IB Biology Topic 1
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Cell Theory
1. All living things are composed of cells
2.The Cell in the fundamental unit of life
3. Cells only arise from pre-existing cells
Striated Muscle
Long Cells, (300 mm), multiple nuclei, questions cell theory
Acetate Fungal Hyphae
challenges idea that cell is a single unit, multi-nucleated, and continuous cytoplasm. Cell walls composed of Chitin
giant algae
challenges that notion that cells must be small, and simple in structure. Size of 5-100mm and complex in form.
response
Living things can respond to and interact with the environment
Homeostasis
The maintenance and regulation of internal cell conditions, e.g. water and pH
Growth
Living things can grow/change
excretion
removal of metabolic waste
reproduction
living things produce offspring, sexually or asexually
nutrition
feeding by either the synthesis of organic molecules (e.g. photosynthesis) or the absorption of organic matter
SA to Volume Ratio
A larger SA:Vol ratio can mean that a cell can act more efficiently. For every unit of volume that requires nutrients or produces waste. There is more membrane to serve it
How to maximize SA to Vol ratio?
Cells divide, They use membranes to carry out processes, organs will fold up to maximize the ratio
Rate of Metabolism
a function of mass/volume
emergent properties
when things are added more properties arise
specialized cells
All specialized cell and the organs constructed are from differentiation
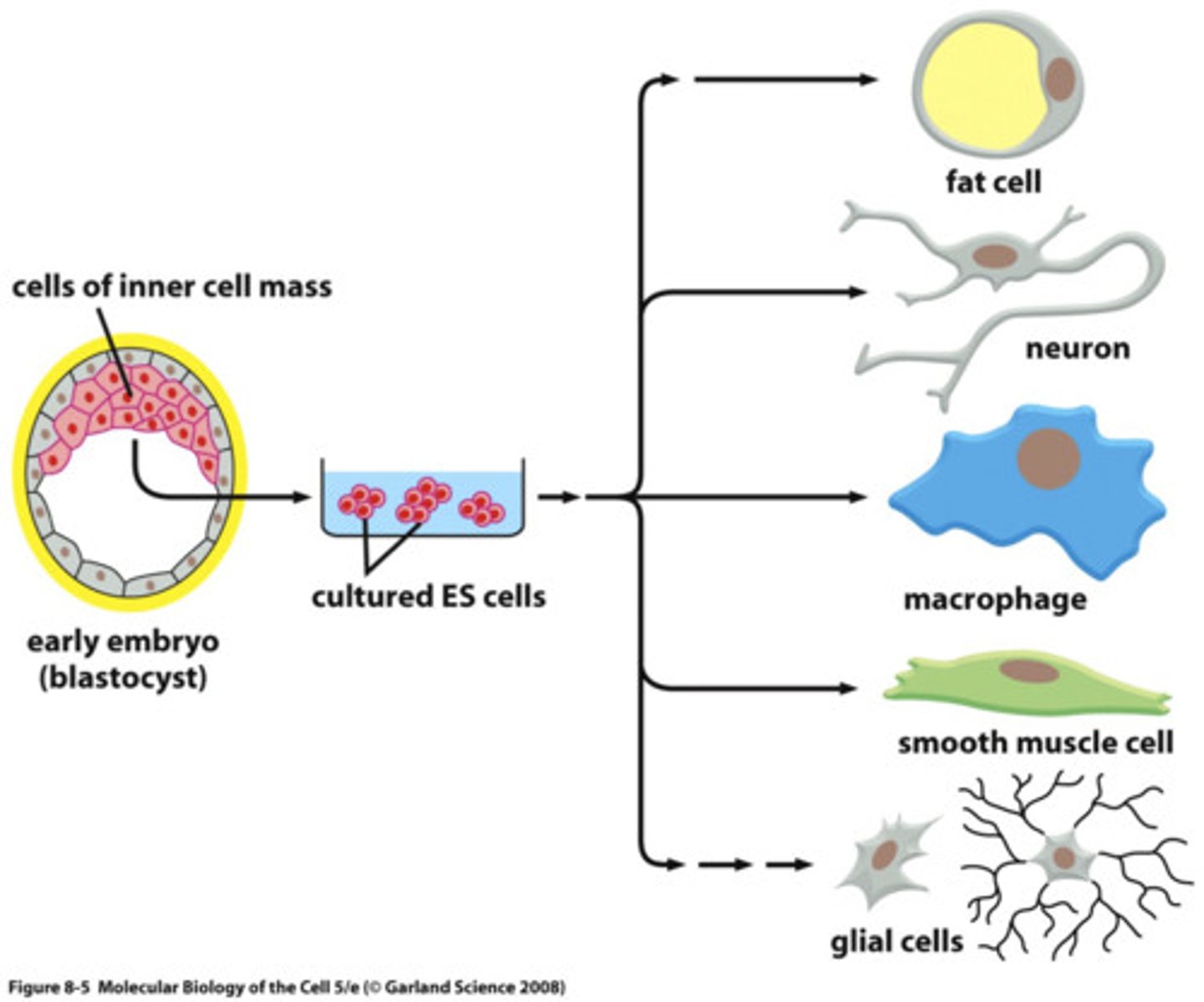
Stem Cells
unspecialized cells that can differentiate into many cell types
Totipotent
Can differentiate into any cell
pluripotent
Can differentiate into many cells
multipotent
can differentiate into a few closely related cells
unipotent
Can regenerate,but only into associated cell type
Stagardt's Macular Distrophy
A recessive condition for the eyes, stem cells are treated to become retinal cells. Cells attach to the retina and improves central vision
Lukemia
Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs) are harvested from bone marrow, peripheral blood or umbilical cord blood
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy used to destroy the diseased white blood cells New white blood cells need to be replaced with healthy cells. HSCs are transplanted back into the bone marrow HSCs differentiate to form new healthy white blood cells
Embryonic Stem Cell Structure
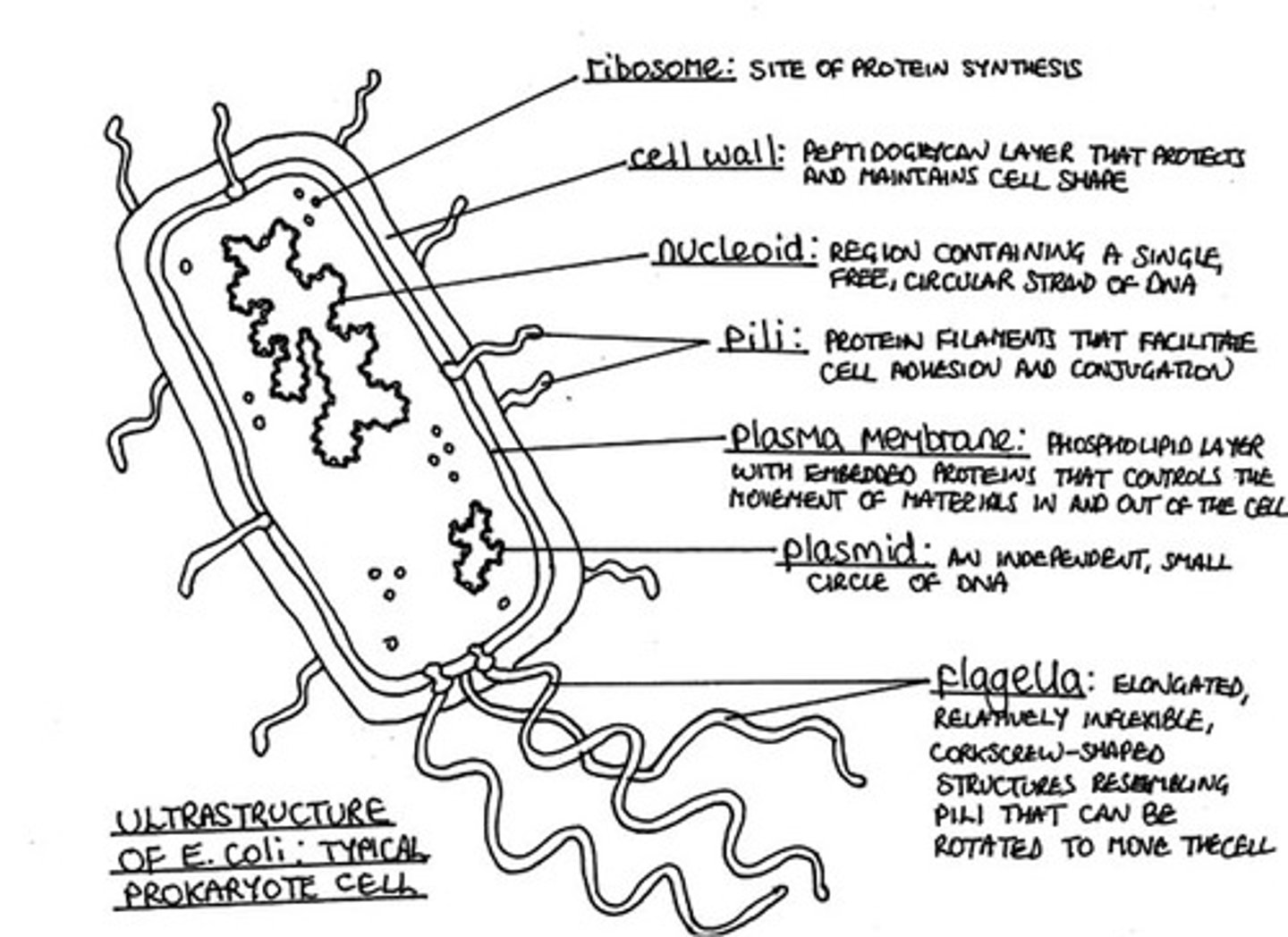
Prokaryote Cell Structure
approximately 0.5 μm
Prokaryotic Reproduction
Asexually through binary fission.
Steps of Binary Fission
1. Two loops attach to membrane
2. Elongation and pinches off
3. Two identical cells
Properties of Prokaryotes
Their DNA is not enclosed in within a membrane and forms on circular Chromosome
Their DNA is free; it is not attached to proteins
They lack membrane-bound organelles. Ribosomes are complex structures within the plasma membrane, but they have no exterior membrane
Their cell wall is made up of a compound called peptidoglycan
They usually divide by binary fission, a simple form of cell division
They are characteristically small in size, usually between 1 and 10 µm
Eukaryote Cell Structure
1 micrometer
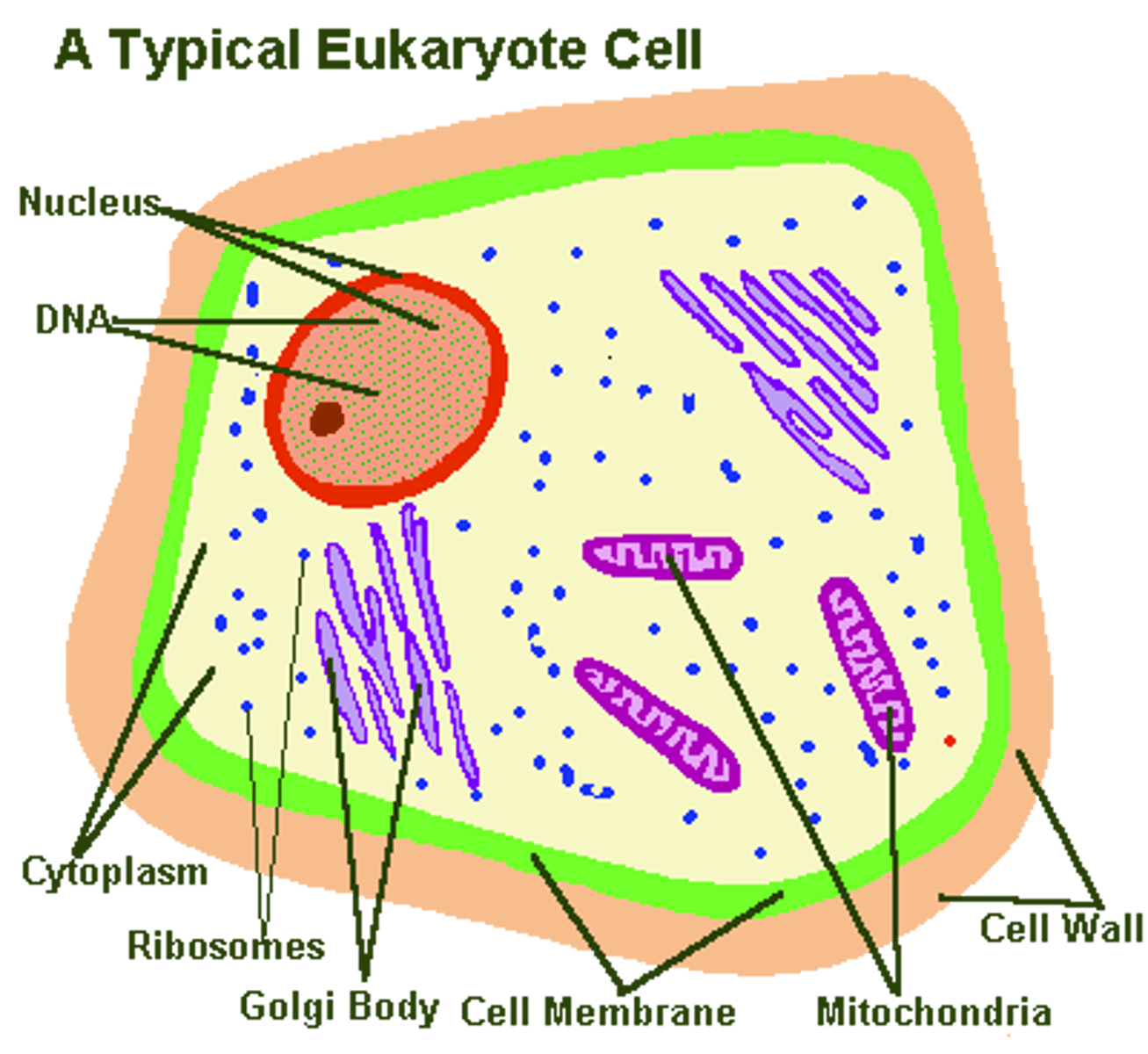
Nucleus
Generally Spherical with a double membrane. Pores and holes are present. Contains Chromosomes.
Mitochondion
Has a smooth outer membrane. Folds are cristae. Variable Shape. Site of ATP production by aerobic energy
Free Ribosomes
80S ribosomes. No membrane, appear as dark granules in cytoplasm. Synthesizes proteins to function in cytoplasm.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Consists of Flattened membrane sacs (cisternae). Located near nucleus. 80S ribosomes are attached to outside of cisternae
rEr synthesizes transported proteins by vesicles to golgi for modification
Golgi Apparatus
Contains cisternae
No attached ribosomes
often sited close to plasma membrane
shorter and more curved than the rER. modifies proteins from the rER , the repackaged in vesicles
Vesicles
A single membrane with fluid
Small
Transport Materials inside cell
Lyosomes
Spherical with single membrane
Golgi vesicles
Digestive enzymes from breakdown of:
food
unwanted organelles
cell itself
High concentration of enzymes, cause this to stain heavily and hence appear dark on micrographs
Vacuoles
Single Membrane with fluid inside
Plant cells vacuoles are large and permanent often occupying cell volume
In animals vacuoles are smaller and used for various other reasons
Flagellum
Thin projection from cell surface. Contain microtubules
Used to move cell
Cillia
Thin projections from cell surface
Contain Microtubules
Used to either move cell or the move the fluids next to the cell
Microtubules
Small Cylindrical fibers
Have a variety of functions, part of flagella. Cell division
Centrioles
Nine triple miroctubules
manly found in animal cells not vascular plants of fungi
Chloroplast(plant only)
Many, but not all plant cells contain chloroplasts
Inside are thylakoids
Flattened membrane
Shape is variable,but usually ovoid
Site of photosynthesis and hence where glucose is produced
Starch grains may be present if photosynthesis is quick
Cell Wall (plants only)
extracellular secreted by plants
permeable
Strong
Hard to Digest
Ribosomes in Prokaryotic
70S
Ultrastructure
is all the structures of a biological specimen that are at least 0.1nm in their smallest dimension
Phospholipid Structure (Words)
Hydrophillic Head
Hydrophobic Tail
Emergent Property of Phospholipid
Heads are wet and tails are dry
Phospholipid Bilayer
is one way that the tails are removed from water
Plasma Membrane Structure
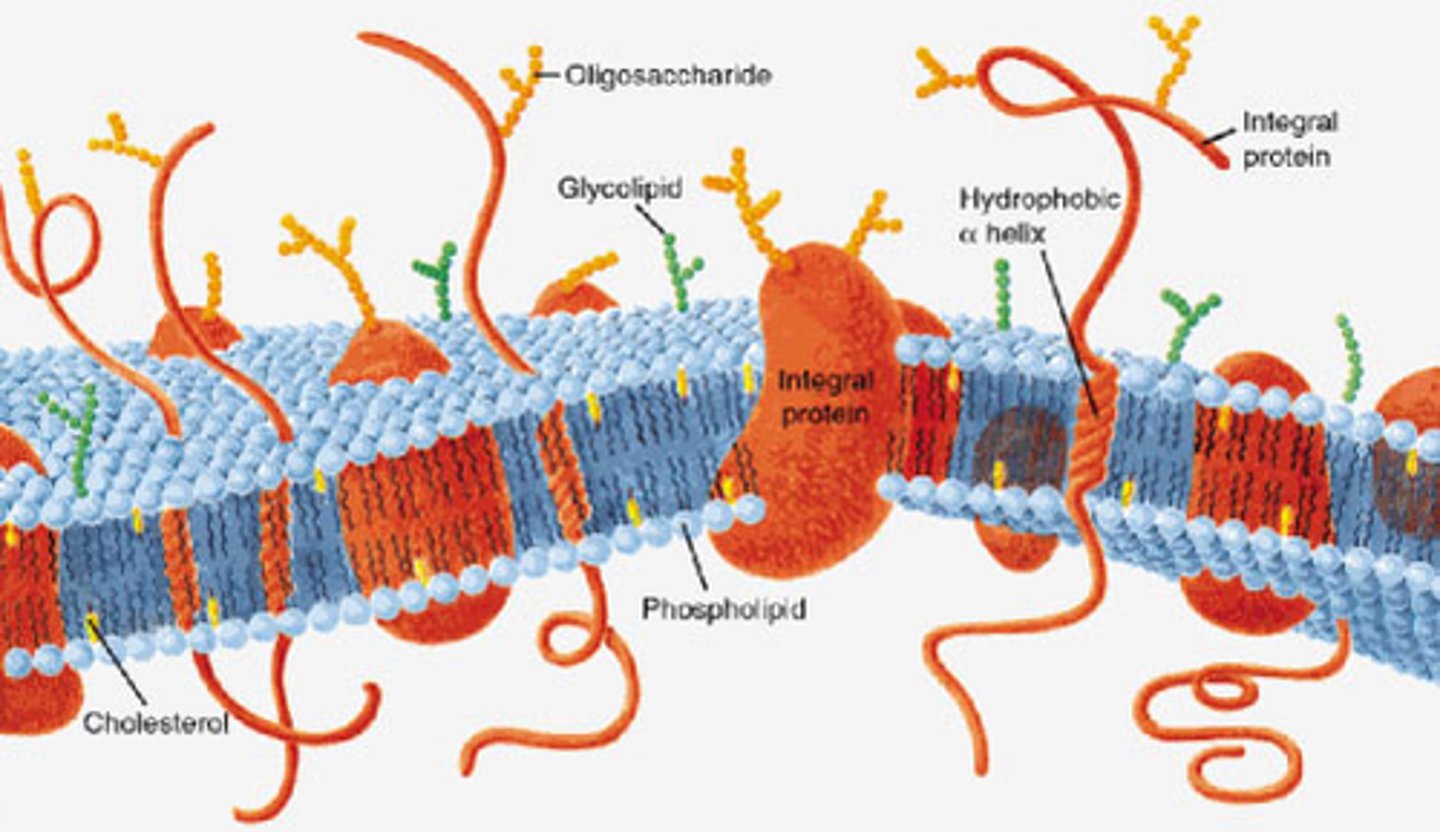
Integral Proteins
Permanently embedded many go all the way through and are polytopic, some are monotopic
Polytopic
Many Surfaces
Peripheral Proteins
Temporary association and are monotopic
oligosaccharide
sugar chain attached. Cell recognition by immune system as hormone receptors
T in Tracie
Transport
R in Tracie
Receptors
A in Tracie
Anchorage
C in Tracie
Cell Recognition
I in Tracie
Intercellular Joinings
E in Tracie
Enzymatic Activity
Transportation
Protein Channels and Pumps
Receptors
Peptide based hormones
Anchorage
Cytoskeleton attachments and extracellular matrix
cell recognition
MHC proteins and antigens
Intercellular joinings
Tight Junctions and plasmodesmata
Enzymatic Activity
Metabolic pathways
Cholestrol
Makes phospholipids pack more tightly and regulates fluidity and flexibility of memebrane.
What does presence of cholesterol do?
restricts movement. Disrupts regular packing of the hydrocarbon tails. This increases flexibility
Signer- Nicolson
Membrane proteins are varied in size and globular. Such proteins are unable to form continuous layers
Davson-Danielli
A protein-lipid sandwich. Proteins coat surface. Do not permeate the bylayer.
Falsification
The fracture occurs along lines of weakness, including the center of membranes.
The fracture reveals an irregular rough surface inside the phospholipid bilayer
Selectively Permeable
Some cannot pass through and different forces
Diffusion
Net movement of particles from high to low concetration.
Osmosis
When a cell is submurged water molecules pass through the cell from low to high solute concentration.
Hyoertonic
Lowe concentration of solutes
Isotonic
When the concentrations are equal on both sides
Hypotonic
higher concentration of solutes
Facilitated Diffusion
proteins recognize a particular molecule and help it move across the membrane.