Geology 8 - Exam #3
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam #3 Study Guide
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What is a synapomorphy?
Shared, derived trait
What animals are archosaurs?
crocodilians, pterosaurs, dinosaurs, and birds
What animals are lepidosaurs?
Lizards, snakes, mosasaurs.
“Scaled Lizards” (Shed skin)
Sprawling stance
Teeth fused to bone (no sockets)
How can we distinguish between archosaurs and lepidosaurs (e.g., skull fenestrae; stance; movement style)?
Archosaurs:
diapsid
upright limb posture
parasagittal movement (like how cats or dogs walk)
Lepidosaurs:
diapsid
sprawling limb posture
side-to-side movement
What were the contributions of William Buckland, Gideon and Mary Ann Mantel, and Richard Owen to our knowledge of dinosaurs?
Buckland → first dinosaur described.
Mantells → first herbivorous dinosaur recognized, highlighting diversity.
Owen → defined Dinosauria, unifying early discoveries into a scientific group.
How did the Crystal Palace help popularize dinosaurs?
creating the world's first life-sized, three-dimensional dinosaur sculptures
What are the historical significances of Megalosaurus, Iguanodon, Hylaeosaurus, and Hadrosaurus?
1824-Megalosaurus("Giant Lizard")
1825-Iguanodon("Iguana Tooth")
1832-Hylaeosaurus("Forest Lizard")
archosaurs
socket teeth
erect limbs
-1858 hadrosaur (big lizard)
1st dino skeleton in museum
similar to iguanodon
duck billed
lived in herds
Megalosaurus, Iguanodon, Hylaeosaurus, and Hadrosaurus. What dinosaur groups do those animals belong to?
Theropod, Ornithopod, Ankylosaurs, Hadrosaurs
How have scientific depictions of the Iguanodon changed over the years?
Used to be a lizard-like quadruped with a nose horn; fossils revealed the “horn” is a thumb spike.
Today it’s shown as a facultative biped dinosaur with a stiff, raised tail.
What were the Bone Wars, and who were the main scientists involved?
Charles Marsh and Edward Cope competed for the discovery and naming of new dinosaur fossils in the American West. Leading to rushed work, errors, and damaged professional reputations.
How did the events of the Bone Wars help and hurt the field of dinosaur paleontology?
Helped:
Led to the discovery and naming of many new dinosaur species
Greatly expanded fossil collections and public interest
Hurt:
Rivalry caused rushed, sloppy descriptions and naming errors
Some fossils were damaged or destroyed to block rivals
What was the significance of animals like Elasmosaurus, Dryptosaurus, Apatosaurus, and Camarasaurus?
Marsh and Cope messed up names or placements of fossils. Prehistoric reptiles lived in the sea.
What do the early Triassic dinosaurs (like Eoraptor) look like (body stance, finger pattern)?
Body stance: Upright, with a horizontal spine and long tail for balance
Limbs: Long hind legs for running, shorter forelimbs
Hands/fingers: Five fingers, some grasping ability; more primitive than later dinosaurs
Overall look: Sleek, agile, lightly muscled, resembling a small lizard-like predator
What is the difference between an ornithischian and a saurischian in the traditional dinosaur cladogram?
saurischian: lizard hipped (pubis points front)
- sauropods and theropods
ornithischians: bird hipped (pubis points back)
- Thyreophora and Marginocephalia
-hollow bristles
What does a sauropodomorph look like?
bipedal and long neck, herbivore
How did their bodies change over time from basal sauropodomorphs through prosauropods, sauropods, and neosauropods?
Over time they became obligate quadripeds because their arms became heavier and heavier in proportion to their bodies. Necks became longer head became smaller in proportion to neck
What were the teeth like in basal sauropodomorphs, Camarasaurus, and Apatosaurus?
Summary memory tip:
Sauropodomorphs: leaf-shaped
chewing or cropping plants
Camarasaurus: spoon-shaped
Good for breaking down shrubbery in mouth
Apatosaurus: pencil-shaped
scraped plant material off branches
Swallows food whole and relies on gastroliths
What line of evidence demonstrates that sauropods (and all other quadrupedal dinosaurs) had bipedal ancestors?
ancestor has long back legs & short front legs
What evidence do we see in their fossils that helps us interpret how their respiratory system worked?
bird-like air sac systems
What do the hips of an ornithischian look like?
bird hipped (pubis points back)
Aside from the pelvis, what other synapomorphies do ornithischians have?
Beak predentary bone, cheeks, hinged jaws.
Which dinosaur groups are ornithischians (remember the cladogram is showing this)?
Thyreophora
Marginocephalia
Ceratopsia
Hadrosaurs
Pachycephalosaurs
stance of an ornithopod
Smaller ones agile and bipedal
Larger ones semi-quadrupedal
Largest fully quadrupedal
How flexible was the tail of an ornithopod?
not a lot of flexibility and they don’t drag their tails
What adaptations did the hadrosaurs have for processing food?
-chopping beak
-stack of teeth for grinding Dental Battery
-multi-directional chewing motion
What did California look like during the Mesozoic era?
During the Mesozoic, California continued to comprise both marine and terrestrial habitats. Local marine life included ammonites, marine reptiles, and oysters. On land, dinosaurs roamed among cycads and conifers.
What did North America look like during the Late Jurassic-Late Cretaceous?
In Middle and early Late Jurassic times, the western regions of North America were covered by shallow seaways that advanced and retreated repeatedly, leaving successive accumulations of marine sandstones, limestones, and shales.
During the most of the Late Cretaceous, North America would be divided in two by the Western Interior Seaway, a large interior sea, separating Laramidia to the west and Appalachia to the east, then receded late in the period, leaving thick marine deposits sandwiched between coal beds.
Where are Laramidia, Appalachia, and the Western Interior Seaway?
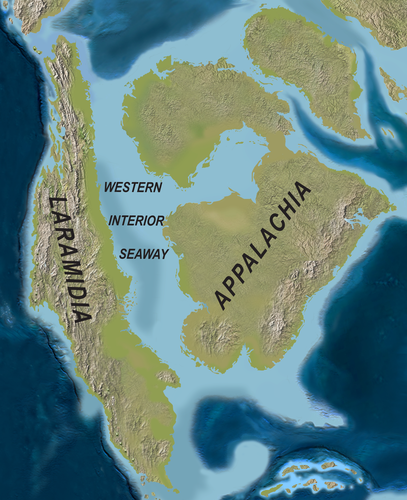
Why do we find different dinosaurs in the western vs. eastern United States?
Not able to travel to other parts of the United States
Where are the best dinosaur fossils found?
Fossils are most often preserved in ancient riverbeds, floodplains, and deserts. More complete fossils in dessert areas like Asia
What is the synapomorphy of Marginocephalia?
- Synapomorphy-"shelf" on back of skull
-Herbivores
What does a Pachycephalosaur look like?
thick dome headed shape
obligate bipeds and short
How do the pachycephalosaurs differ from the other ornithischian groups?
Big dome headed
bipedal lizards
What might the pachycephalosaur dome have been used for?
headbutting
What are the two synapomorphies of the Ceratopsians?
Pointed jugal bones
Rostral bone forms an upper beak
How did the bodies and standing style of
the Ceratopsians change as the group evolves?
Changed from obligate bipeds into obligate quadrupeds.
What important synapomorphy distinguishes the Neoceratopsians from basal Ceratopsians like Psittacosaurus?
psittacosaurus: parrot lizard
bipedal w quills
Lack a true frill
Neoceratopsians:
Frill
Horns
What are the synapomorphies of the Thyreophora?
shield-bearers
osteoderms
paracsapular spines
What did the basal Thyreophorans (e.g., Scutellosaurus) look like?
-bipedal
-still had osteodorms
-small
What clue do we have to the eating-style of Stegosaurus?
small, narrow skull with weak jaw muscles.
low-browsing herbivore, feeding on soft vegetation (like ferns)
How were the plates of a Stegosaurus arranged?
Two staggered, alternating rows down its neck and back
What was its thagomizer for?
-spikes on the tail
-used for active defense
What did Ankylosauria look like?
-armor everywhere...fused osteoderms
What adaptations did the Ankylosaurs have for passive and active defense?
-armor plates all over body(passive)
-osteoderms develop on tail (active)
What are the differences between the subclades Ankylosauridae and the Nodosauridae?
Anky
-no tail club
-parascapular spines
Nodo
-tail club
-no parascapular spine
What do Theropods look like?
"Beast Foot"
Obligate bipeds; good runners
mostly carnivores
Lizard hipped dinos
What kind of hip do theropods they have?
lizard hipped pubis points forward
What are the synapomorphies of the theropods?
● Serrated teeth (saw blade edges)
● No fifth finger
● Three standing toes (like a pigeon foot)
● Furcula (wishbone); Basically a fused collarbone)
What change did theropods make to their hands? How flexible were those hands?
Theropod hand evolution:
Theropods reduced fingers and evolved grasping hands.
Flexibility:
Their hands were highly flexible, with a semi-lunate wrist (like humans)
What were the Coelurosaurs like?
Group of theropods that work on improving their arms
Improved arms
○ 3 fingers
○ Very large brains
○ Feathers
○ Getting birdier
What were the Tyrannosaurs, Ornithomimids, and Maniraptorans like?
Tyrannosaurs:
Large, powerfully built predators with huge skulls, bone-crushing bites, strong legs, and tiny but strong arms.
Ornithomimids:
Fast, ostrich-like dinosaurs with long legs, small heads, and toothless beaks
Maniraptorans:
Small to medium, feathered theropods with long arms, very flexible hands
What adaptations did Tyrannosaurs have for being apex predators?
Huge bite, bone-crushing teeth (Bite and rip), binocular vision, strong legs
How do the hips and leg movements of Maniraptorans change from those of earlier theropods?
-bird hips
-more force on knees rather than hips
What features do dromaeosaurs like Velociraptor have?
-backward toe(1)
-sickle claw(2)
-walks on toes(3,4)
-Vestigial metatarsal(5)
How does a movie monster Velociraptor (i.e.: Jurassic Park) differ from an actual Velociraptor?
movie version:
bigger, flexible tail
pronated hands.
real version:
smaller, has stiff tail
palms inward with no ability to rotate hands. Real are more bird-like(feathers & wing-like features)
What similarities do birds have to the earlier maniraptoran theropods like Archaeopteryx? What differences do they have?
-long tail
-hands/claws
-flat sternum
-teeth no beak
-Late Jurassic
How might birds have developed flight?
Flight model 1: “Trees Down”
Flight involves gliding
○ Need tree-climbing dinos
Flight model 2: “Ground Up”
○ Flight involves running; like a runway
○ Need running dinos with feathers
○ Increasing adaptations for jumping, gliding
What was the primary cause (the leading hypothesis; the one we cover) of the extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous?
The K-Pg Mass Extinction
Where did this event take place, and why did that localized event cause a global extinction?
Yucatan peninsula, Mexico
HUGE sulfur particles in the air and leads to extreme cooling and acid rains
Sediment is ejected out of the atmosphere burns on re-entry
○ Huge temperature spike from all the radiation (stuff burning)
What dinosaur group survived the end of the Cretaceous and what dinosaur clades are still alive today (e.g., are coelurosaurs still alive?)?
Coelurosaurs still alive Jurassic to Today !!!! still exists !!!!
All living dinosaurs are birds, which are coelurosaurian theropods.
Synapomorphy of archosaurs
-diapsid skull
-socket tooth
- upright stance
- appendicular movement
What do the hands of Iguanodon and Edmontosaurus look like?
- Iguanodon:Thumb spike (1)Hooved fingers (2,3,4)Opposable pinky (5)Good for grasping, supporting weight
- Edmontosaurus:No thumb (1)Spiked index (2)Hooved finger (3)Fourth finger bound in "mitten" to 3Short finger (5)Only useful for standing