Radiation Oncology: Indications & Adverse Effects
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
How does radiation therapy kill cells?
• 1/3rd of time the radiation directly hits the DNA
• 2/3rd of time the radiation creates ROS and causes indirect damage
What type of cell death does radiation therapy cause?
Mostly causes mitotic cell death, but some tumor types (lymphoma, MCT, thymoma) have apoptotic death
What is stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT)?
High dose per fraction delivered over a short (<5 fractions) period of time = hypofraction
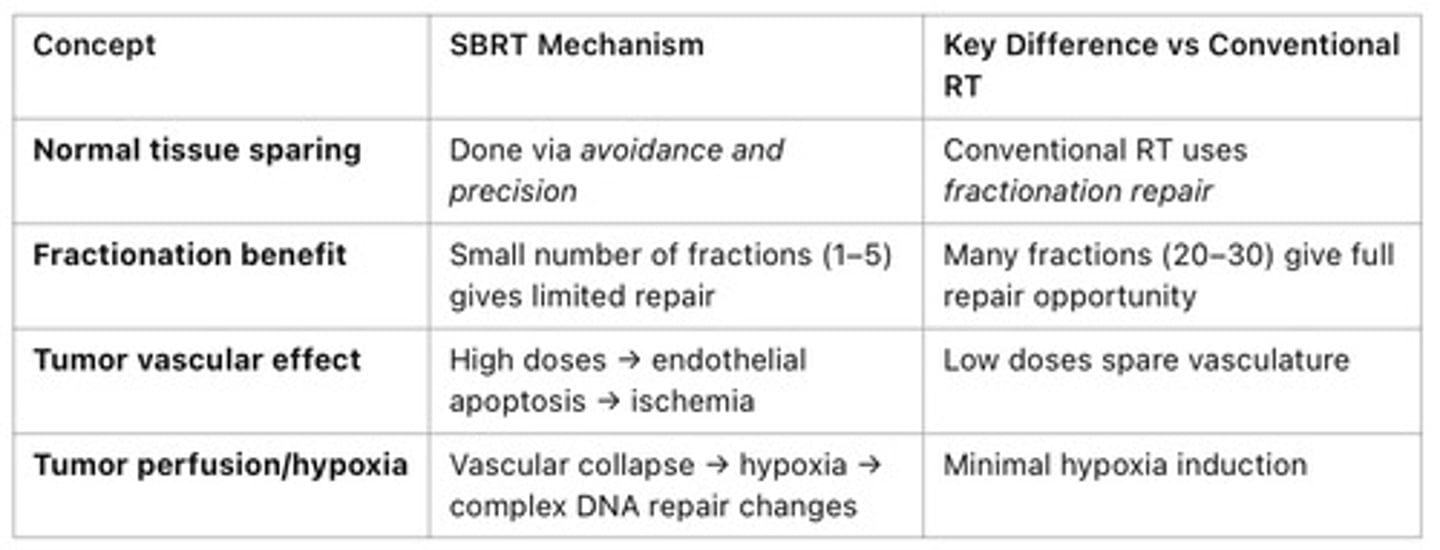
How does SBRT spare normal tissue?
Avoidance through collimation
SBRT qualifications
gross disease, intact, healthy skin
SBRT disqualifications
pathologic fracture, oronasal fistula, inability to adequately avoid normal tissues
SBRT requirements
o CT scan
o Immobilization
o Target localization
OSA biggest risk factors with SBRT
Pathologic fracture and skin changes
SBRT vs conventional RT
How can radiation be used for palliative care?
• Improve function
• Improve hygiene
• Unobstruct urethra/ureter
• Stop bleeding
What is IMRT?
• Conformal radiation therapy based on CT scan
• Fractionated OR hypofractionated
Advantages of IMRT
treats complex tumor shapes and minimizes dose to normal tissues
What are some neoplastic conditions treated with RT?
• Osteosarcoma
• Nasal tumors
• Brain tumors
• Soft tissue sarcomas
• MCT
• Oral malignant melanoma
• TCC
• Cardiac hemangiosarcoma
• Chemodectoma
• Adrenal tumors
• Liver tumors
• Lung tumors
• Thyroid carcinoma
What are some non-neoplastic conditions that can be treated with radiation therapy?
• Sialocele
• OA
• MUO
• Pulmonic stenosis
• Feline idiopathic cystitis
Acute adverse effects
o Within first three months
o Cells with rapid turnover: skin, GI tract, hematopoietic system
Early delayed adverse effects
2 weeks to 4 months to neuro tissue due to demyelination or edema
Late adverse effects
o 3 months to years
o Slow dividing tissues: lung, kidney, heart, bone, liver
Where do radiation effects occur?
within the radiation field and are related to the tissues that have been exposed to radiation
What are some examples of adverse effects?
• Nausea hours after irridiating abdomen from release of 5HT
• Fatigue from ROS
• Pneumositis from destruction of type I pneumocytes
• Mast cell degranuation minutes to weeks
Mast cell degranulation signs
erythema, edema, hypotension, vomiting, hyporexia, melena, coagulation abnormalities
Acute CNS adverse effects management
pretreat with prednisone, mannitol or hypertonic saline for herniation
Skin fibrosis management
pentoxifylline and vitamin E make RBCs and WBCs more flexible so that they can penetrate through smaller vessels and get to fibrosed tissue
Esophageal stricture management
dilations and semi-solid diet, feeding tubes, hydrocortisone injection at stricture site
Ostenecrosis management
surgical debridement, antibiotics, hyperbaric oxygen
Drug interactions
• Use of some chemotherapeutics can exacerbate radiation side effects: dacarbazine, iomustine, doxorubicin, cisplatin, gemcitabine, paclitaxel, toceranib (GI)
• Concurrent use of antioxidants may interfere with radiation cell killing due to interference with damage from ROS