L1-2 Molecular symmetry
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Why is knowing the symmetry of a molecule useful

Starting definition of molecular symmetry
A molecule has symmetry if we can do something to it, and the result is indistinguishable – looks unchanged – from what we started with.
What is rotation symmetry
Rotating the molecule around a certain axis leaves it looking unchanged
What is a symmetry element
A point, line or plane around which a symmetry operation can be performed
What is a symmetry operation
A symmetry opeation is caried out on a symmetry element e.g. rotating around an axis symmetry element. One symmetry element can have more thna one symmetry operation done on it.
In the case of water, it has a C2 axis symmetry element
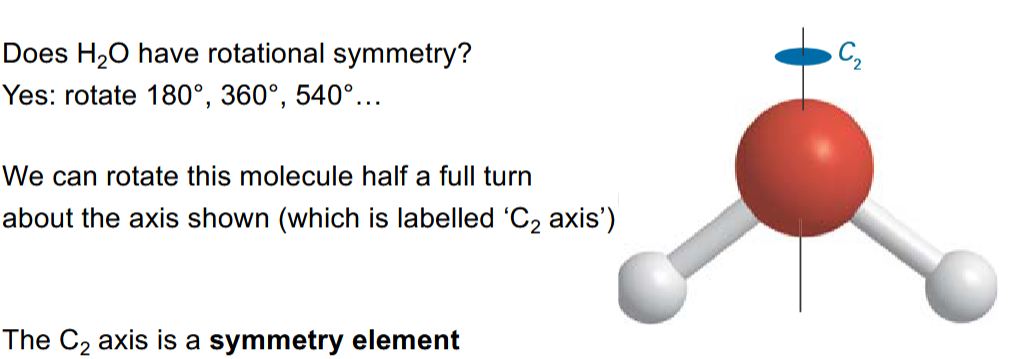
If C2 is “rotate by 180°” then what is C2.C2
Rotate by 180° twice i.e. 360°
What is rotating 360° effectively equal to
The “identity” labelled “E” that is shared by all molecules
What is another way to write C3.C3
C32 - equivalent to 240° rotation
What is the principal axis
it is the axis with the highest order n in Cn e.g C3 in BF3.
not all molecules have a principal axis
The principal axis is by convention the z axis
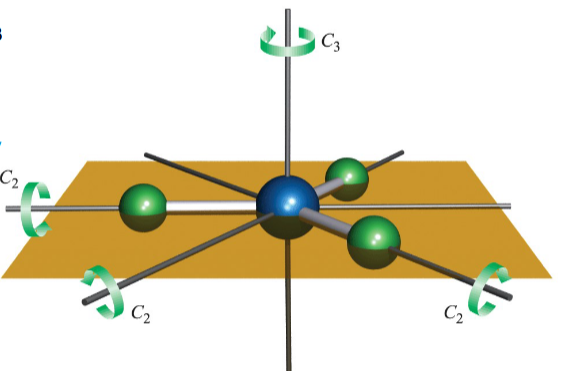
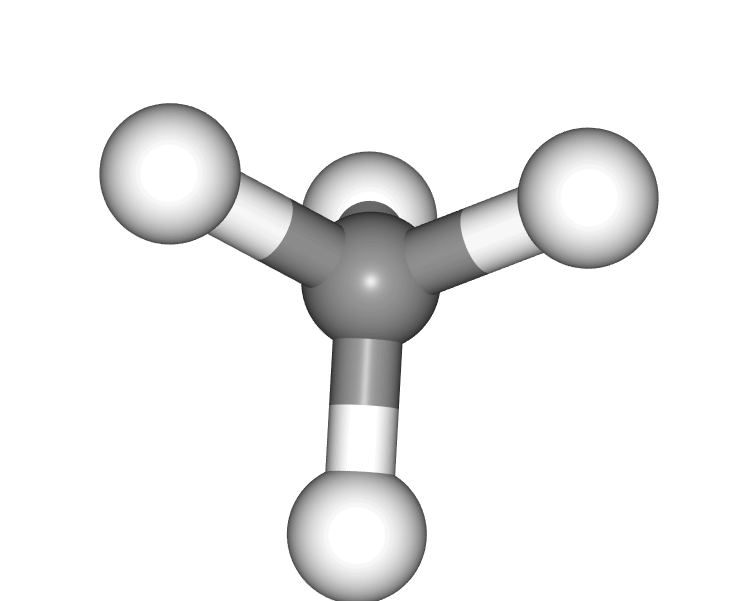
When is there not a principal axis
If there are multiple axes with the same, highest n
Or if the molecule has no rotations
For instance methane here has 4 C3 axes which pass through the carbon atom and 1 of the 4 hydrogens.
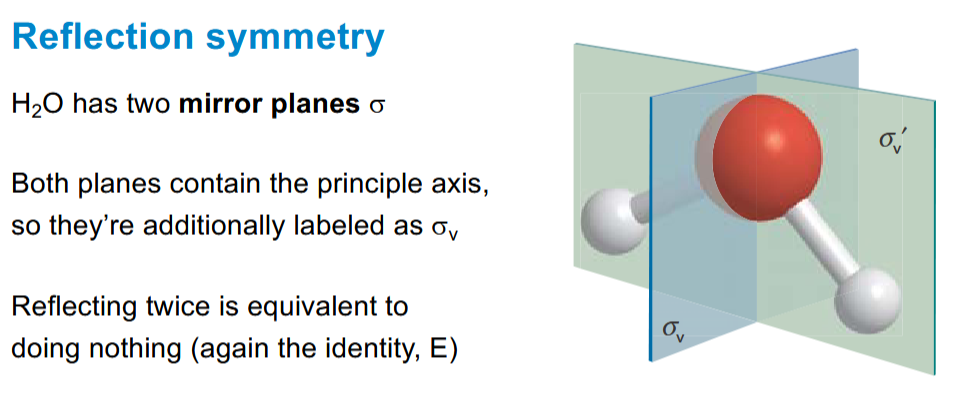
How are mirror planes in a molecule labelled + if the pass through the principal axis
the v means it is vertical
σh and σd
h is for horizontal axes in planar molecules
d id for dihedral and these planes bisect the angle between C2 axes
Inversions
inversion i swaps (x,y,z) with (-x,-y,-z) through a centre of inversion
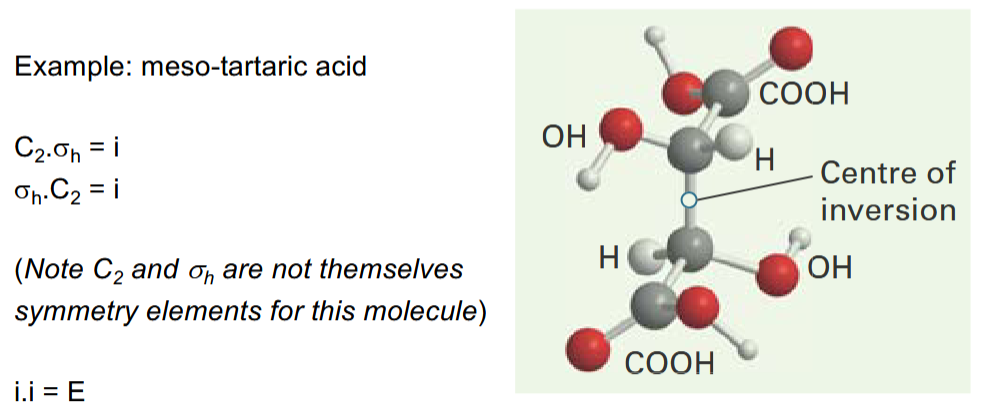
What is Improper Rotation
Denoted by Sn. It is rotation + reflection
Inversion itself “i” is equivalent to S2
it is a C2 rotation followed by reflection in a plane perpendicular to the rotation axis. It leaves the molecule in an indistinguishable state
The rotations and reflections do not have to be working symmetry operations for the molecule
What is a point group
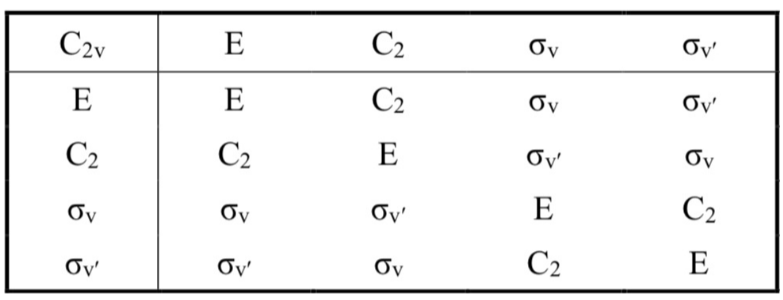
What happens when you “multipy” together two symmetry operations in the same point group
It results in another symmetry operation from the point group. This could be the identity or something else.
What does the number in the point group names typically mean
The order of the principal rotation axis in the molecule.
What do point groups tell you
What symmetry the molecule has
WHat is the order of a point group
The number of symmetry operatiosn within that group
Overview of some ways to determine a molecule’s point group

Point group illustrative/cartoon example
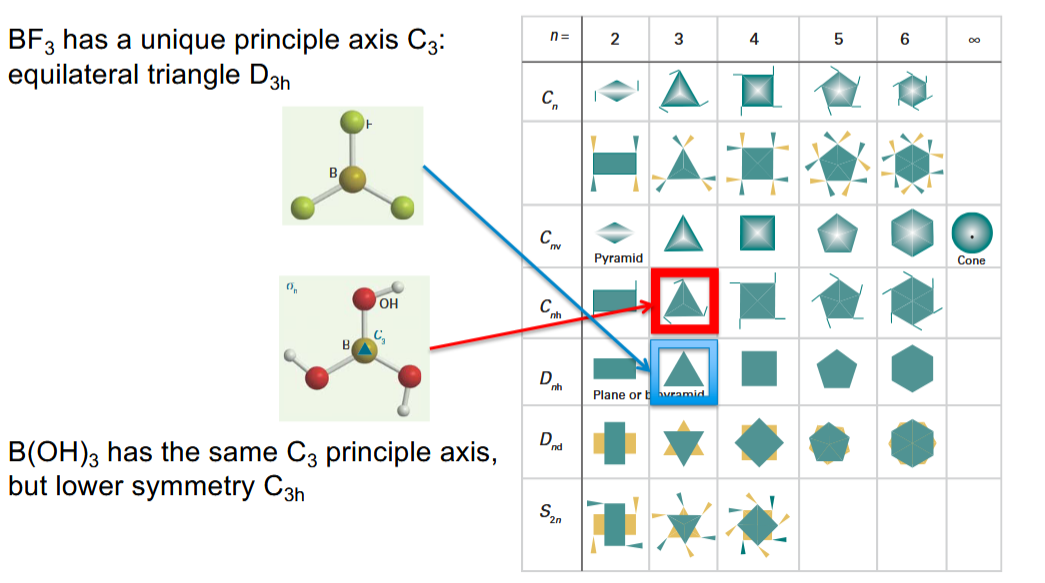
Sub group connections
Some groups can be considered subsets of others i.e. all the symmetry operations form a group + more are contained within another group with more symmetry operations. Substitutions may lower the symmetry of a molecule, losing some of its operatiosn but preserving the rest.
