physics - grav fields
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
in a field, what type of force is felt/present
non contact force
which objects do gravitational fields affect?
all objects (as all objects have mass)
what law does gravitational force follow
inverse square law
in grav fields, the force exerted is always _____
positive
what is newtons law of gravitation
the gravitational force between 2 masses is directly proportional to the product of their masses and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance measured between their centres
what is the equation for gravitational field
note:
in the data sheet, it has a (-) in the front.
this is purely for the physics.
the “-” is added to indicate that work must be done to separate the 2 masses, since they are attracted to each other, and wont just repel or separate by themselves

draw the gravitational field lines for a uniform and a radial field
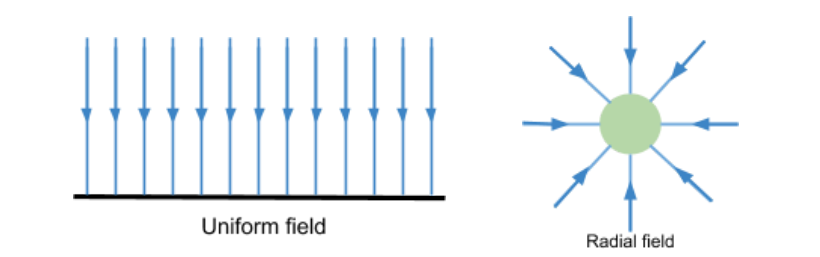
when can a radial filed be considered uniform? (near where)
near the surface of the planet
what is the verbal definition of gravitational field strength.
when does this vary, and when is it constant
the force per unit mass exerted by a gravitational field on an object
varies in a radial field, and remains constant in a uniform field
what are the 2 equations for gravitational field strength?
what is the symbol and unit for gravitational field strength
which of the 2 is used in general
which of the 2 can ONLY be used in a radial field?
gravitational field strength symbol = g
units of gravitational field strength = Nkg-1
the one on the left can be used in general
the one on the right can only be used in a radial field
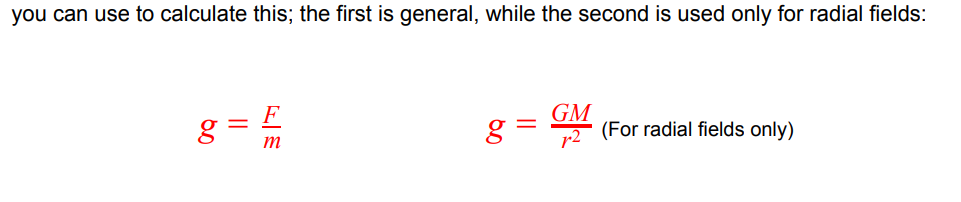
what is the equation that links density, gravitational field strength and radius?
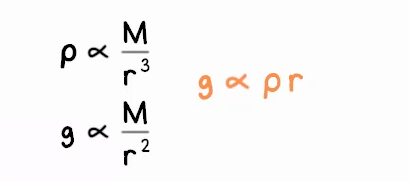
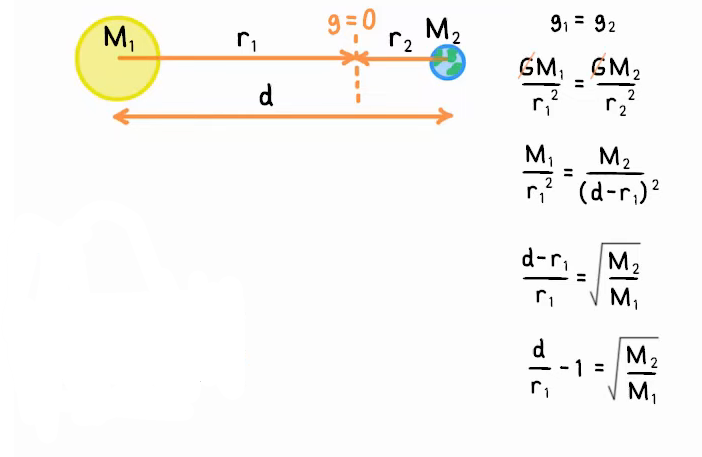
what equation is used to find the neutral point?
what is the verbal definition of gravitational potential.
what is its symbol
what units does it have
gravitational potential (v) is the work done per unit mass against a gravitational field, to move an object from infinity to a given point
units: Jkg-1
what is the value of gravitational potential at infinity
0
is gravitational potential always negative? why/why not
yes
as you move from infinity towards a given point, energy is released, as the grav potential is reduced (because less work is being done to move the point away from the field)
if given the individual potentials, how can u find the total potential and why does this work
sum the individual potentials
this can happen because potential is scalar
what is the gravitational potential equation, for a radial field only?

what is the equation to find work done when moving an object in a gravitational field. what does the m in the equation represent

is work done when moving along an equipotential?
NO. 0 work is done
draw the graph of gravitational potential (v) against r
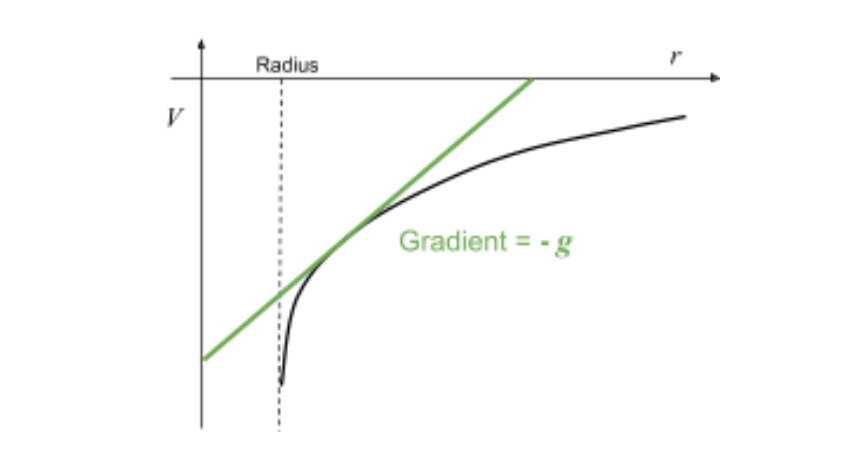
can gravitational field strength be found from the graph of v against r?
if so, how?
yes
the negative of the gradient (gradient multiplied by -1) is the gravitational field strength.
gradient can be found using tangent
using the equation, (for a radial field), based on the graph how do you find the change in potential?
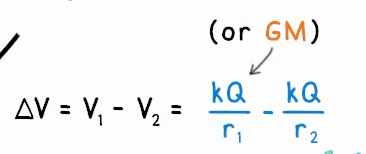
what is the equation for gravitational field strength based on the graph of v against r

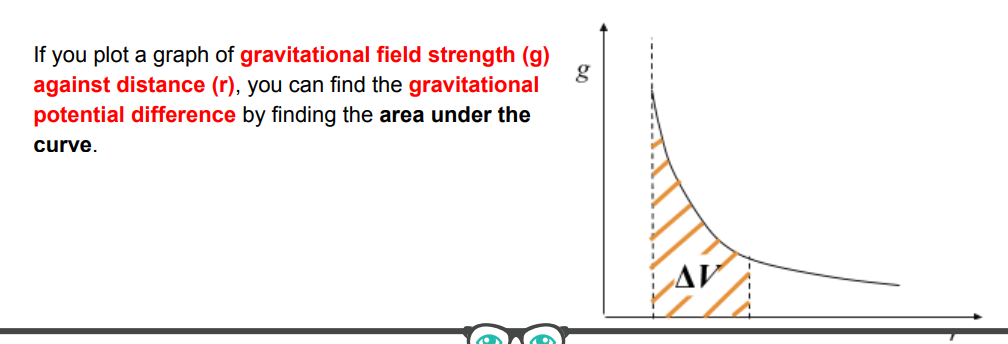
draw the graph of gravitational field strength against r
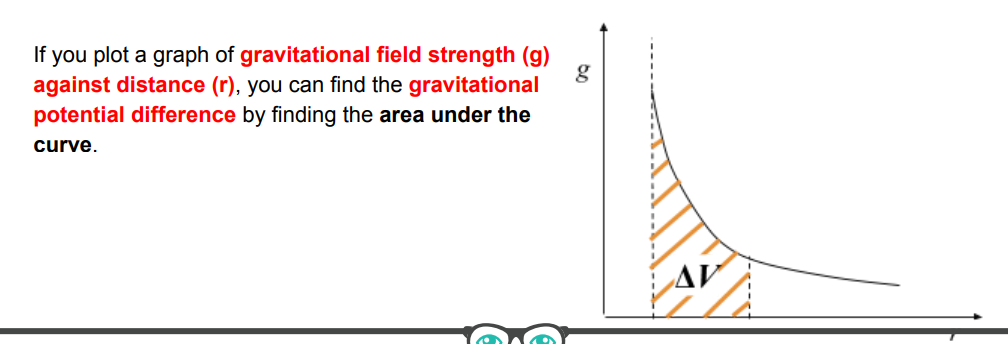
what does the area under a graph of gravitational field strength against r represent
gravitational potential difference (delta v)
what is keplers third law in words
the square of the orbital period (T) is directly proportional to the cube of the radius
derive keplers 3rd law

what is the total energy of an orbiting satellite made up of?
is it always constant?
made up of its kinetic and potential energy
yes, it is always constant

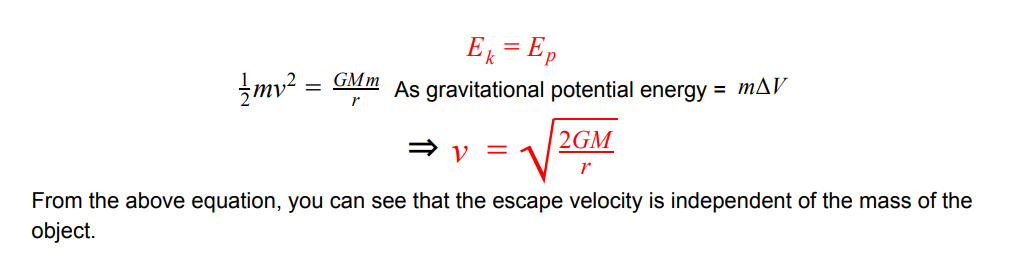
what is the definition of the escape velocity?
the minimum velocity an object must travel at in order to escape the gravitational field at the surface of a mass
how do we find the escape velocity
make kinetic energy = gravitational potential energy and then just rearrange
what is a synchronous orbit?
it is an orbit where the orbital period of the satellite is equal to the rotational period of the object that it is orbiting
what is the orbital period of a synchronous satellite orbiting earth
would have an orbital period of 24 hours
do geostationary satellites follow a specific geosynchronous orbit?
if so what is it
yes they do. their orbital period is 24 hours
geostationary satelites always stay above the same point on earth, because they orbit directly _____ the _____
above the equator
why are geostationary satellites useful
can send TV and telephone signals, as is always above the same point on earth
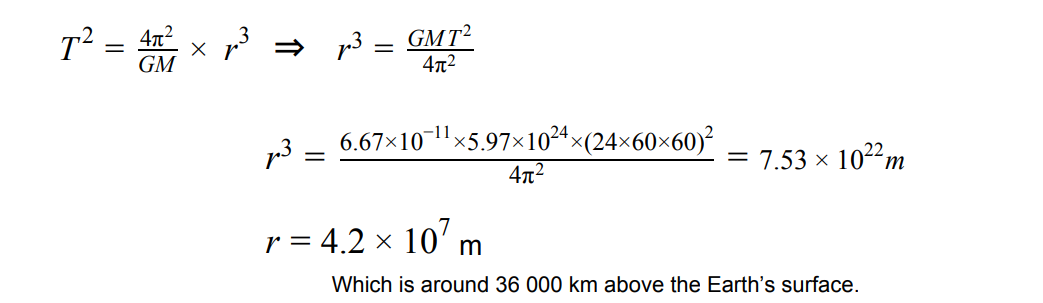
use keplers 3rd law equation to calculate the radius of the geostationary satelite
do low orbit satellites have lower or higher orbits in comparison to geostationary/geosynchronous satellites?
lower orbits
what does travelling in lower orbit mean for low orbit satellites compared to geostationary satellites?
how does this affect their orbital periods?
they travel much faster
this means their orbital periods are much smaller
what are the 3 uses of low orbit satellites?
monitoring the weather
making scientific observations about unreachable places
have use in military
what can they also be used for?
what is complicated about this
can also be used for communication
however, because they travel so quickly, many satellites must work together to allow for constant coverage of a certain region