GAS EXCHANGE OVERVIEW
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
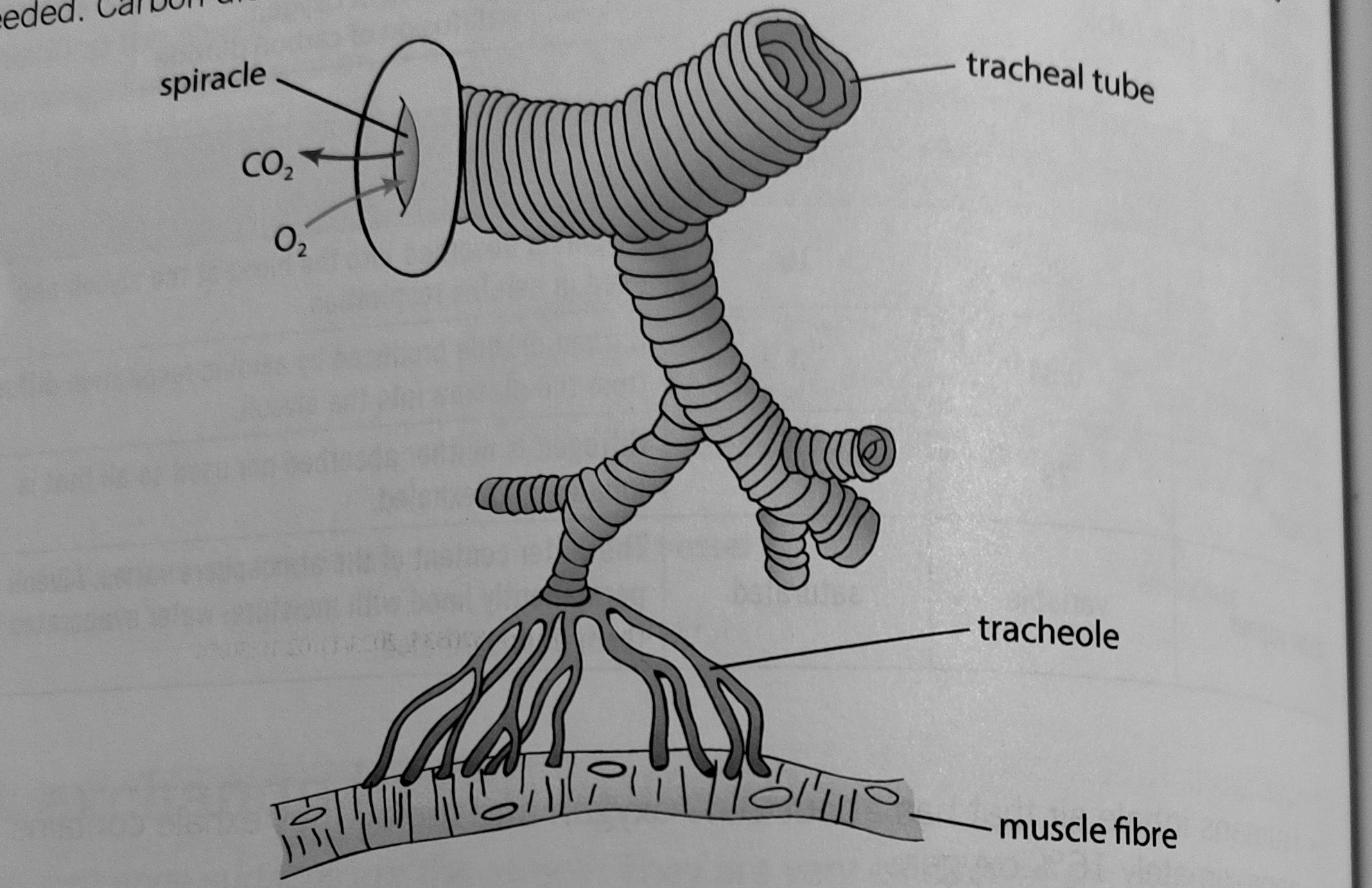
Gas exchange insects:
Insects __________ by moving whole body.
This moved air into a network of tubes called __________.
These branch to make __________ to reach evert cell directly. The gases are not carried in a __________ __________
ventilate
trachea
tracheoles
blood stream
Tracheal system of an insect
Tracheoles end inside muscle fibres
Thoracic spiracles open __________ as abdomen expands (Inspiration)
first
Abdomen spiracles open __________ as the abdomen compresses (Expiration )
later
Insects ventilate through __________
spiracles
Air enters the spiracle allowing _________ to travel along among a network of tubes called __________ to reach the cells in the insect’s body
oxygen
tracheae
Terrestrial Adaptations
Air tubes branching through body
Gas exchanged by diffusion across moist cells lining terminal ends not through open circulatory system
Trachea kept open by circular bands of _______.
chitin
Branch to form ___________ that reach every cell
tracheoles
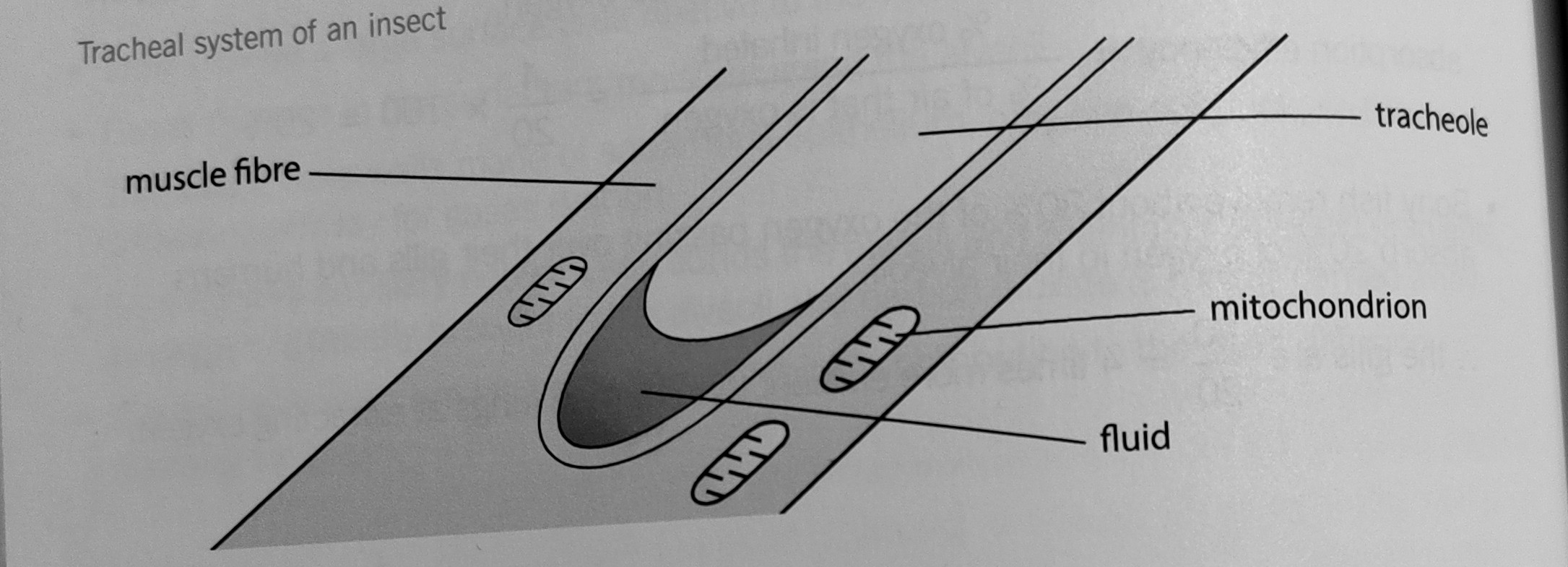
Ends of tracheoles are _______-
moist
Oxygen delivered directly to _________ cells. Insect blood does not carry ___________.
respiring
oxygen
How do the adaptations enhance efficiency?
Oxygen delivered directly to respiring cells
can pump body to move air around in tracheal systems
But size of animal limited by slow _________ rate
diffusion
Alveoli adaptations for gas exchange:
Highly folded
Thin
Moist
Pleural membrane is a _____ fluid filled membrane that surrounds the ______ surface of the lungs and the ________ wall of the chest cavity.
thin
inner
Pleural membrane __________ and prevents friction between lungs and ________ walls
lubricates
friction
Internal lungs ___________ heat and water loss
minimise
Adaptations of lungs for efficient gas exchange
Capillaries and alveoli’s are one cell thick
Blood Circulation
Lung surfactant
Ventilation
Elastic tissue in lungs
Very large surface area
Why is it important for the alveoli and blood capillaries to be one cell think or squamous
To provide a short diffusion pathway
What is the significance of elastic tissue
It helps the lungs expand and contract during breathing
What is the significance of elastic recoil of alveoli?
It helps the alveoli return to their original shape after expanding
What is the significance of ventilation
fresh supply of molecules to maintain diffusion gradient
What is the significance of lung surfactant
reduces cohesive forces between water molecules so lowering water tension
What is the significance of blood circulation
maintains a steep diffusion gradient
What happens to the diaphragm position and muscle state during inhaling?
Diaphragm contracts flat and down, and muscle contracts
What happens to the ribs position during inhaling?
Ribs move up and out
What happens to the external intercostal muscles during inhaling
External intercostal muscles contract
What happens to the thorax volume during inhaling
The volume in thorax increases
What happens to the pressure in thorax compared to atmosphere
The pressure in thorax decreases
What happens to the air movement during inhaling?
Air moves in to lungs
What happens to the diaphragm position and muscle state during exhaling?
Diaphragm relaxes
What happens to the ribs position during exhaling?
Ribs move down and in
What happens to the intercostal muscles during exhaling?
external intercostal muscles relax
What happens to the volume in thorax during exhaling
Volume in thorax decreases
What happens to the pressure in thorax compared to atomospheric during exhaling
Increases
What happens to the air movement during exhaling
Air moves out of lungs
Organisms need to obtain resources from their _______________.
environment
How much they require depends upon their:
Volume (Bulk)
Activity levels
Metabolic rate of diffusion
Surface area
How does an organism’s size relate to it’s surface area to volume ratio?
The larger the organism, the lower the surface area to volume ratio.
How does surface area to volume ratio affect transport of molecules>
The lower the SA/V ratio, the further distance molecules must travel to reach all parts of the organism.
Why do larger organisms require mass transport and specialised gas exchange surfaces.
Small SA/V ratio
Diffusion insufficient to provide all cells with the required oxygen and remove all carbon dioxide
Large organisms are more active than smaller organisms
Four features of an efficient gas exchange surface.
Large surface area
Thin Barrier
Fresh supply of molecules
Ventilation mechanism
Why is a large surface area important for efficient gas exchange?
More space for molecules to pass through
Why is a thin barrier important for efficient gas exchange?
Short diffusion distances
Why is a fresh supply of molecules important for efficient gas exchange?
Maintains a steep diffusion gradient
Why is a ventilation mechanism important for efficient gas exchange?
maintains a steep diffusion gradient
Other features and why they’re important?
Moist — allows gases to dissolve
What type of organism is an amoeba?
Unicellular
Single cells have a very ________ surface area to volume ratio?
large
The cell membrane is _______ so diffusion into the cell is rapid
thin
A single cell is thin so ____________ _______________ inside the cell are short.
diffusion distance
Therefore _________ ______________ across the cell membrane is sufficient to meet the demands of the respiratory processes.
simple diffusion
What type of organisms are earthworms>
Multicellular organisms
What size is the SA/V ratio of an flatworm?
relatively small
However ____ structures provide a large ____________ _____ and reduces the diffusion distance
flat
surface area
__________ _______________ is sufficient to meet the demands of respiratory processes
Simple diffusion
What type of organisms are earthworms?
Cylindrical, multicellular organisms
How large is the SA/V ratio of earthworms?
relatively small
Earthworms are _____ _______________ and have a low ____________ _____ therefore require little oxygen
slow moving
low metabolic rate
Earthworms rely on ___________ ______________ for gas exchange
external surface
Earthworms require a ________________ _________ to transport oxygen to the tissues and remove carbon dioxide in order to ___________ a steep diffusion gradient
circulatory system
maintain
How do fish respire?
Through gills
Define ventilation
The movement of fresh air into a space and stale air out of a space to maintain a steep concentration gradient of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
What are the two main groups of fish
Cartilaginous Fish
Bony Fish
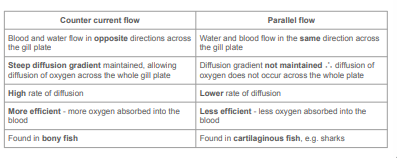
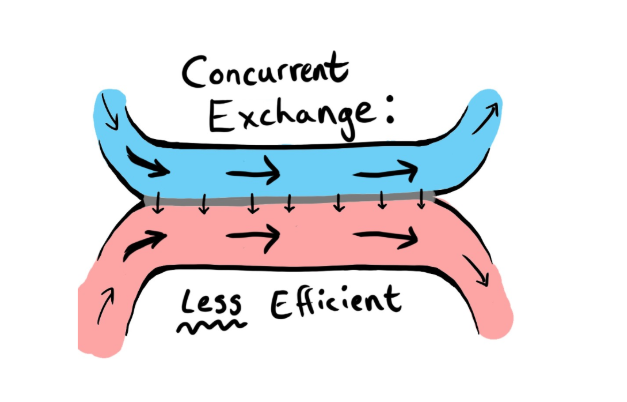
What ventilation system do cartilaginous fish have?
Parallel Flow
Parallel flow is ______ efficient than counter current flow
less
Define Parallel Flow
Blood and water flow in the same direction at the gill lamellae
maintaining the concentration gradient for oxygen to diffuse into the blood only up to the point where its concentration in the blood and water is equal
What are gill filaments
Main site of gaseous exchange in fish over which water flows.
They overlap to gain resistance to water flow
Found in large stacks known as gill plates and have gill lamellae which provide a large surface area and good blood supply for exchange
What happens to the mouth during inspiration?
Mouth opens
What happens to the operculum in inspiration>
The operculum remains closed
What happens to the floor of the mouth during inspiration>
The floor of the mouth lowers
What happens to the volume in mouth cavity during inspiration?
The volume in mouth cavity increases
What happens to the pressure in the mouth cavity during inspiration?
Pressure in mouth cavity decreases
What happens to the water movement during inspiration?
Water movement in as external pressure is higher
What happens to the mouth during expiration?
Mouth remains closed
What happens to the operculum during expiration?
Operculum opens
What happens to the floor of the mouth
The floor of the mouth rises
What happens to the volume in mouth cavity?
Volume decreases in mouth cavity
What happens to the pressure in mouth cavity?
Pressure in mouth cavity increases
What happens to the water movement during expiration?
The water movement - out as external pressure is higher
Define counter current flow?
Water and blood flow in opposite directions
Maintains a concentration gradient
Oxygen diffuses into the blood along the entire length
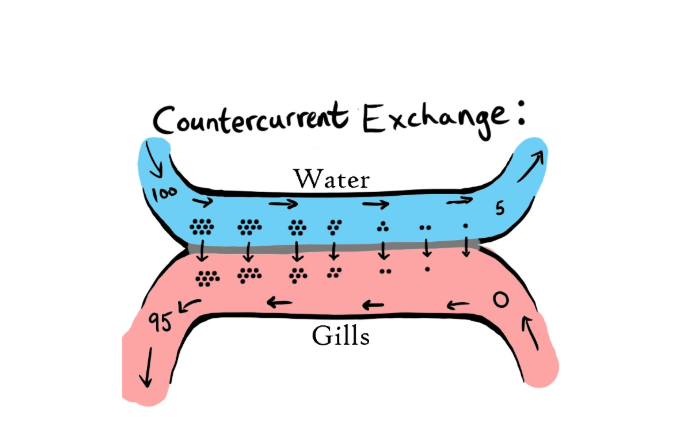
How is the diffusion gradient maintained during counter current flow?
Water is always next to blood of a lower oxygen concentration
Keeps rate of diffusion constant and enables 80% of available oxygen to be absorbed
Compare counter current and parallel flow?