IB Biology 1 Summative - Key Terms Review
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards created to help understand key terms and concepts in IB Biology regarding water, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
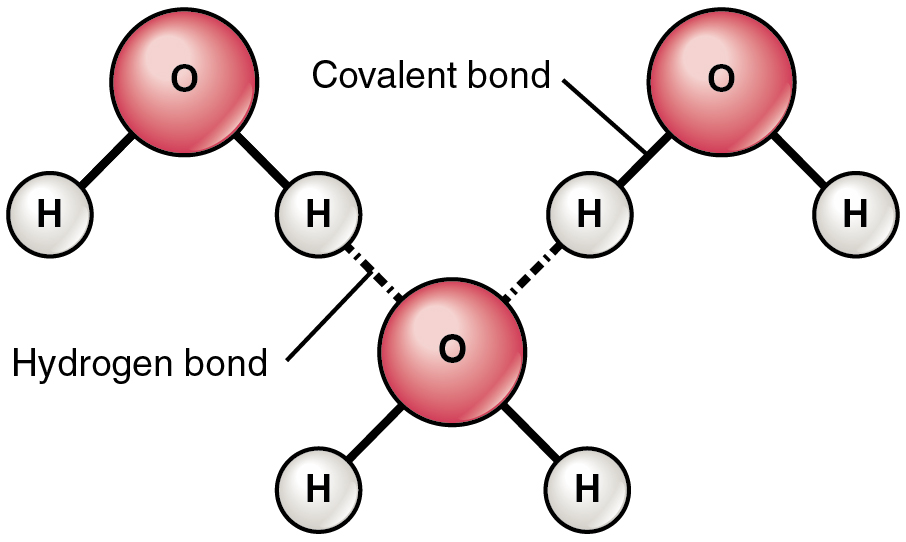
Hydrogen bond
A weak bond formed between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom, contributing to water's cohesive and adhesive properties.
Hydrophilic
Substances that are attracted to water and can interact with it, often polar or charged.
Hydrophobic
Substances that repel water and do not interact well with it, typically nonpolar.
Adhesion
The tendency of water to stick to surfaces, contributing to capillary action.
Cohesion
The attraction between molecules of the same substance, such as water molecules.
Solvent
A substance that dissolves a solute to form a solution.
Solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solvent.
Buoyancy
The ability of an object to float in a fluid due to the upward force exerted on it.
Thermal conductivity
The ability of a substance to conduct heat.
Specific heat capacity
The amount of heat required to change the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius.
Viscosity
A measure of a fluid's resistance to flow.
Condensation reaction
A chemical reaction where two molecules combine to form a larger molecule, releasing water in the process.
Hydrolysis reaction
A chemical reaction that involves the breaking of a bond by adding water.
Glycosidic bond
A type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another molecule.
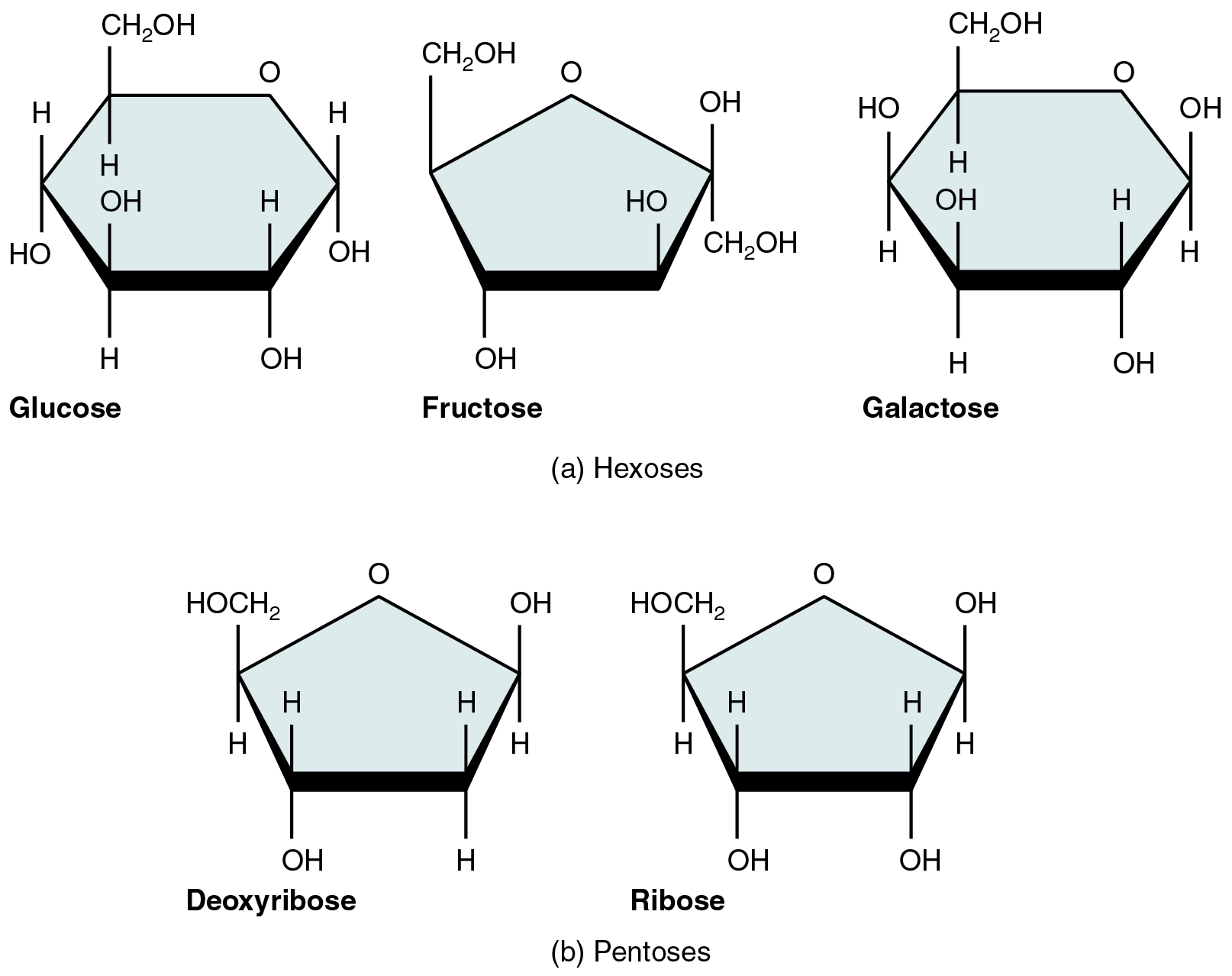
Monosaccharide
The simplest form of carbohydrates; single sugar molecules, like glucose.
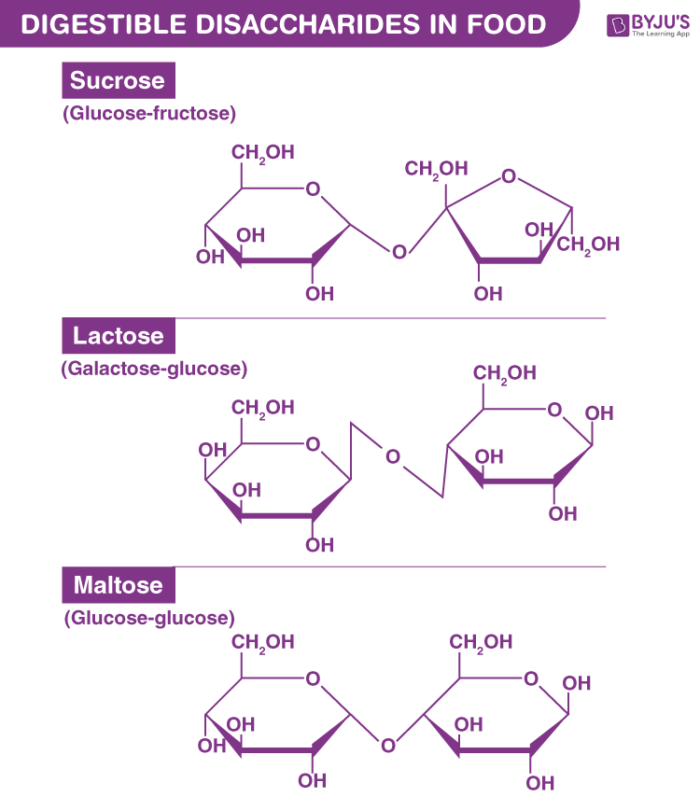
Disaccharide
A carbohydrate composed of two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic bond.
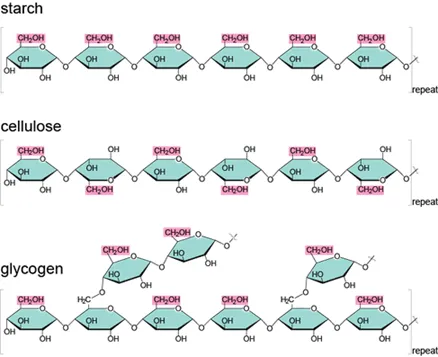
Polysaccharide
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides.
Starch
A polysaccharide that serves as a storage form of energy in plants.
Cellulose
A polysaccharide that is a major component of plant cell walls and is not digestible by humans.
Glycogen
A polysaccharide that serves as a storage form of energy in animals.
Triglyceride
A type of lipid formed from three fatty acids and glycerol, used for long-term energy storage.
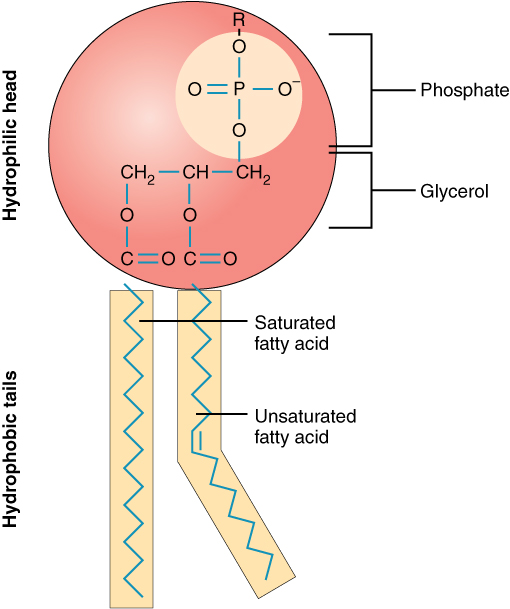
Phospholipid
A lipid composed of two fatty acids and a phosphate group, essential for cell membranes.
Steroid
A type of lipid characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings.
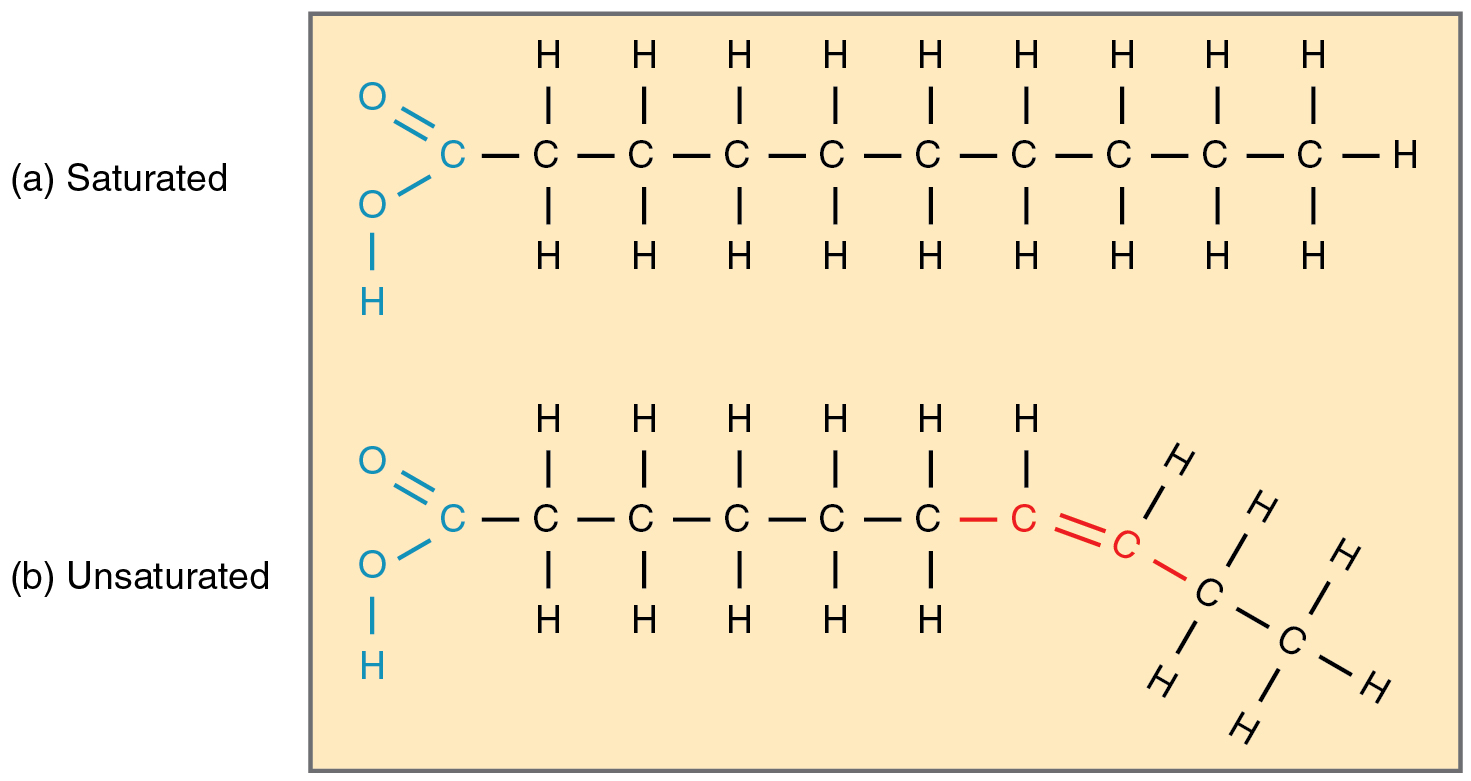
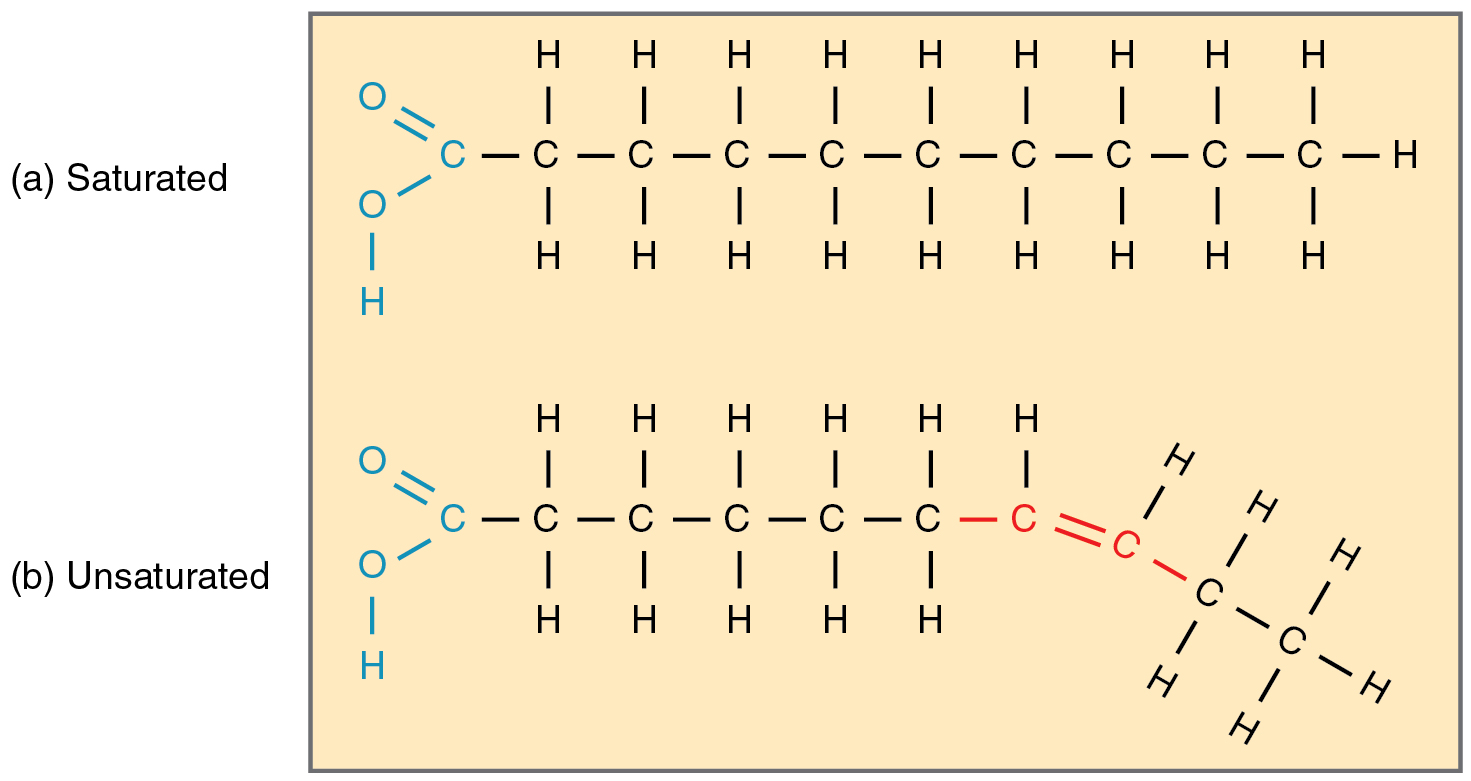
Saturated fatty acid
A fatty acid that contains no double bonds between carbon atoms, saturated with hydrogen.
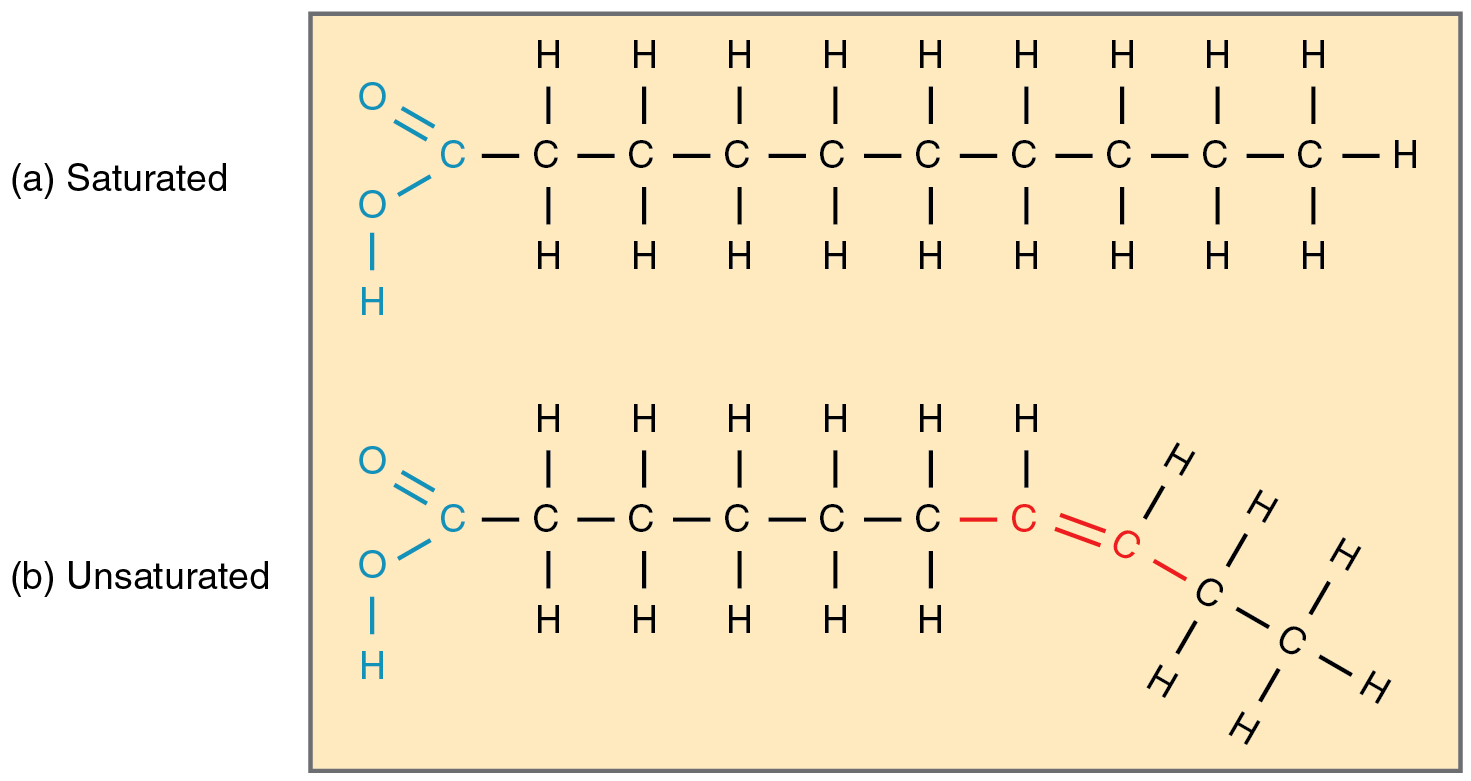
Unsaturated fatty acid
A fatty acid that contains one or more double bonds in its carbon chain.
Oestradiol
A form of estrogen that is involved in the regulation of the female reproductive system.
Testosterone
A steroid hormone that plays a role in the development of male reproductive tissues and promotes secondary sexual characteristics.
Nucleic Acid
Biological macromolecules essential for all known forms of life, including DNA and RNA.
Genetic code
The set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material is translated into proteins.
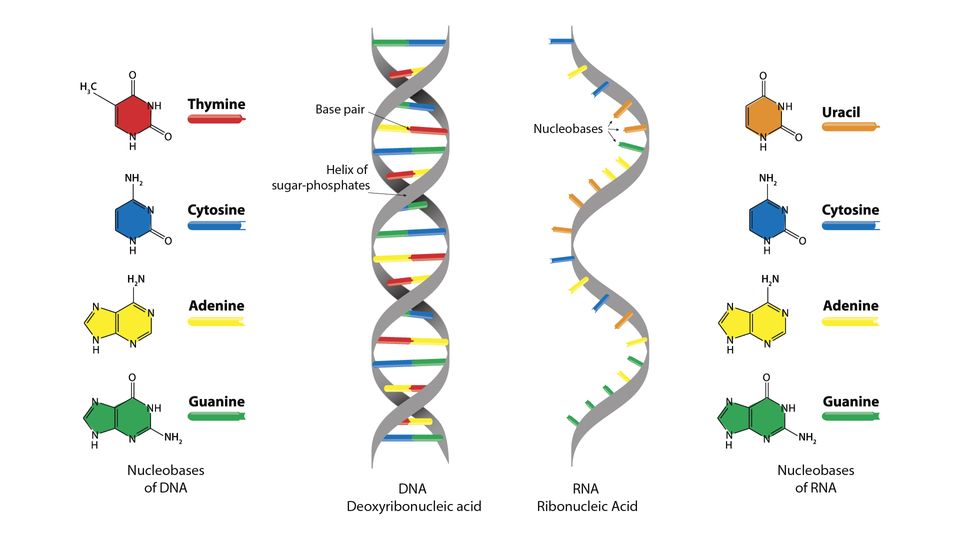
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, the molecule that carries the genetic instructions for life.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid, a nucleic acid present in all living cells that plays a role in protein synthesis.
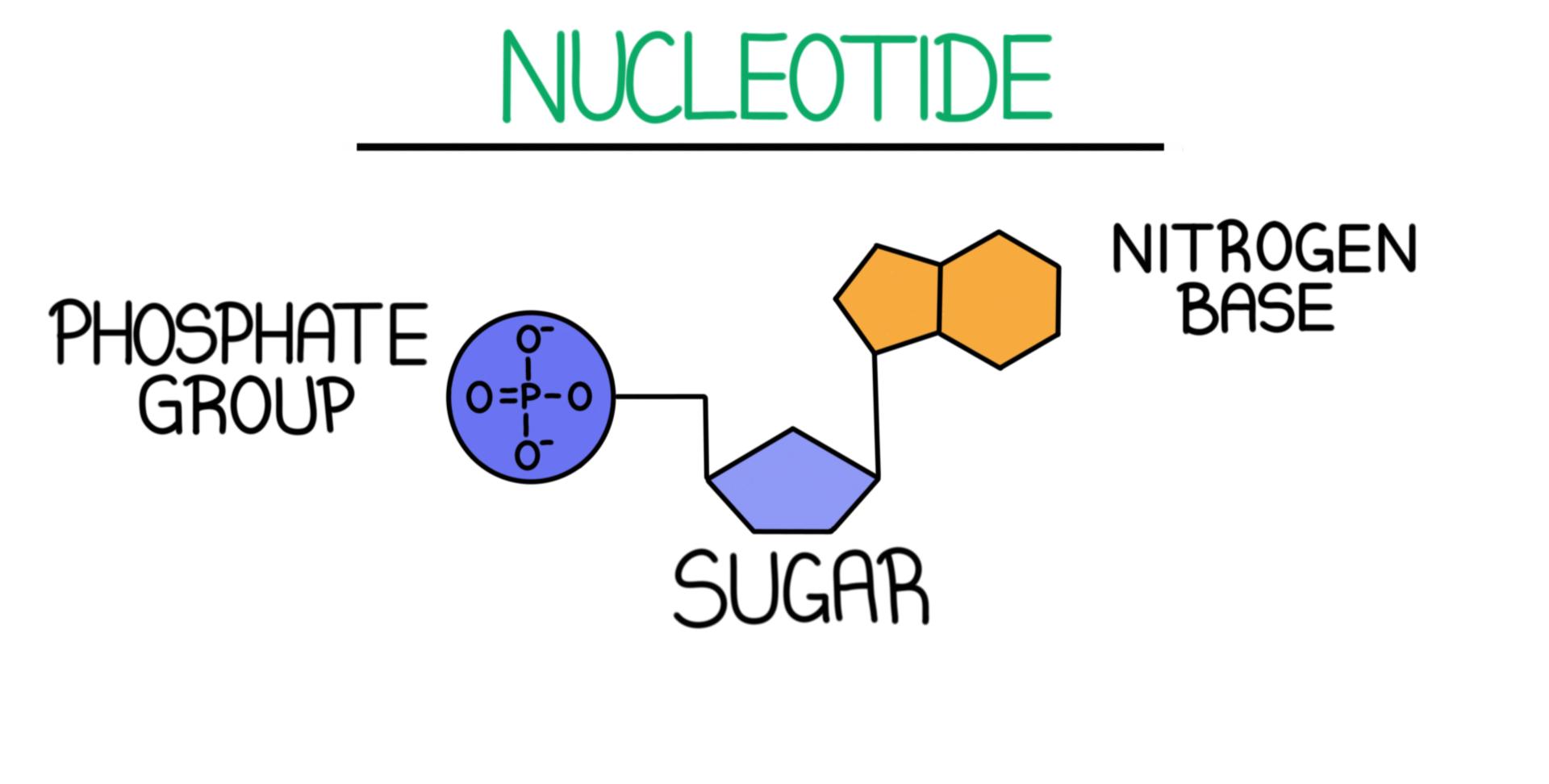
Nucleotide
The basic building block of nucleic acids, consisting of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
Cytosine
A nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA, complementary to guanine.
Guanine
A nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA, complementary to cytosine.
Thymine
A nitrogenous base found in DNA, complementary to adenine.
Adenine
A nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA, complementary to thymine in DNA and uracil in RNA.
Uracil
A nitrogenous base found in RNA, complementary to adenine.
Pentose
A five-carbon sugar molecule, such as ribose or deoxyribose.
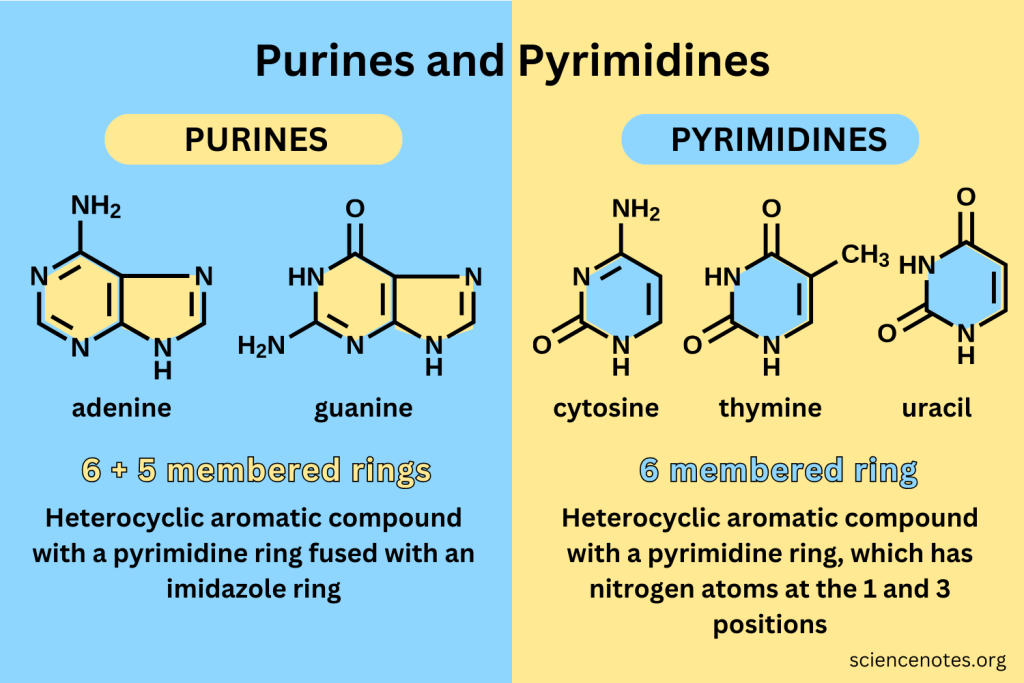
Purine
A class of nitrogenous bases that includes adenine and guanine.
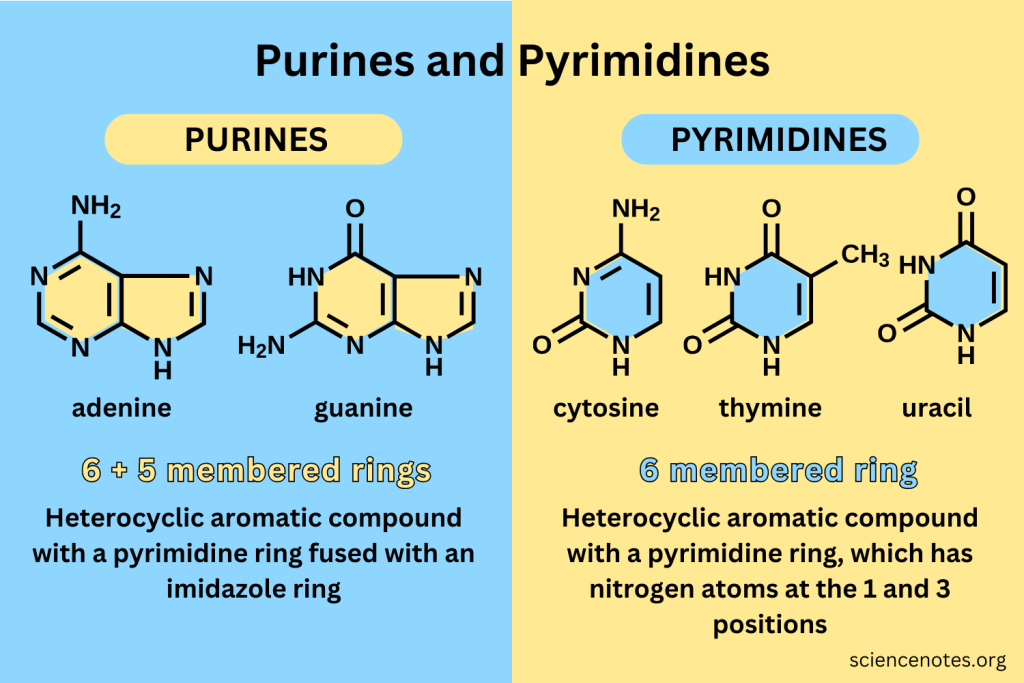
Pyrimidine
A class of nitrogenous bases that includes cytosine, thymine, and uracil.
Polynucleotide
A long chain of nucleotides linked by phosphodiester bonds, which make up nucleic acids.
Codon
A sequence of three nucleotides in mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid.
mRNA
Messenger RNA, the type of RNA that carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosome.
tRNA
Transfer RNA, the type of RNA that brings amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis.
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA, a component of ribosomes that helps in protein synthesis.
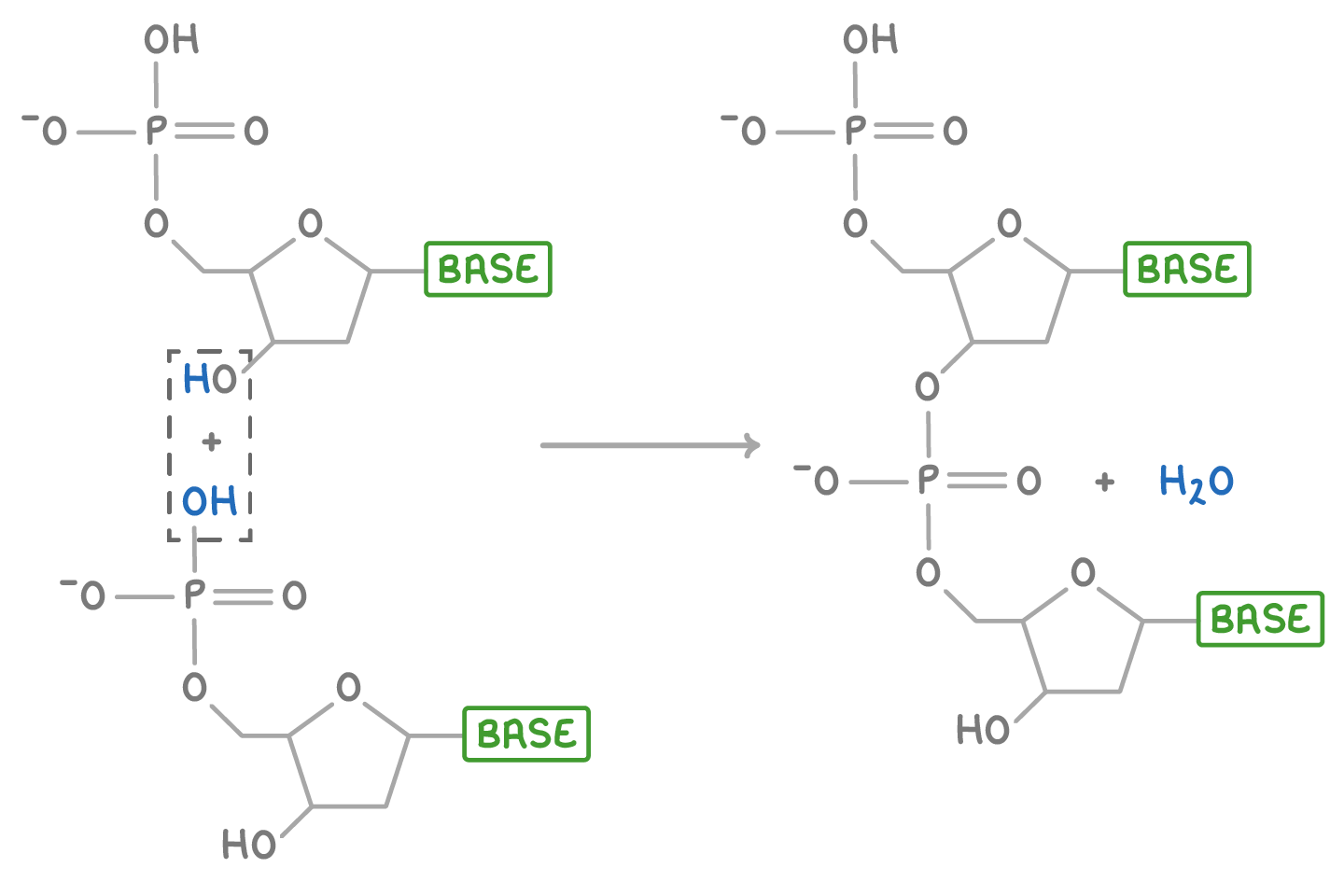
Phosphodiester bond
A type of covalent bond that connects nucleotides in a nucleic acid.
Gene
A segment of DNA that contains the coding information for a specific protein.
Allele
A variant form of a gene that may produce different traits.
Chromosome
A structure composed of DNA and protein, containing genetic information.
Locus
The specific location of a gene on a chromosome.
Homologous chromosomes
Two chromosomes, one from each parent, that are similar in shape, size, and genetic content.
Genome
The complete set of genes or genetic material present in a cell or organism.
Mutation
A change in the DNA sequence that may lead to a change in phenotype.
Nucleosome
A structural unit of chromatin, consisting of DNA wrapped around histone proteins.
Histone
Protein molecules around which DNA is tightly coiled to form nucleosomes.
Non-histone chromosomal protein
Proteins found in chromosomes that are not histones and can contribute to gene expression.
Bacteriophage
A virus that infects bacteria.
Hershey Chase experiment
An experiment that demonstrated that DNA is the genetic material by using radioactive isotopes.
What type of bond is responsible for water’s cohesive and adhesive properties?
Hydrogen bond
Why is water such an important solvent?
Water is a polar molecule that can dissolve many ionic and polar substances due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds with them.
What are three differences between RNA and DNA?
RNA is single-stranded, contains ribose sugar, and has uracil instead of thymine.
What is similar between DNA and RNA?
Both are nucleic acids, consist of nucleotide monomers, and contain genetic information.
What is the monomer of a polysaccharide?
The monomer of a polysaccharide is a monosaccharide, such as glucose or fructose, which can join together through glycosidic bonds to form complex carbohydrate structures.
What type of glucose makes up cellulose? Glycogen? Starch?
Cellulose is made of beta-glucose, while glycogen and starch are composed of alpha-glucose.
What is the monomer of a nucleic acid?
The monomer of a nucleic acid is a nucleotide, which consists of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
What is the structure of a nucleotide?
A nucleotide consists of three main components: a five-carbon sugar (ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine).
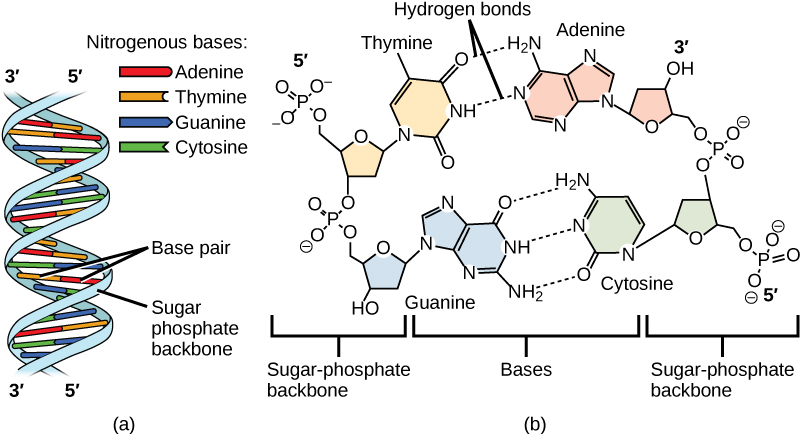
Why do we say DNA strands run antiparallel?
DNA strands run antiparallel because one strand runs in the 5' to 3' direction while the complementary strand runs in the opposite 3' to 5' direction, allowing for proper base pairing.
What type of sugar is found in nucleic acids
includes ribose in RNA and deoxyribose in DNA.
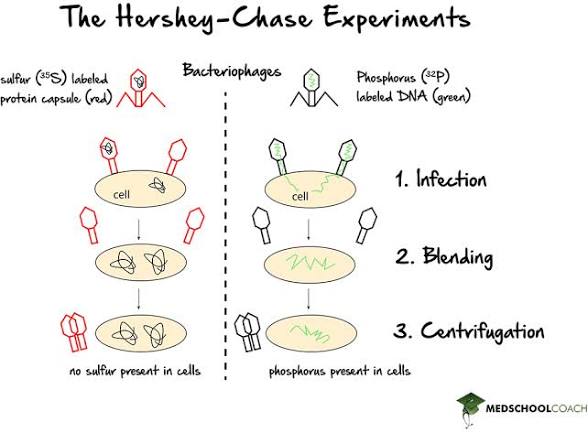
How were radioactive isotopes used in the Hershey Chase experiment
Radioactive isotopes were used in the Hershey-Chase experiment to label DNA and protein, allowing scientists to determine which component was responsible for transferring genetic information in bacteriophages.
Why is the orientation and directionality of DNA important?
The orientation and directionality of DNA are crucial for its replication and transcription processes, as they ensure that enzymes can correctly read the genetic code and that base pairing occurs in a specific manner.