ACCP308 - Chapter 2 Auditing IT Governance Controls (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:39 PM on 3/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
1
New cards
SSAE16
Standard that replaces the SAS70.
2
New cards
SSAE16
the definitive standard by which auditors can gain knowledge that processes and controls at third-party vendors are adequate to prevent or detect material errors.
3
New cards
Carve-out or the Inclusive method
Report provides a description of service provider’s description using…
4
New cards
Risks Inherent to IT Outsourcing
1. Failure to perform
2. Vendor exploitation
3. Outsourcing costs exceed benefits
4. Reduced security
5. Loss of strategic advantage
5
New cards
Virtualization
Unleashed cloud computing
6
New cards
**Network virtualization**
increases effective network bandwidth, optimizes network speed, flexibility, and reliability, and improves network scalability
7
New cards
**Storage virtualization**
pooling of physical storage from multiple devices into what appears to be a single virtual storage device
8
New cards
T or F: Cloud computing is not realistic for large firms.
True.
* Typically have massive IT investments and therefore not inclined to turn over their IT operations to a could vendor.
* May have critical functions running on legacy systems that could not be easily migrated to the cloud.
* Commodity provision approach of the cloud incompatible with the need for unique strategic information.
* Typically have massive IT investments and therefore not inclined to turn over their IT operations to a could vendor.
* May have critical functions running on legacy systems that could not be easily migrated to the cloud.
* Commodity provision approach of the cloud incompatible with the need for unique strategic information.
9
New cards
**Transaction cost economics (TCE)**
suggests firms should retain specific non-core IT assets in house.
10
New cards
**Cloud computing**
location-independent computing whereby shared data centers deliver hosted IT services over the Internet.
11
New cards
Three primary classes of computing services
1. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).
2. Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS).
3. Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS).
12
New cards
Benefits of IT outsourcing
1. Improved core business processes.
2. Improved IT performance.
3. Reduced IT costs.
13
New cards
Core competency theory
Logic underlying ousourcing
14
New cards
Core competency theory
This theory argues an organization should focus on its core business competencies
15
New cards
Commodity IT assets and Specific IT assets
Core competency theory ignores an important distinction between ______.
16
New cards
Commodity IT assets
assets which are not unique to an organization and easily acquired in the marketplace
17
New cards
Specific IT assets
assets which are unique and support an organization’s strategic objectives
18
New cards
DRP Audit Procedures to verify that DRP is a realistic solution
1. Evaluate adequacy of backup site arrangements
2. Review list of critical applications for completeness
3. Verify copies of critical applications and operating systems are stored off-site.
4. Verify critical data files are backed up in accordance with the DRP.
5. Verify that types and quantities of items specified in the DRP exist in a secure location.
6. Verify disaster recovery team members are current employees and aware of their assigned responsibilities.
19
New cards
Enumerate the
Second-Site Backups
Second-Site Backups
1. Manual aid pact
2. Empty shell or cold site plan
3. Recovery operations center or hot site plan
4. Internally provided backup
20
New cards
Mutual aid pact
is an agreement between organizations to aid each other with data processing in a disaster
21
New cards
Empty shell or cold site plan
involves obtaining a building to serve as a data center in a disaster
22
New cards
Recovery operations center or hot site plan
a fully equipped site that many companies share.
23
New cards
Disaster Recovery Planning
a statement of all actions to be taken before, during and after any type of disaster
24
New cards
Four common features of Disaster Recovery Planning
1. Identify critical applications
2. Create a disaster recover team
3. Provide second-site backup
4. Specify backup and off-site storage procedures
25
New cards
Identify critical applications
* Short-term survival requires restoration of cash flow generating functions.
* Applications supporting those functions should be identified and prioritized in the restoration plan.
* ask of identifying critical items and prioritizing applications requires active participation of user departments, accountants and auditors.
* Applications supporting those functions should be identified and prioritized in the restoration plan.
* ask of identifying critical items and prioritizing applications requires active participation of user departments, accountants and auditors.
26
New cards
Create a disaster recovery team
Team members should be experts in their areas and have assigned tasks
27
New cards
Provide second-site backup
Necessary ingredient in a DRP is that it provides for duplicate data processing facilities following a disaster
28
New cards
Specify back-up and off-site storage procedures
All data files, applications, documentation and supplies needed to perform critical functions should be automatically backed up and stored at a secure off-site location
29
New cards
Enumerate the Audit Procedures under the Computer Center
* Tests of physical construction.
* Tests of the fire detection system.
* Tests of access control.
* Tests of RAID. Tests of the uninterruptible power supply.
* Tests of insurance coverage.
* Tests of the fire detection system.
* Tests of access control.
* Tests of RAID. Tests of the uninterruptible power supply.
* Tests of insurance coverage.
30
New cards
Physical controls and insurance coverage are adequate
What must the auditor verify involving auditing the computer center?
31
New cards
Elements of the Computer Center
1. Physical location
2. Construction
3. Access
4. AC should provide appropriate temperature and humidity for computers
5. Fire suppression
6. Fault tolerance
32
New cards
Requirements/Description of the Physical location of the computer center
* Directly affects risk of destruction from a disaster.
* Away from hazards and traffic.
* Away from hazards and traffic.
33
New cards
Requirements/Description of the Construction of the computer center
* Ideally:
single-story, solidly constructed with underground utilities.
* Windows should not open and an air filtration system should be in place.
single-story, solidly constructed with underground utilities.
* Windows should not open and an air filtration system should be in place.
34
New cards
Requirements/Description of Access to the computer center
* Should be limited with locked doors, cameras, key card entrance and sign-in logs
35
New cards
Requirements/Description of Air conditioning of the computer center
Air conditioning should provide appropriate temperature and humidity for computers.
36
New cards
Requirements/Description of Fire Suppression of the computer center
Alarms, fire extinguishing system, appropriate construction, fire exits
37
New cards
Fault tolerance
the ability of the system to continue operation when part of the system fails
38
New cards
Fault tolerance
Total failure can occur only if multiple components fail
39
New cards
**Redundant arrays of independent disks (RAID)**
involves using parallel disks with redundant data and applications so if one disk fails, lost data can be reconstructed.
40
New cards
Fault tolerance include
1. Redundant arrays of independent disks (RAID)
2. Uninterruptible power supplies
41
New cards
Audit procedures in a distributed IT organization
1. Review relevant documentation to determine if individuals or groups are performing incompatible duties.
2. Verify corporate policies and standards are published and provided to distributed IT units.
3. Verify compensating controls are in place when needed.
4. Review system documentation to verify applications, procedures and databased are in accordance with standards.
42
New cards
Audit procedures in a centralized IT organization
1. Review relevant documentation to determine if individuals or groups are performing incompatible functions.
2. Review systems documentation and maintenance records to verify maintenance programmers are not designers.
3. Observe to determine if segregation policy is being followed.
43
New cards
Controlling the DDP Environment
* Implement a corporate IT function:
* Central testing of commercial software and hardware.
* User services to provide technical help.
* Standard-setting body.
* Personnel review.
* Central testing of commercial software and hardware.
* User services to provide technical help.
* Standard-setting body.
* Personnel review.
44
New cards
Risks Associated with DDP
1. Inefficient use of resources
2. Destruction of audit trails
3. Inadequate segregation of duties
4. Hiring qualified professionals
5. Lack of standards
45
New cards
Inefficient use of resources in DDP includes
1. Mismanagement of IT resources by end users.
2. Operational inefficiencies due to redundant tasks being performed.
3. Hardware and software incompatibility among end-user functions.
46
New cards
Hiring qualified professionals:
Risk of programming errors and system failures increase directly with the level of employee incompetence.
47
New cards
Variant of centralized model with terminals or microcomputers distributed to end users for handling input and output.
\
48
New cards
Distributes all computer services to the end users where they operate as stand alone units.
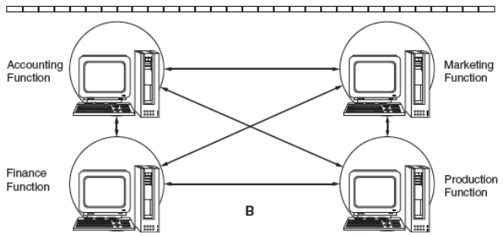
49
New cards
Two alternatives of the Distributed Model
1. Variant of centralized model with terminals or microcomputers distributed to end users for handling input and output.
2. Distributes all computer services to the end users where they operate as stand alone units.
50
New cards
Distributed Data Processing (DDP)
involves reorganizing central IT function into small IT units that are placed under the control of end users.
51
New cards
Segregation of Incompatible IT Functions
1. Systems development from computer operations.
2. Database administration from other functions.
3. New systems development from maintenance.
52
New cards
Systems development from computer operations.
Relationship between groups should be formal and responsibilities should not be comingled.
53
New cards
Database administration from other functions.
DBA function responsible for many critical tasks and needs to be organizationally independent of operations, systems development and maintenance.
54
New cards
New systems development from maintenance.
* Improves documentation standards because maintenance group requires documentation.
* Denying original programmer future access deters program fraud.
* Denying original programmer future access deters program fraud.
55
New cards
Two control problems with segregating systems analysis from applications programming.
1. Inadequate documentation a chronic problem.
2. When system programmer has maintenance responsibilities, potential for fraud is increased
56
New cards
Inadequate documentation a chronic problem.
* Documenting systems is not an interesting task.
* Lack of documentation provides job security for the programmer who coded it.
* Lack of documentation provides job security for the programmer who coded it.
57
New cards
When system programmer has maintenance responsibilities, potential for fraud is increased
* May have concealed fraudulent code in the system.
* Having sole responsibility for maintenance may allow the programmer to conceal the code for years.
* Having sole responsibility for maintenance may allow the programmer to conceal the code for years.
58
New cards
Alternative Organization of Systems Development
Separates systems analysis and applications programming
59
New cards
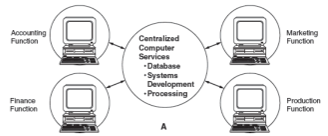
Centralized data processing Model
* all data processing performed at a central site.
* End users compete for resources based on need.
* Operating costs charged back to end user.
* End users compete for resources based on need.
* Operating costs charged back to end user.
60
New cards
Primary service areas of a Centralized data processing Model
* Database administrator
* Data processing consisting of data control/data entry, computer operations and data library.
* System development and maintenance
* Data processing consisting of data control/data entry, computer operations and data library.
* System development and maintenance
61
New cards
System professional, end users, and stakeholders
Participation in systems development activities include…
62
New cards
Three IT governance issues addressed by SOX and the COSO internal control framework:
1. Organizational structure of the IT function.
2. Computer cnter operations.
3. Disaster recovery planning.
63
New cards
IT Governance
* Subset of corporate governance that focuses on the management and assessment of strategic IT reso
* Key objects are to reduce risk and ensure investments in IT resources add value to the corporation.\\
* All corporate stakeholders must be active participants in key IT decisions.
* Key objects are to reduce risk and ensure investments in IT resources add value to the corporation.\\
* All corporate stakeholders must be active participants in key IT decisions.
64
New cards
Key Objectives of IT Governance
1. Reduce risk
2. Ensure investments in IT resources add value to the corporation
65
New cards
All corporate stakeholders
They must be active participants in key IT decisions.