Chapter 25 - The History of Life
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A collection of flashcards based on major concepts from the lecture notes regarding the history of life on Earth and key evolutionary events.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
What is true about the origin of life?
-It is a hypothesis
-Extremely speculative
-No fossil evidence
In the 1920s, what hypothesis did A. I. Oparin and J. B. Haldane propose about the early atmosphere?
They hypothesized it was a reducing environment (electron adding); conducive to forming organic compounds.
-Energy for organic compound synthesis was supplied by lightning or UV radiation
-Haldane suggested early oceans were a primordial soup of organic molecules that gave rise to life
What did Stanley Miller and Harold Urey demonstrate in their 1953 experiments?
They showed abiotic synthesis of organic molecules was possible in a reducing atmosphere.
What is the endosymbiont theory?
It suggests that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once independent prokaryotes that began living symbiotically within larger cells.
What major biological event occurred around 3.5-3.2 billion years ago?
The evolution of photosynthesis
What were stromatolites?
Fossilized bacteria that formed from sedimentary layers on bacterial mats, indicating life existed 4.0 billion years ago.
How did the first eukaryotes evolve according to the notes?
They evolved from prokaryotes through processes including endosymbiosis.
What changes did the 'oxygen revolution' cause in Earth's biological communities?
It likely led to the extinction of many prokaryotic organisms that could not survive in an oxygen-rich environment.
The Domains
Eukaryotic, Archaea, and Bacteria
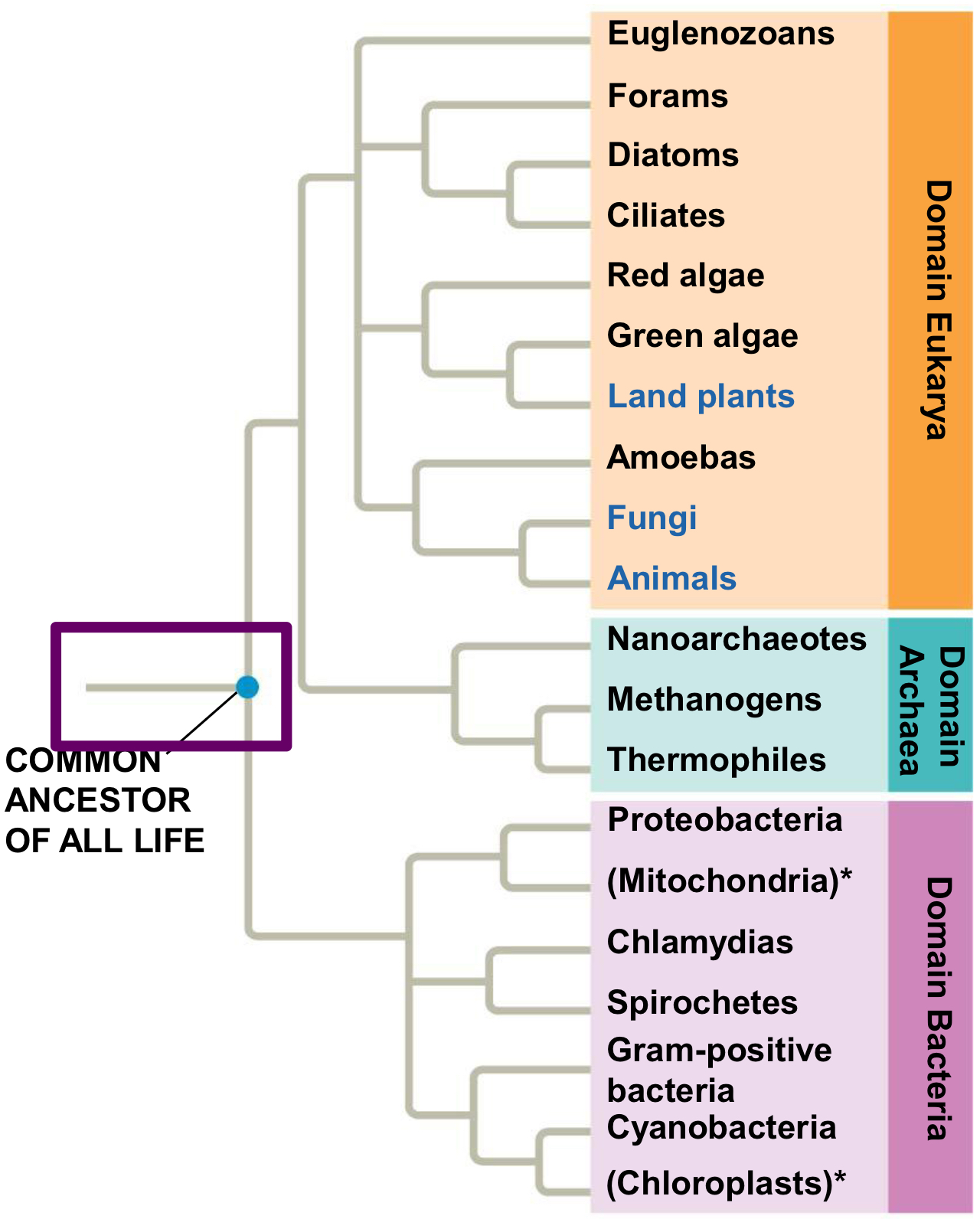
Which domains are the most closely related?
Eukarya and Archaea are sister taxa
Conditions on early earth
Abiotic synthesis of small inorganic molecules
Joining of these small molecules into marcromolecules
Packaging of molecules into protocells
Original of self-replicating molecules that made inheritance possible
What are protocells?
Structures formed from abiotic (non-living) components
Made of lipids, membrane-bound, maintaining internal chemistry
When was earth formed and what is the name of this period?
About 4.6 billion years ago during the formation of the solar system. This period is known as the Hadean Eon (pre-life).
The bombardment by rocks and ice likely vaporized water during the Hadean Eon preventing what from happening?
Formation of seas
During the Hadean Era, what was the atmosphere on earth like?
Atmosphere likely contained water vapor and chemicals released by volcanoes (nitrogen, nitrogen oxides, CO2, methane, ammonia, hydrogen)
In 1953, Stanley Miller and Harold Urey showed that what was possible?
Abiotic (non-living) synthesis of organic molecules in a reducing atmosphere is possible
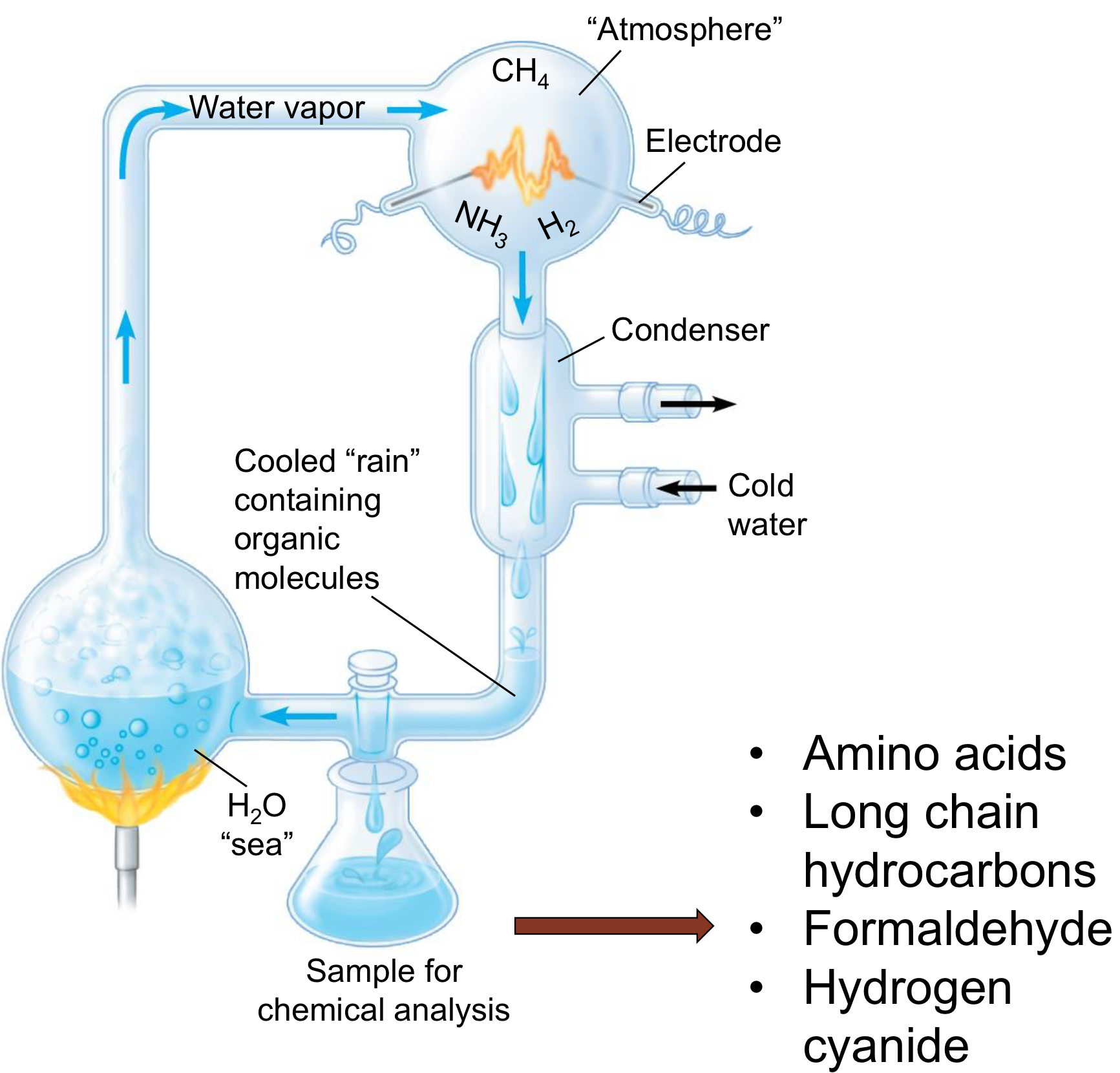
How was the Miller and Urey experiment conducted?
-Used conditions similar to what Oparin and Haldane hypothesized
-Created a variety of acids and other compounds
What abiotic (non-living) molecules were created in the Miller and Urey experiment?
Amino acids
Long chain Hydrocarbons
Formaldehyde
Hydrogen cyanide
Other hypotheses
-Hydrothermal vents: The first organic compounds may have been synthesized near volcanoes or deep-see vents (“Black Smokers” or Alkaline vents)
-Panspermia: The first organic compounds may have been transported by means space dusts, comets, or meteorites.
RNA monomers can be produced spontaneously from what?
Simple molecules
Small organic molecules __________ when they are concentrated on hot sand, clay, or rock
polymerize (combine into larger molecule)
The first genetic material was likely ___?
RNA not dna
RNA is central to ______ _________ and can function as an enzyme-like catalyst (ribozymes)
protein synthesis
What are ribozymes and what can they do?
catalytic RNA molecules that function as enzymes Can make complementary copies of short stretches of RNA
What way are protocells thought to have formed?
Formed from fluid-filled vesicles with a membrane-like structure
What can lipids and other organic molecules do in water?
They can spontaneously self-assemble to form vesicles with a lipid bilayer
What is montmorillonite and what does it do?
Montmorillonite is a clay mineral from volcanic ash that can catalyze the formation of RNA and other organic molecules, providing a surface for the assembly of protocells.
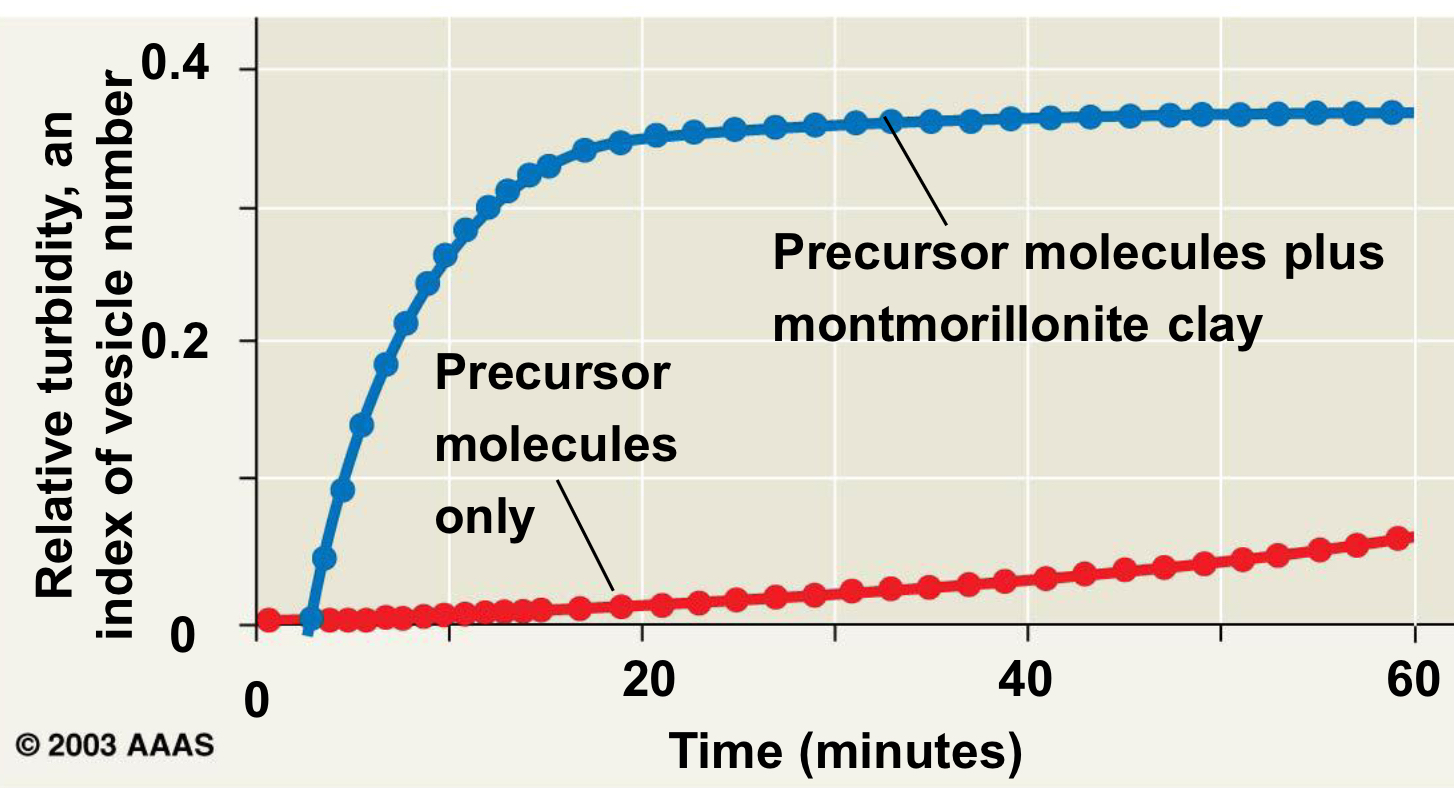
True of false? Vesicle with self-replicating RNA would differ from neighbors that lack it
True
If vesicles with self-replicating RNA could grow and split and pass on their RNA to their daughters, what would the daughters become?
They would become protocells
Inherited features specified by the RNA would be acted on by natural selection. True or false?
True
Most atmospheric oxygen is of biological origin, produced during what?
During the water splitting step of photosynthesis
Early photosynthesis evolved 3.5-3.2 billion years ago
How were red bands of rock created?
Oxygen dissolved into the water, reacted with iron, and precipitated out as iron oxide resulting in the build up in sediment, forming red bands of rock containing iron ore
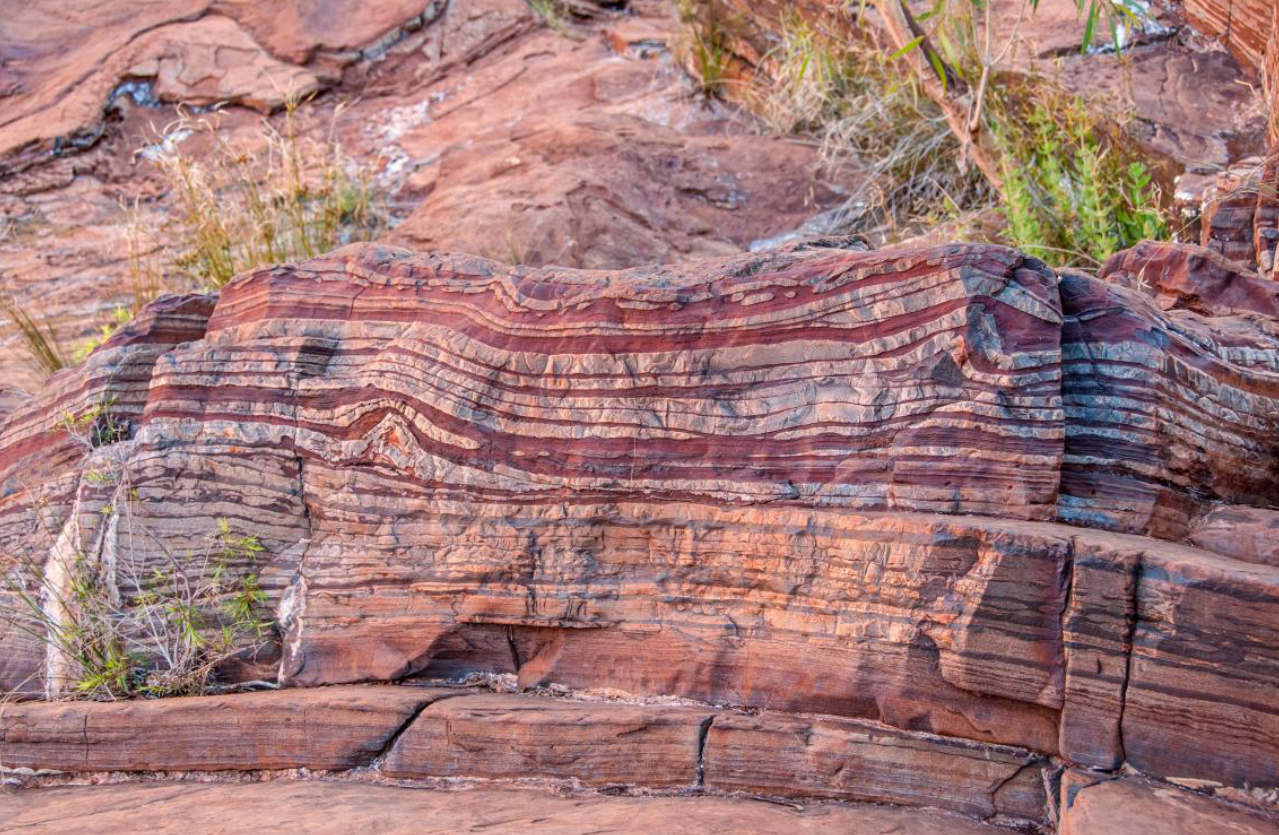

Once all of the dissolved iron precipitated, oxygen began saturating what?
The lakes and seas
Only after the saturation of bodies of water with oxygen, what happened around 2.7 billion years ago?
Oxygen began to build up in the atmosphere
Aerobic vs anaerobic
Refers to processes or organisms that require oxygen (aerobic) versus those that do not need oxygen to survive and can thrive in oxygen-free environments (anaerobic).
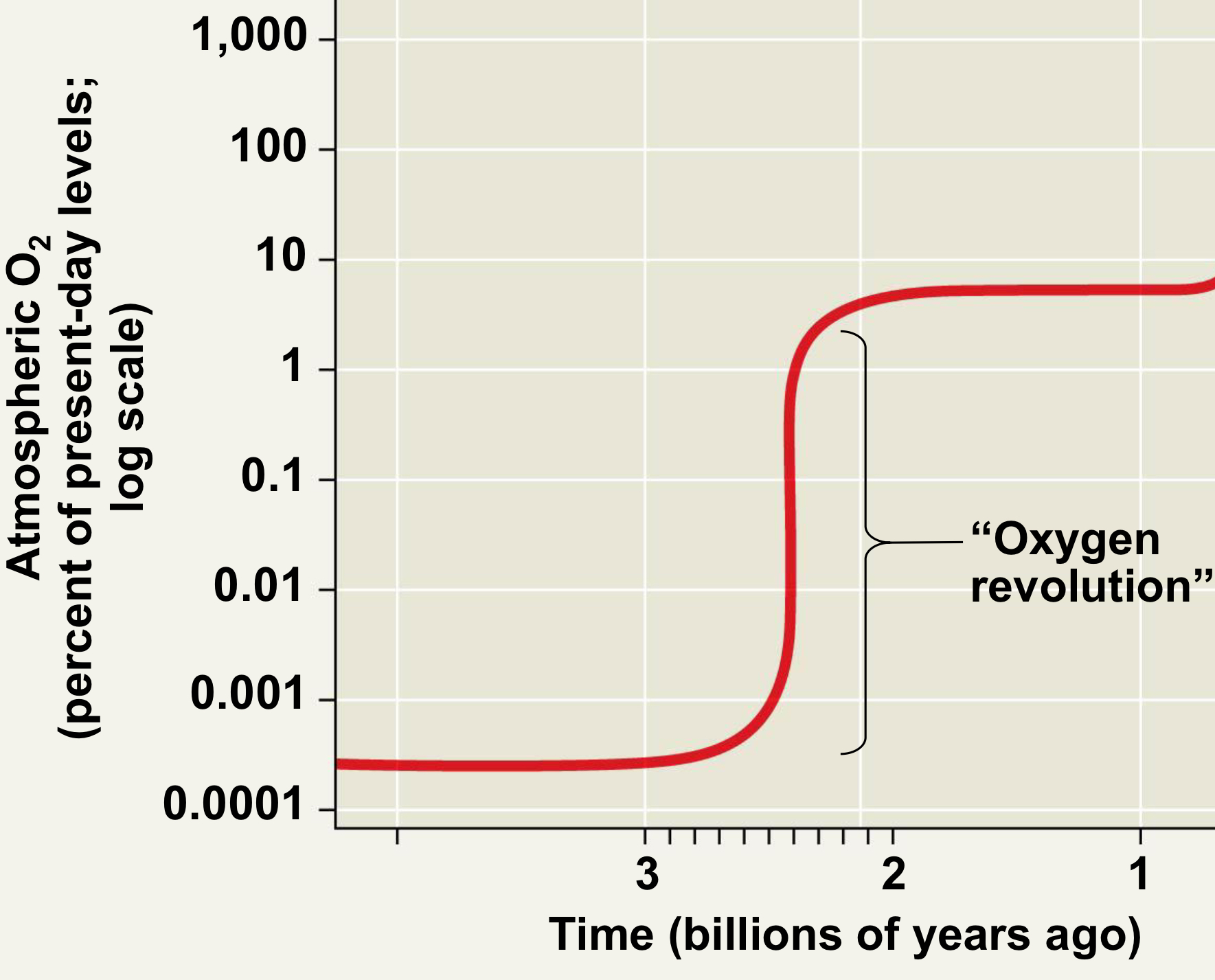
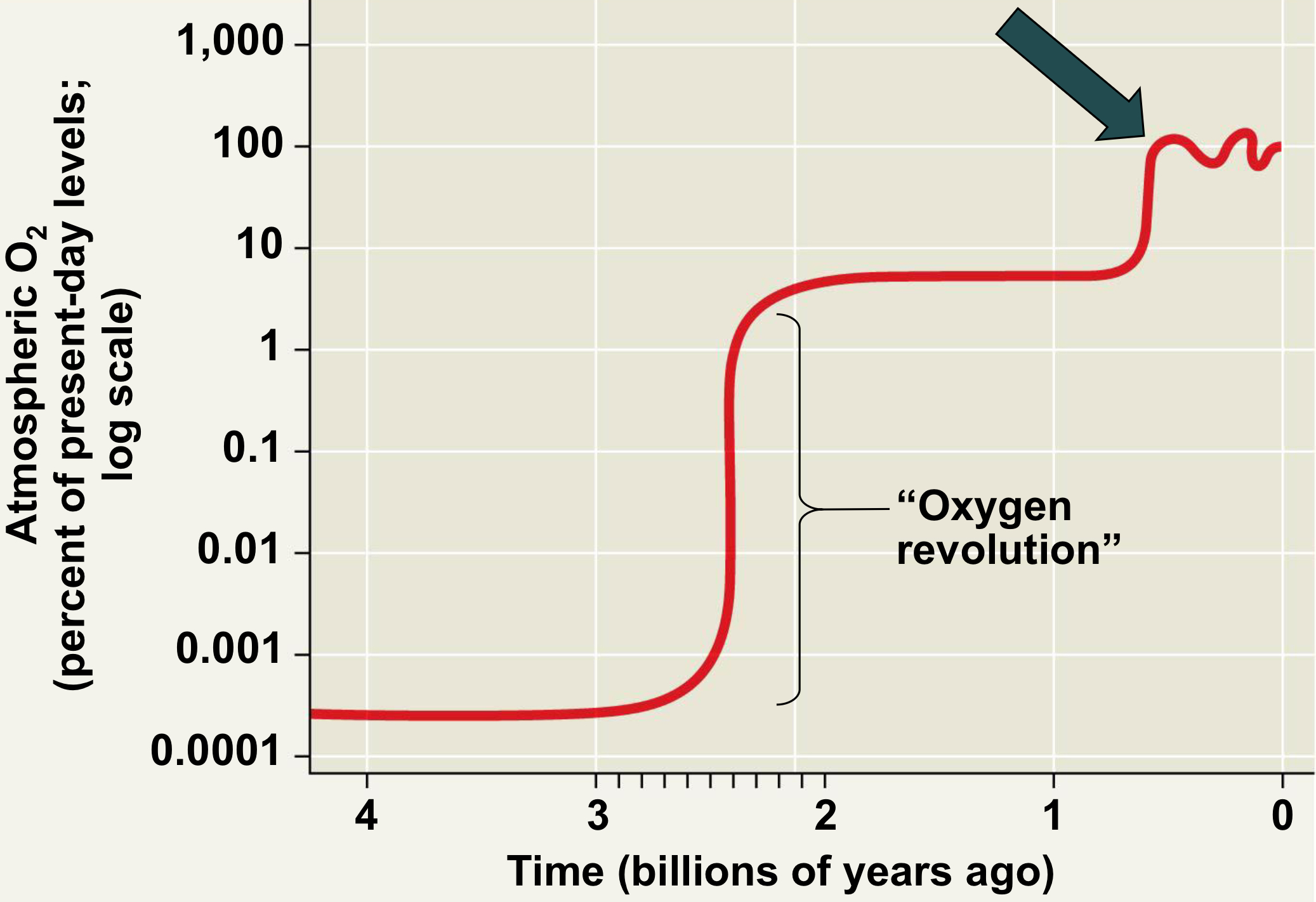
What is the Oxygen Revolution and what did it do?
-2.7-2.4 billion years ago, atmosphere oxygen levels increased from 0.001% to around 10% of the present level
-Likely caused the extinction of many prokaryotes
-However, some groups survived and adapted using aerobic cellular respiration to harvest energy
-Also, some survived by being confined to anaerobic habitats, led to divergence of many anaerobic prokaryotes
How old are the oldest eukaryotic fossils?
1.8 billion years old
Eukaryotes contains what that prokaryotes do not?
-Nuclear envelope
-Mitochondria
-Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
-Chloroplasts
-Lysosomes
-Golgi apparatus
-Cytoskeleton
-Rod-shaped chromosomes
Endosymbiotic Theory
The Endosymbiotic Theory posits that eukaryotic cells originated through a symbiotic relationship between different species of small independent prokaryotes, becoming mitochondria and chloroplasts, living as symbionts within other larger cells; essential organelles in eukaryotic cells.
Ancestors of mitochondria and plastids likely entered their host as what?
undigested prey or internal parasites
Evidence of Endosymbiotic theory
1.Mitochondria and chloroplast inner membranes are similar to plasma membranes of prokaryotes
2.”Cell” division and DNA structure is similar in these organelles and related prokaryotes
3.Transcribe and translate their own DNA
4.Ribosomes are more similar to prokaryotic than eukaryotic ribosomes
Endosymbiosis in action in Paulinella chromatophora
-Cercazoan (amoeba)
-Around 60 Mya developed an endosymbiosis with a cyanobaterium
-New origin of a chloroplast-like structure known as the chromatophore
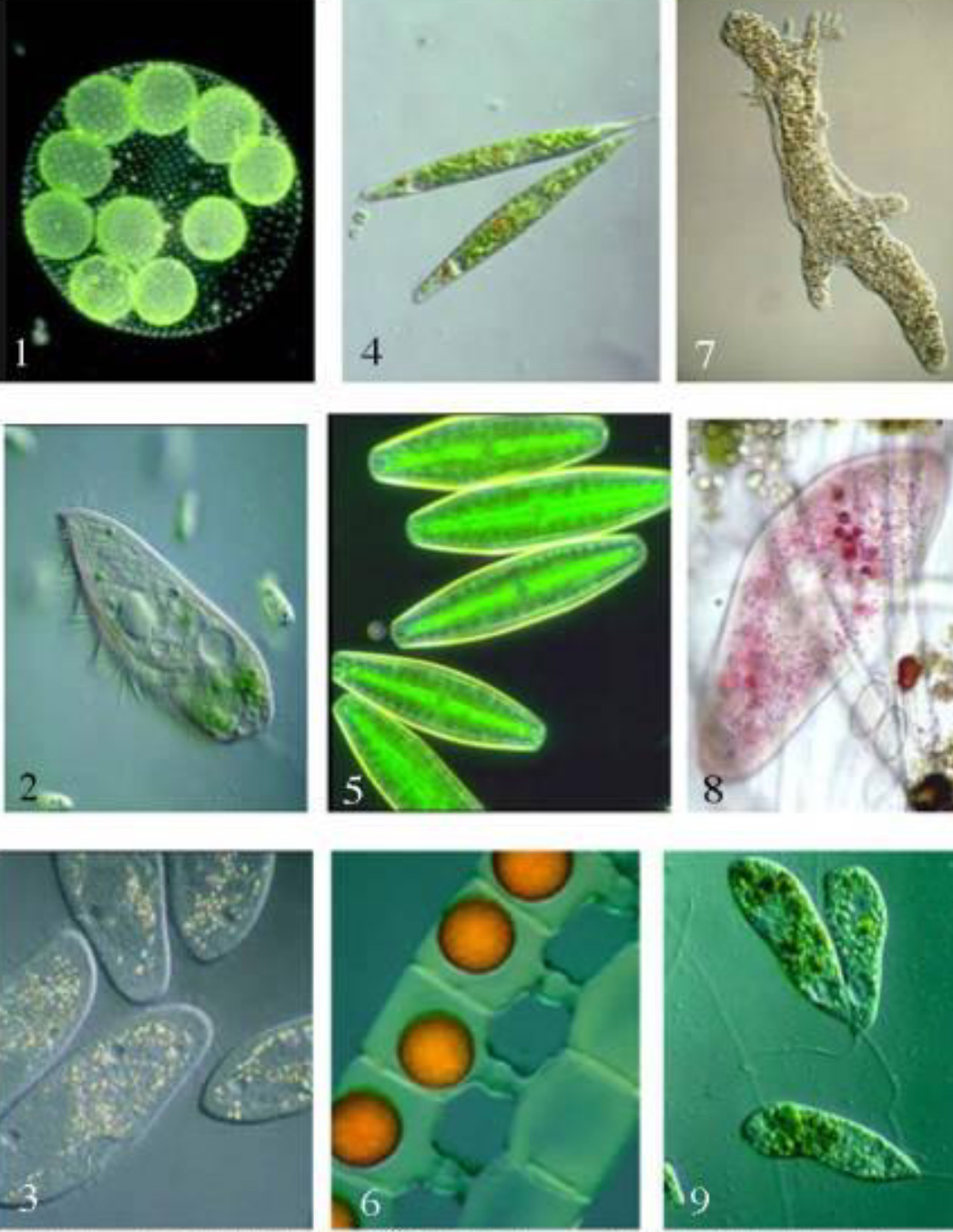
Multicellular organisms can only be found in what domain?
Domain Eukarya (excluding: Euglenozoans, Forams, Diatoms, Ciliates, Amoebas)
True or false? The evolution of eukaryotic cells allowed for a greater range of unicellular forms
True
Larger and more diverse multicellular eukaryotes emerged in what period?
Example: soft-bodied organisms (most preserved impressions)
Ediacaran Biota - 635 to 540 Mya

Second wave of diversification occurs (based on fossil record)
-Evolution of hard bodied animals and evidence of predator-prey interactions (larger size, claws, vs. spines, body armor)
-Linked to higher atmospheric oxygen levels, ozone, CaCO3
Cambrian explosion - around 535 Mya
When did fungi, plants, and animals begin to colonize land?
What happened?
-Around 500 mya
-Associated with adaptations that made it possible to reproduce on land and resist desiccation (moisture loss)
What animals were the first to colonize land?
Arthopods (marine animals) around 450 Mya followed by Tetrapods (four limbed vertebrates) around 365 mya
What is a common cause of mass extinctions?
What most happen for it to be considered a mass extinctions?
-Global environmental disruptions leading to a significant loss of species.
-50% or more of marine species became extinct
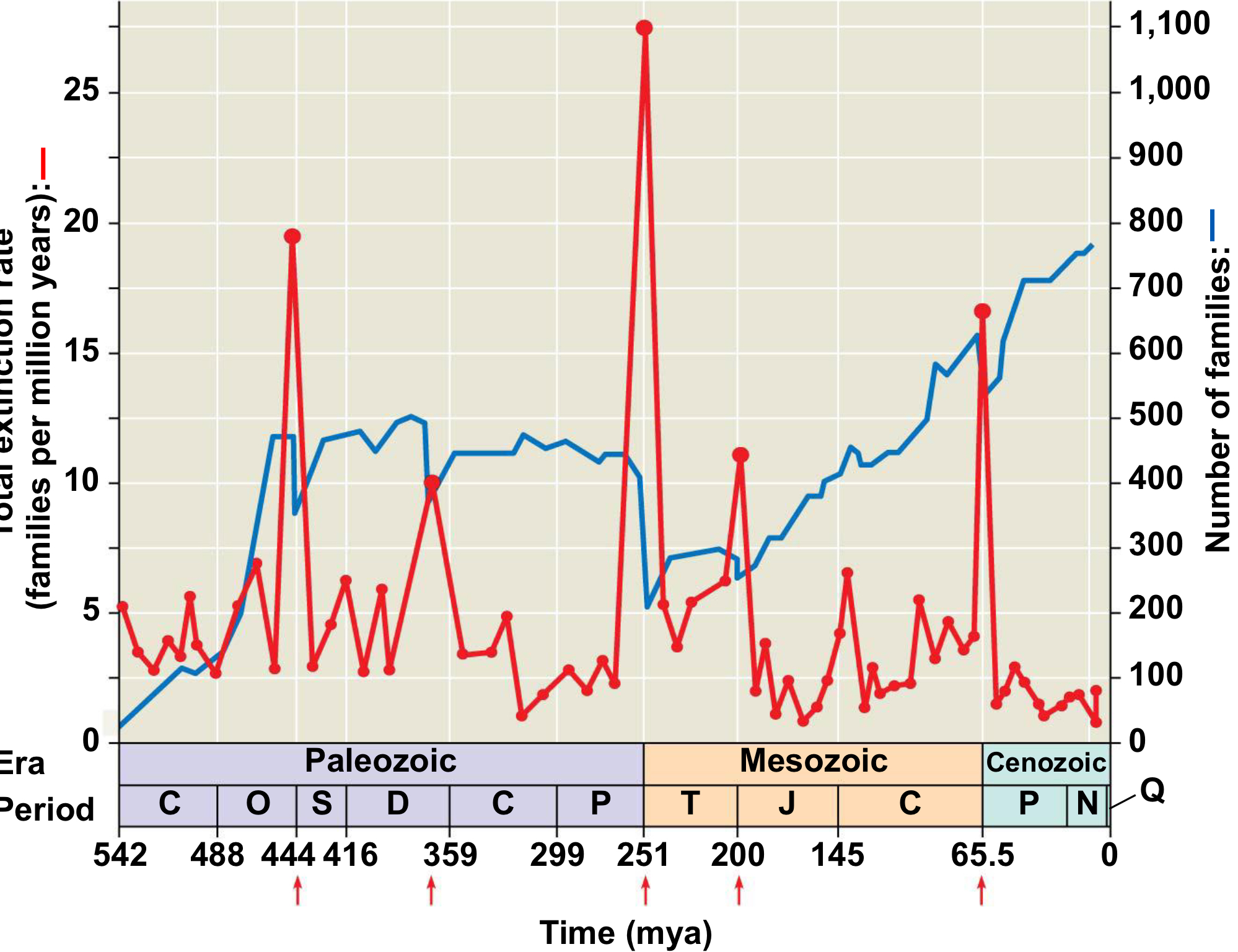
How many mass extinction events have occurred?
Five major events recognized in Earth's history.
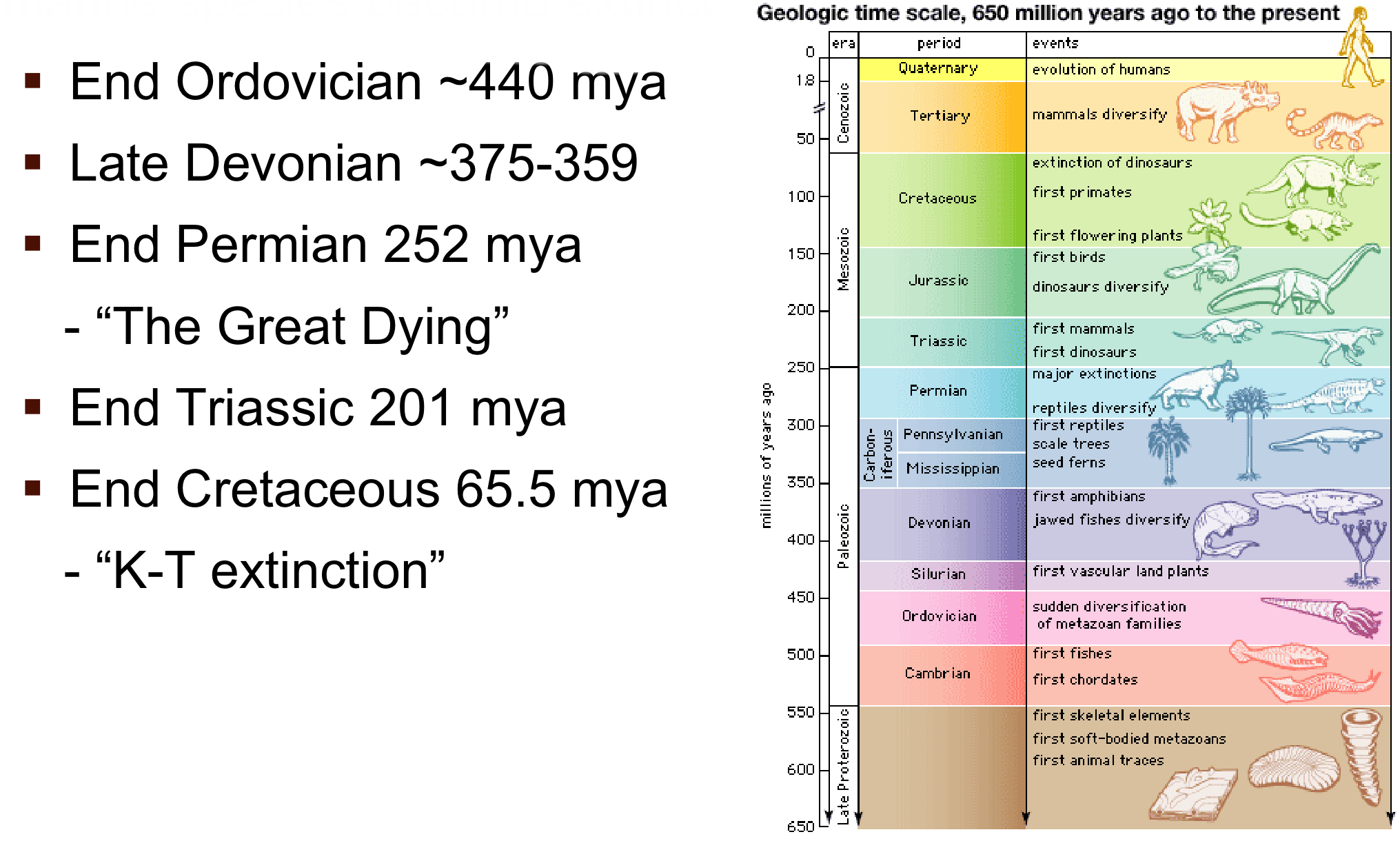

End Ordovician
Years: around 440 Mya
Extinction: 85% of marine species
What happened: Supercontinent (Gondwana) moves to South Pole. Glacial and interglacial episodes caused sea levels to rise and fall
dramatically, moving shorelines repeatedly. Continental
erosion changed atmosphere and ocean chemistry. Cooling climate especially hazardous to organisms adapted to warmer temperatures. Glaciation caused loss of intercontinental waterways and continental shelves
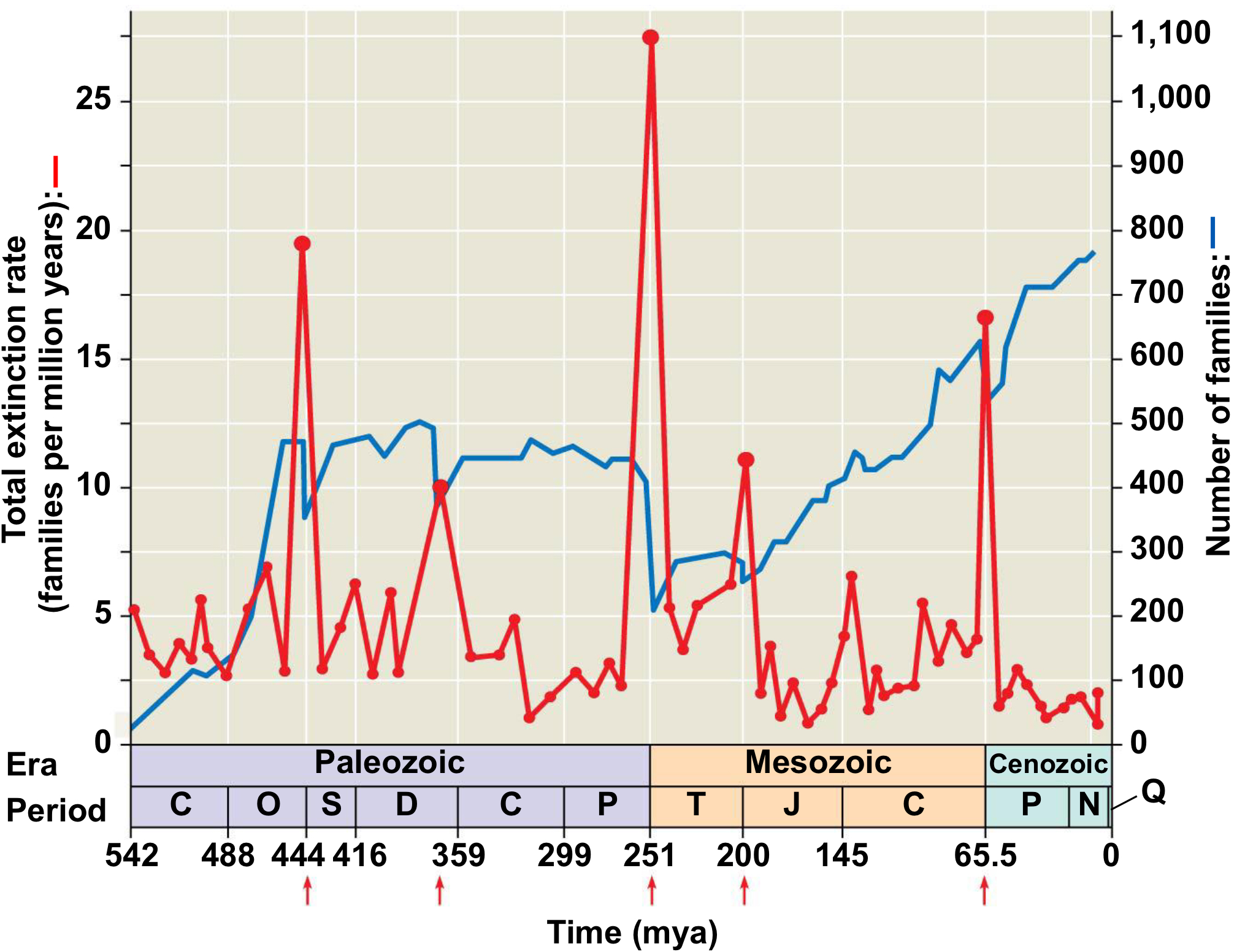

Late Devonion/ Kellwasser Event
Years: around 375-360 Mya
Extinction: 75%
What happened: Rapid growth of land plants causes mass consumption of atmospheric carbon dioxide, which causes global cooling. Weathering plant roots release nutrients into the sea,
causing algal blooms and oxygen depletion
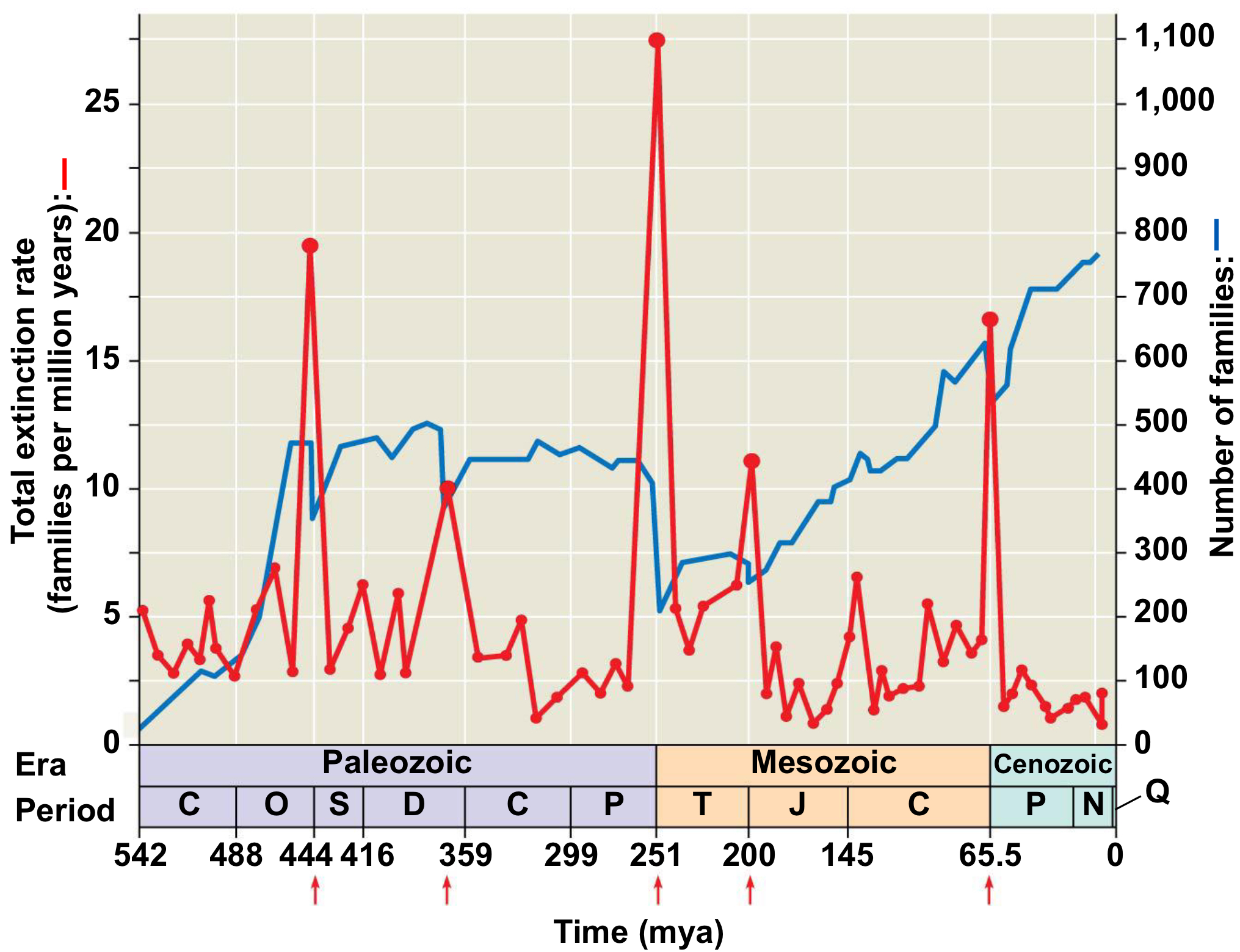

End Permian (The Great Dying)
Years: around 252 Mya
Extinction: 57% and lasted around 60,000 years
What happened: Massive amount of volcanic gas (carbon dioxide, methane, hydrogen sulfide, etc.) released from Siberian Traps.
Volcanic eruption estimated to last for ~1,200 years
Carbon dioxide levels reach
~2000 ppm (Currently ~423ppm)
NOTE: Enough lava to bury the continental United States in
a kilometer of volcanic rock.
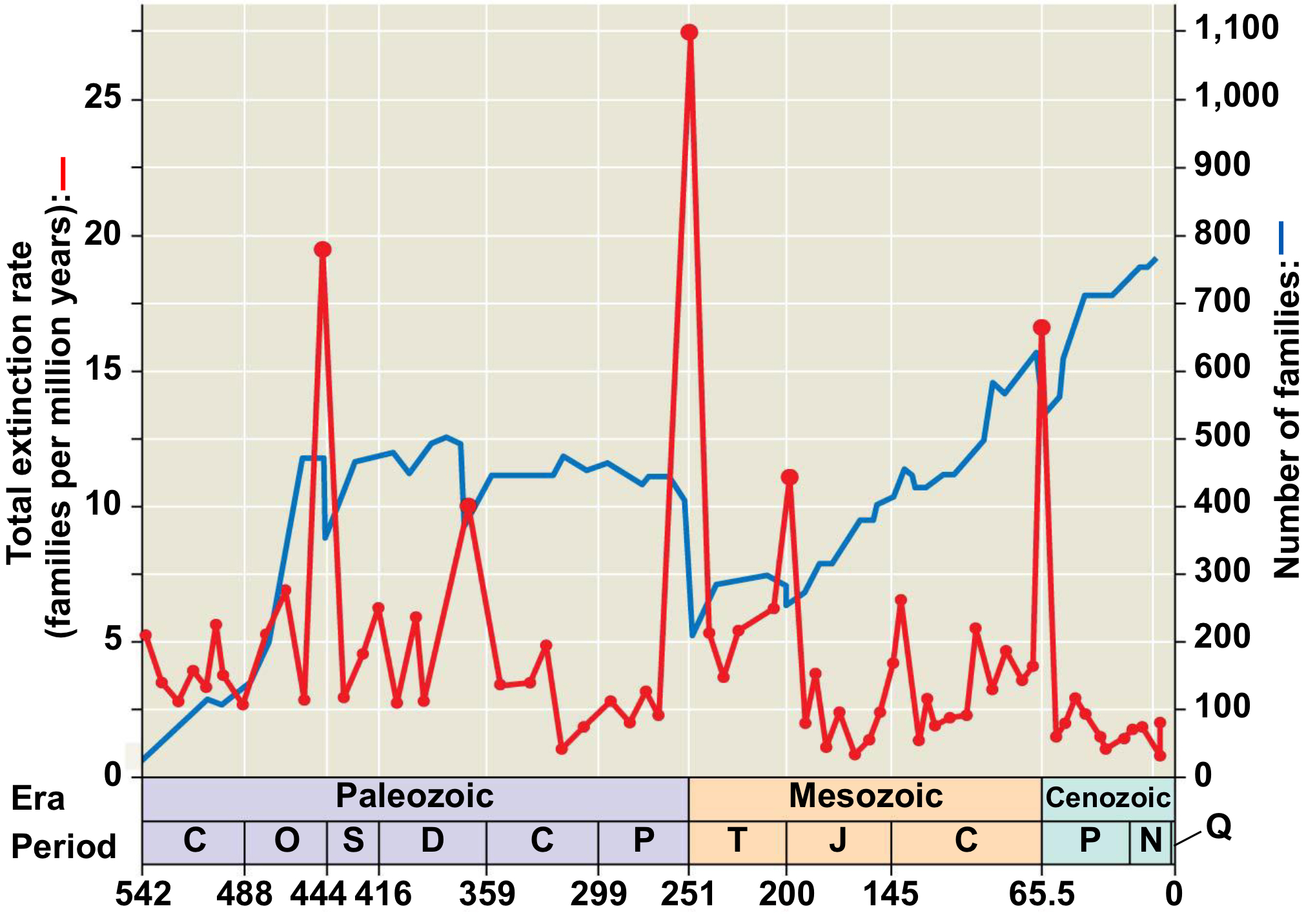

End Triassic
Years: around 201 Mya
Extinction: 80%
What happened: Underwater volcanic activity cause the mass release of carbon dioxide + hydrogen sulfide into the atmosphere.
Causes global warming and ocean acidification
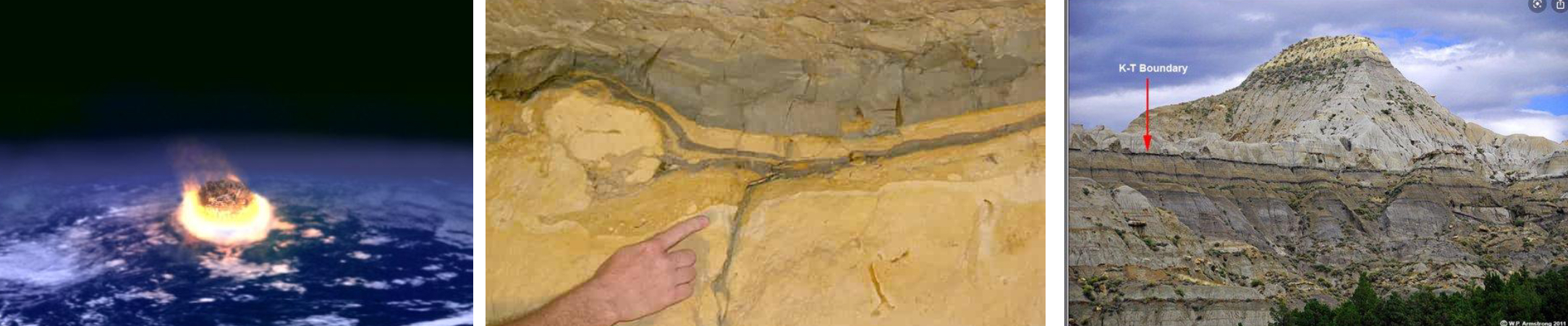
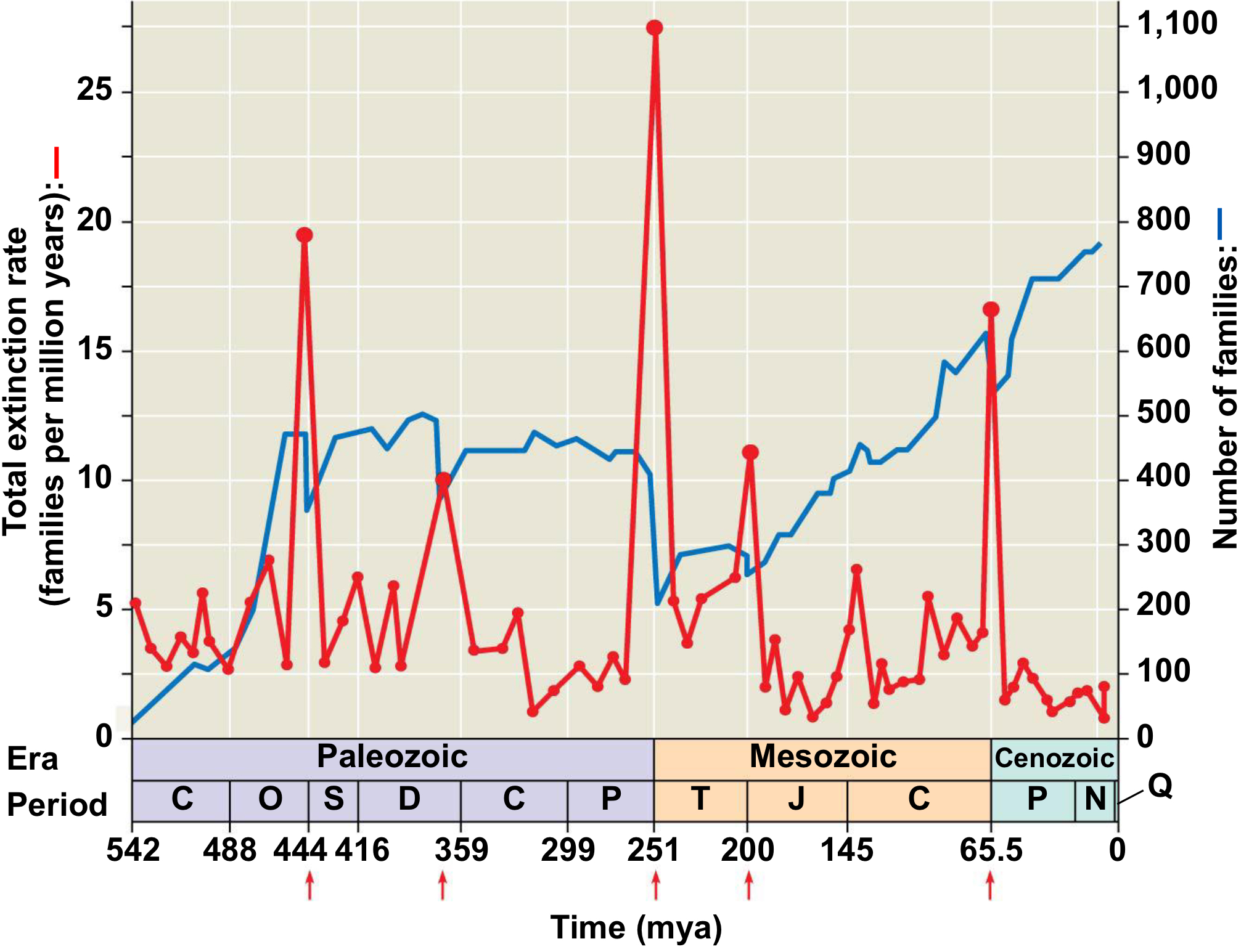

End Cretaceous (K-T extinction)
Years: around 65.6 Mya
Extinction: 60%
What happened: Large asteroid (6-9 miles wide) hit Earth at speed of 12,000 km/hr. Debris from strike came down for thousands of miles, set forests on fire, and started a nuclear winter (sun blackened out). Events led to the collapse of the food web. Process
took ~32,000 years
Consequences of Mass Extinctions
-It can take from 5-10 million years for diversity to recover following a mass extinctions
-Alter ecological communities and the habitats available to organisms
-Changes the types of organisms found in ecological communities
-Mass extinctions have drastically altered ecological communities
-Many lineages are lost; elimination of many species
What is adaptive radiation?
Periods of evolutionary change in which groups of
organisms form many new species whose adaptations
allow them to fill different habitats
When does large scale adaptive radiations usually occur?
Occurred after each of the “big five”
also occur after major evolutionary
events (ex: photosynthesis)colonization of new
areas
Example: mammalian radiation following the Cretaceous extinction
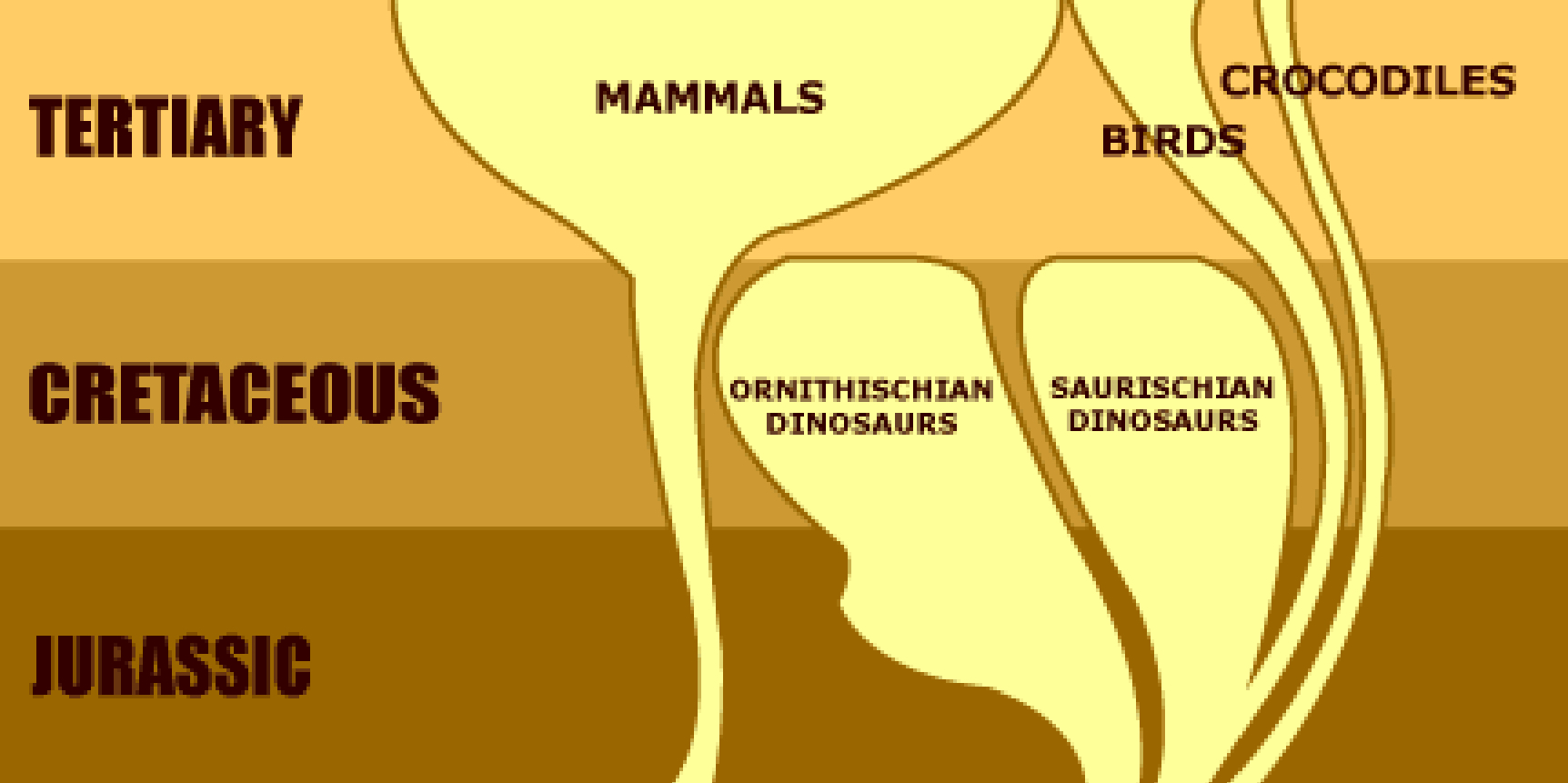
What is an ecological opportunity?
Availability in new resources
Morphological Innovation
Evolution of a key trait that allowed descendants
to live in new areas, use new resources, or move in new way
Plant Evolution
1.Bryophytes (610-500 Mya)
2.Seedless Vascular plants (425-360 Mya)
3.Angiosperms (245-202 Mya)