TEAS 7 Life and physical sciences
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Biological hierarchy of the body
chemicals, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms
Chemicals
help build cells- macromolecules are chemicals that are essential to life
Cells
The basic unit of life
Tissues
Made up of cells that have similar structure and function
Organs
Made up of tissues that work together to carry out a specific function
Organ system
Group of organs that work together to carry out a specific function
Organism
Made up of one or multiple organs
The cell is composed of
cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, Golgi apparatus, Mitochondria, lysosomes, Ribosomes, Rough endoplasmic reticulum, Smooth endoplasmic reticulum ,Vacuole
cell membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell. (Selective permeability)
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
-Transfers material for cellular processes
Golgi apparatus
Helps packaging and processing of molecules
Lysosomes
Organelles that contain enzymes that break down molecules
-Functions in digestion and recycles old cell material
-Destroys invading bacteria as well as viruses
Mitochondria
Produces energy for the cell and converts nutrients into ATP
-
Nucelus
Part that contains cells hereditary information
-Responsible for cells growth, reproduction and function
Ribosomes
Helps synthesize proteins
-Found in cytoplasm and rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rought Endoplasmic Reticulum
Aids in packaging and transport of molecules within the cell
-ALSO SYNTHESIZES PROTEINS
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Aids in the packaging and transport of molecules, specifically lipids within the cell (No ribosomes)
-Metabolizes carbon
-Activates toxins along with harmful metabolic products
Vacoule
Stores water and other materials for the cell (Also maintains shape of cell)
Mitosis
process of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells
Five main stages of the cell cycle
Interphase
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Interphase
Is the first stage of the cell cycle. Is when the cell grows and carries out its normal functions
Prophase
Second stage of the cell cycle. The chromosomes condense and become visible. The nuclear envelope breaks down
Metaphase
Third stage, chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase
Fourth stage, chromosomes are pulled apart to the opposite sides of the cell. (Cell division begins)
Telophase
The fifth and final stage of mitosis, during which daughter nuclei form at the two poles of a cell. Telophase usually occurs together with cytokinesis.
-Cell divides and two daughter cells are made
Meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms
-Produces 4 daughter cells
Meiosis stages (two cycles in this)
Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II
Prophase 2
sixth stage of meosis. Daughter cells contain half of the chromosomes from the original cells
Metaphase 2
Seventg stage of meiosis. The chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell again
Anaphase 2
Eight stage of meiosis. The sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite sides of cell
Telophase 2
9th and final stage, the cells divide into four genetical diverse daughter cells also known as HAPLOIDS
Chromosomes
Long thread like structures that are round in the nucleus of the cell
-EX 46 chromosomes in every cell of the body (EXCEPT IN GAMETES)
Genes
the basic units of heredity and are made up of DNA
-Responsible for characteristics of an organism
strucutral genes
Responsible for physical traits of an organism
-COLOR OF YOUR EYES OR HAIR is determined by structural genes
Regulatory genes
Control the activity of other genes
-EX: Regulatory genes can turn other genes on or off
DNA
Made up of two long chains of nucleotides that twist to create a double helix
Four bases in nucleotides in DNA that determines proteins
GCAT
GUANINE, CYSTENINE, ADENINE, THYMINE
Base pairs
Two nucleotides that are bonded together by hydrogen bonds
AT
CG
Codon
a sequence of three nucleotides that together form a unit of genetic code for a specific amino acid in a DNA or RNA molecule.
-TOTAL OF 64 POSSIBLE CODONS
-3 of those are stop codons
RNA (ribonucleic acid)
Translates the genetic code of DNA into proteins
Differences between DNA:
-One strand
-Contains Uracil instead of thymine
Processes of RNA
transcription and translation
Transcription
Process of making RNA from DNA
RNA polymerase
Enzyme that catalyzes the formation of RNA from nucleotides. This enzyme attaches to one end of the DNA template and then moves along the template, adding nucelotides one at a time.
Three forms of RNA
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
mRNA (messenger RNA)
RNA that carries the genetic code from the DNA in the nucelus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm
tRNA (transfer RNA)
Helps assemble amino acids into proteins that act as adapters in the translation of the genetic sequence
Ribosomal RNA
RNA that makes up the ribosomes; clamps onto mRNA and uses its information to assemble amino acids in the correct order
Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
How does translation happen
MRNA attaches to small subunit of ribosome and then tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome. As the amino acids are brought to the ribosome, they are joined together by peptide bonds to form protein
-Genetic code is read in groups of three nucleotides, called codons. Each codon codes for a specific amino acid
Inhertiance (Mendels law)
Process by which traits are passed from parents to their offspring
Mendel's law of inheritance states
Two alleles for each trait. Alleles are alternative forms of a gene
one allele is dominant and the other is
recessive
Phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits. (Usually dominant allele)
How many alleles are transferred to the offspring by parent
1 allele each
Genotype
genetic makeup of an organism
dominant trait
a genetic factor that blocks another genetic factor
recessive trait
a genetic factor that is blocked by the presence of a dominant factor
Heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a trait
Homozygous
An organism that has two identical alleles for a trait
Dihybrid cross
A cross between individuals that have different alleles for the same gene
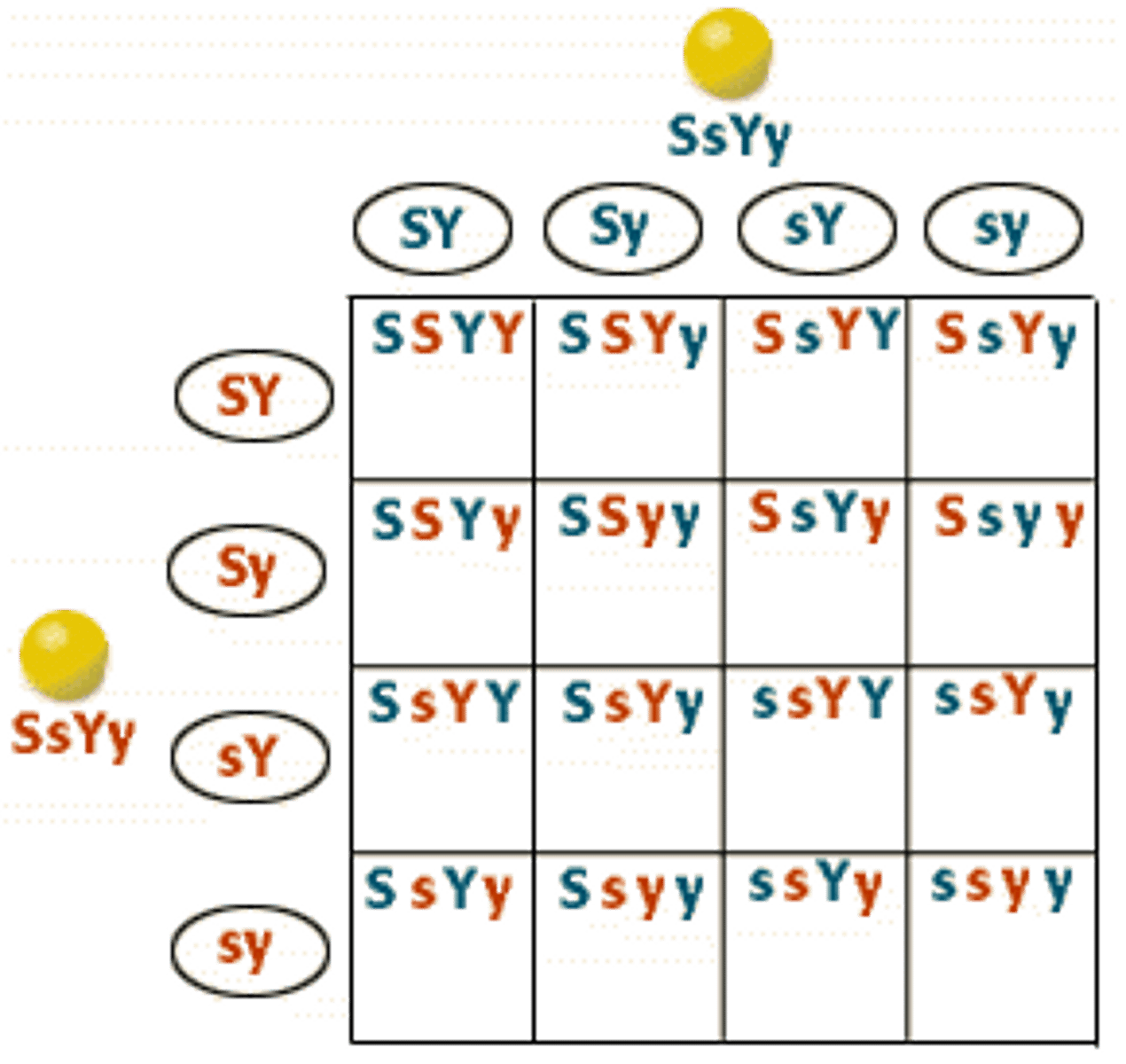
Exception to mendels law of inheritance
Incomplete dominance
Codominance
Incomplete dominance
the phenotype of the offspring is a blend of the phenotypes of the parents
Example of incomplete dominance
If a red flower (RR) is crossed with a whote flower (WW), the offspring will be pink (RW)
Codominance
Phenotype of the offspring is a combination of the phenotype of parents
Example of Codominance
If a black chicken(BB) is crossed with a white chicken (WW), the offspring will be black and white
Macromolecule's
Large molecules that are essential for the structure and function of cells
Polymer
A macromolecule that is made up of smaller units called covalent bond linked monomers
Two reactions that can occur
Dehydration and Hydrolysis
Dehydration
Synthesis is the formation of larger molecules from smaller reactants accompanied by the loss of a water molecule
Hydrolysis
The process of breaking down bonds to break monomers
What are the four major types of macromolecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Carbohydrates
composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
-Known as sugars or starches
Monosaccharides
Simplest type consisting of one unit
-Cannot be hydrolyzed to make smaller units
-Glucose, fructose and galactose
Disaccharides
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis.
-Sucrose, lactose and maltose
Polysaccharides
Long chains of monosaccharides that are joined by covalent bonds
-Starch and cellulose
Linear Carbohydrates
Long unbranched chains of monosaccharides that form structures.
-Cellulose is a major component of rigid cell walls in plants
branched carbohydrates
Shorter chains of monosaccharides with branches.
-Maltose is a common disaccharide found in germinating seeds that are used for energy storage
Helix-Shaped carbohydrates
Coiled chains of monosaccharides that form structures.
-EX: DNA is a double helix shaped nucleic acid
Lipids
Molecule that is composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
Function of lipids
Energy storage
Structure
Hormones
How are lipids formed?
By linear arrangement of carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms called fatty acid chains
Four groups of lipids
Fat molecules
Waxes
Phospholipids
Steroids
Fat molecules
Composed of glycerol molecule and three fatty acid chains
-Fats are used for long term energy storage in the body
-Cushion
Waxes
Long chain of fatty acids that are linked to long chain of alcohol
Phospholipids
Composed of glycerol molecule, two fatty acid chains and a phosphate group
Steroid
Four interconnected carbon rings. Steroids include cholesterol, which is a structural component of cell membranes and hormones like testosterone and estrogen
Proteins are composed of
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen , and sometimes sulfur
What are proteins made of
amino acids that are linked together by peptide bonds
What are the four groups of proteins
enzymes, structural proteins, storage proteins, transport proteins
Enzymes
proteins that can catalyze biochemical reactions without being consumed by the reaction.
-Speed up reactions by lowering energy required to initiate the reaction/
-These reactions can be exergonic(release energy) or endogenic(require energy)
Structural proteins
provide support and structure
Storage proteins
Store nutrients
Transport proteins
Transport molecules in a membrane
nucleic acids are composed of
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorus
Function of nucleic acids
store and transmit genetic information
Microorganisms
Are tiny living organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye and can only be seen with a microscope
Bacteria
Single celled micro-organisms that can live in many different environments. Some bacteria cause diseases such as tuberculosis, meningitis, food poisoning and more
Virus
Even smaller than bacteria and can only be seen with an electron microscope.
EX: Covid 10, measles, mumps, HIV
Protozoans
Are single celled micro-organisms that are found in water, soil and air. Some protozoans cause diseases such as malaria, giardiasis and amoebic dysentery
Fungi
Micro-organisms that are classified as eukaryotes. Some fungi are helpful, such as those used in the production of bread, cheese and beer
-Other fungi can cause disease such as athletes foot, ring worm and candidiasis
Animals
Such as parasitic worm are large enough for people to see with naked eye and live on the body. Flatworms can live in the intestines and round worms can live in the GI and lymphatic systems.