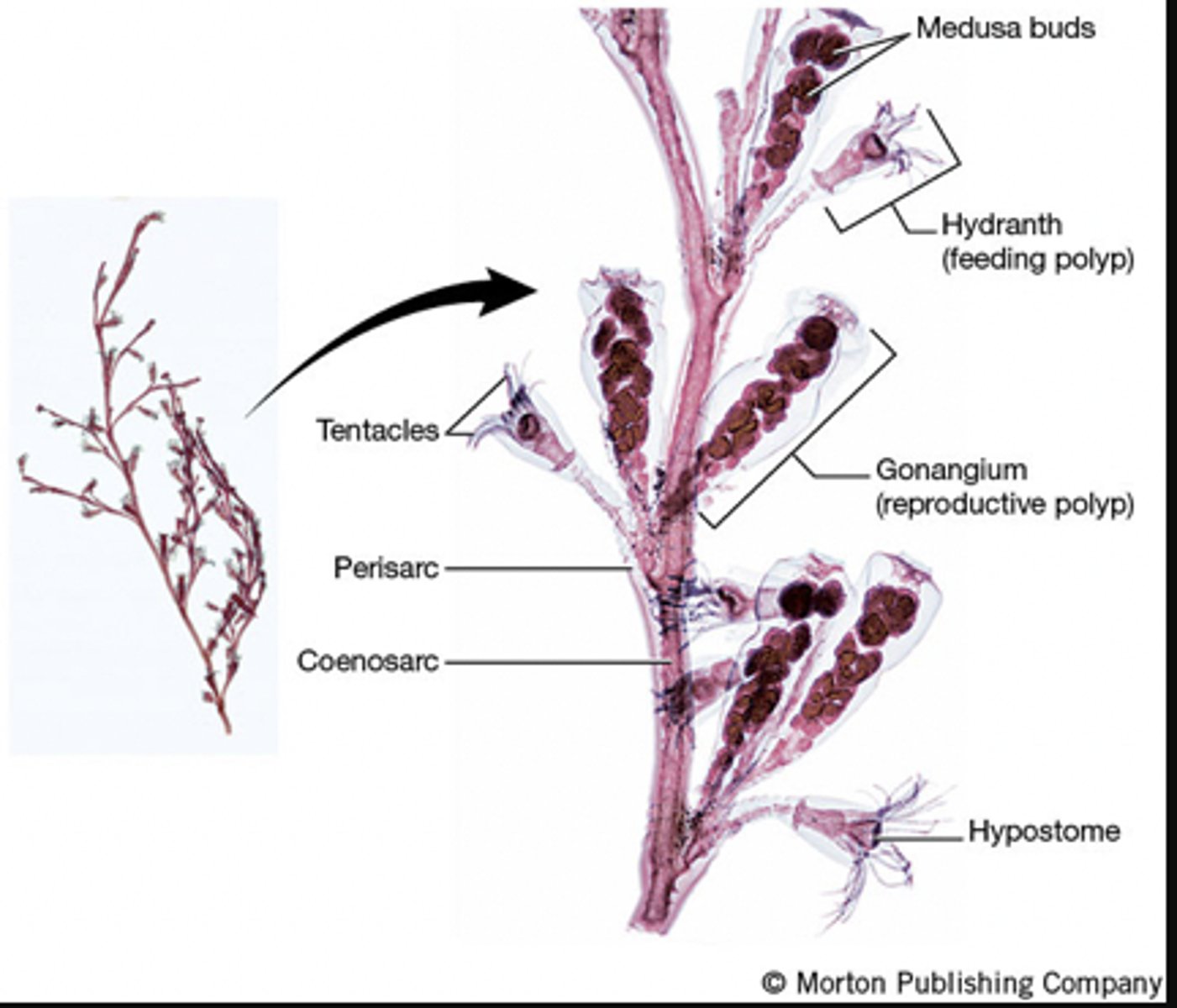
Cnidarians often form colonies that consisting of many zooids (polyps). These zooids are often polymorphic and are specialized for certain functions:
- Gastrozooid = feeding polyp
-Gonozooid = sexually reproductive polyp
-Gactylzooids = defense polyp
What is a zooid?
polyp
What is the function of the gastrozooid of Obelia?
Feeding polyp
What is the function of the gonozooid of Obelia?
Sexually reproductive polyp
What is the function of the gactylzooids of Obelia?
Defense polyp
What is the phylum, class, genus, and body form of this organism?
pay attention to labels
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Hydrozoa
Genus: Obelia
Body Form: Medusa
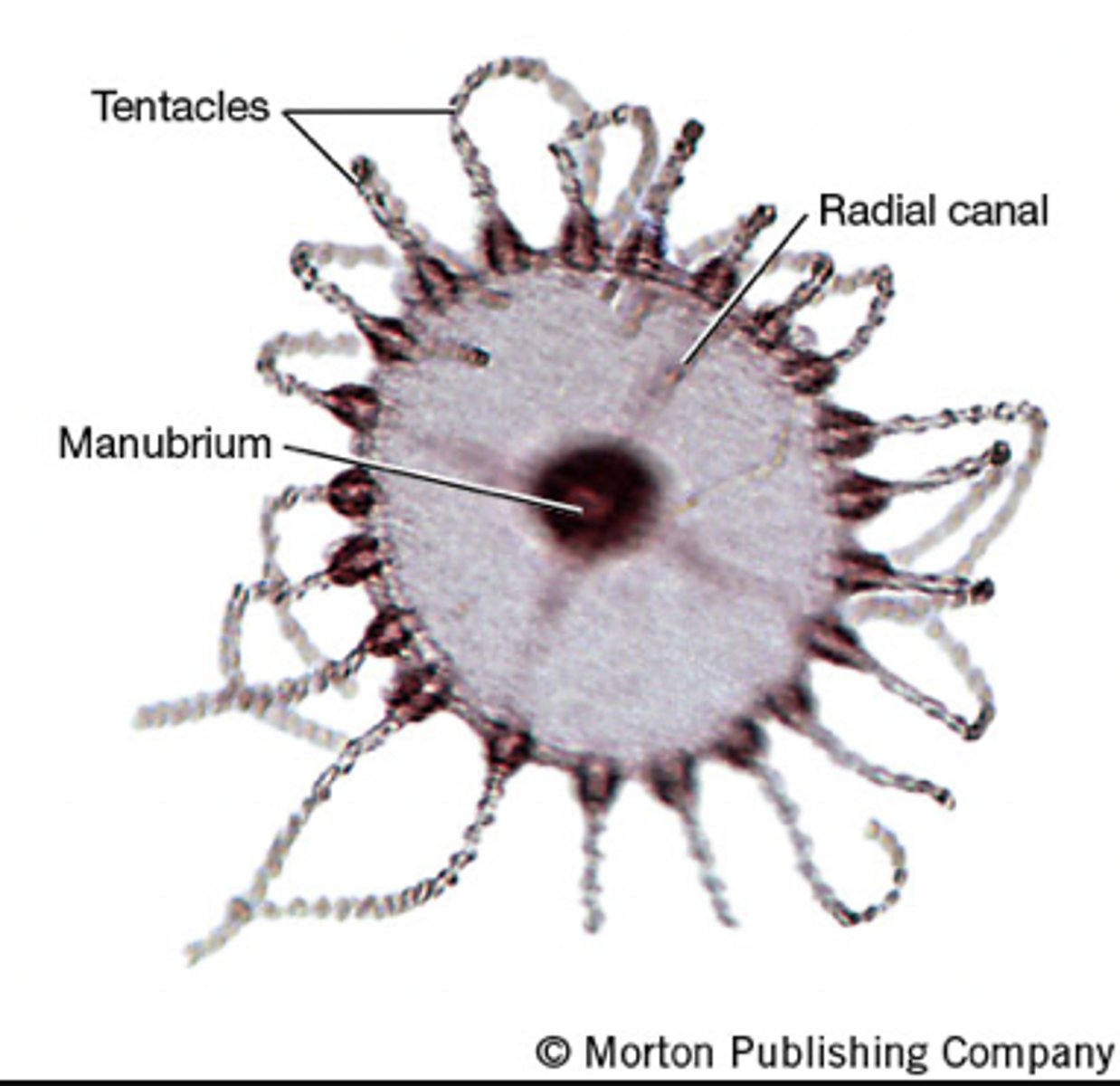
What is the phylum, class, and body form of this organism?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Hydrozoa
Body Form: Medusa
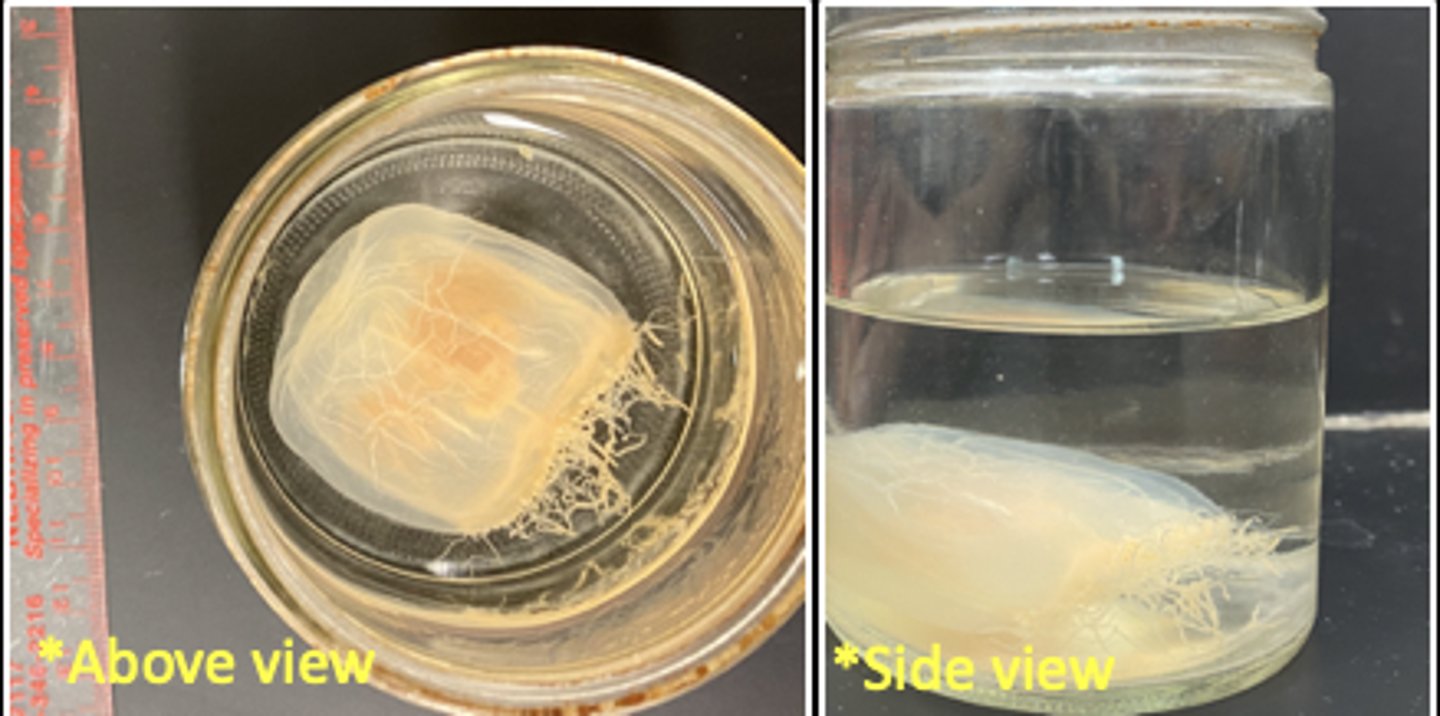
What is the phylum, class, genus, and common name of this organism?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Hydrozoa
Genus: Millepora
Common name: Fire Coral
What is the phylum, class, genus, and common name of this organism?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Hydrozoa
Genus: Millepora
Common name: Fire Coral
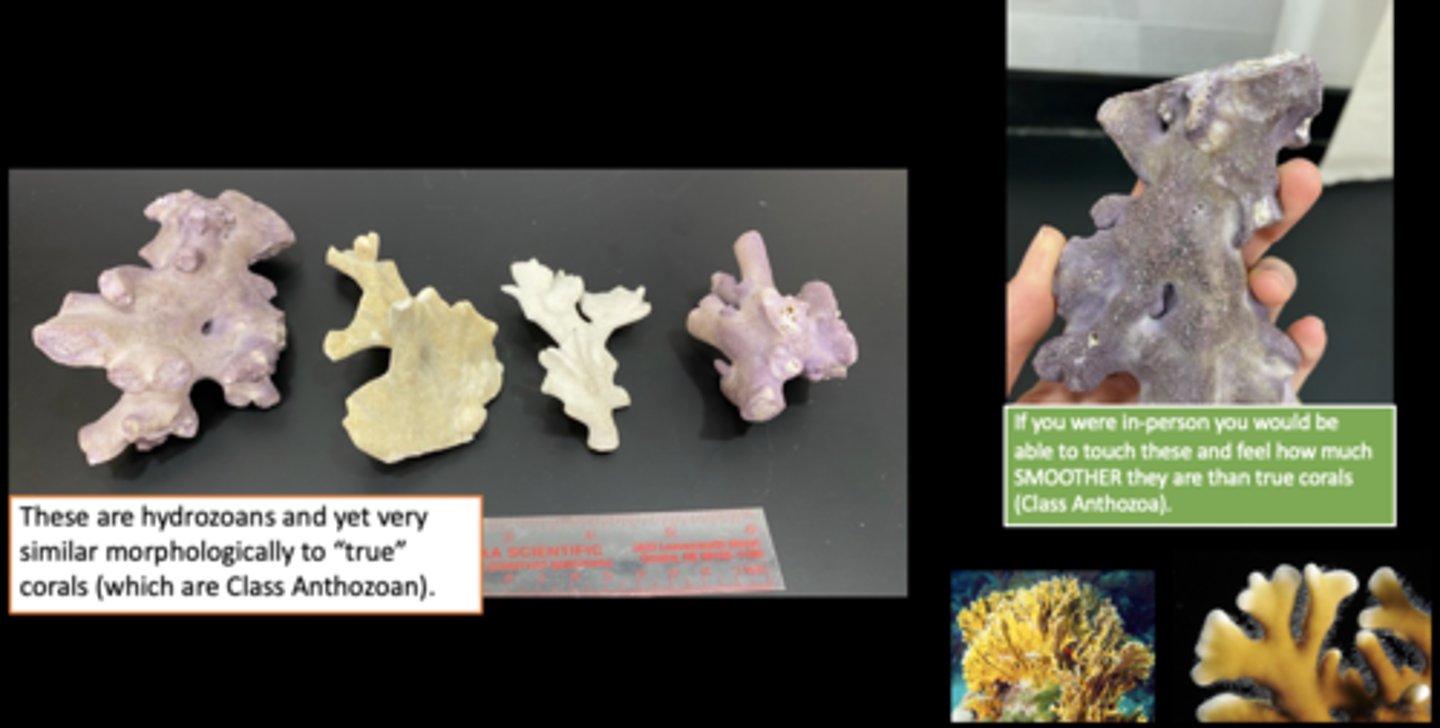

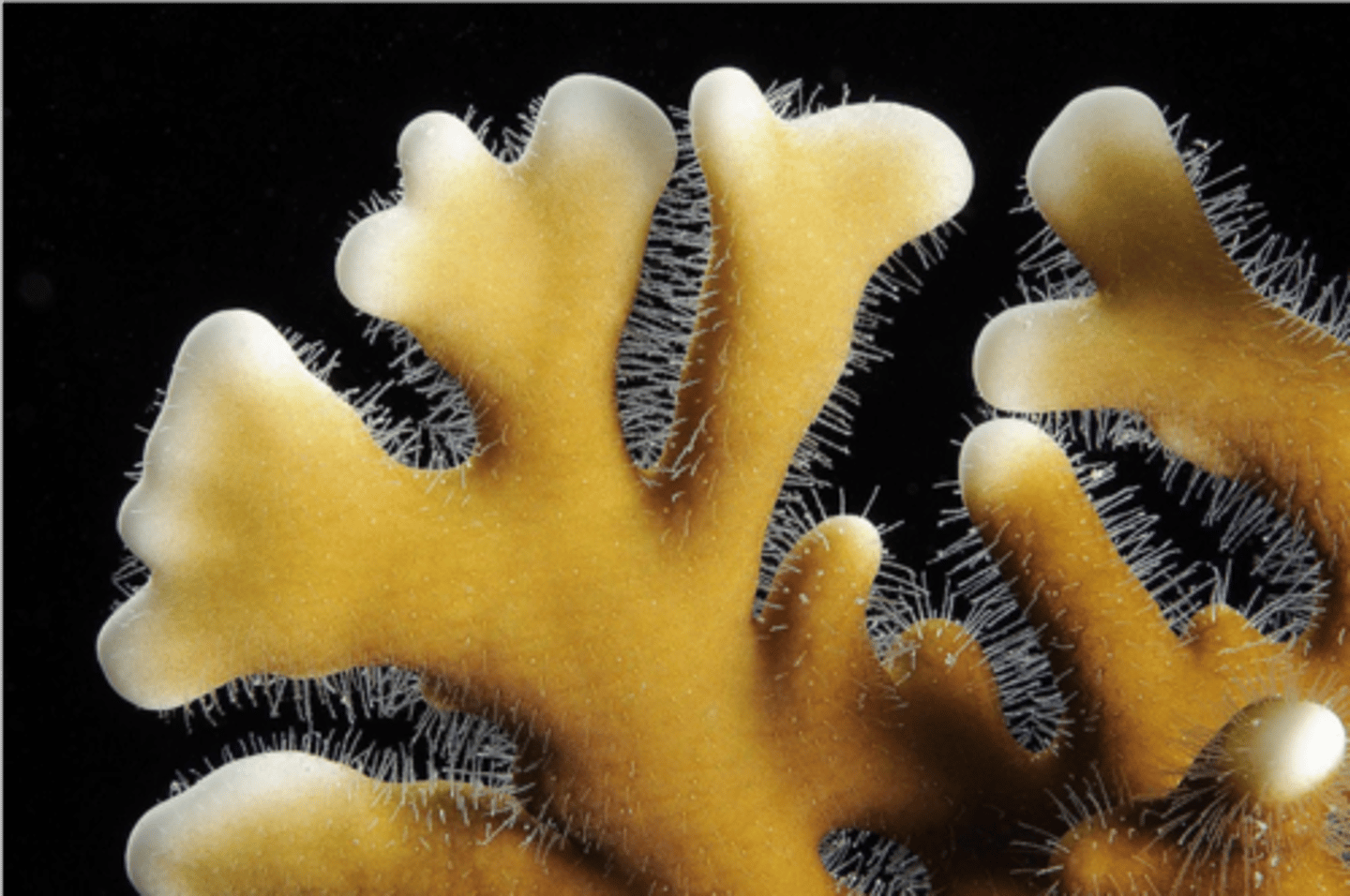
What is the common name of millepora?
Fire Coral
- Not true coral
-- Hydrocorals
- Nematocysts contain tentacles that protrude through surface pores
-- Produce painful sting
- Calcified skeleton is sharp and easily scrapes skin
Phylum Cnidaria Class Hydrozoa
Genus Millepora Characteristics
(Fire Coral)
What is the phylum, class, genus, and common name of this organism?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Hydrozoa
Genus: Physalia
Common name: Portuguese man o' war
Physalia physalis
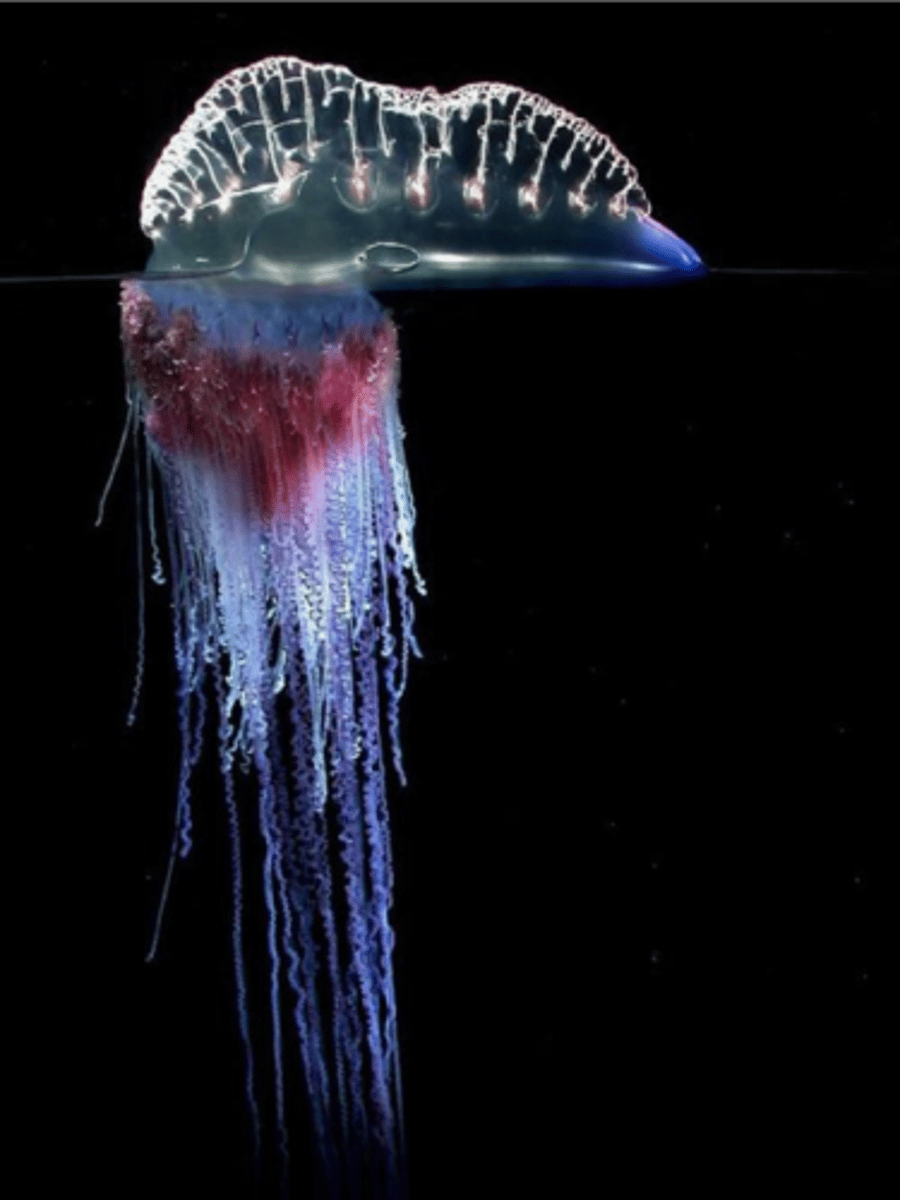

- Polymorphic colony
- Highly specialized polyps
- Venom filled with nematocysts which paralyze and kills prey
Phylum Cnidaria Class Hydrozoa
Genus Physalia Characteristics
(Portuguese man o' war) - Physalia physalis
What is the name of this organism?
Portuguese man-of-war
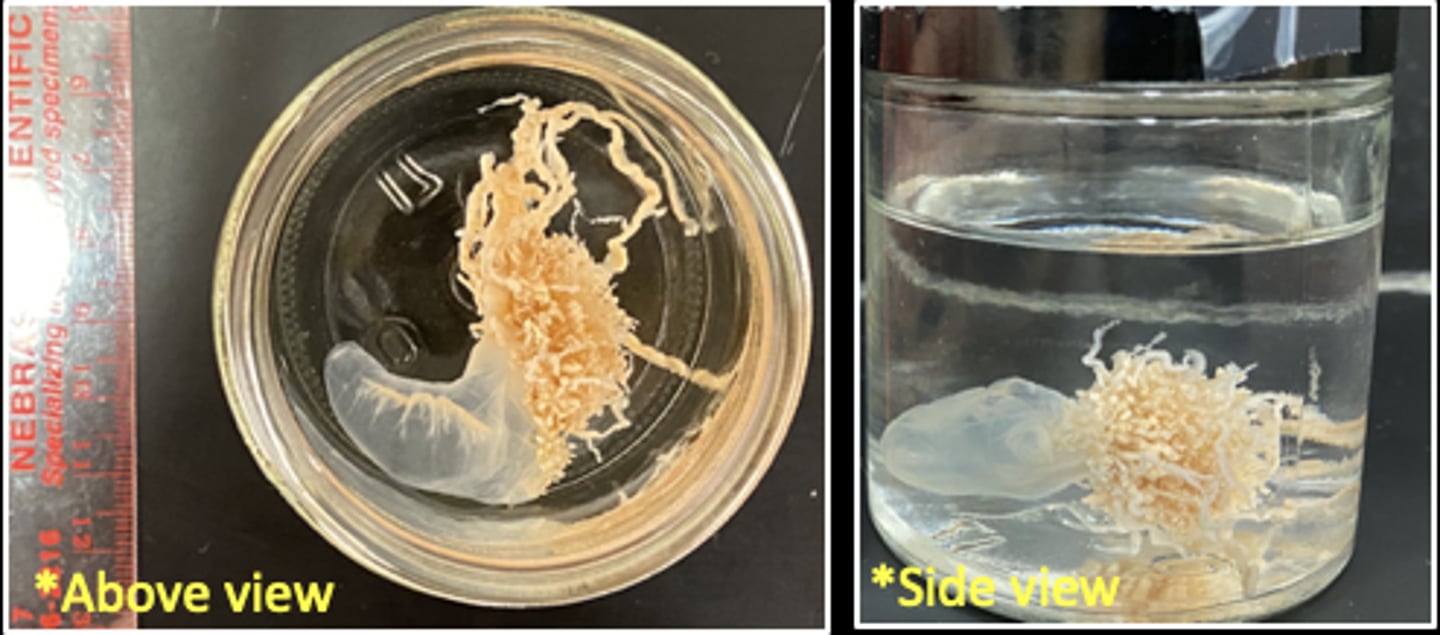
True or False?
The Portuguese man-of-war is a pelagic colony of polymorphic zooids.
True
Pelagic means relating to open sea
What class do these organisms belong to?
Class Hydrozoa
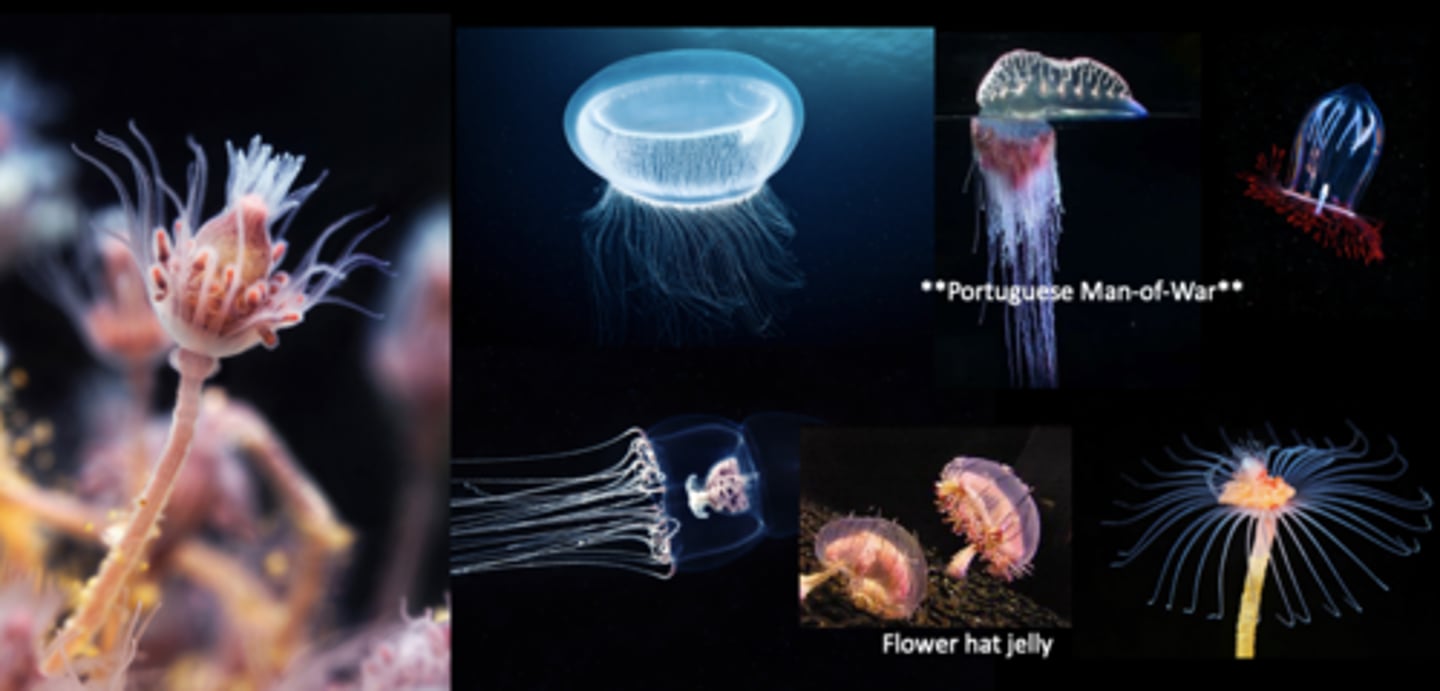

What are the representative animals of the Phylum Cnidaria Class Scyphozoa?
Jellyfish (Aurelia)
What is the phylum, class, and common name of these organisms?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Scyphozoa
Common Name: True sea
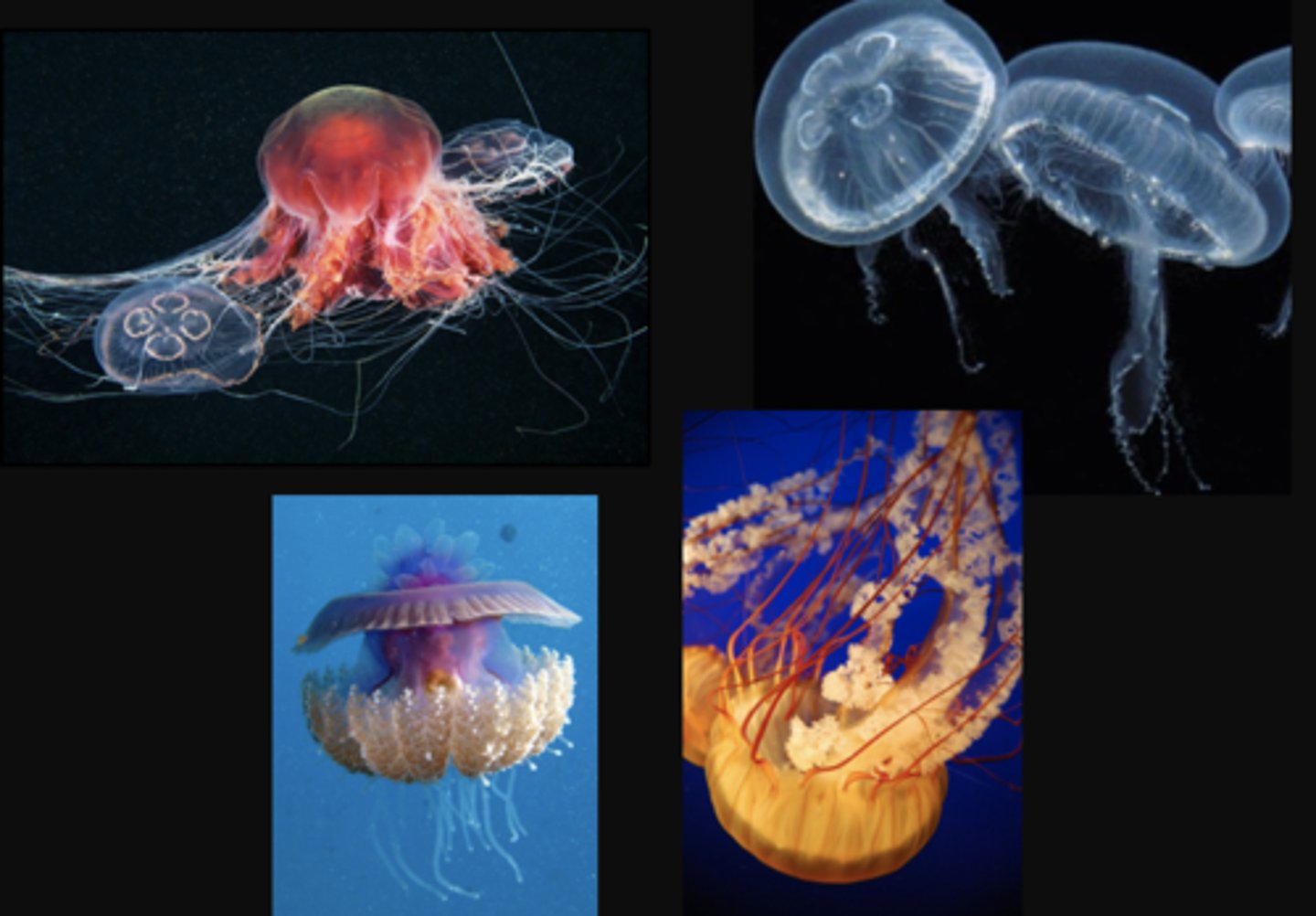

- True sea jelly
- Thick layer of mesoglea
- Medusa is the dominant life stage
-- Very reduced polyp stage which buds off medusae
- Largest in Lion's Mane
-- 6ft in diameter, 100 ft long
Phylum Cnidaria Class Scyphozoa Characteristics
Oral Arms (Scyphozoa)
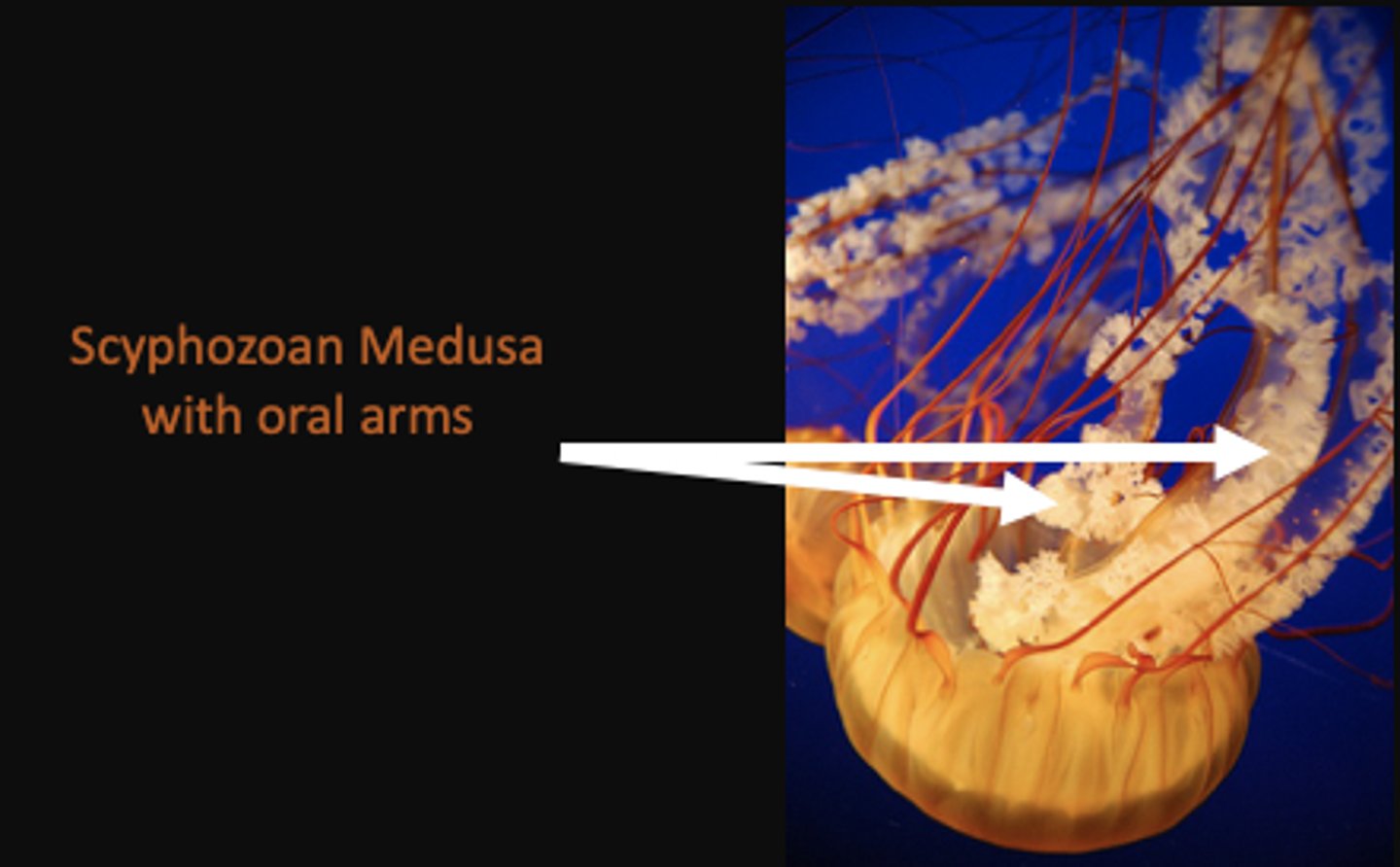
Besides tentacles, what else do Phylum Cnidaria Class Scyphozoa have?
Oral arms
What phylum, class, and genus do these organisms belong to?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Scyphozoa
Genus: Aurelia
(preserved specimens)
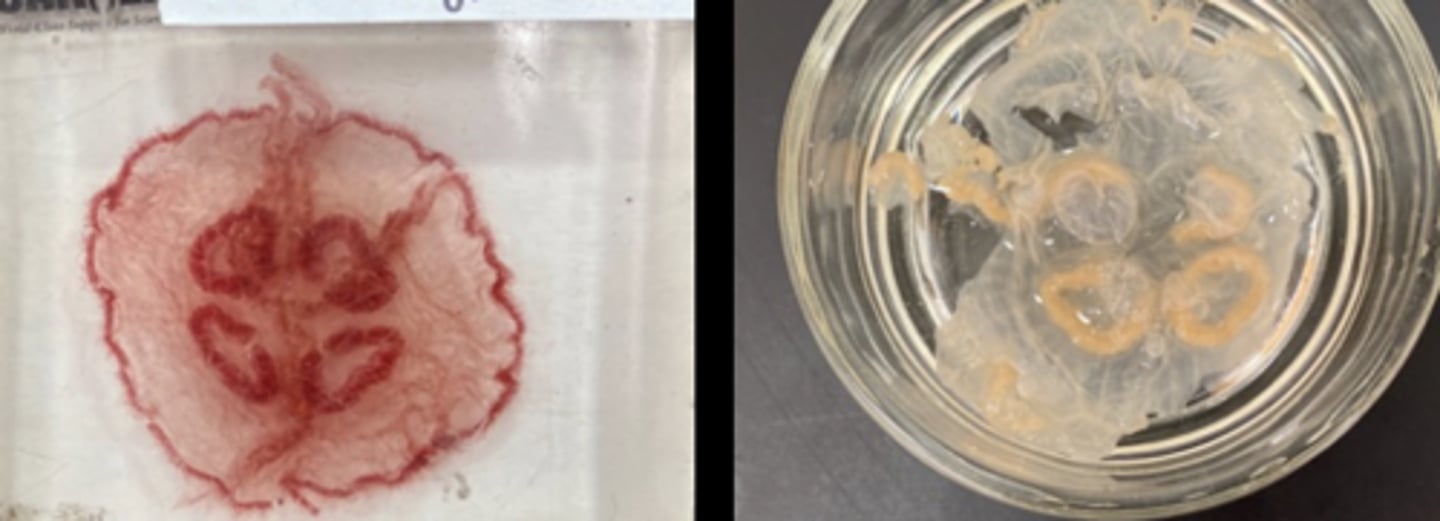
What phylum, class, and genus do these organisms belong to?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Scyphozoa
Genus: Aurelia

What phylum and class do these organisms belong to?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Scyphozoa

What phylum, class, and common name does this organism belong to?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Scyphozoa
Common Name: cannonball jellyfish
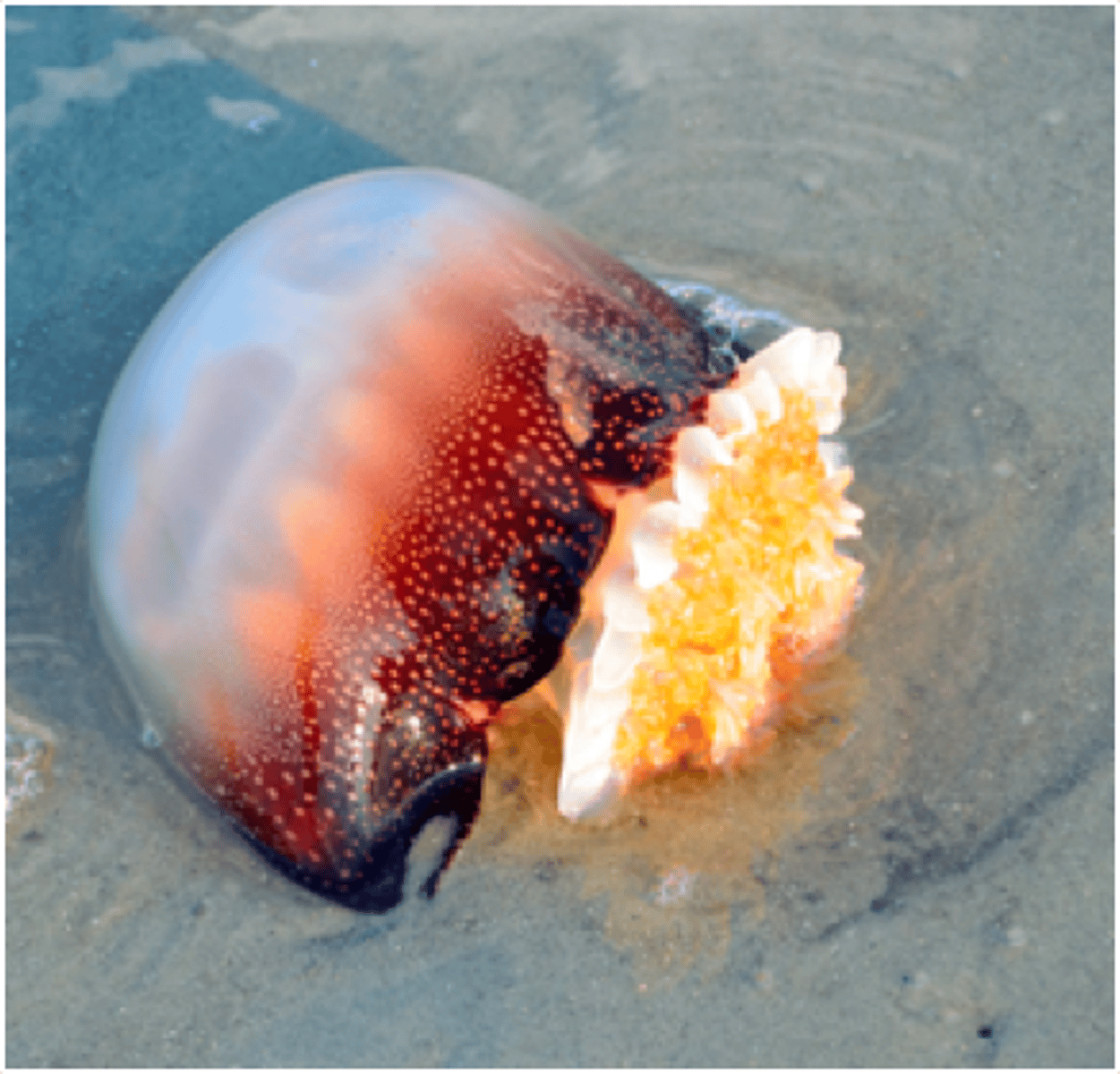

Why is the cannonball jellyfish named so?
This scyphozoan is called the Cannonball jellyfish because the mesoglea is so thick.
To protect themselves from predators, juvenile jacks (a type of fish) position themselves about the stinking tentacles of this jellyfish.
What phylum, class, and common name does this organism belong to?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Scyphozoa
Common Name: Mangrove Jellyfish
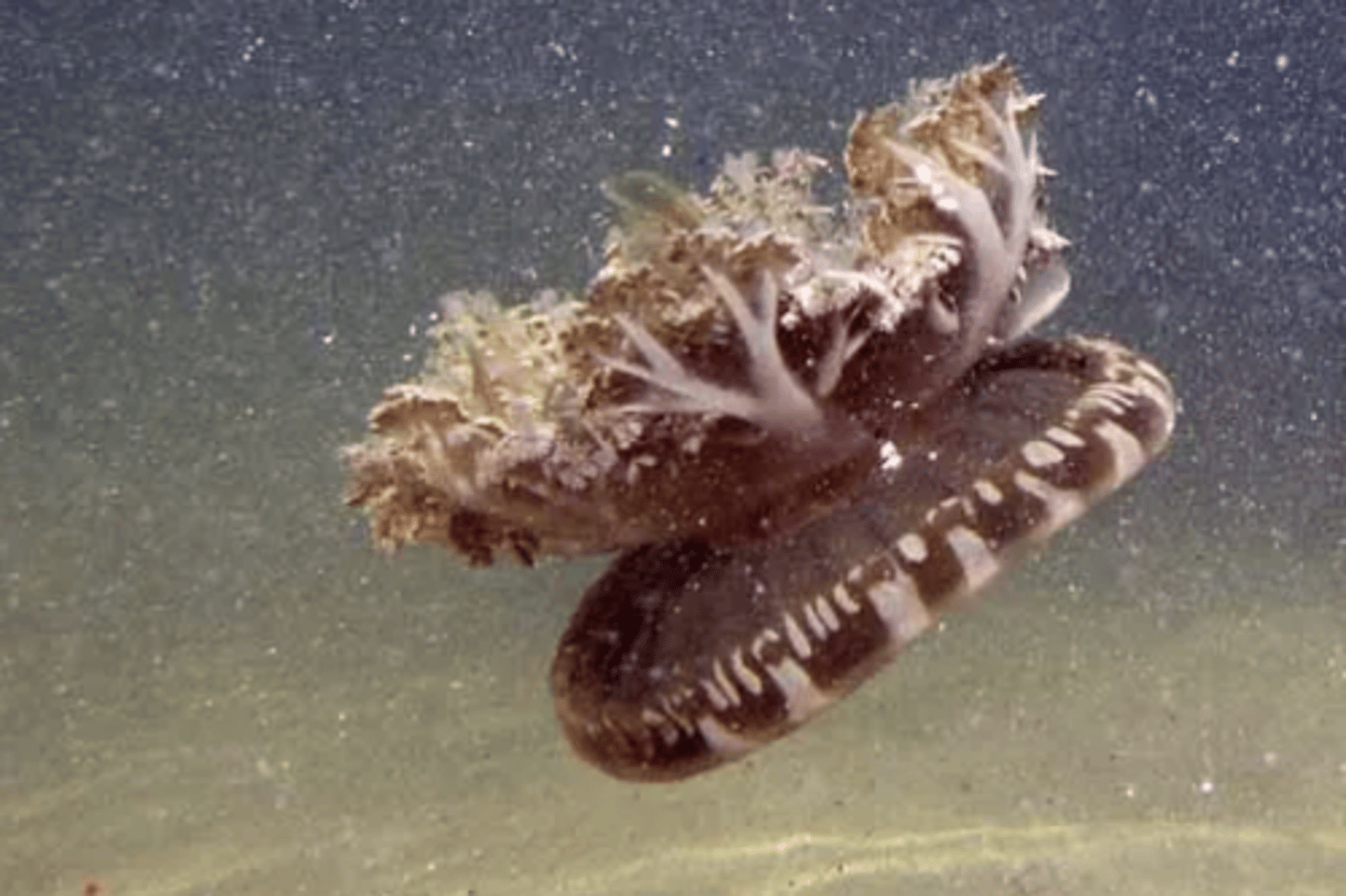

Why is the Mangrove Jellyfish called the upside-down jellyfish?
This scyphozoan is called the upside-down jellyfish because it rests upside down on the bottom of shallow areas in mangrove embayments. This allows sunlight to reach the symbiotic photosynthetic algae (zooxanthellae) it has in its mesoglea.
Reproductive Stages of Phylum Cnidaria Class Scyphozoa
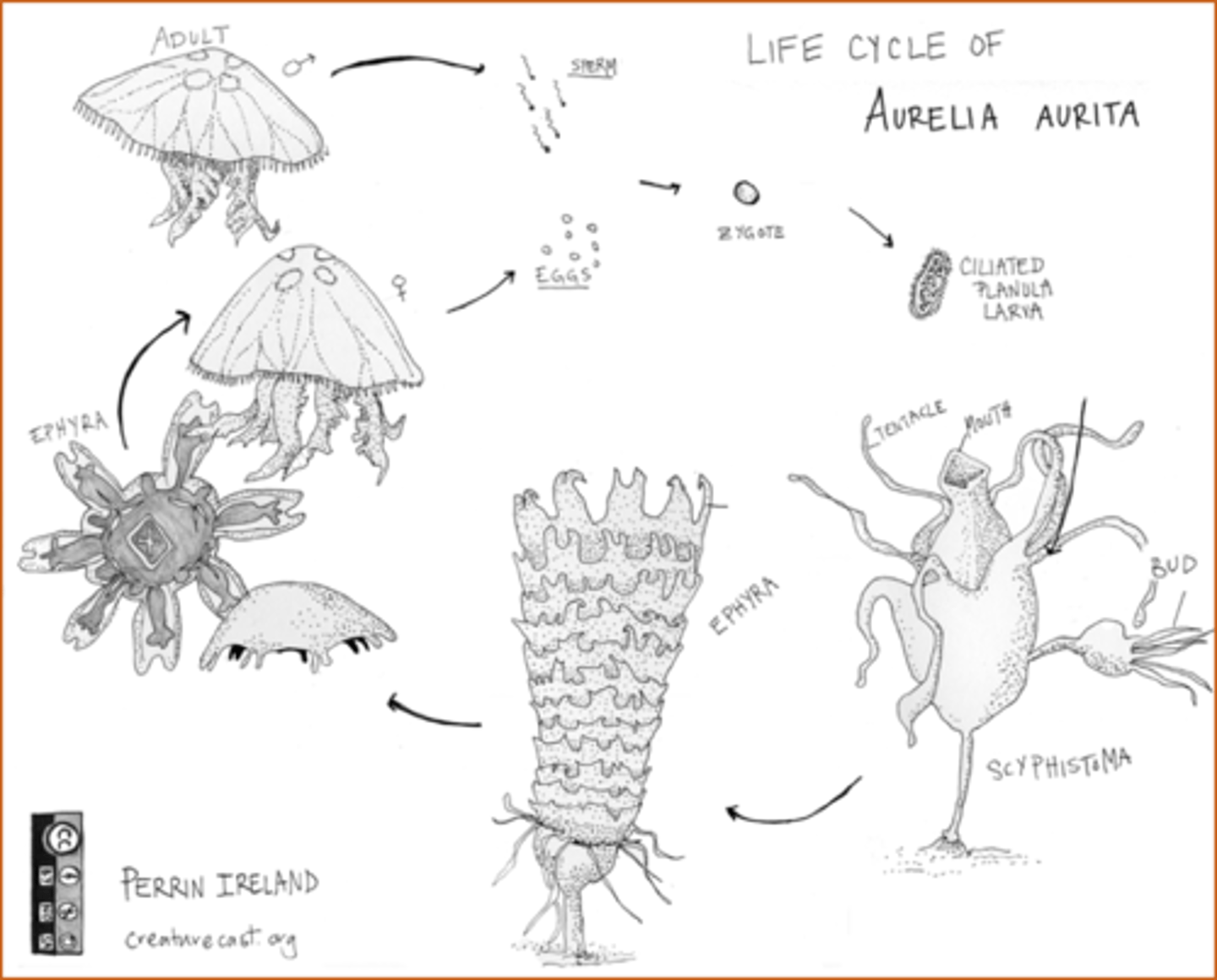
What is the order of the reproductive cycle of Phylum Cnidaria Class Scyphozoa?
1. Ciliated Planula Larva
2. Scyphistoma
3. Strobila
4. Ephyra
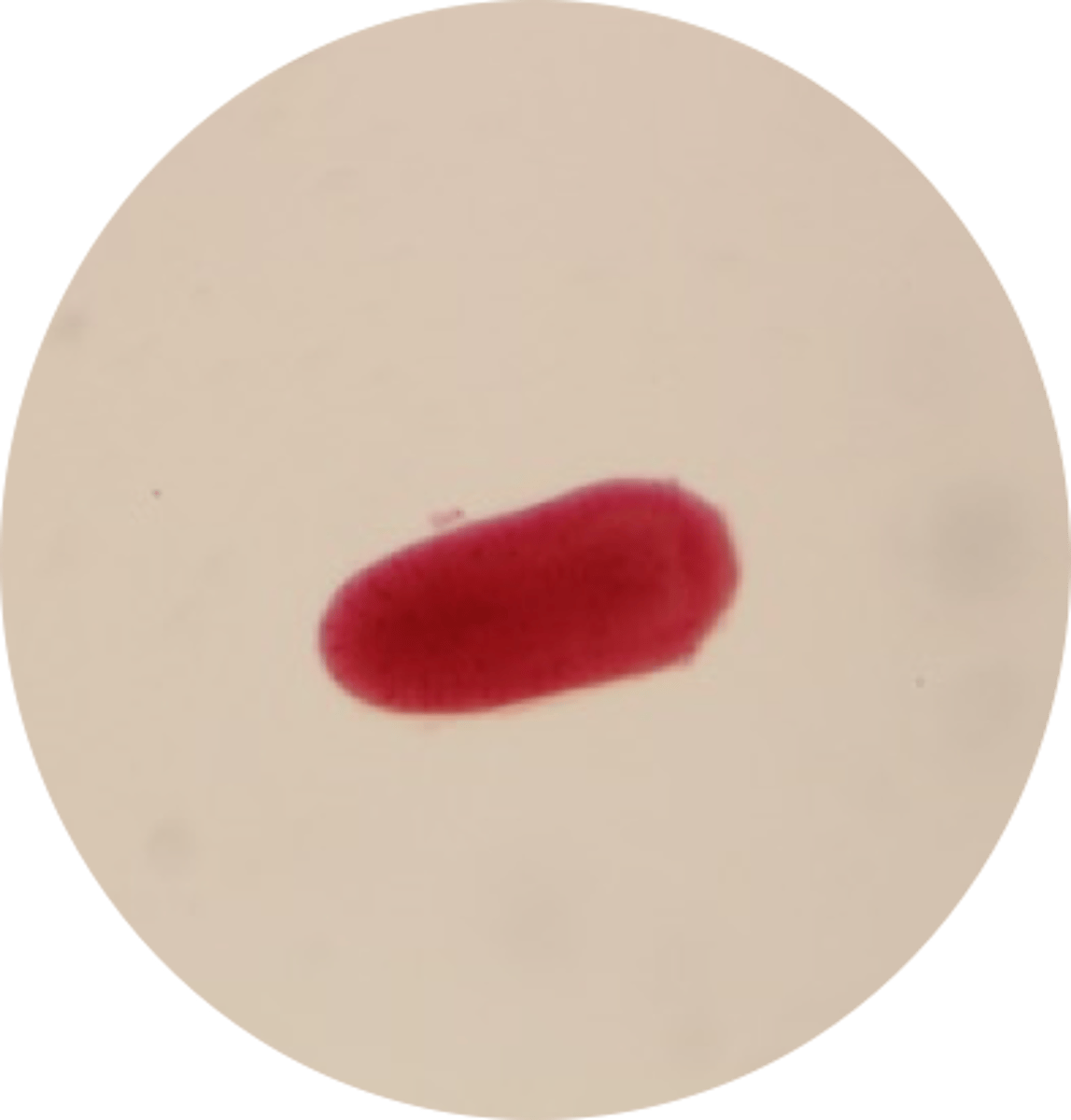
What is the first stage of the reproductive cycle of Phylum Cnidaria Class Scyphozoa?
Ciliated Planula Larva
(free-swimming larvae)
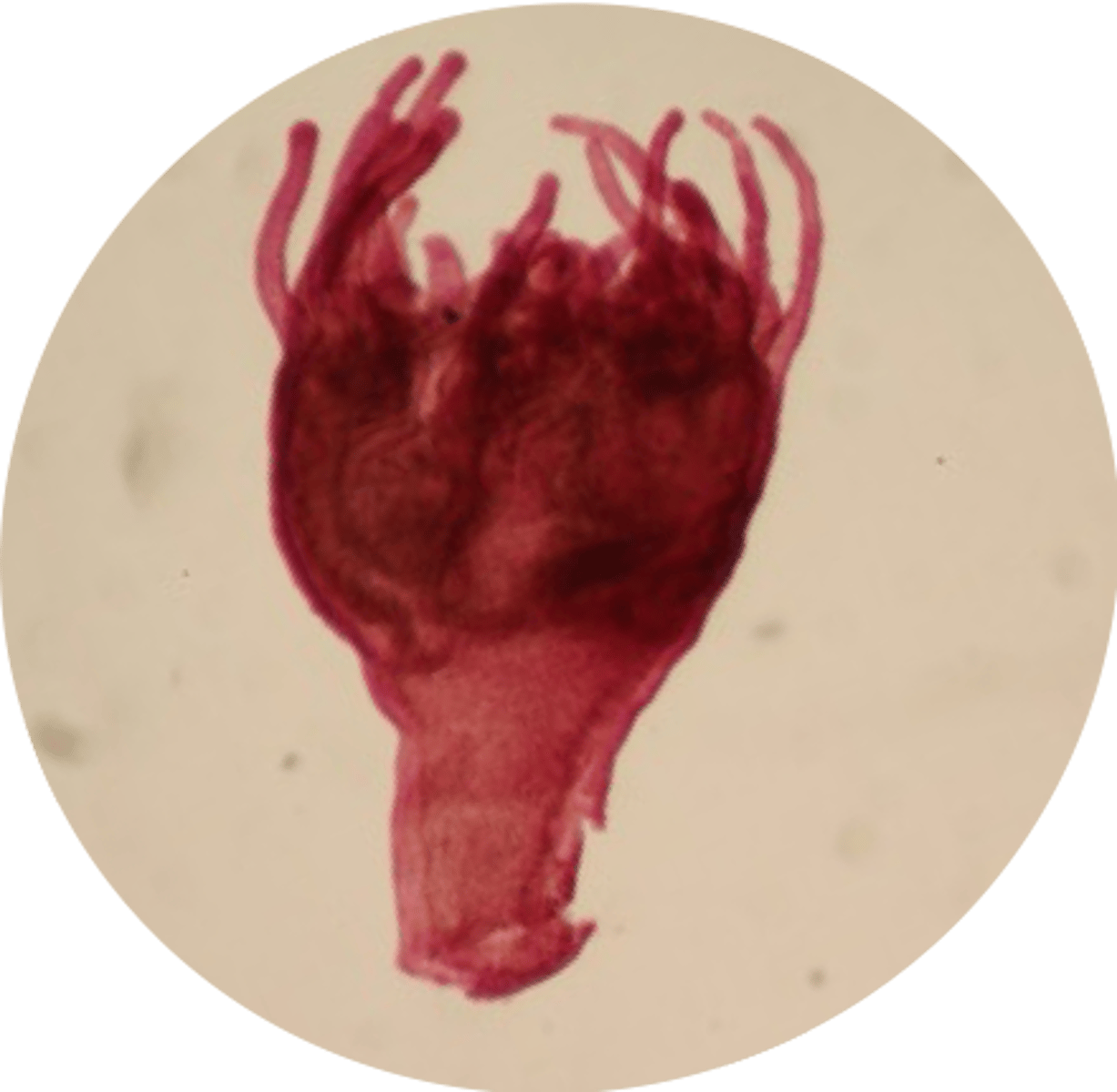
What is the second stage of the reproductive cycle of Phylum Cnidaria Class Scyphozoa?
Scyphistoma
(polyp)
What is the third stage of the reproductive cycle of Phylum Cnidaria Class Scyphozoa?
Strobila
(contains many immature medusae
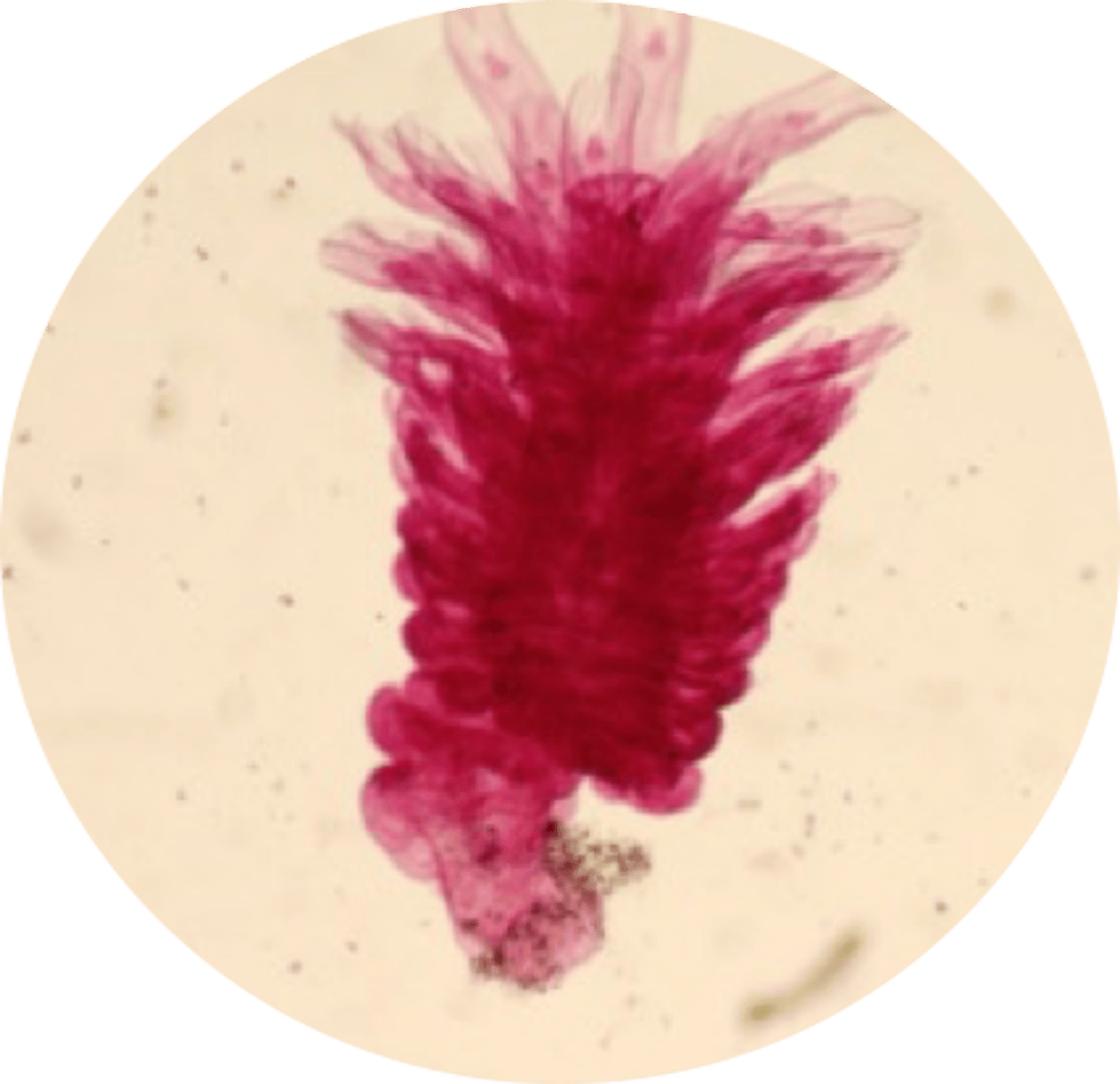

What is the fourth stage of the reproductive cycle of Phylum Cnidaria Class Scyphozoa?
Ephyra
(immature medusa)
What are the representative animals of the Phylum Cnidaria Class Cubozoa?
Box jellyfish (Chironex)
What is the phylum, class, and common name of this organism?
Phylum: Cnidaria
Class: Cubozoa
Common name: Box jellyfish
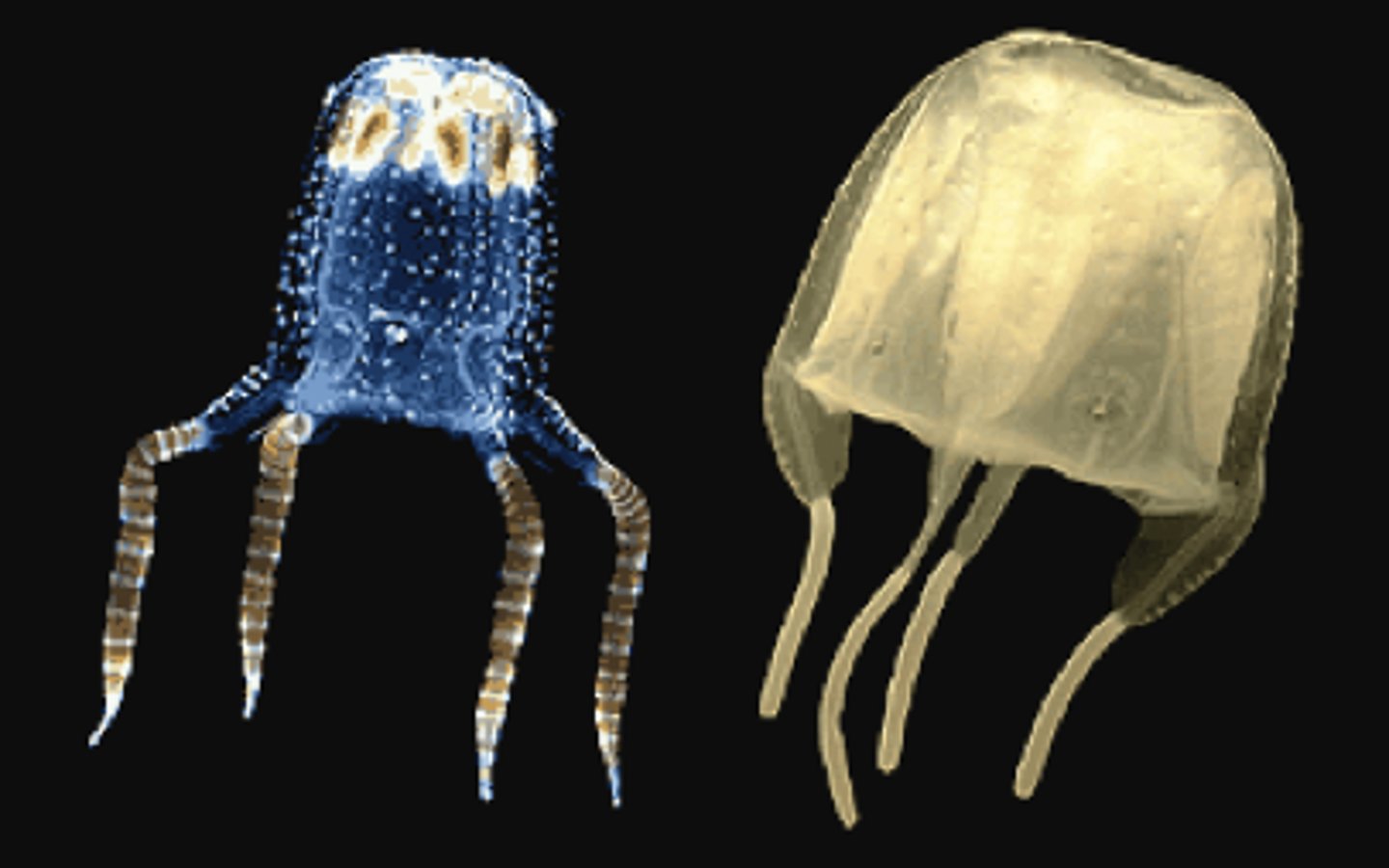

- With a cube shaped dominant medusa stage
- With four evenly spaced out tentacle or bunches of tentacles and well-developed eye
- The Australian stinger Chironex fleckeri is among the deadliest creatures in the world, having caused human fatalities
-- Tentacles up to three meters long
-- One "sting" can easily kill a human, with death occurring in as little as three minutes
Phylum Cnidaria Class Cubozoa Characteristics
What are the representative animals of the Phylum Cnidaria Class Anthozoa?
Sea Fan (soft coral), Sea Pansy, Anemone, and Coral (hard coral)
- Sessile with only a polyp stage (no medusa stage)
- Exist as solitary individuals (e.g. anemones) or as true colonies (e.g. corals)
- Most specialized and diverse of all cnidarians
- All marine
Phylum Cnidaria Class Anthozoa Characteristics