Chem 302 Organic Chemistry Intro
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
# carbons in meth-
1 carbon
# carbons in ethane
2 carbons
# carbons in propane
3 carbons
# carbons in butane
4 carbons
# carbons in pentane
5 carbons
# carbons in hexane
6 carbons
# carbons in heptane
7 carbons
functional groups
reactive parts of a molecule that undergo the same chemical reaction regardless of position
alkene
organic compound with a double bond
alkyne
organic compound with a triple bond
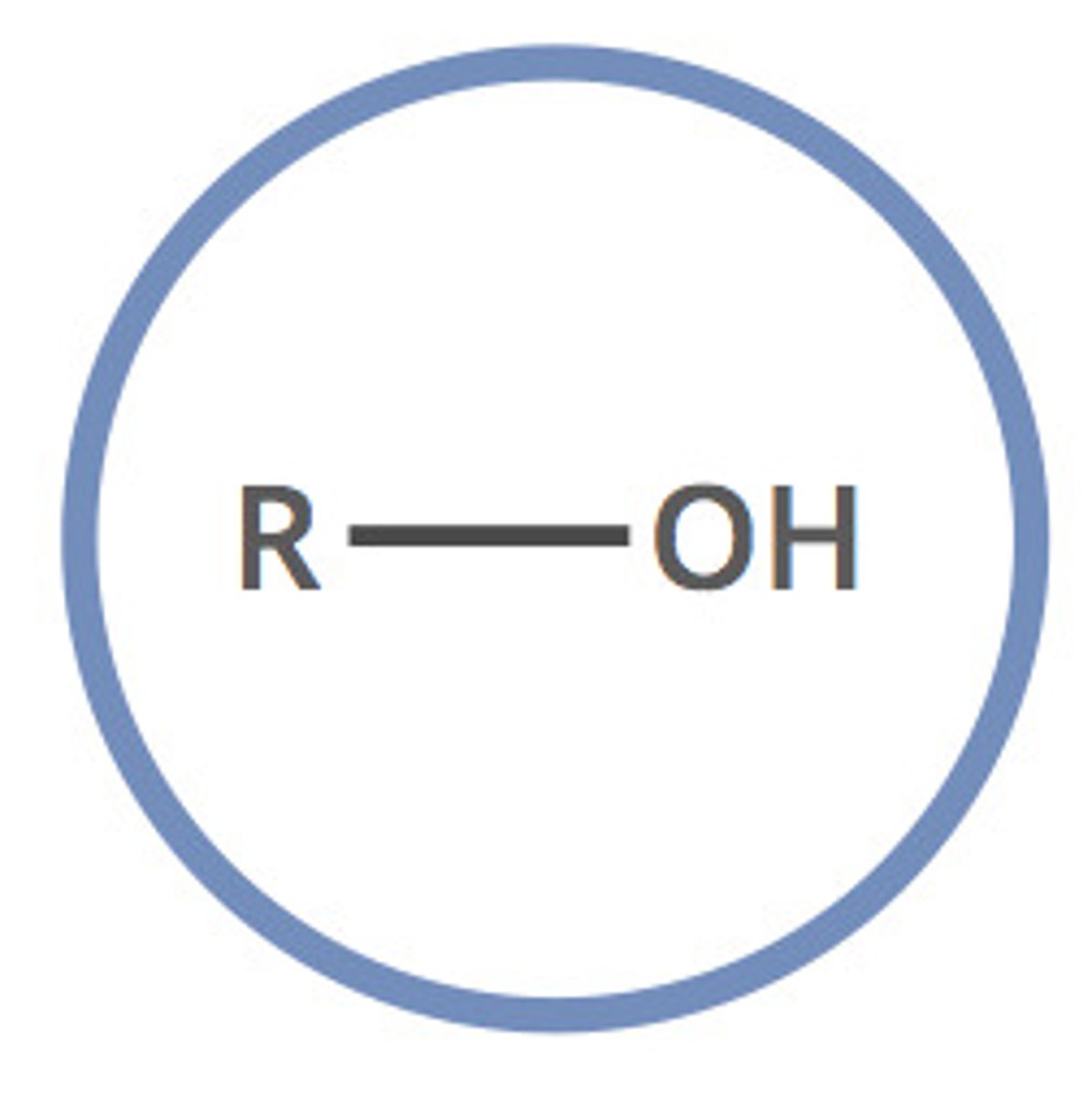
alcohol
R-OH (-ol)
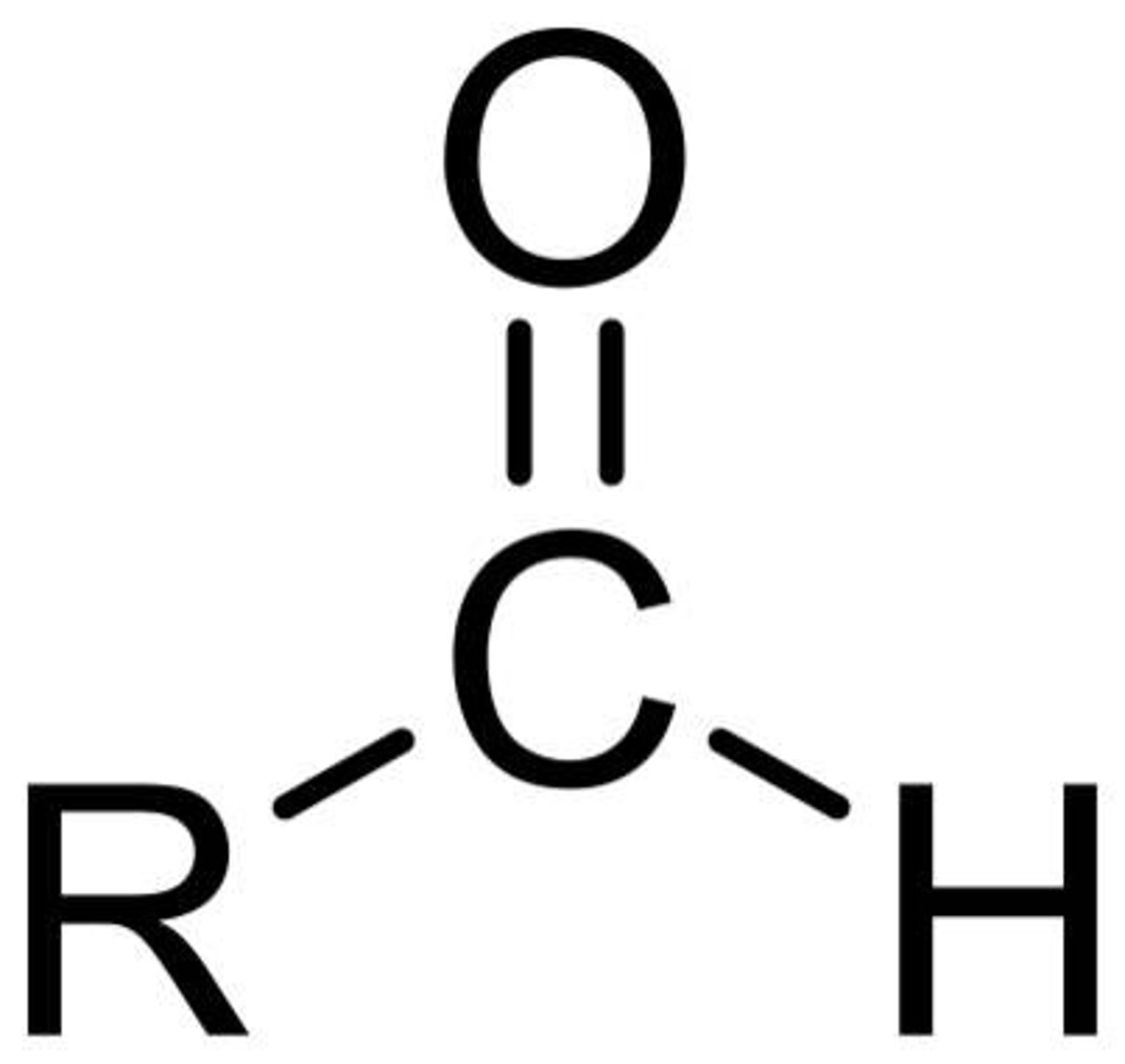
aldehyde
R-C=O-H
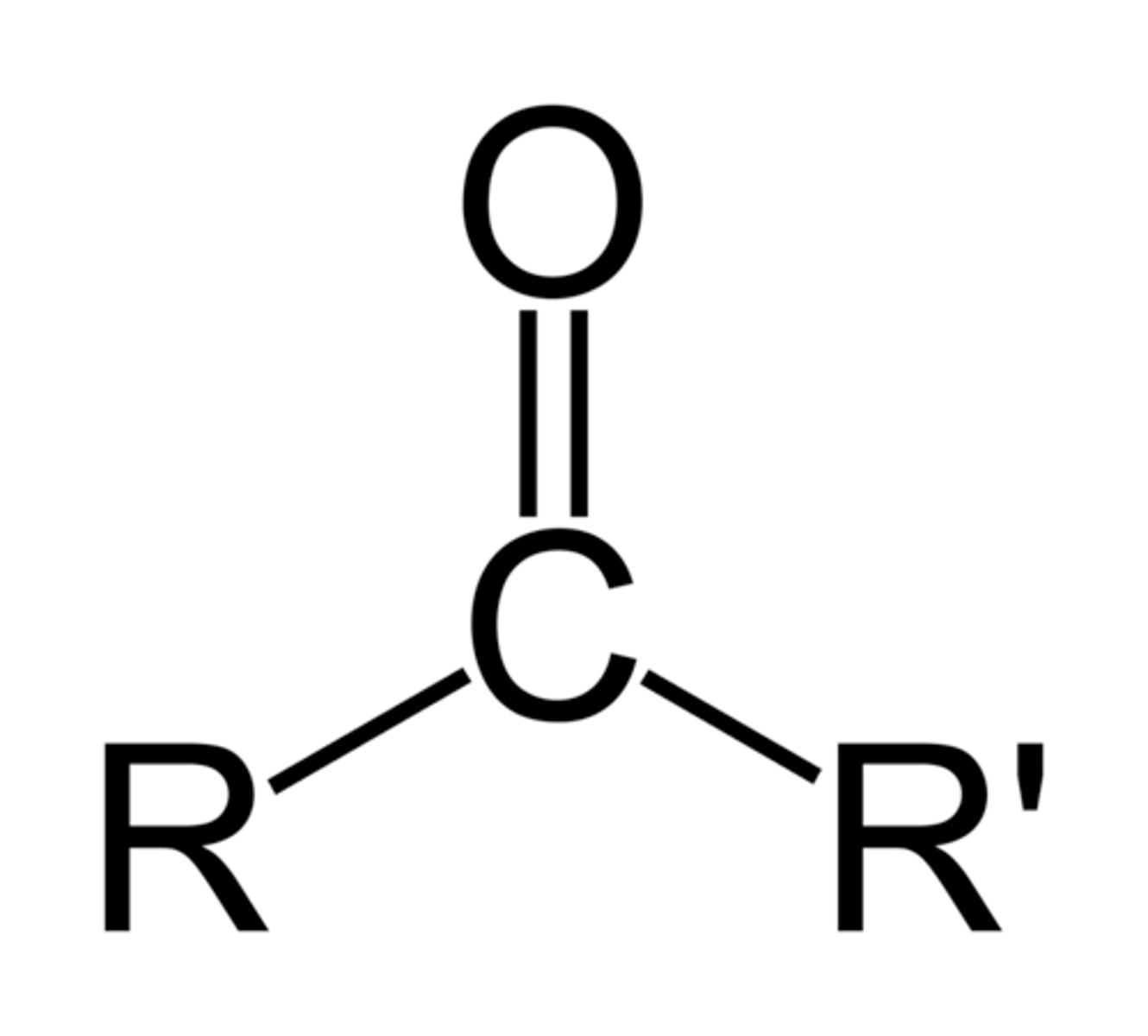
ketone
R-C=O-R
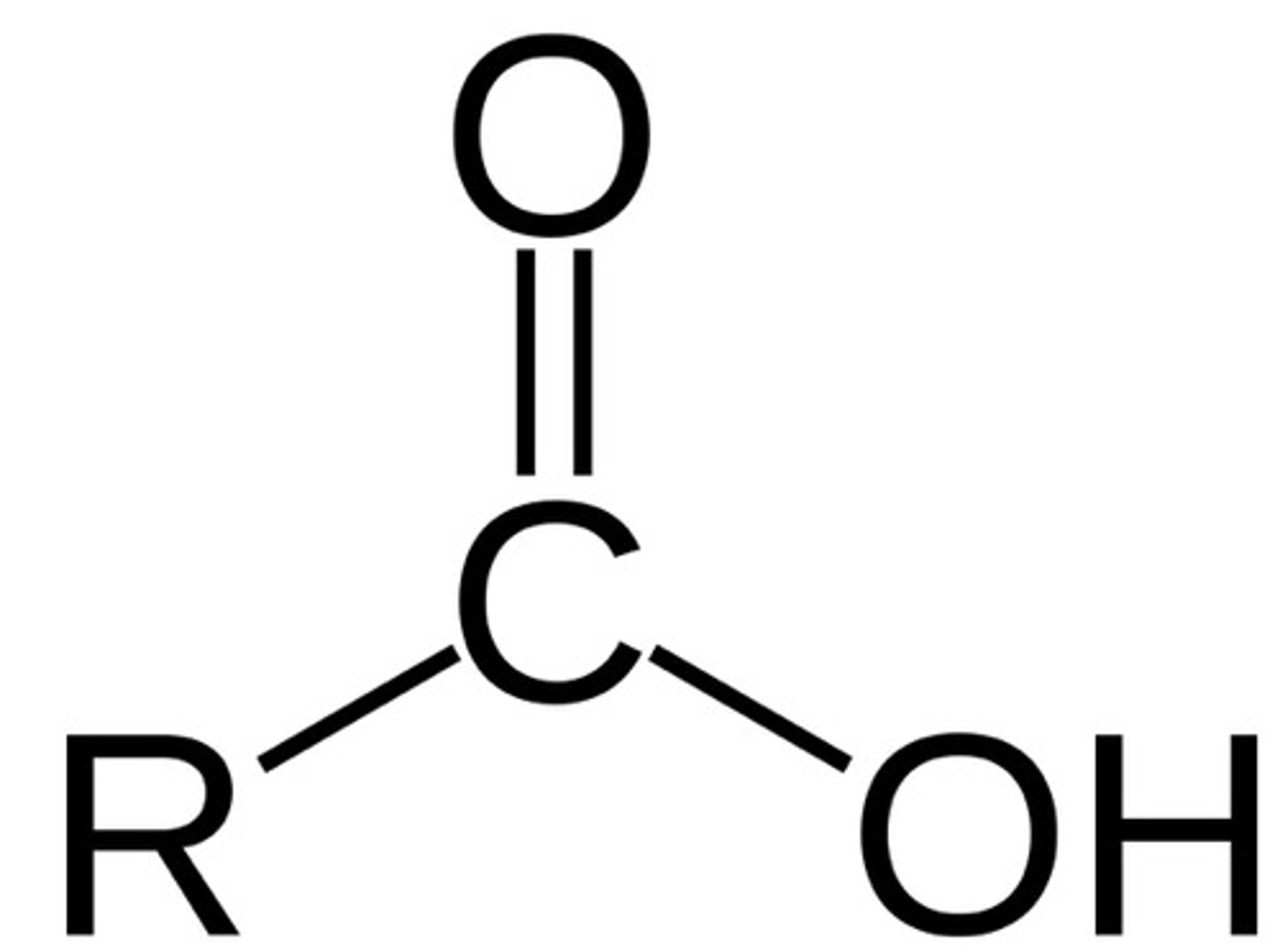
carboxylic acid
R-COOH
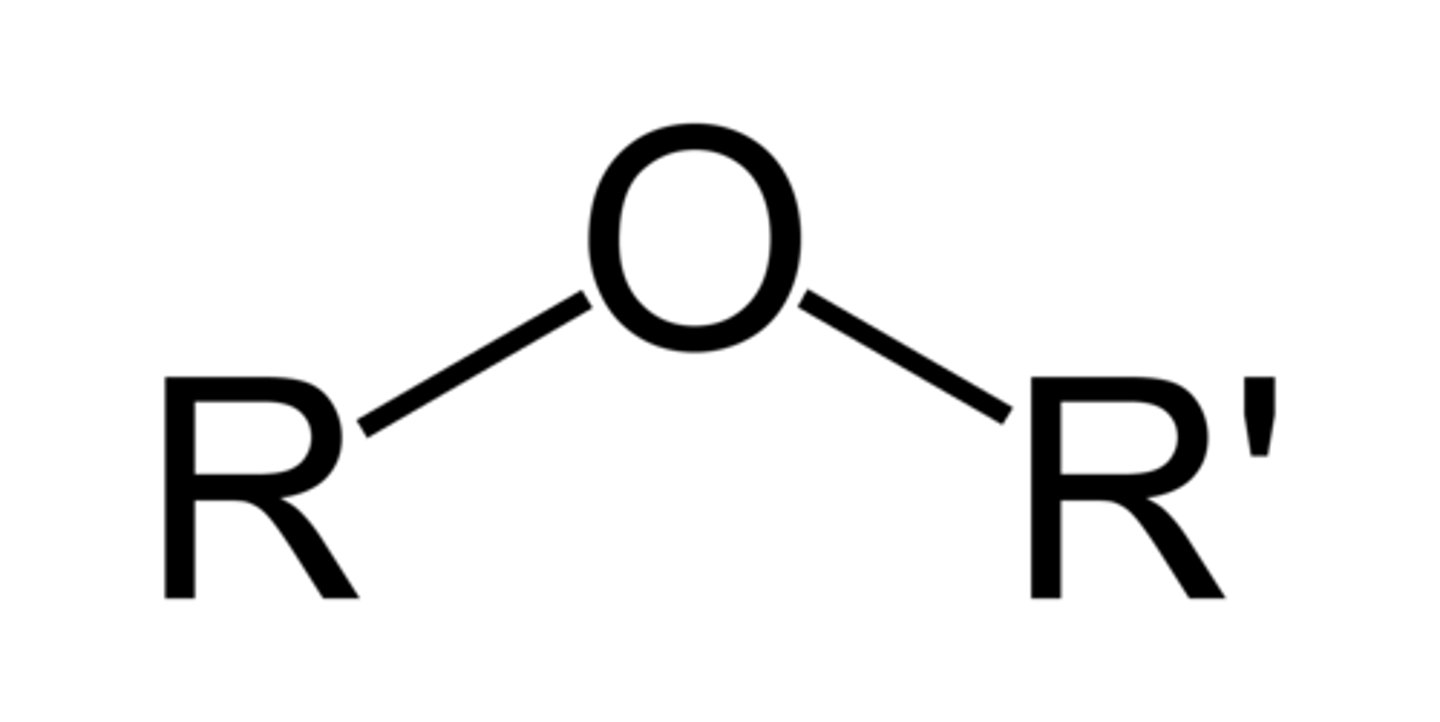
ether
R-O-R
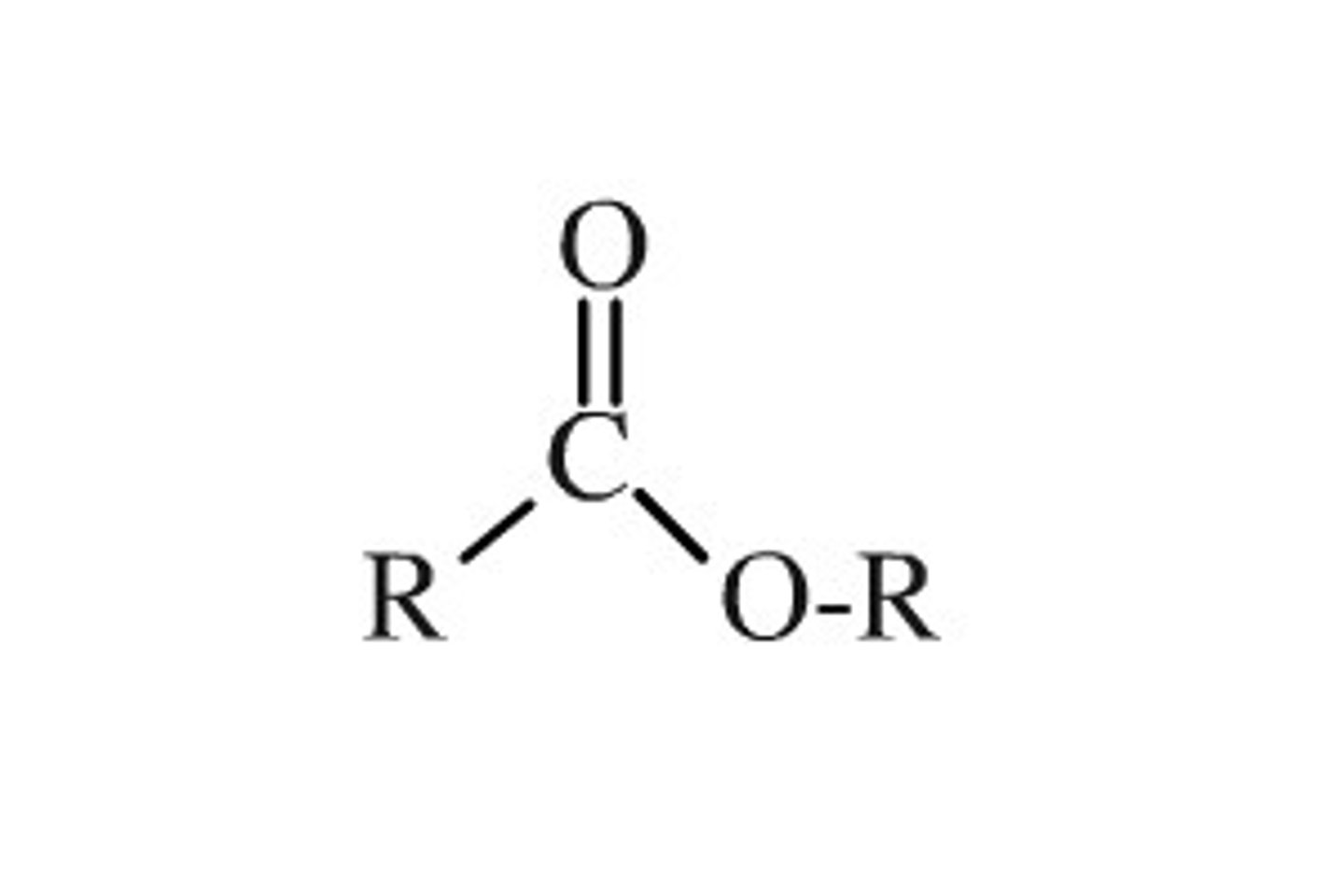
ester
R-C=O-O-R (-oate)
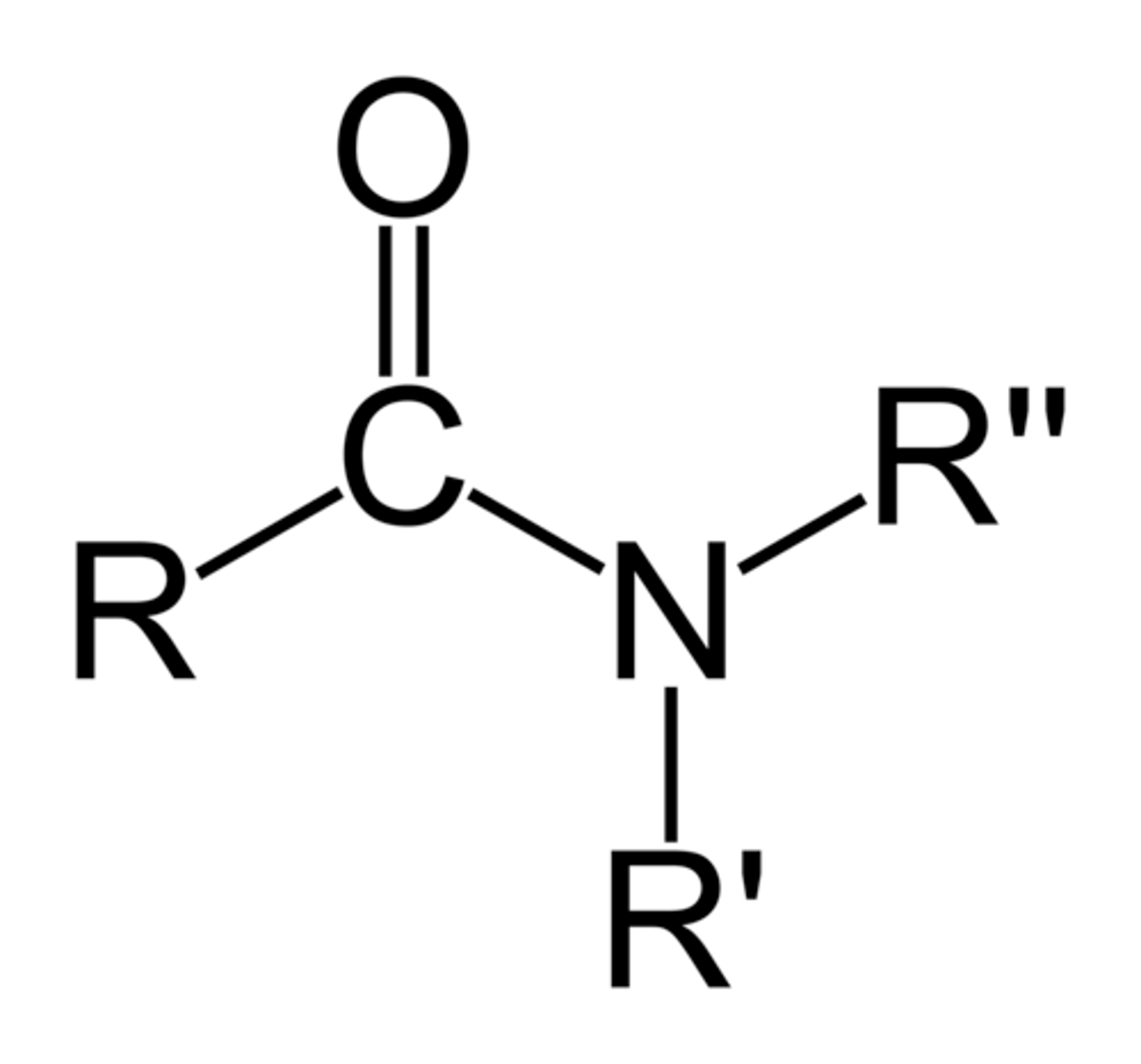
amide
R-C=O-N-R-R
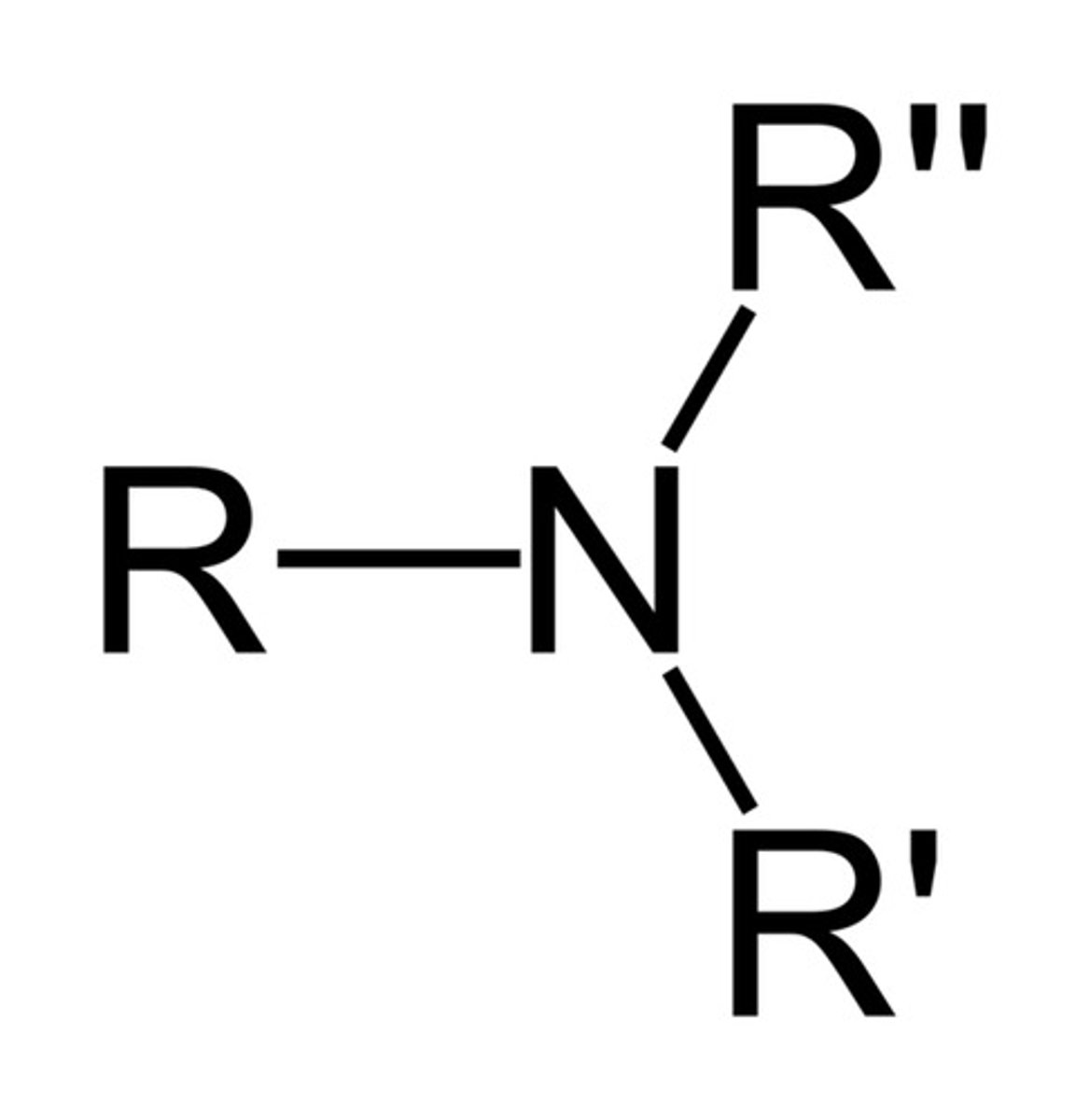
amine
R-NR
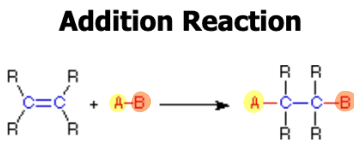
Addition
Addition of adjacent atoms to a molecule--seen in organic
polymer reactions. Has a double in the beginning that turns into a single bond
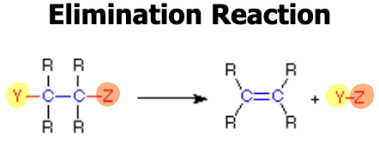
Elimination
Removal of adjacent atoms from a molecule. carboxylic acid + amide = amide linkage
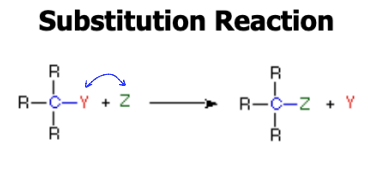
Substitution
atom or group of atoms are replaced by another
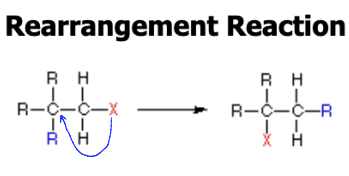
Rearrangement
An atom or group of atoms move to different carbons.
Carboxylic acids combine with hydrocarbons to make …
fatty acids
Monosaccharides combine to make polysaccharides to form …
carbohydrates
amino acids make polypeptides that make …
proteins
The monomers (basic building blocks) form
polymers through …
dehydration synthesis (water is eliminated).
Polysaccharides (polymerized sugars) are
formed from what kind of bonds?
ether
polystyrene
addition reaction
polyurethane
addition reaction
polypropylene
addition reaction
polyvinylchloride
addition reaction
polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
condensation polymerization reaction
polyamide (PA)
condensation polymerization reaction
polyethylene
addition reaction
Collision theory is based on …
kinetic molecular theory of gas
Ek = ½ kT = ½ mv2
A collision must occur for the reaction to happen
doesn’t explain first order decay.
Collision must be effective which requires
1) sufficient energy (high enough temp)
2) correct orientation of collision
The rate of reaction is concentration dependent
Kinetic Theory – Transition State
Most easily depicted on a reaction profile of E vs. t
Based on energy not collisions
Kinetic Theory – Transition State
In this profile, that has been used in thermo, an energy hill, called the activation barrier, rises, positively above the thermodynamic profile.
This barrier is what spontaneous - ΔG (-) – processes don’t happen (like combustion)
The top of the activation barrier is the “transition state” or
“activated complex.”
It is theoretical. It is not an intermediate.
At top of energy hill, a transition state is equally likely to fall to
the left or the right
Combined Arrhenius
Looks like Van’t Hoff and Clausius Clapeyron
Ea Always (+) so T increasing means k increases
k = Ae-Ea/RT
Give [ ] vs t at 2 temperatures yields x, k, A, Ea, data
The pre-exponential factor provides a measure of the frequency of collisions and therefore is larger for gases
Combined Arrhenius
The activation energy term describes an endothermic process
Combined Arrhenius
Because the temperature term is the denominator of the
exponent term, as temperature increases, the rate constant
increases
Combined Arrhenius
Structural Isomers
Due to the flexible nature of carbon bonding, the same chemical formula can exist in many different forms
carbohydrates
functional groups before polymerization - 2 alcohols
functional group after polymerization - ether sugars
monosaccharides make up the polymer
protein
functional groups before polymerization - carboxylic acid + amine
functional group after polymerization - amide
amino acid make up the polymer
lipids
functional groups before polymerization - carboxylic acid + alcohol
functional group after polymerization - ester
glycerol make up the polymer
bond energies
IMF - 10^0 to 10^1 kJ/mole
Covalent bonds: 10^2 to 10^3 kJ/mole
Nuclear reactions (fission and fusion): 10^9 to
10^10 kJ/mole
Hydrogen > Ion-dipole> ionic> nuclear
nuclear fusion and fisson are both
exothermic
Transiton states can have more (can’t be less) energy than the prior species.
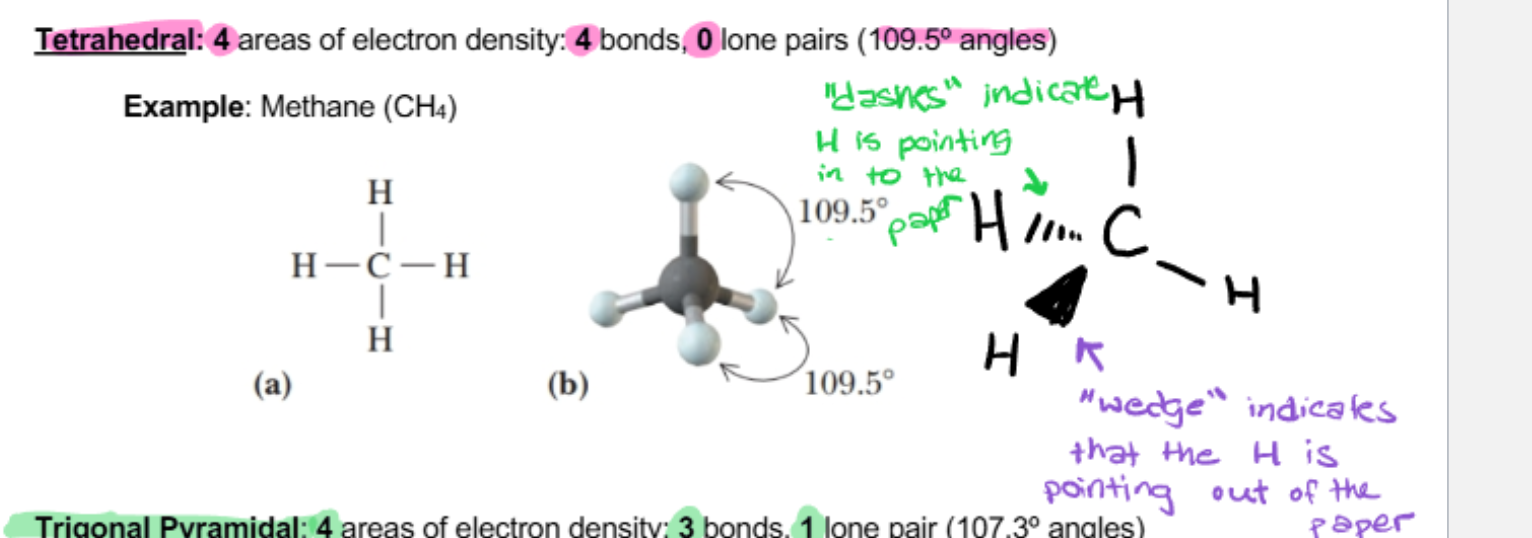
tetrahedral
4 areas of electron density: 4 bonds, 0 lone pairs
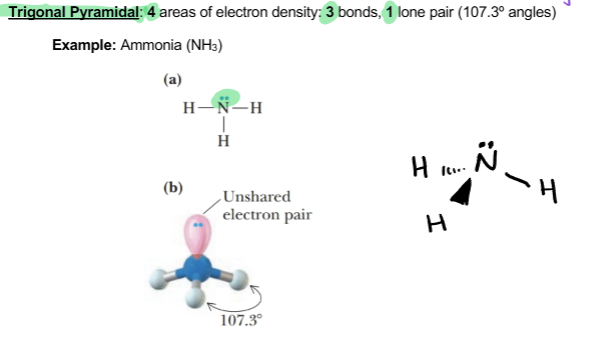
Trigonal pyramidal
4 areas of electron density: 3 bonds, 1 lone pair
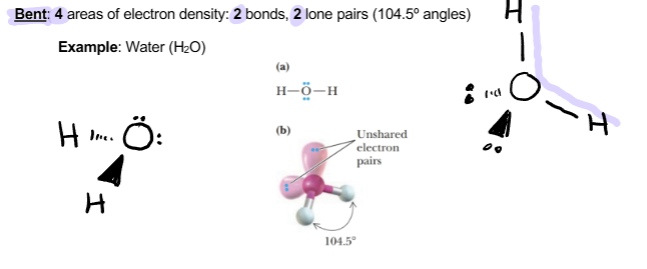
Bent
4 areas of electron density 2 bonds, 2 lone pairs
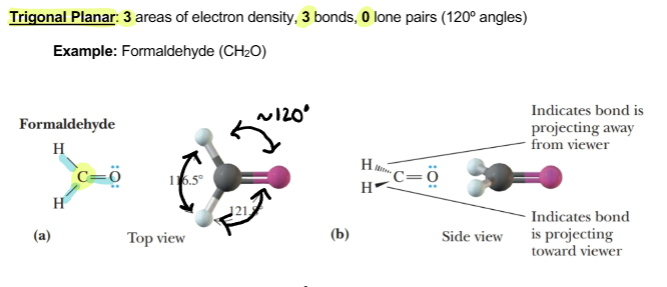
Trigonal planar
3 area of electron density, 3 bonds, 0 lone pairs
Linear
2 areas of electron density, 2 bonds, 0 lone pairs
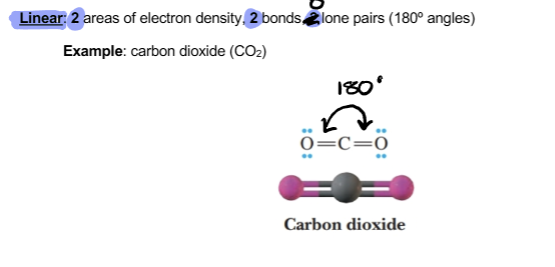
Nonpolar covalent bonds
< 0.5
Polar covalent bonds
0.5-1.9
Ionic bond
>1.9
Enantiomers
Isomers
Diastereomers