chapter 11 - membrane structure
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
membranes are _ barriers
selective barriers
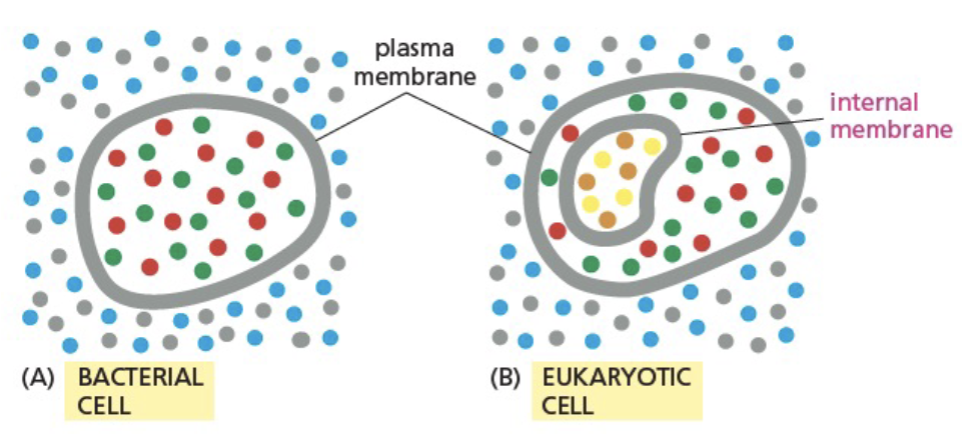
molecular composition of a cell is same/different from its environment
different
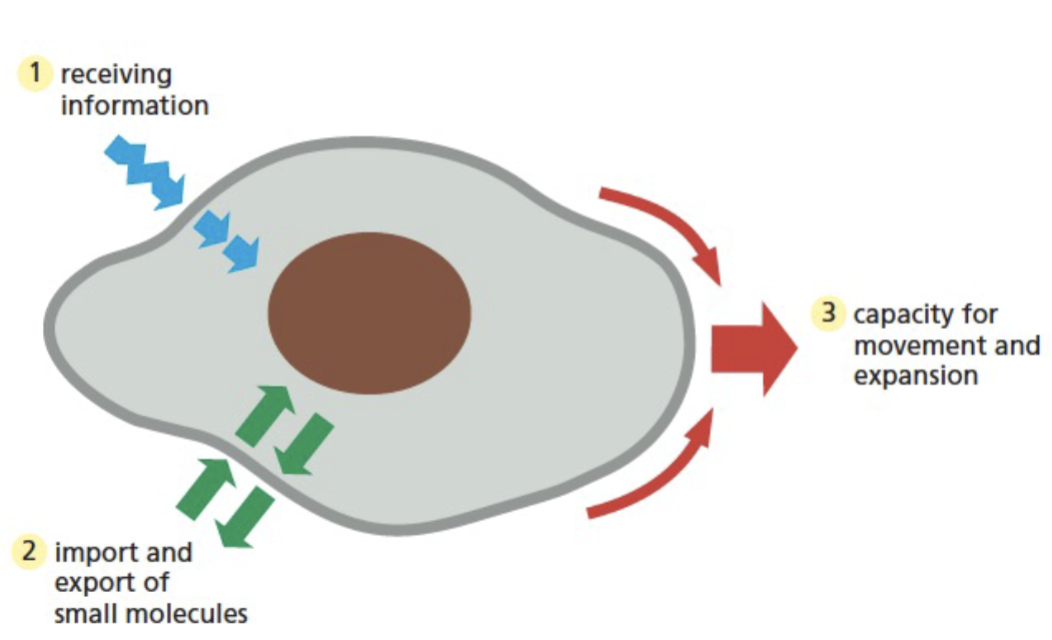
the plasma membrane is involved in
cell communication
import and export of molecules
cell growth
motility
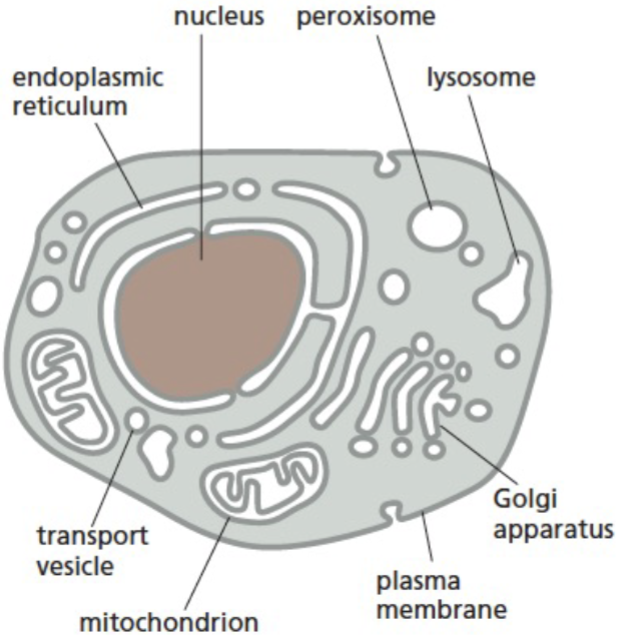
internal membranes form different _ in eukaryotic cell
form different compartments
membrane composition
lipids
phospholipids
glycolipids
sterols
amphipathic
proteins
integral
peripheral
lipids - phospholipids
most abundant component
lipids - glycolipids
sugar part of head group
lipids - sterols
e.g. cholestrol
proteins - integral
directly attached to membrane
proteins - peripheral
loosely associated with membrane
fluid mosaic model of cell membrane
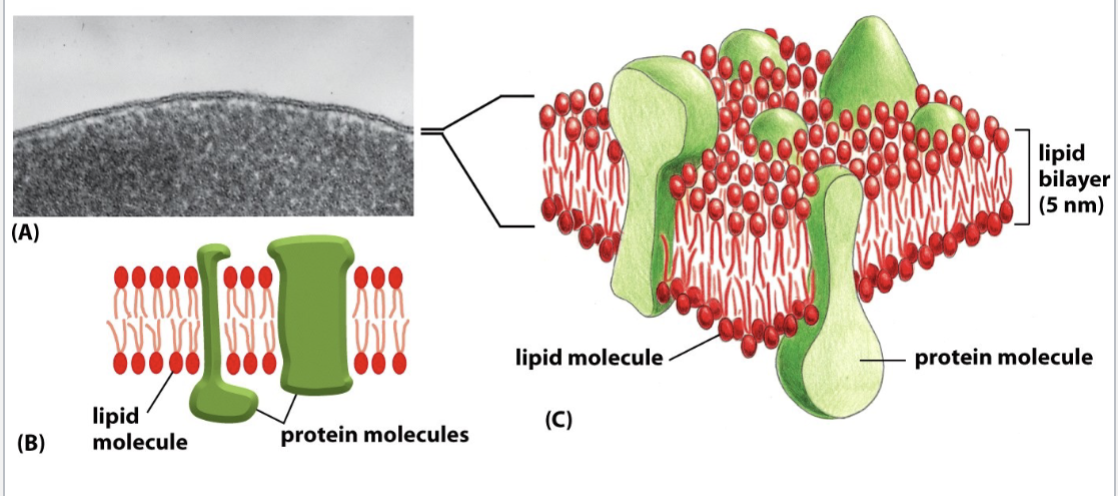
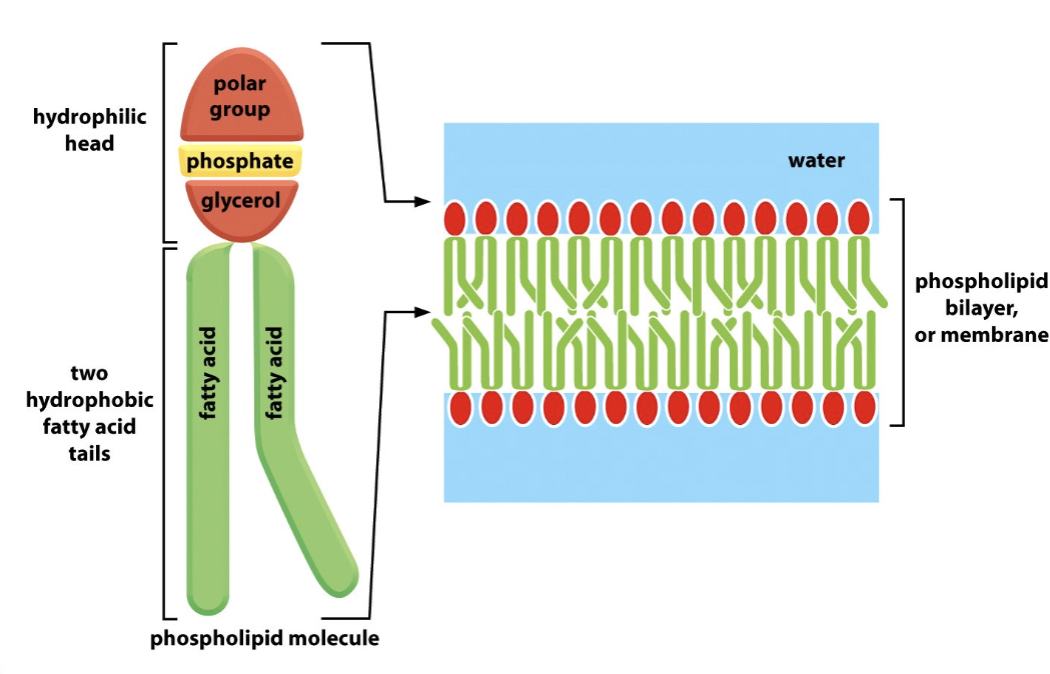
amphiphatic phospholipids for a lipid _
lipid bilayer
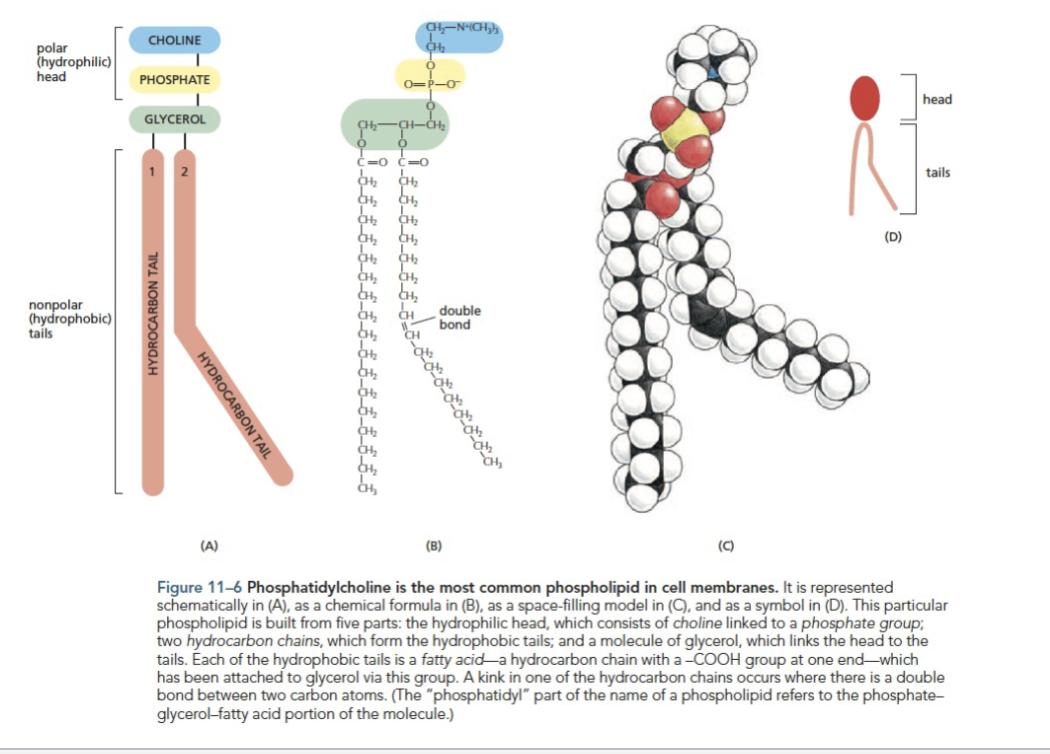
_ is the most common phospholipid in cell membranes
phosphatidylcholine
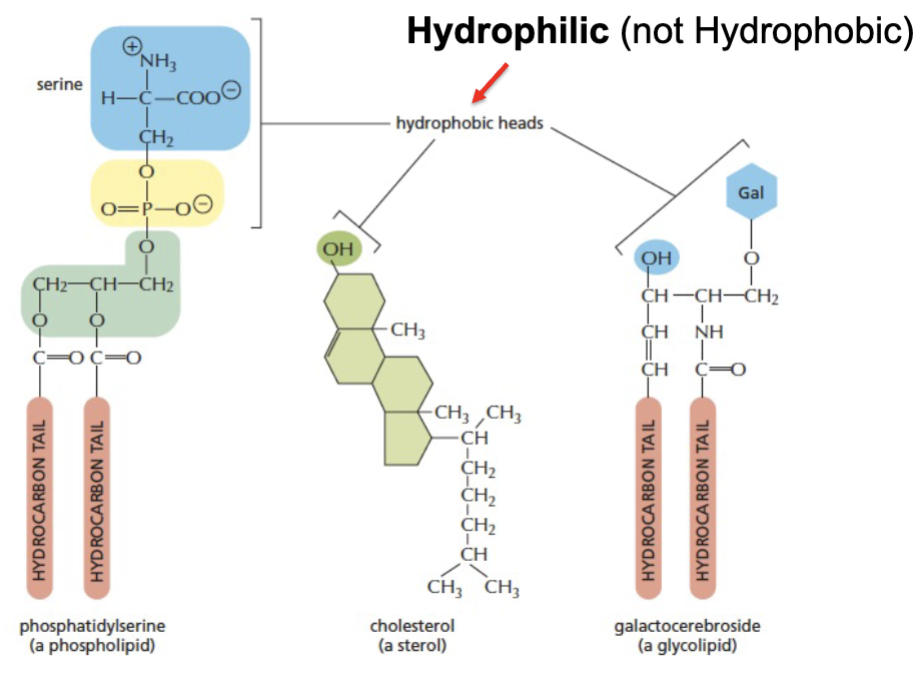
different types of membrane lipids are _
amphiphatic
a phospholipid bilayer with spontaneously rearrange to eliminate _
eliminate free edges
helps repair damage
helps with formation of a closed compartment - liposome
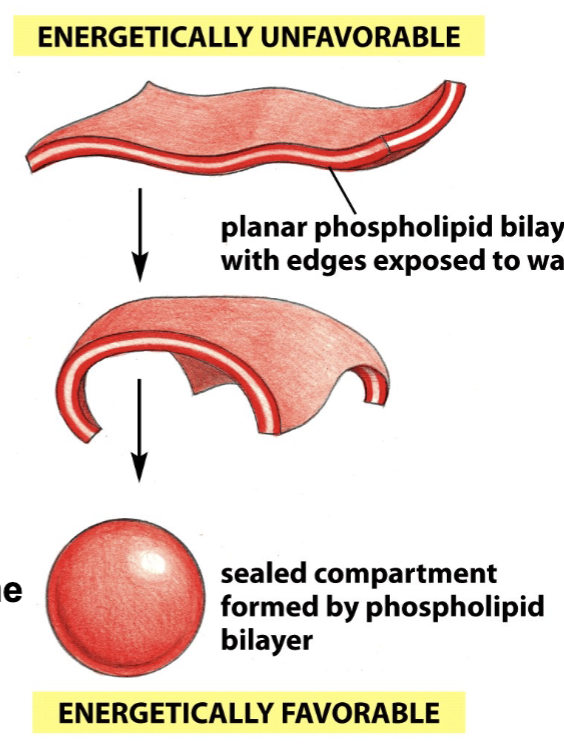
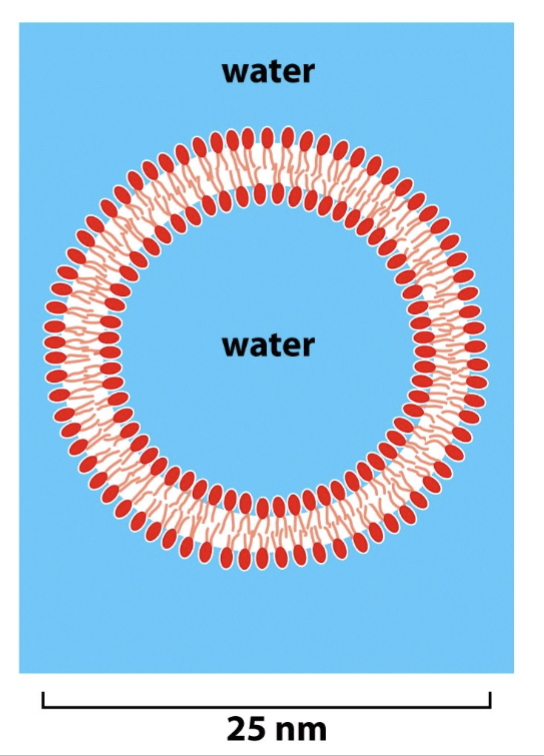
liposomes ( and vesicles) have a _ bilayer and an _ interior
have a phospholipid bilayer and aqueous interior
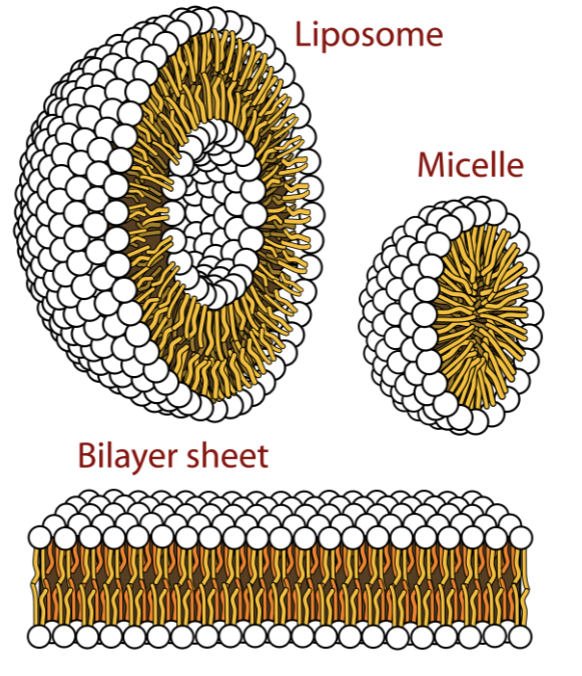
liposome vs micelle
membranes behave as a _ fluid
behave as a two dimensional fluid
molecules move
the fluidity of a cell membrane
the ease with which its lipid molecules move within the plane of the bilayer
its important for membrane function and has to be maintained within certain limits
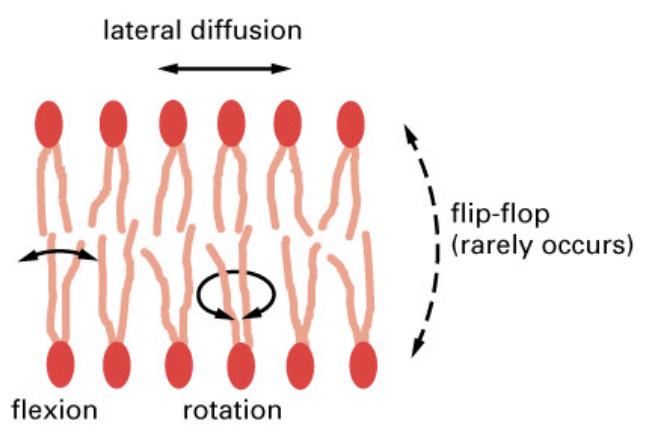
fluidity is/is not the same as flexibility (bending)
fluidity is not the same as flexibility (bending)
factors affecting membrane fluidity
phospholipid composition
sterols
phospholipid composition and fluidity
fatty acid chain length - short chains increase fluidity
fatty acid chain saturation - double bonds increase fluidity
chain length and level of saturation determines the properties of fats
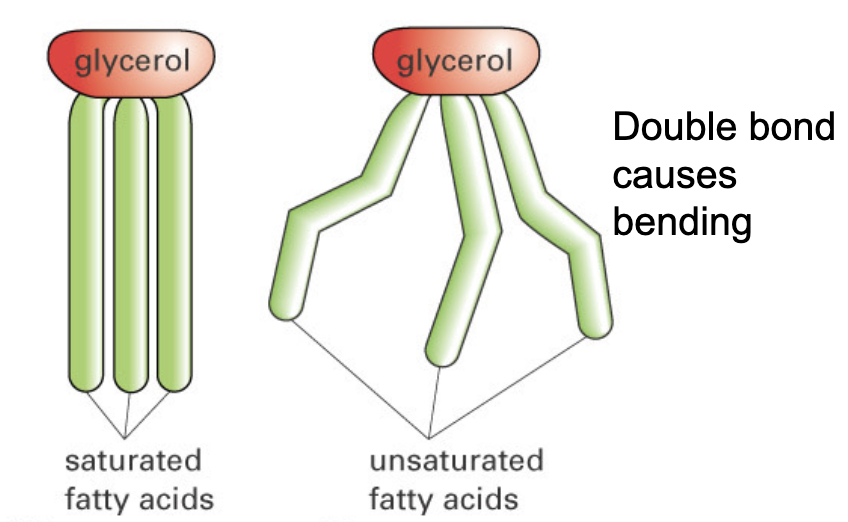
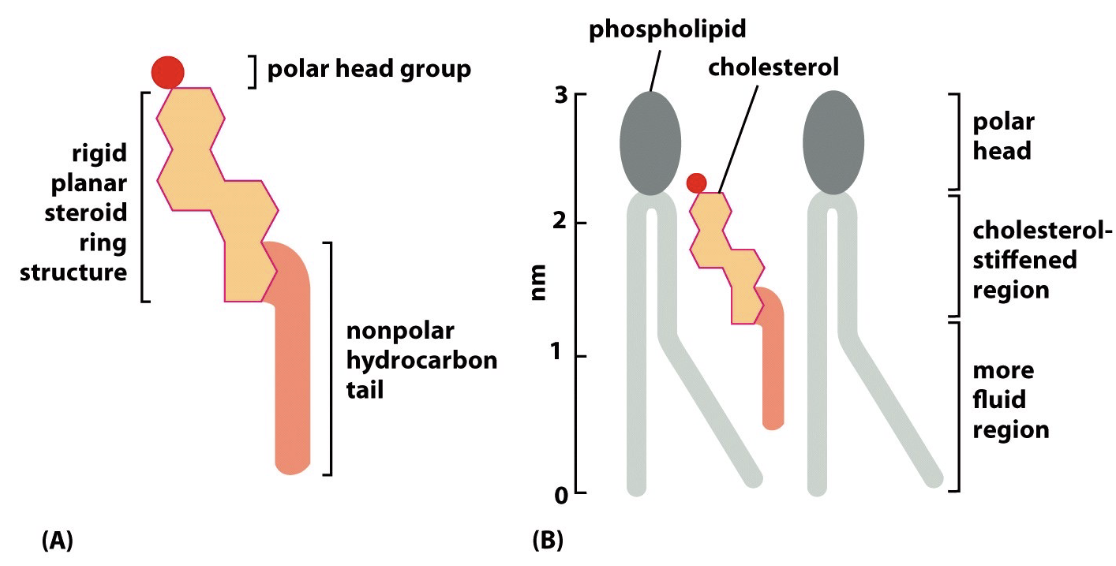
sterols and fluidity
cholestrol - more cholestrol decreases fluidity
adds rigidity
but cholestrol can increase fluidity if most fatty acids are saturated
_ fills spaces in the bilayer
cholestrol fills spaces
makes the bilayer more rigid
amphipathic
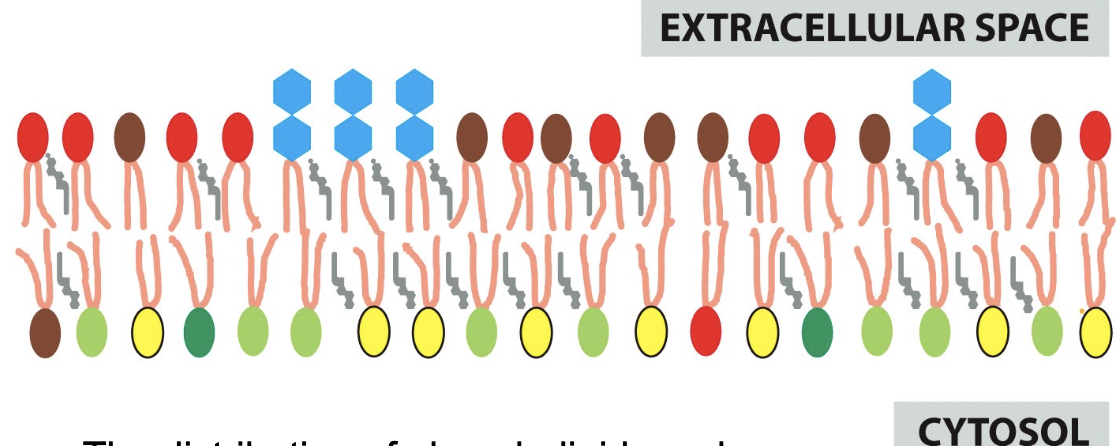
membranes are symmetrical/asymmetrical
asymmetrical
the distribution of phospholipids and glycolipids creates different surfaces
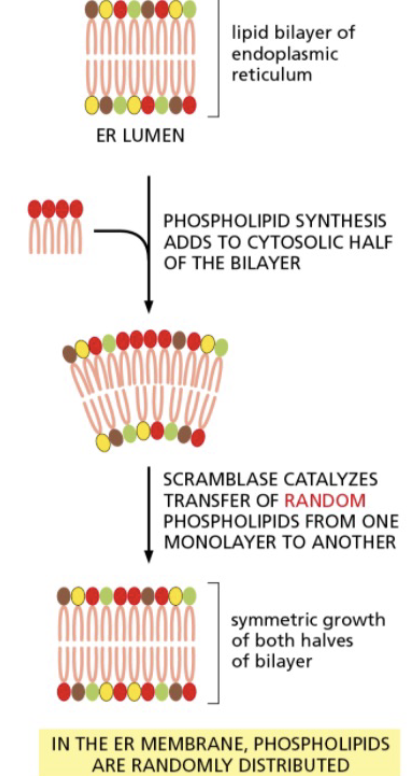
membrane assembly beings in the _
begins in the ER
flippases have specificity for different types of phospholipids
newly synthesized phospholipids are added to the cytosolic side of the ER membrane and then redistributed by transporters that transfer them from one half of the lipid bilayer to the other
biosynthetic enzymes bound to the cystosolic monolayer of the ER membrane produce new phospholipids from free fatty acids and insert them into the cytosolic monolayer
transporters called scramblases then randomly transfer phospholipid molecules from one monolayer to the other, allowing the membrane to grow as a bilayer in which the two leaflets even out continuously in size and lipid composition
cell molecular structure
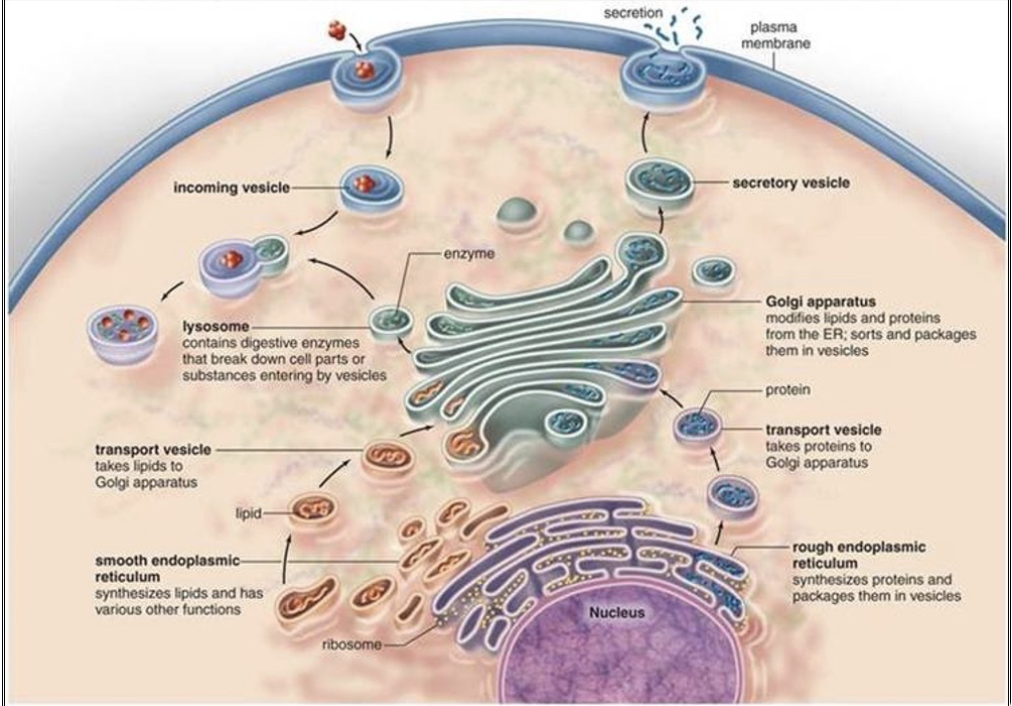
certain phospholipids are confined to one/multiple side of the membrane
confined to one side of the membrane
flippases help to establish and maintain the asymmetric distribution of phospholipids characteristics of animal cell membranes
when membranes leave the ER and are incorporated in the golgi, they encounter a different set of transporters called flippases, which selectively remove phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine from the noncytosolic monolayer and flip them to the cytosolic side
this transfer leaves phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin concentrated in the noncytosolic monolayer
the resulting curvature of the membrane may help drive subsequent vesivle budding
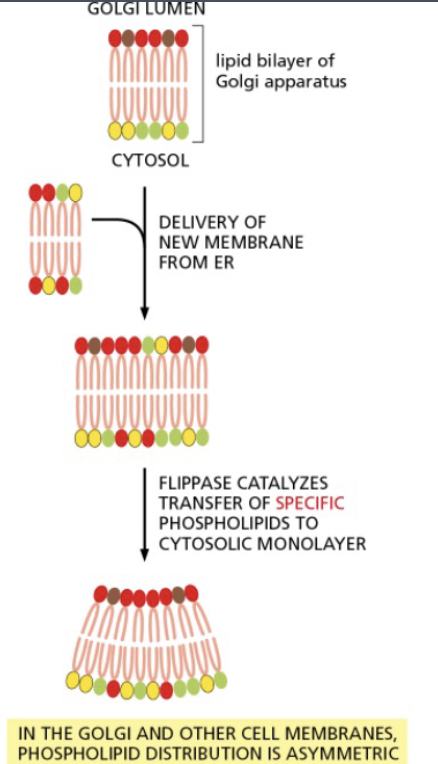
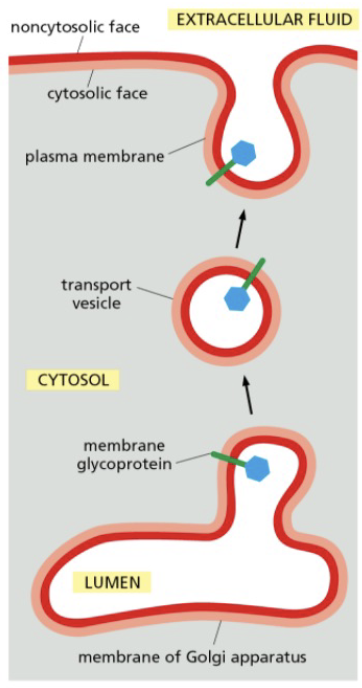
membranes retain their orientation during transfer between _
transfer between cell compartments
membranes are transported by a process of vesicle budding and fusing
a vesicle buds from the golgi and fuses with the plasma membrane
the orientation of both membrane lipids and proteins are preserved during the process
the original cytosolic surface of the lipid bilayer remains facing the cytosol
the noncytosolic surface continues to face away from the cytosol, toward the lumen of the golgi and the transport vesicle or towards the extracellular fluid
the glycoprotein remains the same orientation with its attached sugar facing the noncytosolic side
glycolipids obtain their sugar from _
from the inside of the golgi
when these membranes are transferred to the plasma membrane, the sugar groups remain oriented on the no cytosolic face
membrane proteins carry out
carry out most membrane functions
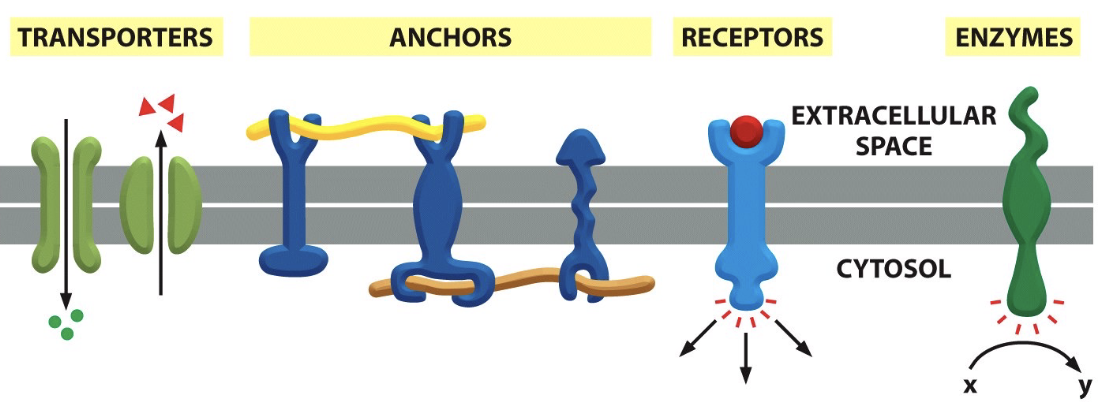
different ways in which membrane proteins can associate with a lipid bilayer
integral
transmembrane
membrane associated
lipid-linked
peripheral
protein -ttached
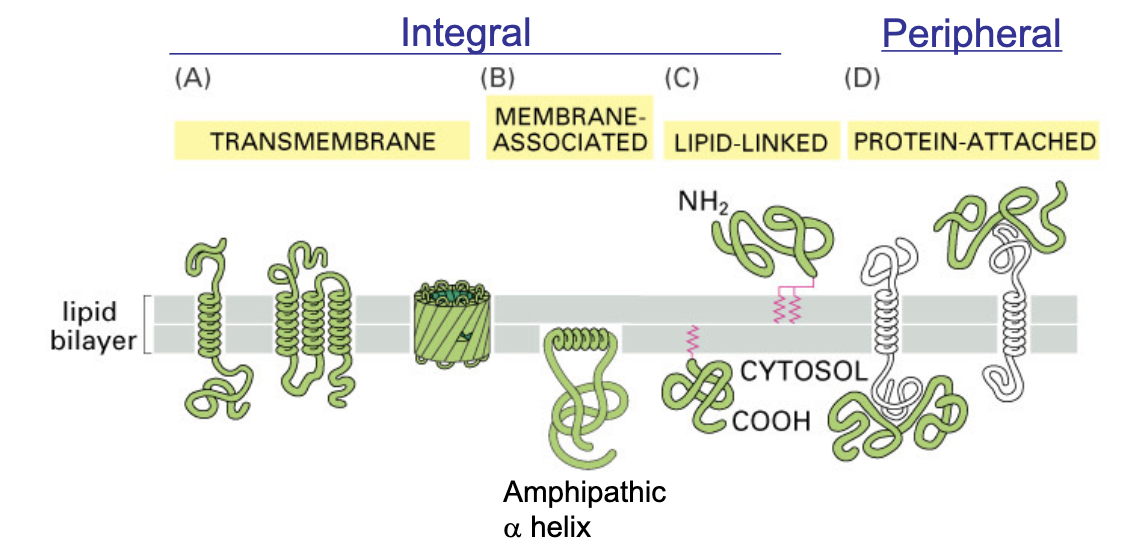
integral membrane proteins can be removed from membranes only by _
removed only using detergents
peripheral membrane proteins can be removed by _
removed by more gentle extraction methods
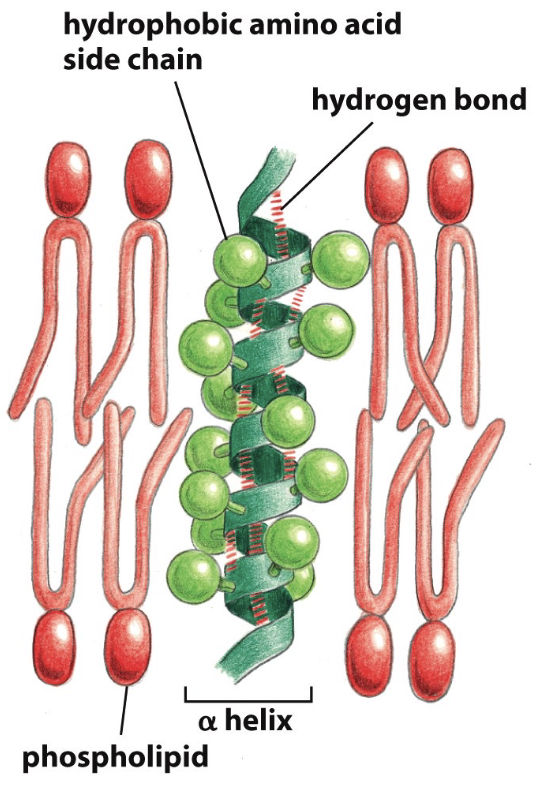
an alpha helix containing many _ can span a membrane bilayer
many nonpolar amino acids
the hydrophilic polypeptide backbone (stabilized by h bonds) is shielded from the hydrophobic lipid carbons
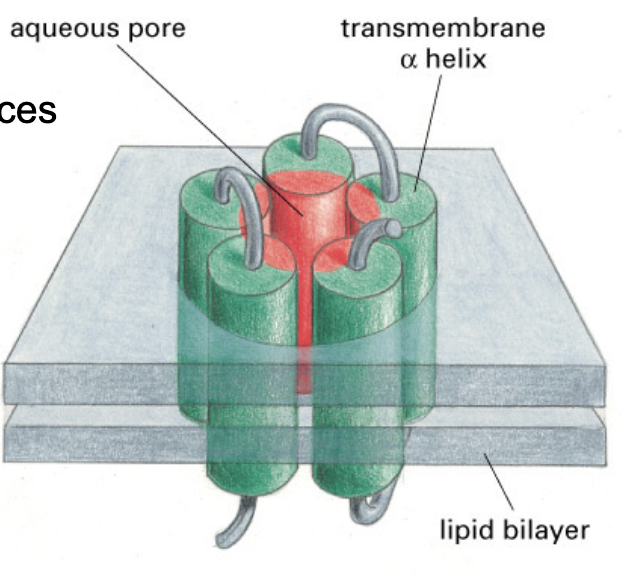
multiple amphiphatic alpha helices can associate to form a _
form a hydrophilic core
individual helices would not be stable in the membrane due to their hydrophilic side chains
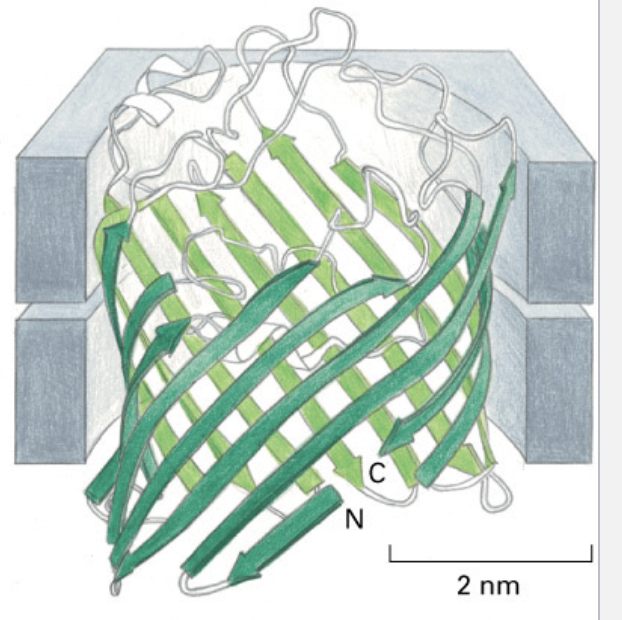
a large. curved beta sheet can form a _ that spans the membrane
can form a beta barrel
the amino acid side chains alternate between hydrophilic and hydrophobic to create a water filled interior and hydrophobic exterior that facets the bilayer core
a single beta strand cannot shield its hydrophilic backbone regardless of the side chain composition
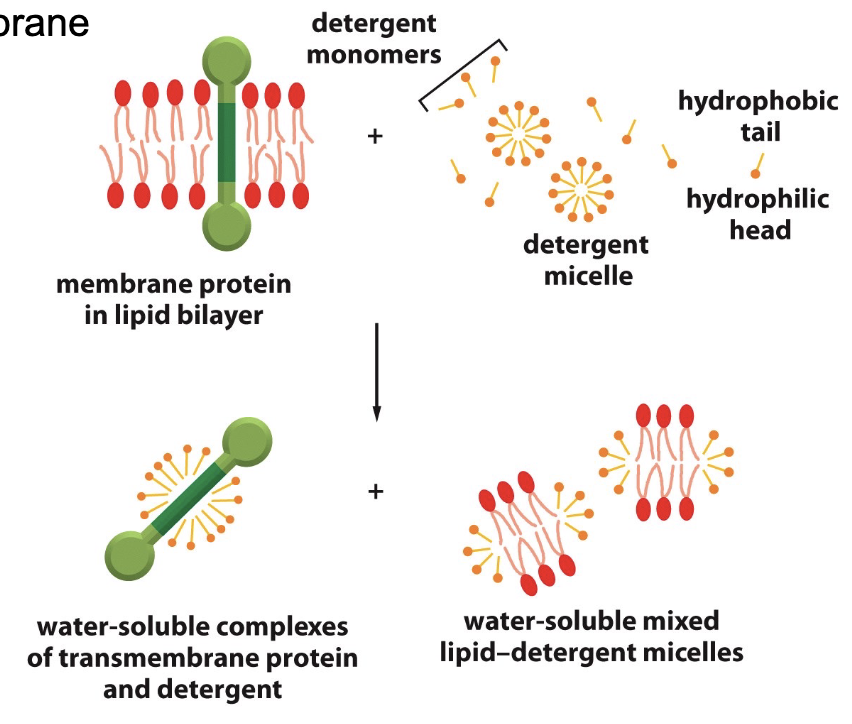
detergents are used to separate
separate integral membrane proteins from the lipid bilayer
disrupt hydrophobic associations
solubilization of integral membrane proteins
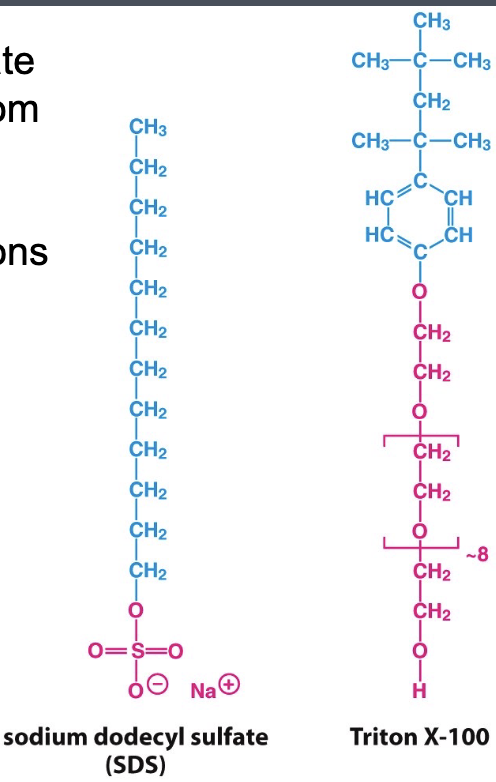
properties of detergents
amphiphatic
single hydrophobic chain
do not form bilayers
carbohydrate layer of cell surface - composition
glycoprotein
proteoglycan
glycolipid
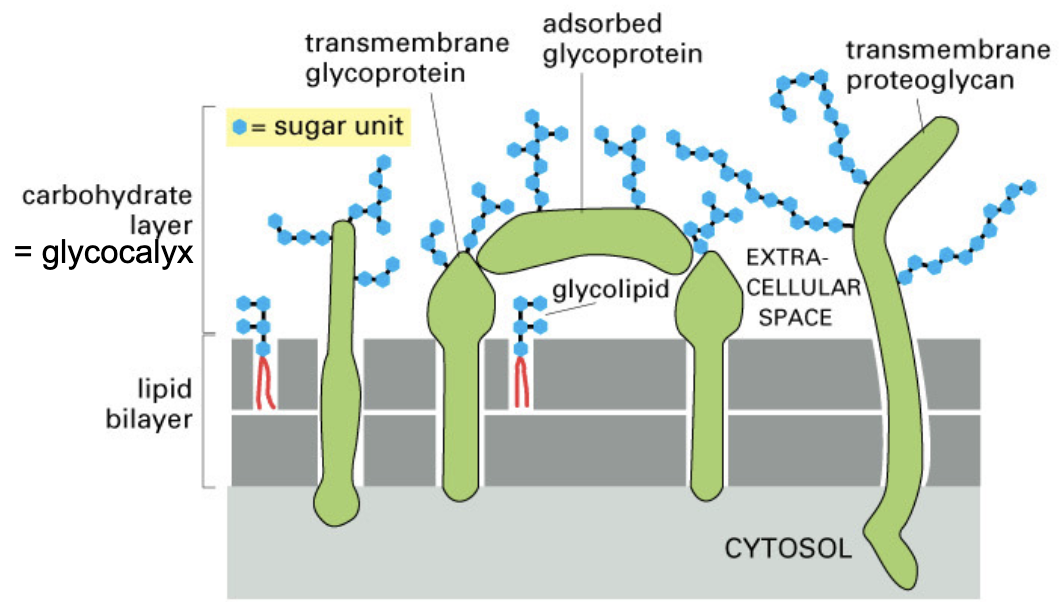
carbohydrate layer - glycoprotein
protein with short, covalently attached oligosaccharide
carbohydrate layer - proteoglycan
protein with one or more long oligosaccharide
carbohydrate layer -glycolipid
lipid with covalently attached oligosaccharide
function of carbohydrate layer
protection from chemical and mechanical damage - lubrication
cell-cell recognition
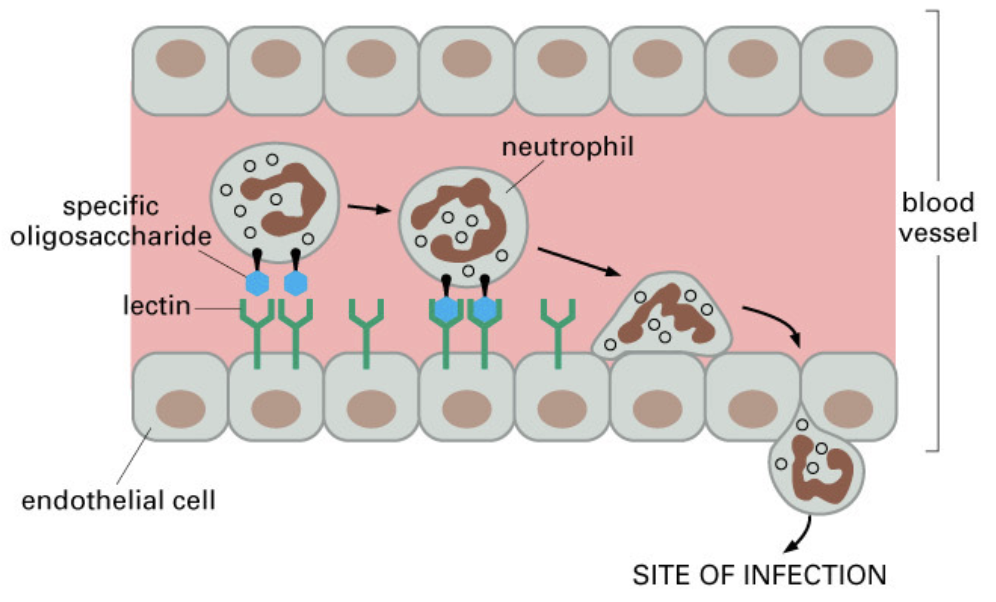
lectins - proteins that bind oligosaccharide chains
lectin binding is responsible for recruitment of _ to sites of _
recruitment of white blood cells to sites of infection
mobility of membrane proteins
some, but not all, proteins are freely diffusible in the membrane
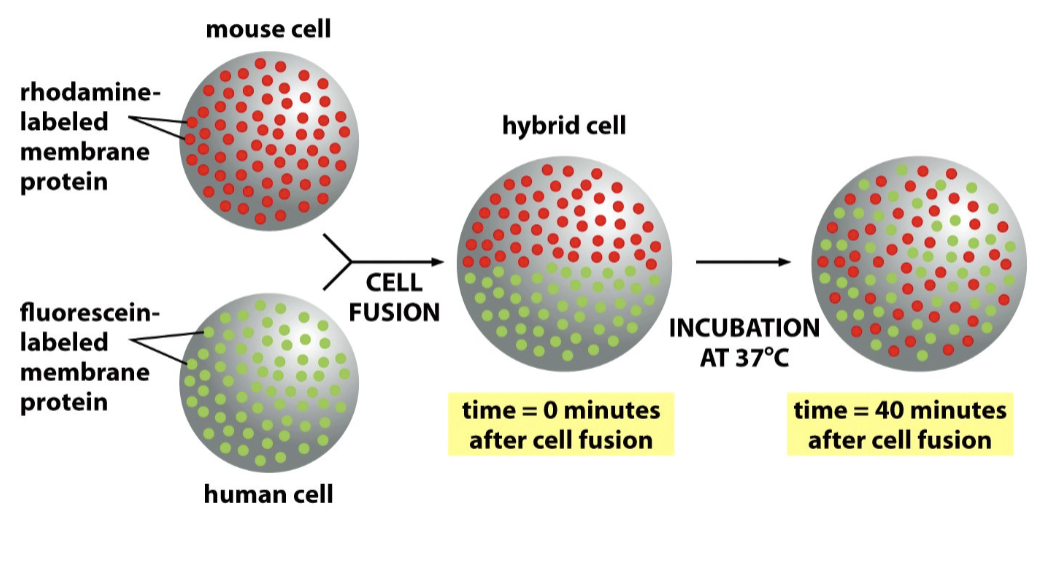
not all proteins are mobile, some are restricted to _
membrane domains
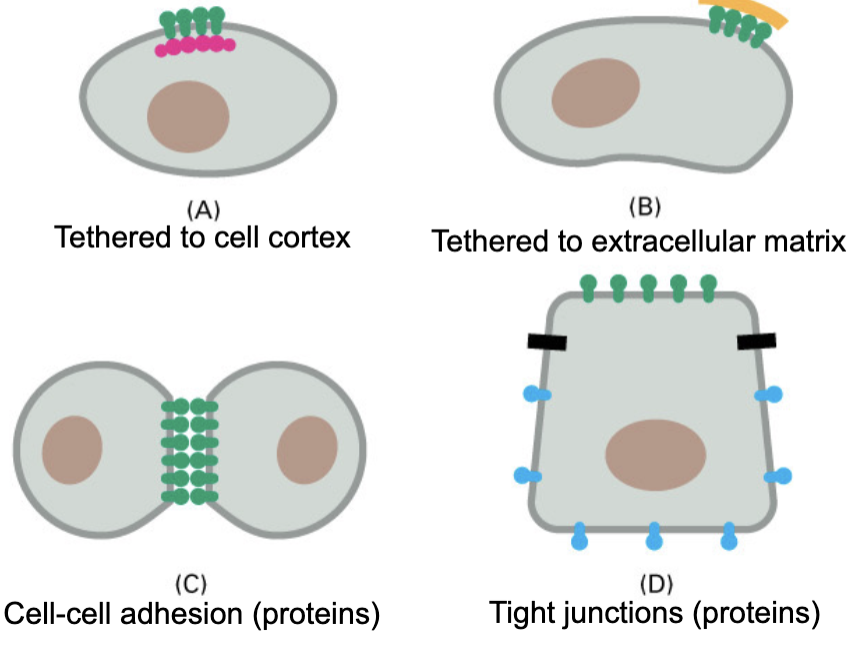
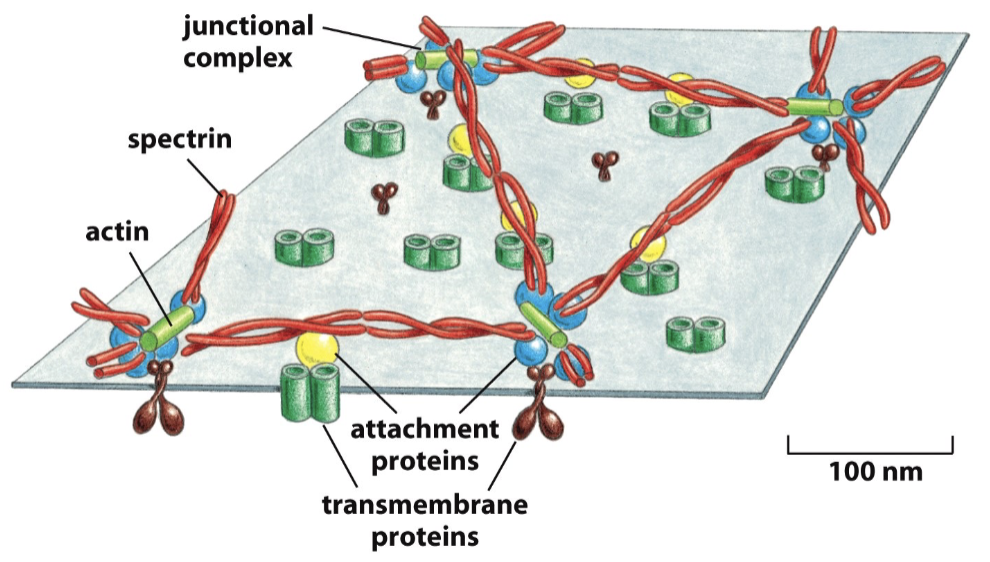
the cell cortex is
is a framework of proteins
largely spectrin
attaches to membrane proteins, restricting their mobility
a given membrane protein will exist as a mixed population of anchored and unanchored proteins
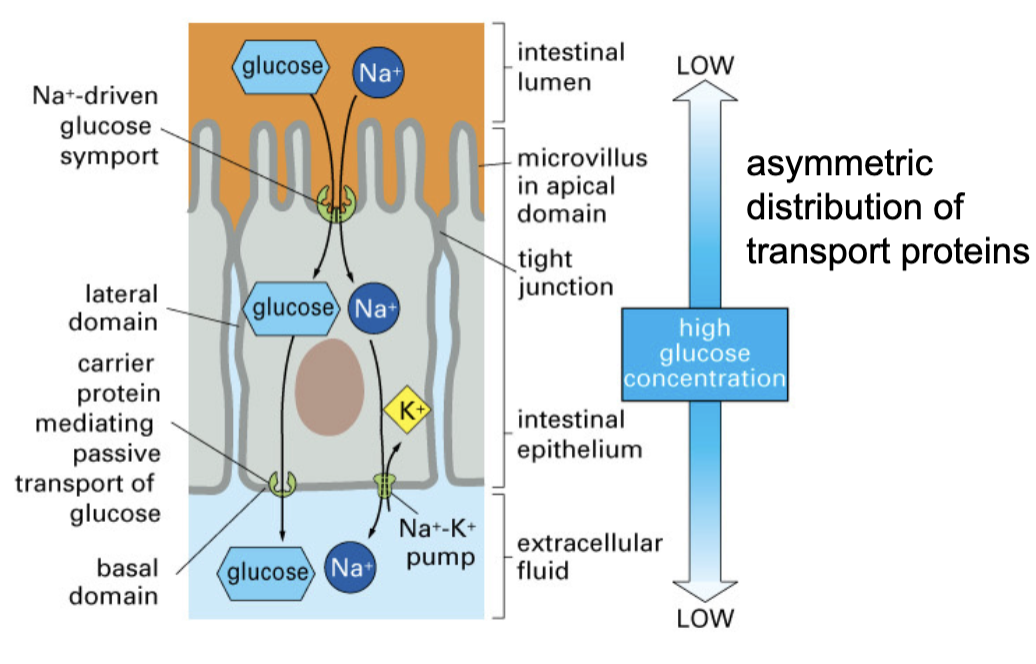
tight junctions in the cell cortex preserve the _
preserve the asymmetric distribution of membrane proteins
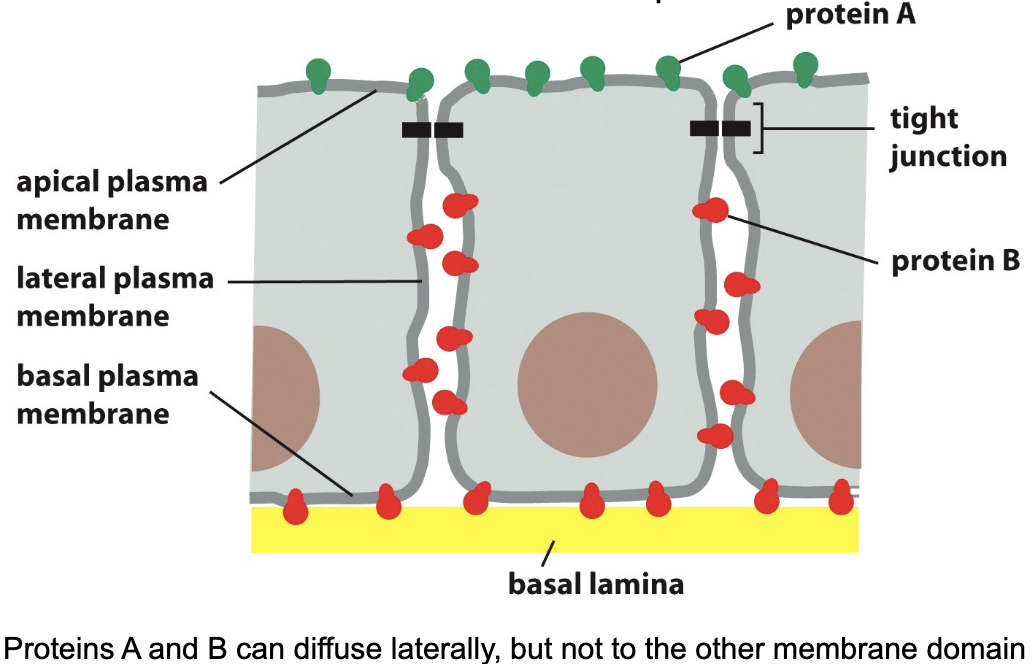
asymmetric distribution of transport proteins