UCM Biochem Chapter 5
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
catalyst
agent that enhances rate of chemical rxn without being consumed by it
enzyme
biological macromolecule that acts as a catalyst for biochem rxn
although almost all enzymes are composed of protein, some RNA molecules are catalytically active
dramatically enhance and control rates of chem rxn
substrates
a reactant in chem rxn
An enzyme catalyzes a single chemical rxn or set of closely related rexns, and the components of those rxns are called the …
protease
This enzyme class hydrolyzes the peptide bonds between amino acids, thus digesting proteins
free energy of products minus free energy of reactants
What does delta (change in) G of a rxn depend on?
transition state
What is image shown?
has higher free energy than either S or P
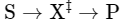
Gibbs free energy of activation
The difference in free energy between the transition state and the substrate is called…
Enzymes accelerate reactions by decreasing this.
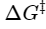
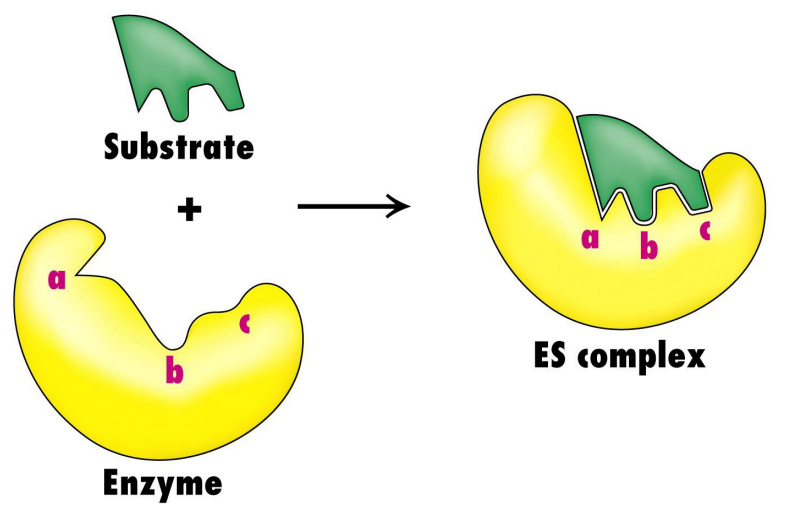
active site
A specific region of an enzyme that binds the enzyme’s substrate and carries out catalysis
3D cleft or crevice formed by groups that come from different parts of the AAs sequence
kinetics
study of reaction rates
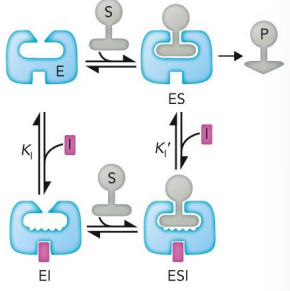
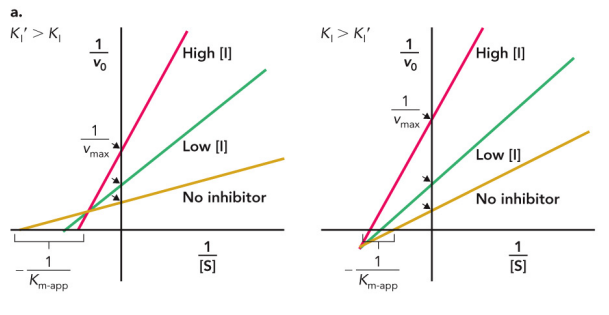
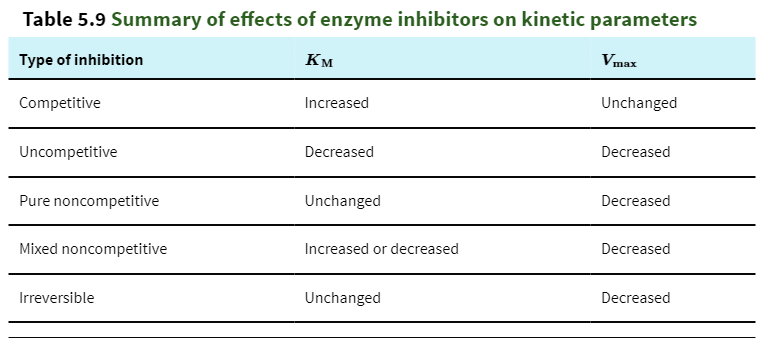
competitive inhibitor
What inhibitor competes with substrate for binding to the enzyme and thus reduces the proportion of enzyme molecules bound to substrate?
Can be relieved by increasing substrate concentration
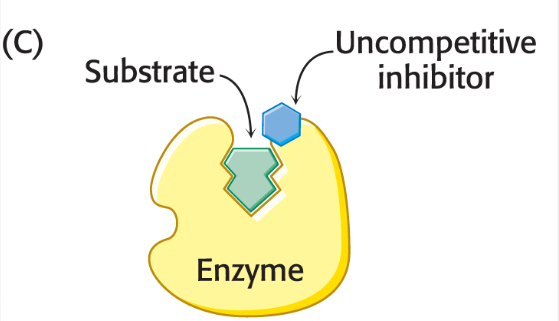
uncompetitive inhibitor
What inhibitor binds not to the enzyme itself but to the enzyme-substrate complex?
It is a substrate dependent
pure noncompetitive inhibitor
What inhibitor along with substrate can bind simultaneously to an enzyme molecule at two different binding sites?
binds to either free enzyme or ES complex, but will decrease the rate catalysis
cannot be overcome by increasing substrate mix
exergonic reactions
A reaction will occur without the input of energy, or spontaneously, only if ΔG is negative
at equilibrium
there is no net change in the amount of reactant or product. ΔG =0
endergonic reactions
A reaction will not occur spontaneously if the ΔG is positive
ΔG of a reaction
What depends only on the free energy difference between reactants and products and is independent of how the reaction occurs
And provides no information about the rate of the reaction
transition state
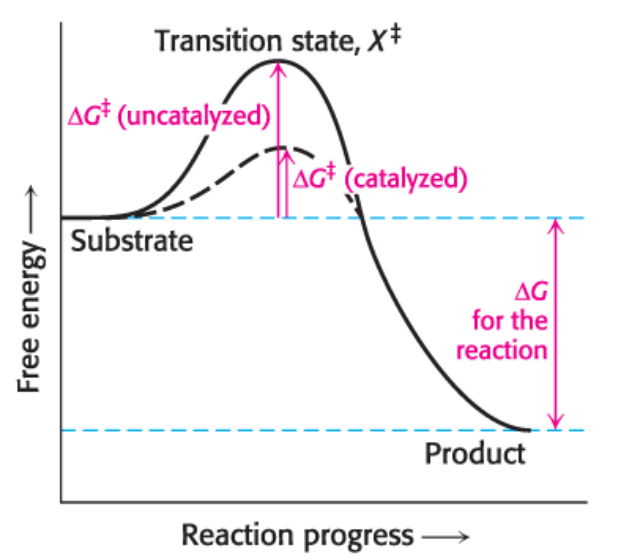
Enzymes Accelerate Reactions by Facilitating the Formation of the…
a molecular form that is no longer substrate but not yet product
activation energy
The energy required to form the transition state from the substrate is called
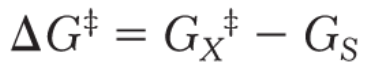
The rate of reaction is proportional to the concentration of X‡
because only X‡ can be converted into product.
The concentration of X‡ depends on the energy difference between X‡ and S, the activation energy.
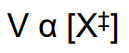
enzyme decrease the activation energy
overall reaction rate of V
depends on ΔG‡
k = Boltzmann’s constant
h is Planck’s constant
Using this equation, we can show that a 20% decrease in ΔG‡ results in a 10-fold increase in rate
Enzymes function by lowering the activation energy
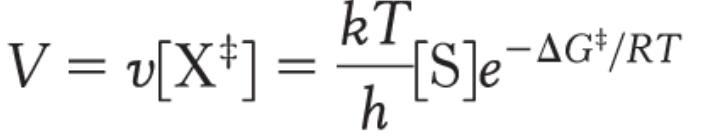
enzyme active sites list
1. Cleft or Crevice in the enzyme typically composed amino acids from different parts of primary structure
2. Small part of whole protein
3. Create unique microenvironments
4. Substrates bind through many weak interactions
5. Specificity for substrate depends on unique position of atoms
6. Active site is designed to stabilize the reaction’s transition state
induced fit model of substrate binding
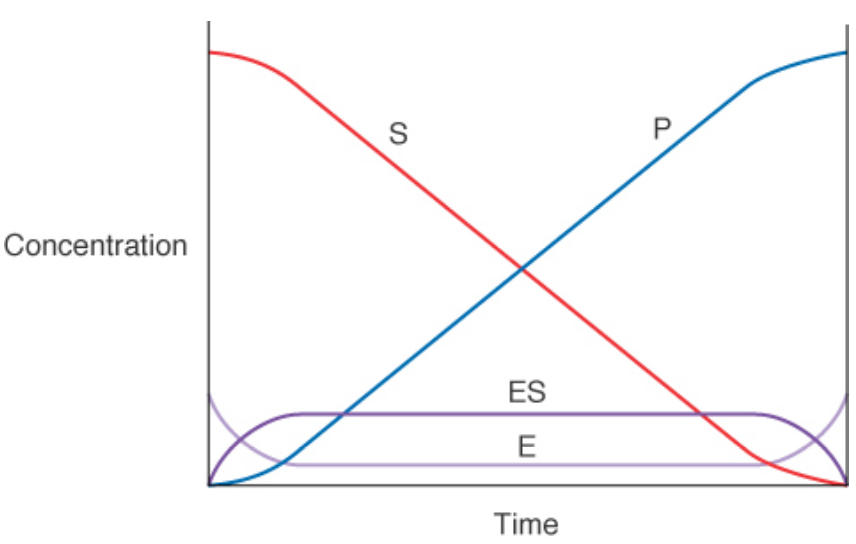
steady state conditions
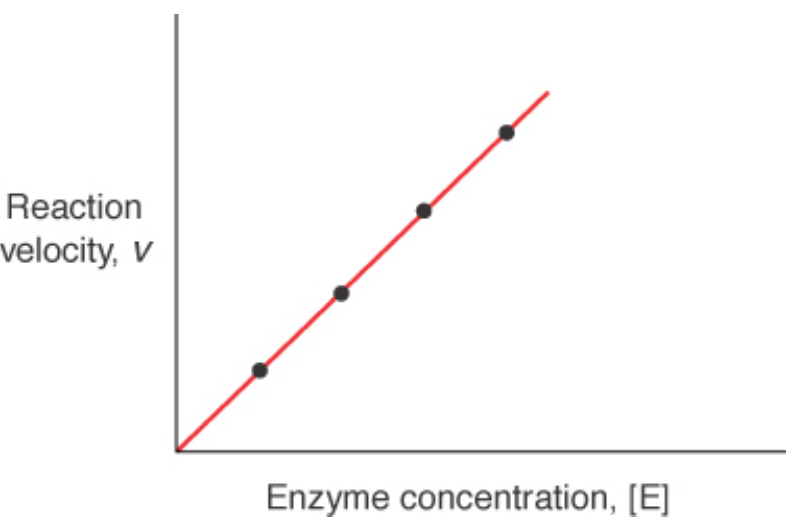
Reaction Velocity –vs- Enzyme Conc. At Steady State Conditions
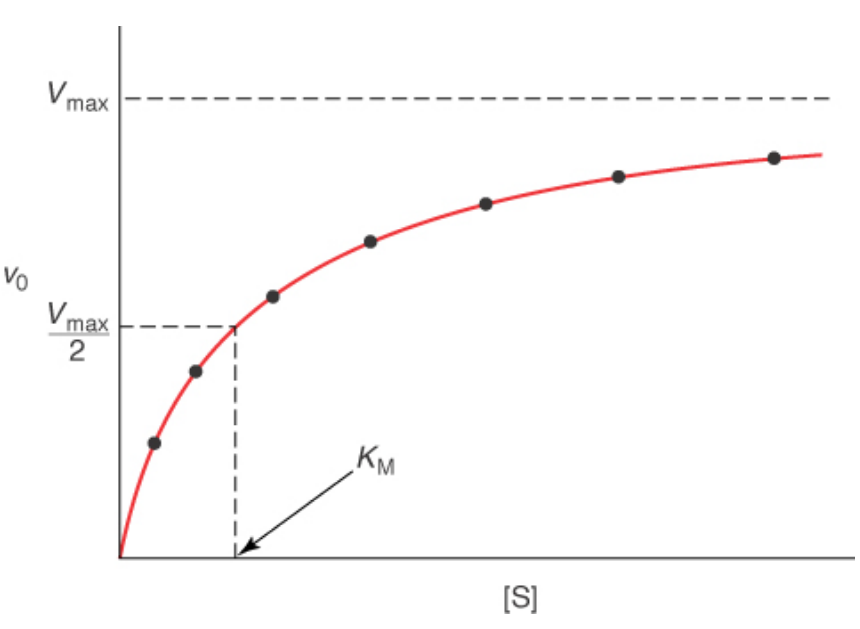
Reaction Velocity –vs- Substrate Conc. At Steady State Conditions
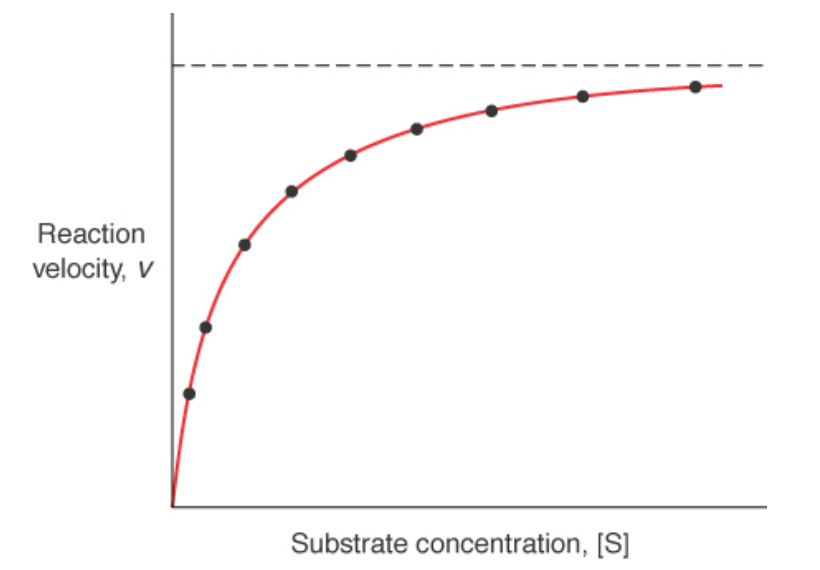
Michaels-Menten Diagram
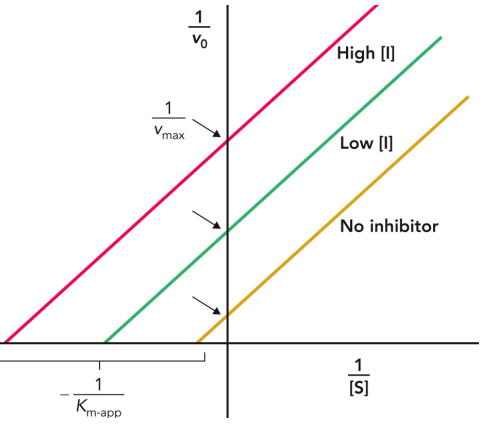
A Lineweaver—Burk plot
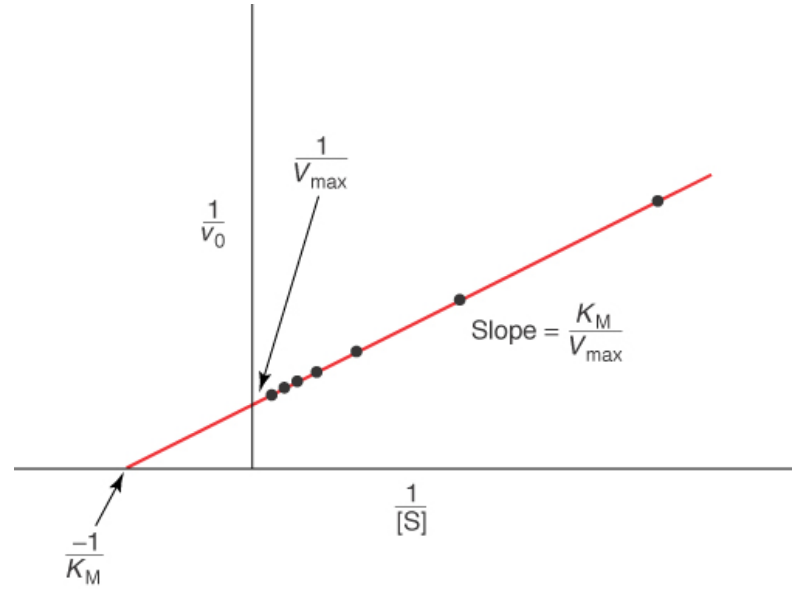
allows for you to find enzyme saturation at a given [S]
related to the rate constants of each step in the pathway
equal to the dissociation constant of the ES complex when k-1 >> k2. Measurement of binding affinity
Most [S] in the cell are similar to KM values
no dependent on enzyme
Significance of Km
if VMax is known, then kcat or Turnover # can be determined
Number of substrate molecules converted to product molecules by an enzyme molecule in a unit time when the enzyme is full saturated
kcat cannot be greater than the diffusion controlled limit ≈10^6 - 10^7
randomly bouncing in solution until it reaches active sites
significance of VMax
k2*[Etot]
VMax equation
can be found experimentally
you know [Etot] cause you set up the experiment'
enzyme efficiency
kcat / KM
temp changes
pH change (picking up proton/protonated or deprotonated states)
inhibitor molecules (slow rxn down)
Reversible Inhibitors
Competitive, Uncompetitive & Noncompetitive
Irreversible Inhibitors
considered negative allosteric effector'
control rxn rates of enzyme in cells
modulating enzyme activity
the rxn unfolds
Rxn rates increase …
substrate can’t get into active sites
enzyme is out of actions
once binded, cant be undone
completely inactivate the enzyme
usually form an unbreakable covalent bond with functional group in active site
could bind enzyme so tightly that it does not dissociate from the enzyme
irreversible inhibitors
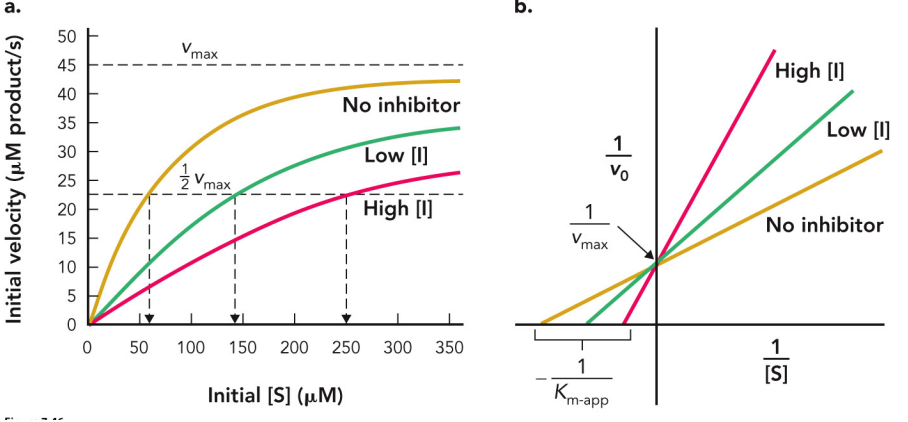
A molecule that inhibits substrate binding at the active site
Can bind to the active site or obstruct the substrate from binding through steric clash
Can be overcome by increasing [S]
Vmax is unchanged, but Km values change
binds to active site on enzyme
looks similar to substrate/product
competitive inhibition
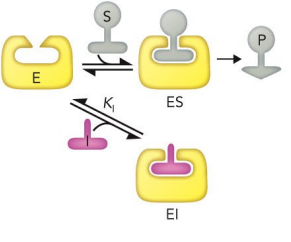
uncompetitive inhibition
Binds to the enzyme-substrate complex and alters the active site conformation
Often acts upon enzymes with multiple substrates
Both Km and vmax are decreased.
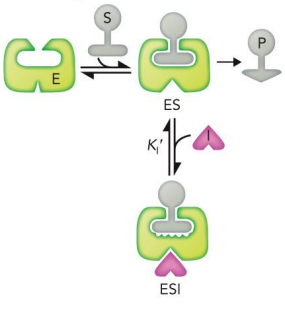
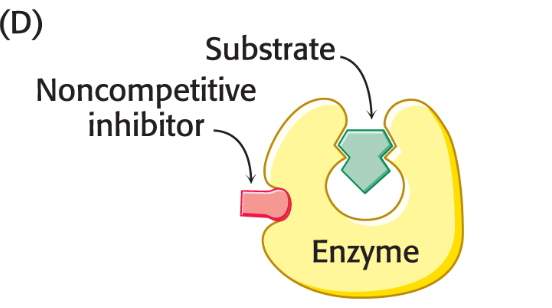
mixed inhibition
Binds to sites unique from the active site
Can bind to both the enzyme and the enzyme-substrate complex
Lowers vmax and may increase or decrease Km