C11: Analysis of Variance
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
A type of hypothesis testing that uses sample data on categorical variable to draw inferences about a population.
Tests whether the means of multiple groups are different by comparing the variance between the group means to the variance within each group.
What are two types of anova (as discussed)? and differentiate them.
One-way ANOVA
—> requires one factors
—> determines if the means from groups within one factor differs
Two-way ANOVA
—> require two factors
—> determines if the means from groups across two factors differ
—> calculates whether there is a statistically significant interaction involving two factors.
What is one-way ANOVA’s null and alternative hypotheses?
H(0) = All means are equal. The is the baseline or “default”hypothesis
H(1) = At least one of the means differs from the others. (This is the research hypothesis)
In a one-way ANOVA, what happens when you reject H(0)?
If you reject H(0), it requires a post hoc (or “after the fact”) analysis, the Tukey Test:
List each pairwise comparison (e.g., A versus B / A versus C)
Calculate the absolute value of the difference between each mean in the comparison.
Calculate Q critical
For each pairwise comparison, examine the absolute difference to Q critical:
(i) If the absolute difference > Q critical, then difference in means is statistically significant.
(ii) If the absolute difference < Q critical, then difference in means is statistically insignificant.
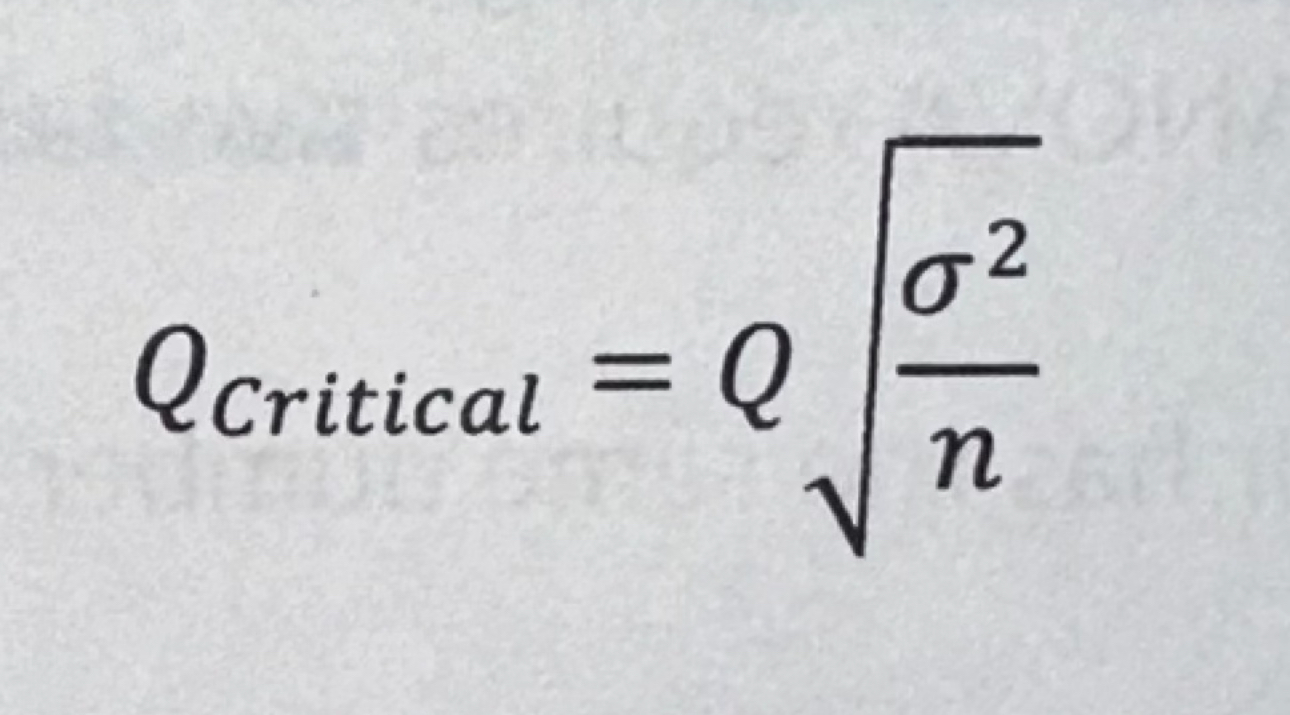
When excel performs two variations of two-way ANOVA tests?
Two-factor with replication: each factor has multiple observations
Two-factor without replication: each factor has one observation
What are the null and alternative hypotheses for two-way ANOVA test?
Hypothesis Test:
(i) H(0) = All means are equal.
(ii) H(1) = At least one of the means differs from the others
Hypothesis Test on Interaction between factors:
(i) H(0) = There is no interaction between factors.
(ii) H(1) = There is an interaction between factors.
For two-way ANOVA test, how do you reject or not the hypotheses? and conclusion
If p < alpha = reject H(0)
If p > alpha = do not reject H(0)
Conclusion should reference the original data/problem
What is the excel process for One-way ANOVA?
State H(0) and H(1)
Select Anova: Single Factor that calculates descriptive statistics and calculate the p-value.
Then, determine to reject H(0) or do not reject H(0).
Finally, the conclusion should reference the original data/problem.
What are the types of examples that will be used?
Only balanced examples will be worked on which mean like each group has same number of observations.
What is the usual alpha?
0.05 or 0.01