oxygenation
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
oxygen
inspired air
percentage of o2 in room air
21%
what co2 is too high what happens?
you stop breathing
what is pulse ox the measure of
how much o2 is getting into the body when taking a breath in
why is o2 so important
so make brain and organs function properly
co2
pulmonary circulation, very little in room air (all contained in exhaled air)
upper respiratory tract
mouth, nose, pharynx, larynx
lower respiratory tract
trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, pulmonary capillaries
what do the alveolis work for
exchange between o2 and co2
how do alveolis open
get enough o2 and pressure
ventilation
breathing= inhalation & exhalation
inhalation
active process
what is inhalation
air into lungs, diapragm contracts (goes down to increase chest wall), decrease in pulmonary pressure
what is exhalation
air out of lungs, diaphragm relaxes, increase in pulmonary pressure
exhalation
passive process
when does gas exchange occur
post alveolar ventilation
what happens to o2 during diffusion
o2 from alveoli to pulmonary capillaries
what happens to co2 during diffusion
co2 from pulmonary capillaries into the alveoli
respiratory process
alveolar ventilation, diffusion of o2 and co2, transport of o2 and co2
alveolar ventilation
increase to decrease in concentration
diffusion of o2 and co2
partial pressure of o2 (alveolar vs pulmonary arterial)
partial pressure of co2 (pulmonary arterial vs alveolar)
transport of o2 and co2
o2 transport (lungs TO tissues)
co2 transport (tissues TO lungs)
comprehensive assessment
factors influencing respiratory physiology (age continuum, env, lifestyle, comorbidities, meds, stress)
impaired respiratory status
work of breathing
hypoxemia
low o2 lvls in BLOOD (poor lung uptake)—> lungs not breathing it in= low levels
hypoxemia s&s
hypoxia less severe AND SPO2 below 90 (but depends on pt baseline)
how to measure hypoxemia
measure w arterial blood gas test
treatment for hypoxemia
PRBCs, mechanical ventilation
hypoxia
low o2 levels in TISSUES (poor flow/hypoxemia)—→ bringing it in but not getting into the tissues
s&s of hypoxia
SOB, headaches, cyanosis, confusion, tachycardia, restlessness
why should you find out what the cause is of restlessness
because if u give a sedative and are already not getting enough o2, then o2 lvls will go even lower
what is hypoxia a sequela of
hypoxemia
what is the treatment for hypoxia
rest, breathing exercise
what does it mean if a patient cant complete a sentence and stops to breathe
they have a problem with breathing
nursing interventions to promote respiratory functions
positioning, breathing exercises, cough techniques, hydration
positioning for promoting respiratory function
prone
breathing exercises for promoting resp function
diaphragmatic, pursed lip
diaphragmatic
2 hands, one on chest and one on abdomen (for calming) in and out slowly
pursed lip
ppl w copd usually do this, allows for smaller thinner stream but better stream
cough techniques
huff, cascade, quad
huff
inhale,exhale,huff (deeper each time)→ like fogging a mirror
cascade
huff 3 times, deeper breathing as you go
quad
abdominal thrust inward and upward
make sure people are well hydrated during the cough techniques
especially the huff
hydration
med administration and teaching
promoting respiratory function
multi-disciplinary therapeutic interventions, meds, resp therapies
meds for respiratory function
bronchodilators, anti-infl meds, cough supressants, expectorants
why does wheezing occur
breathing tunnels are getting narrower
respiratory therapies
incentive spirometry, percussion, vibration, postural drainage
co2 retaining pts
chronic high levels of co2, they lose their drive to breathe if o2 is high, minimize o2 therapy, purse lip breathing
what is different w co2 levels in pts that are co2 retainers
normally high co2 levels, need to give them more co2 than o2 to make them feel better
what should you find out if a patient has copd
if theyre co2 retainers
fine o2 levels for co2 retainers
87-88
what level should co2 retainers not be on in terms of oxygen
94% or above
what is a good amount of o2 to give a co2 retainer
0.5 L
o2 therapies
MD ordered
FlO2
inspired O2 percentage
opti-flow
nasal increase flow of o2 (21-100% o2, humid/warm)
what is a complaint of nasal cannula
long-term skin breakdown of the ears
nasal cannula
24-44% o2
what happens if you don’t give someone humidified o2
mucus will fry and plug and block o2 from getting in
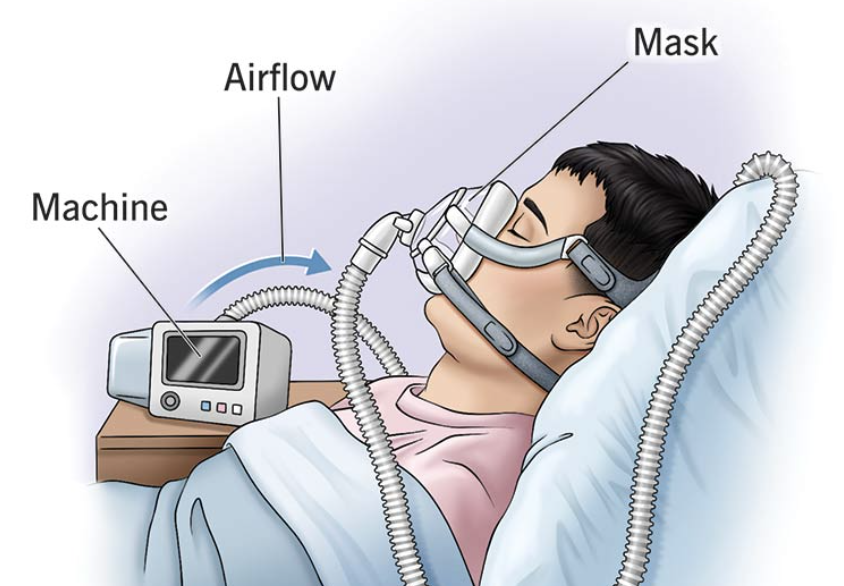
CPAP
enhances inhalation of o2 past larger throat structures, seal is important for the machine
what condition are CPAPs used for
sleep apnea
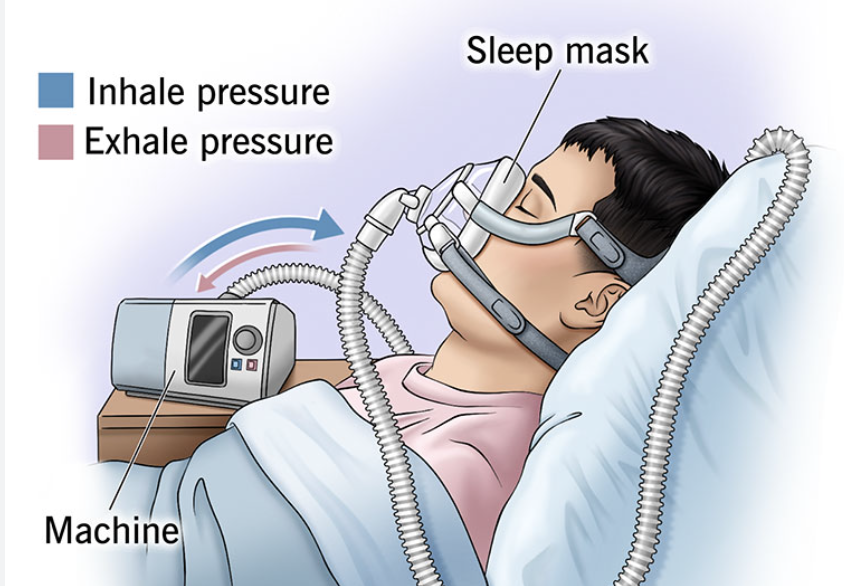
BIPAP
enhances ventilation to avoid mechanical ventilation, not long term
what is mechanical ventilation
a medical treatment that uses a machine called a ventilator to help a person breathe when they cannot do so effectively on their own
what are BIPAPs treatments for
exacerbations of CHF, COPD, short term inability to manage oxygenation AND ventilation
what is the only exception for when BIPAP would be a long-term solution
for palliation, when comfort is the goal and not curing
pts w copd and end stage HF
don’t get off ventilators easily
if ventilation isnt improved with bipap what should you do
consider mechanical ventilation
diff between bipap and cpap
CPAP delivers a single, continuous level of air pressure, while BiPAP delivers two different pressure levels: a higher pressure for inhalation and a lower pressure for exhalation
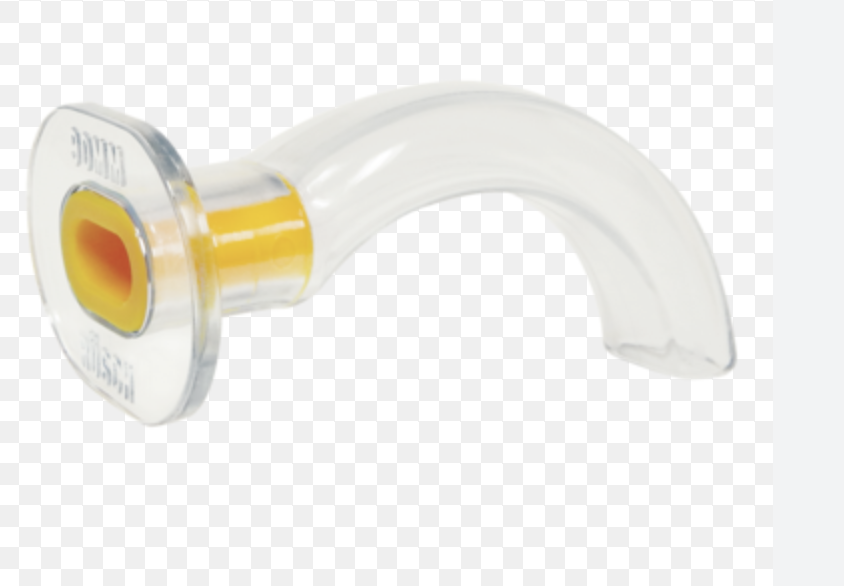
oral airway
don’t use on awake patients
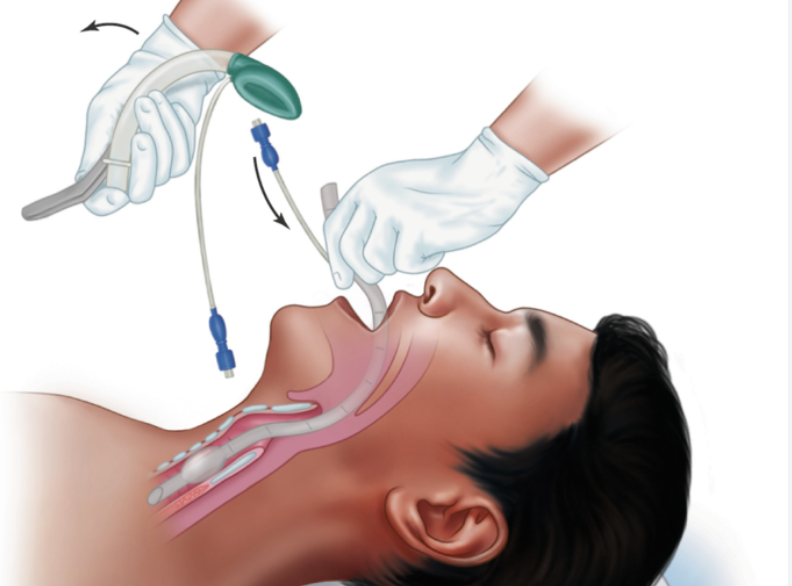
laryngeal mask
short-term for surgery
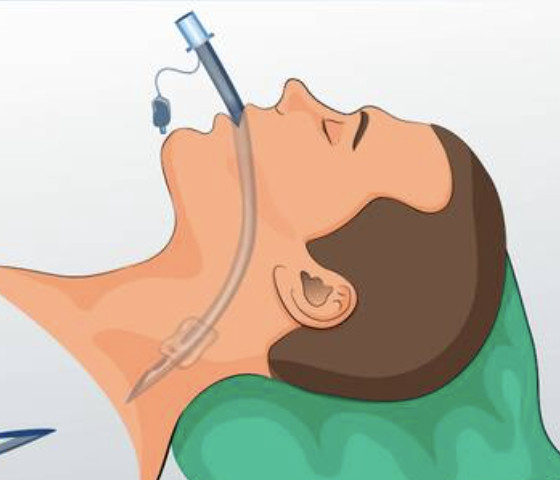
ETT (endotracheal)
goes down to the lung
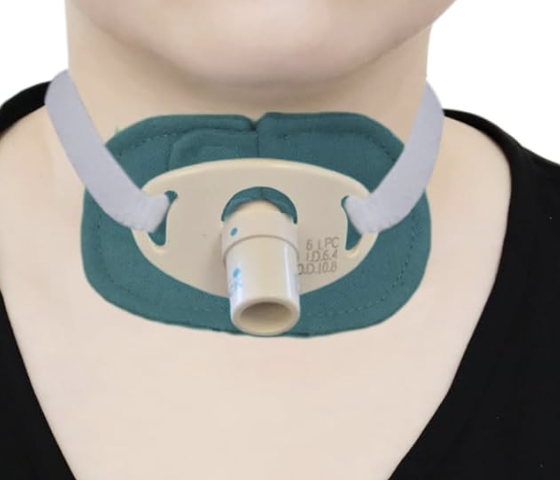
trach tube
corrogated tubing, HAS TO BE HUMIDIFIED/WARM
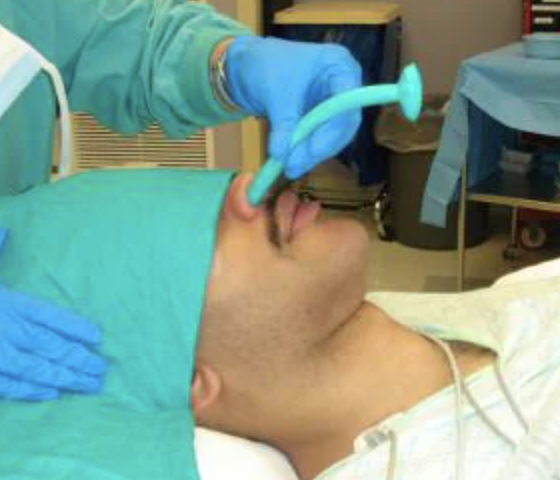
nasotracheal tube
causes you to cough but not gag, keep airways open
what is suctioning for
to clear airways
what does suction cause
swelling and inflammation
when should you suction
ONLY when needed
what should you avoid when suctioning
saline (unless needed)
how long should you suction for
NO MORE THAN 3 SECONDS
what should you assess for pre and post suctioning
pulse oximetry levels, strength of cough, time between each pass, assess how much o2 is needed btwn passes
reasons to suction
junky cough, drop in pulse ox
how many passes should you give max
2 is about the max (pass= passing in and out)
who gets trachs
when you cant get to the airway, cant put tube thru trachea, usually happens during anaphylaxis or have broken their face bones
after how many days will the trach stay open
after 7 days
what will happen to the trach before 7 days
it will close
why are trachs good
helps pts get things in and out quicker bcs only has to get it up to the throat, not any higher than that
chest tubes
drainage systems, pneumothorax, hemothorax, pleural effusion
what should you do if you insert a chest tube
medicate, cough, and deep breath
effusion
collection of fluid within the tissues, lung doesn’t inflate right away
always ask
if pt is on suction or room air
what is a priority action if pt is getting worse when suction is taken off
turn suction back on, if pt immediately gets better, then it was that
how should drainage look in a patient administered a pneumothorax chest tube
no drainage in tube box is normal
how should drainage look like in a pt administered a hemothorax chest tube
the tube should be lower, blood clots are common, look at drainage, slowly decreasing= fine, suddenly stops= might be a clot
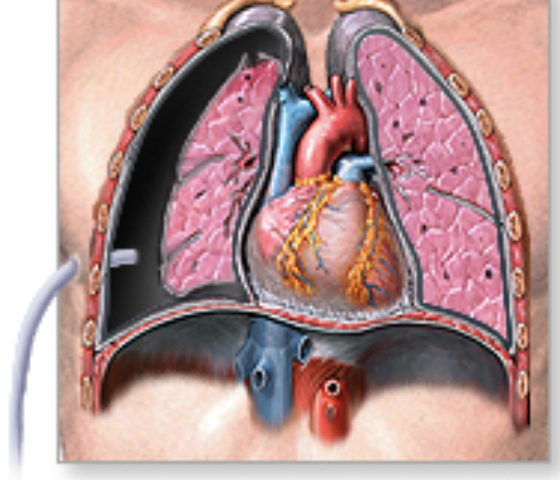
pneumothorax chest tubes
to allow a collapsed lung to re-expand
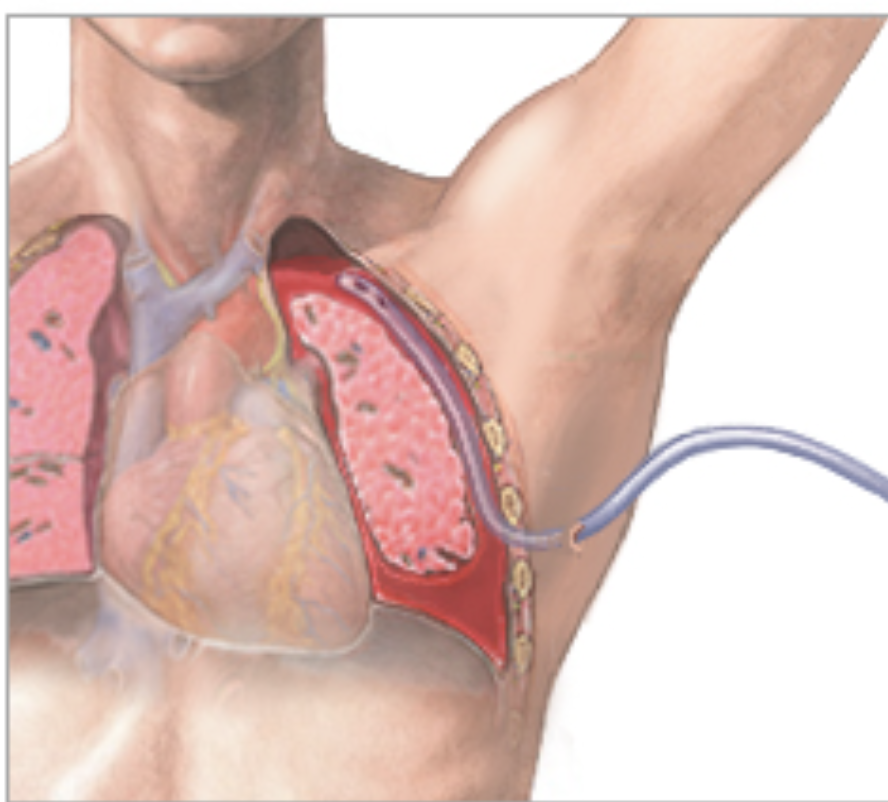
hemothorax chest tube
drains blood from the lungs
pleural effusion
to drain the excess fluid from the space between the lungs and chest wall