A LEVEL PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY I FACTS
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
State the meaning of the term electron impact ionisation. (1)
(High energy) electrons (from an electron gun) are used to knock out an electron (from each molecule or atom.) (1)
Define the term relative atomic mass (2)
average/mean mass of 1 atom (of an element) /1/12 mass of one atom of 12C (2)
State how the relative abundance of an ion is determined in a TOF mass spectrometer. (2)
at the detector/(negative) plate the ions gain an electron (1)
(relative) abundance depends on the size of the current(1)
Define relative molecular mass (1)
average mass of one molecule x 12 /mass of a 12C (1)
State the equation that links number of particles, no. of moles and avogardro’s constant (1)
N=nL
State the equation that links the mass of one ion, relative isotopic mass and avogardro’s constant (1)
mass of an ion(kg) = relative isotopic mass x 10^-3 / 6.022 x10²³ (1)
What are four factors that affect the size of Ionisation energy?(4)
size of nuclear charge (1)
distance of outer electrons from the nucleus (1)
shielding effect of inner electrons (1)
Spin-pair repulsion (1)
What is spin-pair repulsion ? (1)
It is the repulsive force experienced between two electrons when they’re forced to occupy the same atomic model. (1)
What happens to IE across a period ? (1)
IE increases (1)
What happens to IE down a group? (1)
IE decreases (1)
State the equation in electron impact (1)
X(g) → X+(g) + e⁻ (1)
State the equation in electrospray ionisation (1)
X(g)+H+ → XH+(g) (1)
Name four stages of mass spectrometry (4)
Ionisation (1)
Acceleration (1)
Ion drift (1)
Detection (1)
Describe how the molecules are ionised using electrospray ionisation. (3)
(Sample is) dissolved (in a volatile solvent) (1)
(Injected through) needle at high voltage/positively charged (1)
Each molecule/particle gains a proton/H+(1)
Give two reasons why it is necessary to ionise the isotopes of an element before they can be analysed in a TOF mass spectrometer. (2)
Ions create a current when hitting the detector (1)
(Ions will interact with and) be accelerated (by an electric field/negative plate) (1)
The first ionisation energies of the elements in Period 2 change as the atomic number increases.
Explain the pattern in the first ionisation energies of the elements from lithium to neon. (6)
Stage 1: General Trend (Li → Ne)
1a. 1st IE increases
1b. More protons/increased nuclear charge
1c. Electrons in same energy level / shell
1d. No extra/similar shielding
1e. Stronger attraction between nucleus and outer e OR outer e closer to nucleus
Stage 2: Deviation Be → B
2a. B lower than Be
2b. Outer electron in (2)p
2c. higher in energy than (2)s
Stage 3: Deviation N → O
3a. O lower than N
3b. 2 electrons in (2)p need to pair
3c. pairing causes repulsion (do not award if it is clear reference to repulsion is in s orbital)
State the role of water in the reaction with calcium. (1)
Oxidising agent (1)
What happens during stage 2 in Mass spectrometry (2)
Acceleration-The positive ions are attracted to the negatively-charged plate (1)
so they accelerate (1)
What happens in stage 3 of mass spectrometry? (1)
Ion drift- Ions pass through a hole in the negatively-charged plate and move into the flight tube (1)
What happens in stage 4 of mass spectrometry? (3)
Detection - after they have passed through the mass spectrometer,
1+ ions will hit the - charged detector plate (1)
where they gain an electron (1)
a current is produced as ions are discharged (1)
Explain why a M+1 peak can be produced (1)
the presence of heavier and rarer isotopes (1)
Give the meaning of the term molecular formula (1)
Actual number of atoms of each element (1)
Give the name of the equation pV=nRT (1)
Ideal Gas Equation(1)
Fill in the blank
To get temperature from °C to K, you …(1)
+273 (1)
Fill in the blank
To get volume from cm3 to m3 , you…
To get volume from m3 to dm3 ,you … (2)
Answer in correct order
divide by 106 (1)
multiply by 103(1)
State the equation that is used to calculate percentage atom economy (1)
mass of desired product/total mass of reactants x100 (1)
State the equation that is used to calculate percentage yield (1)
actual mass of product/theoretical max mass of product x100 (1)
OR
actual moles of desired product/theoretical moles of desired product (1)
Sketch a linear bond shape and state how many bonded pairs and lone pairs are in the structure (2)
2 bonded pairs and no lone pairs (1)
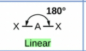
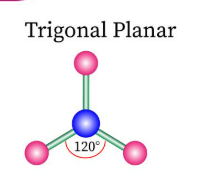
Sketch a trigonal planar bond shape and state how many bonded pairs and lone pairs are in the structure (2)
3 bonded pairs and no lone pairs (1)
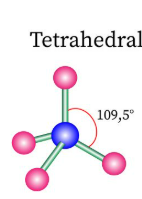
Sketch a tetrahedral bond shape and state how many bonded pairs and lone pairs are in the structure (2)
4 bonded pairs and no lone pairs (1)
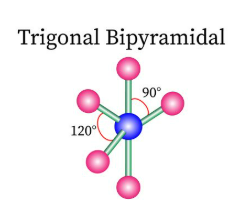
Sketch a trigonal bipyramidal bond shape and state how many bonded pairs and lone pairs are in the structure (2)
5 bonded pairs and no lone pairs (1)
Sketch a octahedral bond shape and state how many bonded pairs and lone pairs are in the structure (2)
6 bonded pairs and no lone pairs (1)
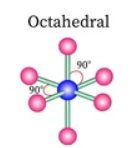
Sketch a square pyramidal bond shape and state how many bonded pairs and lone pairs are in the structure (1)
5 bonded pairs and 1 lone pair (1)
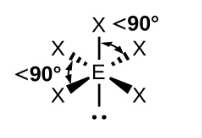
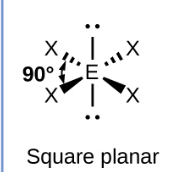
Sketch a square planar bond shape and state how many bonded pairs and lone pairs are in the structure (1)
4 bonded pairs and 2 lone pairs (1)
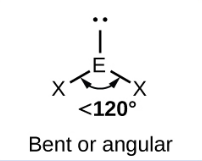
Sketch a Bent bond shape with 2 bonded pairs and state how many lone pairs are in the structure (1)
1 lone pair (1)
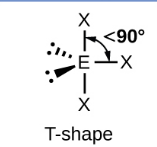
Sketch a trigonal pyramidal bond shape and state how many bonded pairs and lone pairs are in the structure (2)
3 bonded pairs and 1 lone pair (1)
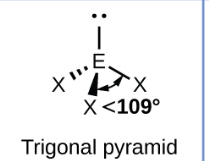
Sketch a See Saw bond shape and state how many bonded pairs and lone pairs are in the structure (1)
4 bonded pairs and 1 lone pair (1)
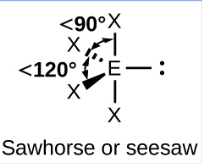
Sketch a T-shaped bond shape and state how many bonded pairs and lone pairs are in the structure (1)
3 bonded pairs and 2 lone pair (1)
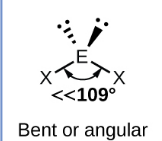
Sketch a Bent bond shape with 2 bonded pairs and state how many lone pairs are in the structure (1)
2 lone pairs (1)
Explain how permanent dipole-dipole forces arise between hydrogen chloride molecules. (2)
Difference in electronegativity leads to bond polarity (1)
(dipoles don’t cancel therefore the molecule has an overall permanent dipole) and there is an attraction between ∂+ on one molecule and ∂− on another (1)
State the definition of the enthalpy change (1)
heat energy change measured at constant pressure (1)
State the Hess’s Law (1)
The enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of the route taken (1)
What are the standard conditions of the standard enthalpy changes (3)
Pressure =100kPa (1)
Temperature=298K (1)
All substances in their normal physical states under these conditions (1)
State the meaning of the term standard enthalpy of combustion. (2)
Enthalpy change when one mole of a substance burns completely in oxygen (1)
With all substances in their standard states (1)
State the meaning of the term standard enthalpy change of formation (2)
Enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is formed from its elements(1)
With all substances in their standard states (1)
State the meaning of mean bond enthalpy (2)
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of covalent bonds is broken (1)
Averaged over a range of different compounds (1)
State the equation that is used to calculate the heat change q (1)
q=mcΔT (1)
State the equation that is used to calculate the enthalpy change ΔH (1)
ΔH = -q/nx1000
Draw the Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution and label (1)
(1)
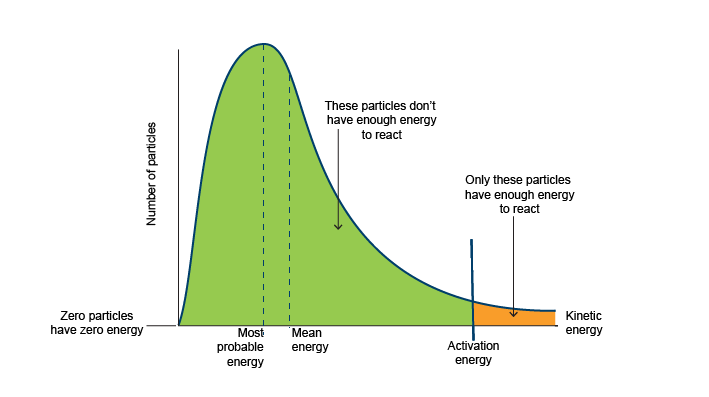
State the meaning of the Le Chatelier’s Principle (1)
when changes occur to the condition, the system will respond to counteract the change(1)
Explain why using a catalyst has no effect on the percentage yield (1)
Increases the rate of forwards and reverse reactions equally(1)
What happens to the value of Kc when temp increases in exothermic reaction (1)
Kc decreases (1)
What happens to the value of Kc when temp increases in endothermic reaction?(1)
Kc increases (1)
State, in terms of electrons, the meaning of the term oxidising agent. (1)
Electron acceptor (1)