MLSP 5513 W1: Transfusion
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is Landsteiner’s Rule?
If an antigen is present on a person’s RBCs, the corresponding antibody is absent in their plasma; if the antigen is absent, the antibody is present.
What is the difference between quality control, quality assurance, and quality improvement?
QC: Checks daily performance of reagents/equipment
QA: Ensures the entire system meets standards
QI: Identifies problems and improves processes to prevent recurrence
What is the difference between phenotype and genotype in blood banking?
Genotype: The inherited genes (e.g., AO, BO)
Phenotype: The observable antigen expression on RBCs (e.g., type A, type B)
What conditions are required for agglutination to occur?
Correct antigen–antibody specificity, optimal temperature, proper pH, adequate antibody concentration, appropriate incubation time, and suitable ionic strength.
What occurs during Stage 1 and Stage 2 of agglutination?
Stage 1 (Sensitization): Antibody binds antigen; no visible reaction
Stage 2 (Lattice Formation): Antibodies cross-link RBCs, producing visible clumps
What role does complement play in hemolytic reactions?
Complement enhances antibody reactions and can cause intravascular hemolysis, especially with IgM antibodies.
What is the difference between polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies?
Polyclonal: Derived from multiple clones; less specific
Monoclonal: Derived from a single clone; highly specific and consistent
What are reagent red cells used for in blood banking?
To detect or identify antibodies in patient serum through screening and antibody identification panels.
What antibodies and antigens are found in each A blood group?
A antigen, anti-B antibody
What antibodies and antigens are found in each B blood group?
B antigen, anti-A antibody
What antibodies and antigens are found in each AB blood group?
A and B antigens, no antibodies
What antibodies and antigens are found in each O blood group?
No antigens, anti-A and anti-B antibodies
What type of antibodies are ABO antibodies and why are they clinically significant?
ABO antibodies are naturally occurring IgM antibodies that react at room temperature and can activate complement, causing severe hemolytic transfusion reactions.
What is the function of the ABO and H genes?
H gene: Produces the H antigen foundation
A/B genes: Encode glycosyltransferases that modify H antigen
O gene: Produces a nonfunctional enzyme (no antigen added)
What type of chain are precursor type I and type II chains that are the base structure for A, B, and H antigens?
oligosaccharide
What are three "unique identifiers" used in clinical or medical settings to verify patient identity.
Full name, DOB, Medical Record number
Which part of ABO typing tests the patient's red cells?
forward typing
This antibody can cross the placenta:
IgG
What is the expected antigen expression on Red Cells with someone with the genotype: OO, Hh, and Sese?
H only
This antibody is a potent opsonin
IgM
How many antigen binding sites does IgG display?
two
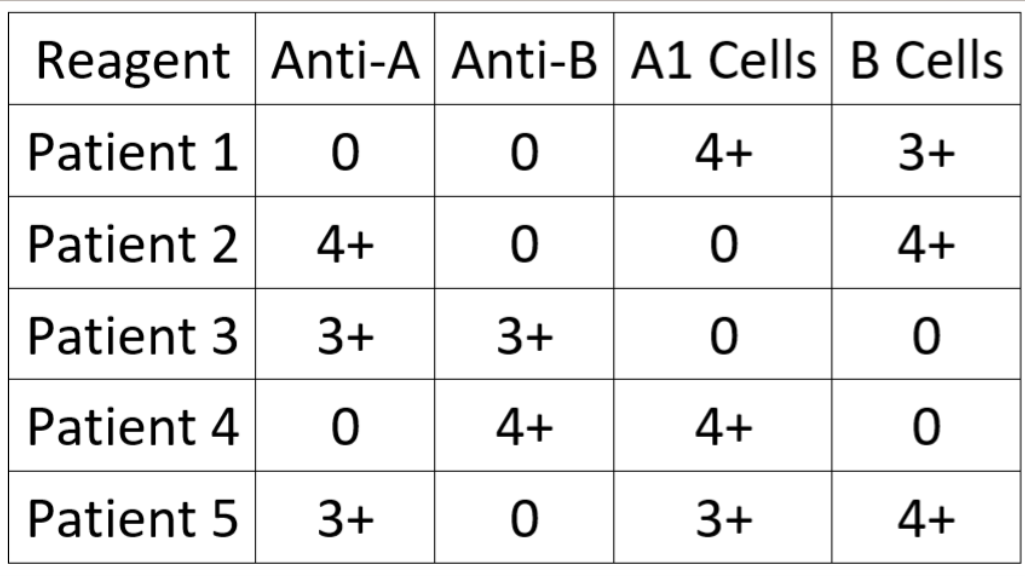
Interpret the ABO typing results for Patient 1:
O
What is the endpoint detection in blood bank testing?
agglutination
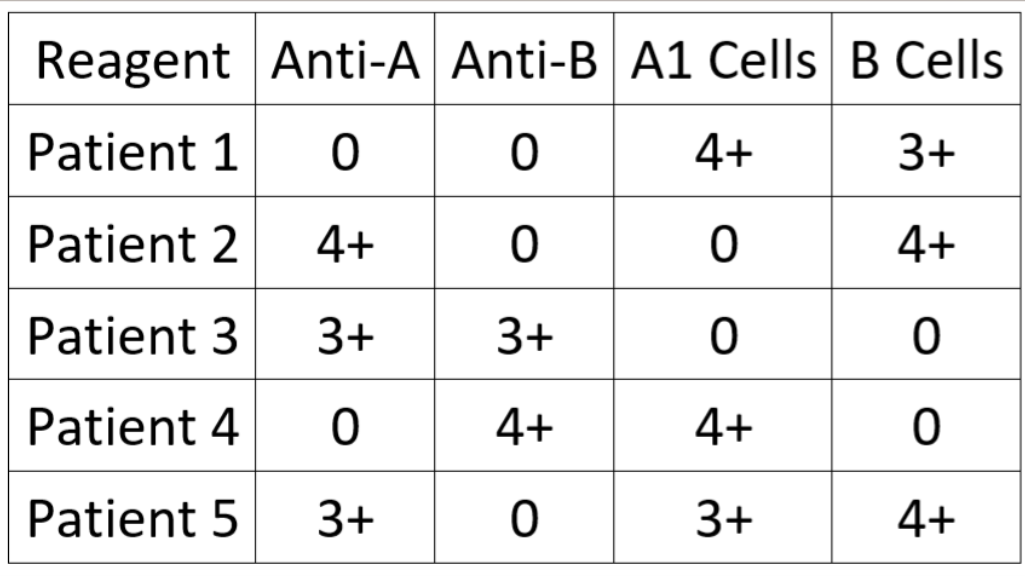
Interpret the ABO typing results for Patient 4:
B
This antibody is associated with the primary immune response
IgM is the primary immune response
What is the difference between a 1+ and a 2+ agglutination reaction?
1+ has a cloudy background, 2+ has a clear background
A patient with the genotype AO, Hh, sese is considered a:
non-secretor
This antibody is more likely to activate the Membrane Attack Complex (MAC) than any other:
IgM is most likely
The first class of antibody found in plasma following antigenic challenge is:
IgM is the first class of antibody
A 3-5% red cell suspension is made to achieve the Zone of Equivalence, meaning:
optimal concentration of antigen and antibody