The Amazing Fetus
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What major physiologic changes occur from fetal to neonatal life transition?
respiration, circulation, feeding and digestion, temperature regulation
What is the first challenge in a newborn’s life?
perfusing their body and oxygenating their blood
As the fetus is passed through the birth canal, what happens?
there is a sudden change in temperature and environment
What does the change in temperature and environment trigger?
the infant to take first breath in about first 10 seconds
What does the placenta do?
EVERYTHING!!!
responsible for respiratory gas exchange
fetus received all necessary nutrition and O2 through this by blood vessels in umbilical cord
waste is passed through to mother
In fetal circulation/oxygenation, the normal cord is …?
3 vessels - 1 vein and 2 arteries
What does the umbilical vein do?
carries oxygenated blood from placenta to fetus
What do the umbilical arteries do?
paired and carry deoxygenated blood from fetus to placenta
What are the lungs like in the womb?
non-functioning and receive little blood flow
How do the fetal lungs develop?
as fluid of liquid filled organ
with a high pulmonary vascular resistance
Fluid in the lungs is a component of …? What does the fluid do?
the epithelial lining
play a crucial role in lung growth and development due to keeping them in a distended state
What allows the blood to be diverted to the placenta for gas exchange?
high pulmonary vascular resistance
Oxygenated blood bypasses the lungs through what?
the ductus arterioles and foramen ovale
What happens at 24-28 weeks?
cuboidal epithelium flattens out and begins to produce pulmonary surfactant
Was does surfactant do?
it provides alveolar stability and is necessary to maintain normal lung expansion after birth
what allows our lungs to expand
When is a sufficient amount of surfactant present?
after 34 weeks gestation
What happens to the lungs at birth?
in order to have functional lungs, we need the PVR to drop
outward recoil of the chest at delivery aids in filling the lungs with air
What is the most important trigger in reducing PVR at birth?
ventilation of the lungs and exposure to oxygen
What does the first breath do?
drops other PVR and increases the surface area available for gas exchange
over the next 30 seconds, pulmonary blood flow increases and is oxygenated as it flows through the alveoli of the lungs
What is the most common cause of respiratory distress in newborns?
respiratory distress syndrome - not enough surfactant in the lungs
What is the pathophysiology of RDS?
noncompliant, stiff lungs that are structurally immature that contain insufficient surfactant
surfactant decreases surface tension in the alveoli during expiration, which allows the alveolus to remain partly expanded and maintain a functional residual capacity
What happens in the absence of surfactant?
poor lung compliance and atelectasis - infant must expend a great deal of effort to expand lungs
What are the treatments for RDS?
Best is PREVENTION
multidisciplinary approach
Basic principles of neonatal care - thermoregulation, cardio and nutritional support, early infection care
Nasal cpap
supplemental O2
Surfactant replacement
What is prevention of RDS?
prevention of prematurity, asphyxia, avoidance of maternal fluid overload
Prenatal administration of a single course of steroids to women in preterm labor between 24-34 weeks gestation
Prenatal administration of steroids between 24-34 weeks gestation good prevention of RDS?
less likely to have respiratory distress syndrome and lower mortality rate
hastens the development and maturity of the lungs
stimulates surfactant production
What is the circulatory path during fetal life?
oxygenated blood coming from the placenta is carried via the umbilical vein to the left branch of the portal vein - part carried via the ductus venosus to the inferior vena cava, then passes from the IVC to the right atrium
Then, the right atrial anatomy preferentially directs blood flow from the inferior vena cava through the foramen ovale into the left atrium - then passes to the left ventricle and then the aorta
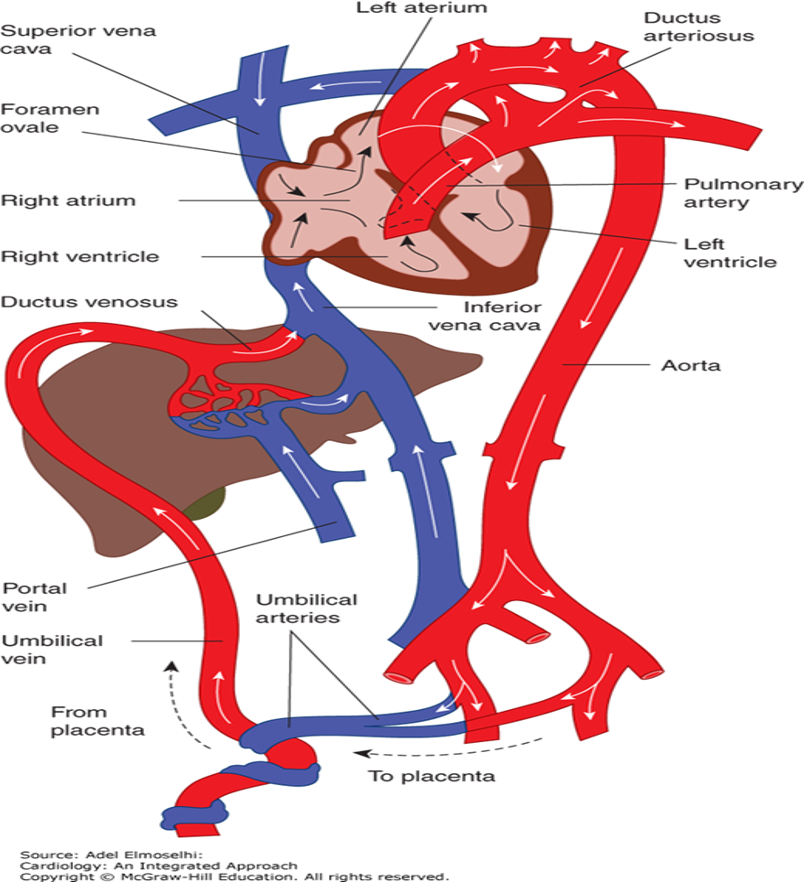
How oxygen saturated is blood flow in inferior vena cava?
67% oxygen saturated
What does most of the oxygenated blood supply?
the heart itself, head, neck, brain, and upper limbs
What does the ductus arteriosus connect?
the pulmonary artery to the proximal descending aorta to allow blood from right ventricle to bypass fetus’s fluid-filled non-functioning lungs
Why does the ductus arteriosus constrict?
as a result of the increased O2 concentration
to ensure all blood pumped to the pulmonary circuit will be oxygenated by the newly functional neonatal lungs
What does the ductus arteriosus become?
ligamentum arteriosum
When the placental circulation stops, what happens?
the umbilical vein becomes obliterated and forms the ligament teres of the liver
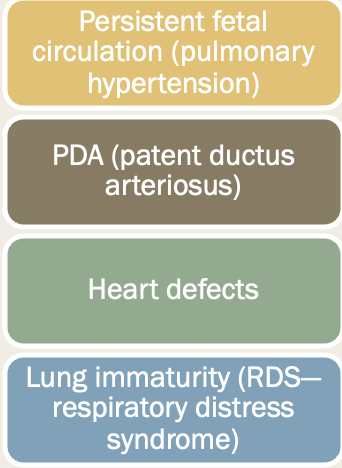
What are problems of cardiopulmonary systems?
persistent fuel circulation, PDA, heart defects, lung immaturity
What is the temperature in utero?
98.6 with little fluctuation
Why do infants produce less heat and lose more heat?
they have immature musculature that limits their ability to produce heat by shivering
nervous system is underdeveloped so they cannot quickly constrict superficial blood vessels in response to cold
little subcutaneous fat for insulation
How do newborns generate heat?
nonshivering thermogenesis - breakdown of brown adipose tissue distributed over the chest, back, and shoulders
How does brown adipose tissue differ from white fat?
it is highly vascularized, allowing for faster delivery of O2, which leads for faster cellular respiration
packed with special types of mitochondria that are able to engage in cellular respiration that produce less ATP and more heat than standard cellular reactions
What does the first consumption of breastmilk or formula do?
floods the neonatal GI tract with bacterial flora
When do newborns need to being to take oral feeding?
within hours of birth
Breast milk “comes in” when? What is prior to that?
2-4 days post partum
colostrum
What is the colostrum?
pre-milk secretion
yellowish alkaline secretion that is present for the first 2-3 days after delivery
What are the characteristics of colostrum?
high protein, vitamin A, immunoglobulin, sodium, chloride content
lower carbs, potassium and fat content than mature breast milk
normal laxative action and is an ideal natural starter food
What are the reflexive feeding patterns?
gag - sucking in air, forceful letdown, abundance of milk
rooting
What are the feeding patterns?
negative pressure is suction, positive is expression
suckling
sucking
What is meconium?
newborn’s first stool - sticky, thick, dark green and composed of materials ingested during the time the infant spend in the uterus
How many newborns develop jaundice during the first week of life?
65%
How is bilirubin produced?
by the breakdown of heme
conjugated in liver and excreted through the bile into intestines
What causes stasis of conjugated bilirubin in the intestinal lumen?
absence of gut flora and slow GI motility
What is breast milk jaundice?
unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia lasting until 2-3 months of age
What is breastfeeding associated jaundice?
unconjugated serum bilirubin levels greater than formula fed - poor enteral intake and increased enterohepatic circulation
also called lack of breast milk jaundice
What is the treatment for breastfeeding associated jaundice?
supplement with formula and instruct mom to nurse more frequently and use an electric breast pump to enhance milk production
What happens if breastfeeding associated jaundice is not fixed?
bilirubin toxicity
What is vernix caseosa?
Waxy or cheese-like white substance coating the skin of newborn infants - disappears closer to term
What is lanugo?
hair that covers the fetus in gestation, usually disappears by term gestation - evidence that infant may be pre-term
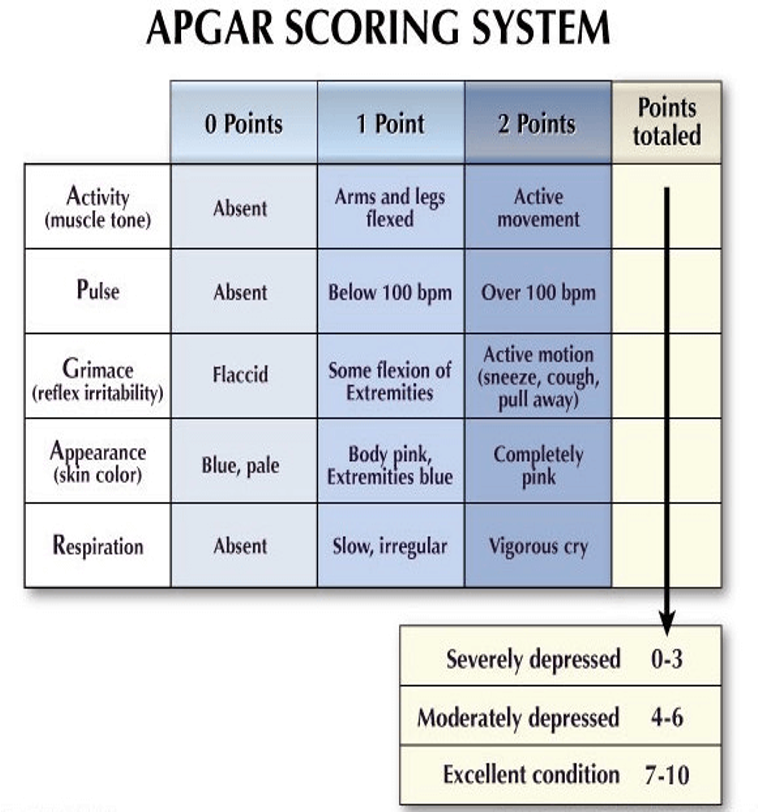
What are APGAR score used for?
to help the dr. determine the newborn’s general condition at birth
provide useful description of the severity of perinatal depression and response to resuscitative efforts
What APGAR score is wanted?
7 - lower than that, baby may be healthy but just need attention in one area
What do you want to look at when using the APGAR scoring system?
appearance
pulse
grimace (reflex irritability)
activity
respiration