Renal
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Normal things to find in urine
urea
creatinine
potassium, Na, Cl, phosphate
uric acid
urobilinogen
abnormal things to find in urine
glucose
blood
albumin/protein
ketones
bacteria
WBC
crystals
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
Sudden decline in kidney function that is often treatable and reversible
causes of AKI
Pre-renal issues (hypovolemia, hypotension, obstruction, vasoconstriction)
Intra-renal (inflammation, glomerulonephritis, nephrotoxic meds, ischemic damage)
Post-renal (ureter, urethra, bladder obstruction)
How do we treat AKI
treat the underlying cause (if hypovolemia give fluids, if infection give abx, etc)
Common nephrotoxic agents
- ibuprofen/advil
- Gadolinium (contrast dyes)
- Acetaminophen
- Macrolides Abx (gentamicin, erythromycin, -mycin/micin)
Why do patient with kidney disease develop anemia?
reduced kidney function reduces erythropoietin leading to reduced production of RBC => anemia
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
progressive, irreversible loss of kidney function
Some main causes of CKD
1) Diabetes Mellitus (injury of the endothelial layers of the blood vessels)
2) Hypertension (uncontrolled)
3) AKI
S/Sx of Chronic Kidney disease
- itching (build up of urea in the blood and on skin)
- fatigue (anemia and decrease CO due to fluid build up)
- increase waste products in blood (urea and amonia)
- HTN (fluid retension)
Normal GFR
125ml/min/1.73m^2
General Trends of CKD Stages
Stage 1: kidney damage with normal GFR (≥90)
Stage 2: mid GFR impairment (60-89)
Stage 3: moderate GFR impairment (30-59)
Stage 4: severe impairment of GFR (15-29)
Stage 5: end-stage (GFR<15) almost no urine output at this point
Types fo dialysis
hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis
hemodialysis
the process by which waste products are filtered directly from the patient's blood using an external device with semipermeable membranes that allow for waste to be diffused out of the blood.
What do you need to assess before dialysis
1) BP (should be high before dialysis)
2) Port site (for signs of infection)
3) Electrolytes (esp potassium)
4) medications
Hemodialysis Catheter
Large lumens accommodate hemodialysis, usually temporary
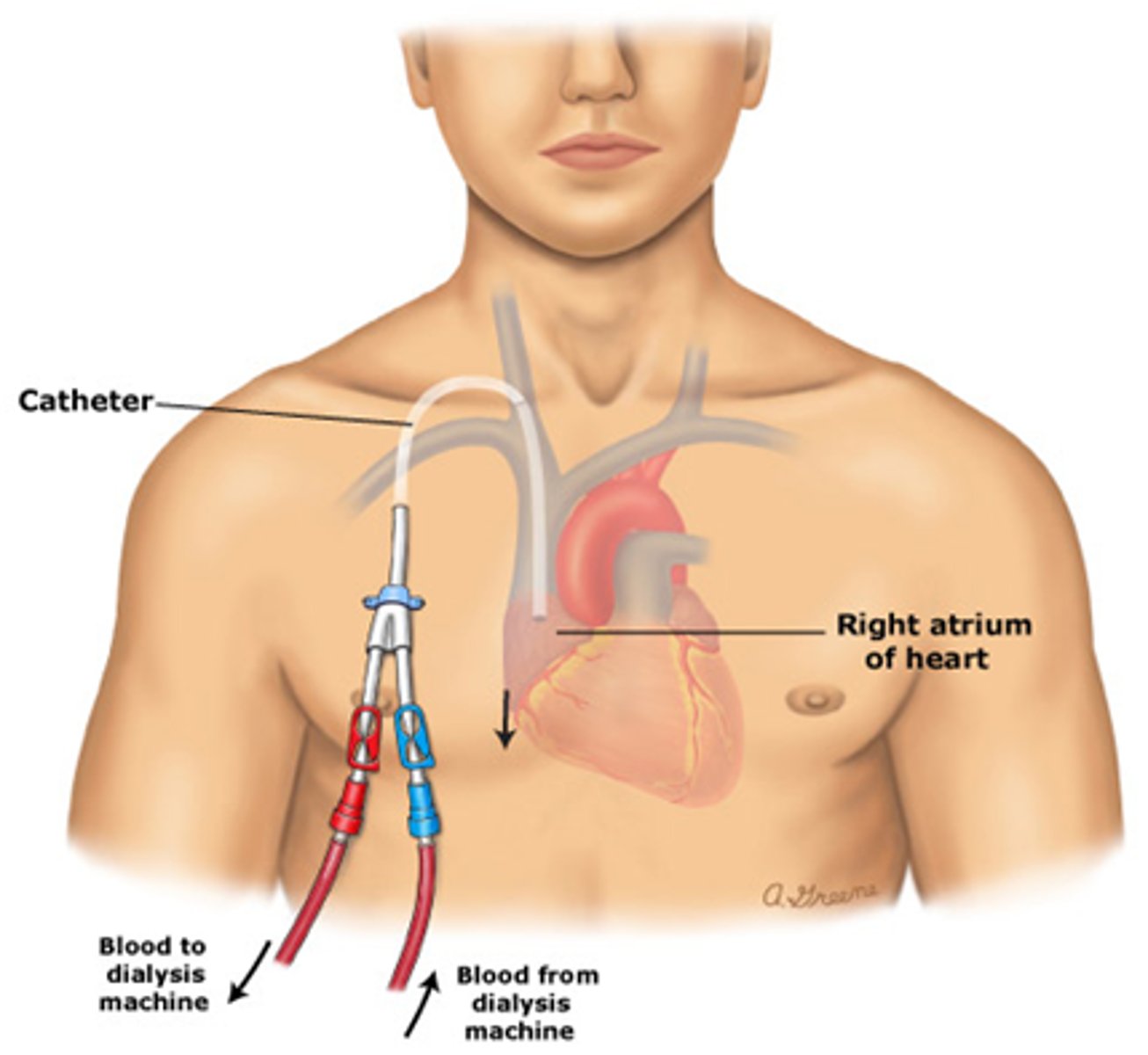
Nursing notes about hemodialysis catheter
- red and blue caps SHOULD NOT BE USED FOR ANYTHING OTHER THEN DIALYSIS!!!!!
- assess frequently for signs of infection
- places into he vena cava from subclavian so high risk of infection
Internal Arteriovenous Fistula and Graft
- Surgical procedures... take 2-3 months to mature
- take artery and vein, cut them and sew them together leading to blood flow from the artery into the vein to increase strength of vein walls to allow for the fluid volume from dialysis to be accommodated
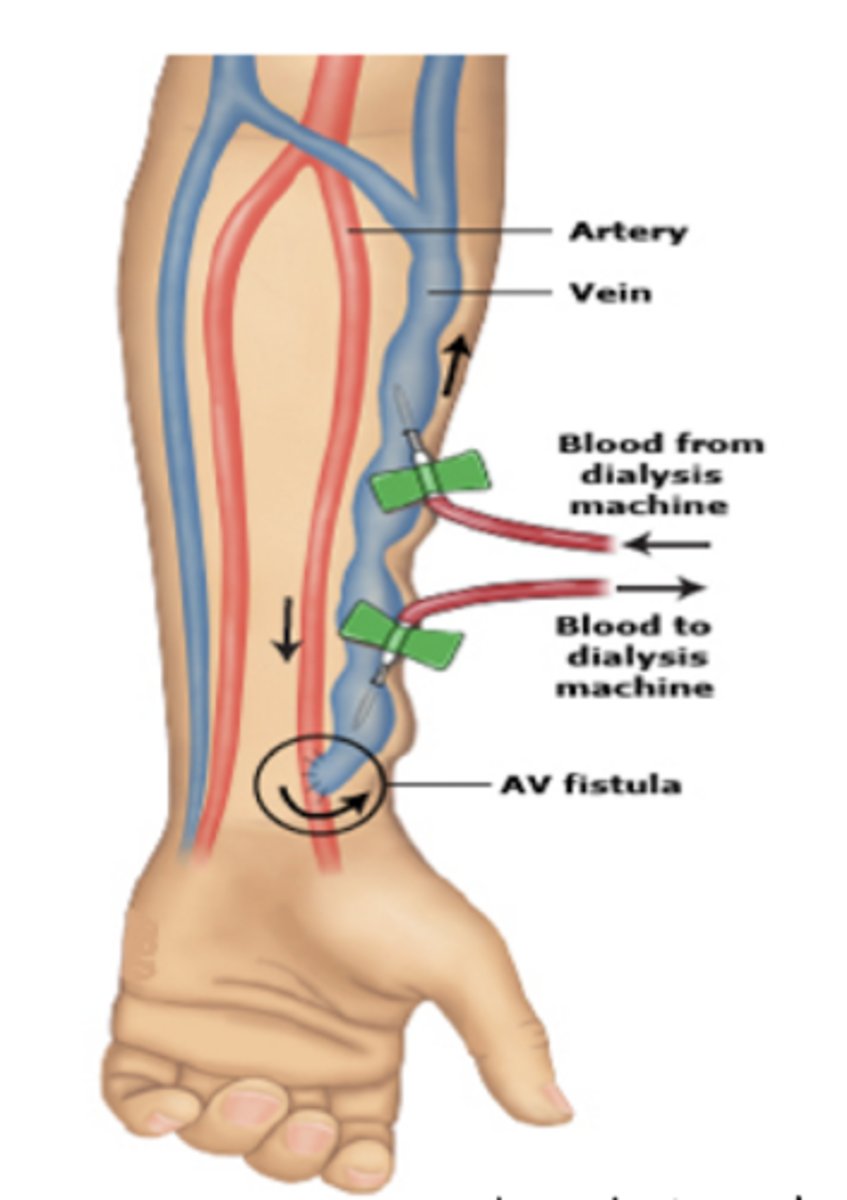
Fistula Nuring Considerations
1) Do not use it for IV sticks
2) Do not use that arm for blood pressure readings
3) Assess for trills and bruits (normal findings)
Peritoneal Dialysis
the lining of the peritoneal cavity acts as the filter to remove waste from the blood
used when ESKD is <10% GFR
high risk of sepsis and peritonitis
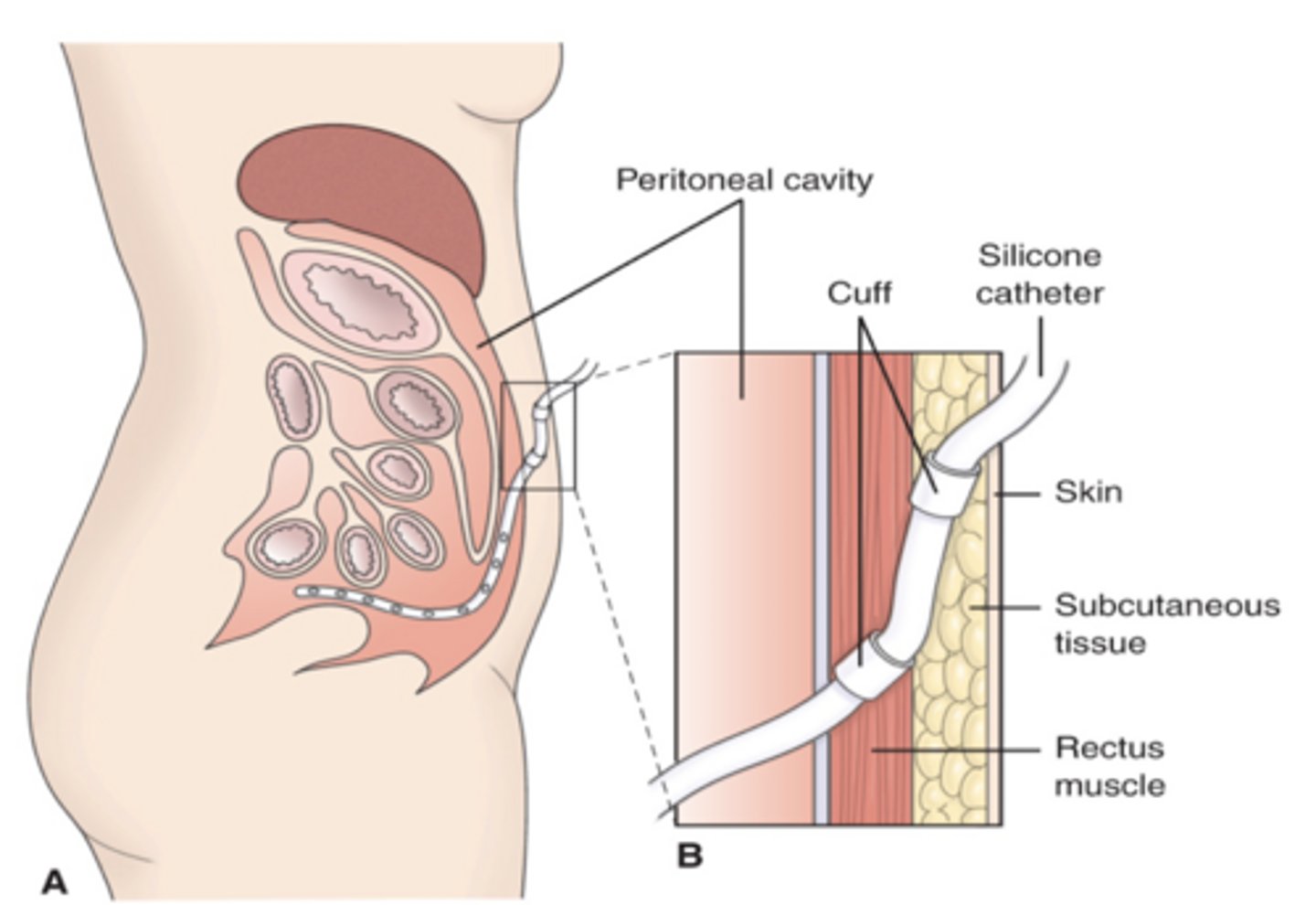
Peritoneal Dialysis Nursing interventions
- assess for signs of infection at insertion site
- assess for signs of peritonitis
- help reposition patient if they are SOB due to fluid in abdomen
Concerns with Peritoneal Dialysis
there is less monitoring so increased risk of fluid overload and infection
S/Sx of peritonitis
- abd pain and rigid abdomen
- cloudy dialysate solution
- Fever/chills
- elevated WBX
- malaise
Med consideration for dialysis
Important to think about med administration before dialysis b/c many will immediately be removed from the bloodstream during dialysis
1: EPO medications (darbepoetin) and iron
2: electrolyte supplements
3: blood pressure meds
Sodium Polysterene (Kayexalate)
bind to K so it can be excreted in feces to help to lower K levels in the bloodstream
Renale Diet
- low Na
- low K
- low phosphorus
- may reduce protein
Why is phosphorus an issue with CKD
extra phosphorus in the blood stream can pull calcium in the blood and lead to deposits in blood vessels, soft tissue, heart, etc.
Foods high in phosphorus
- dark colas or beers
- deli meats
- protein foods
- dairy
Normal urinary output
1ml/kg/hr or ~30ml/hr
Oliguria
decreased urinary output
<0.5ml/kg/hr
anuria
absence of urine
<50mL/day
Bacteriuria
bacteria in the urine
Dysuria
painful urination
enuresis
involuntary discharge of urine
Frequency
frequent voiding (more then every 3 hours)
Hematuria
blood in the urine
hesitancy
delay, difficulty in initiating voiding
incontinence
inability to control bladder and/or bowels
nocturia
excessive urination at night
polyuria
excessive urination
Proteinuria
protein in the urine
Azotemia
urea and nitrogenous waste in the blood
urgency
strong desire to void
1 c = ____ oz
8 oz
30mL = __ oz
1 oz
1 cup = ___ mL
240mL (also 8oz)
BUN
blood urea nitrogen
indicates kidney function
Normal BUN
5-20mg/dL
Why would BUN be high?
reduced kidney function, dehydration, increased protein consumption
Creatinine
nitrogenous waste excreted in the urine, indicated GFR
What can impact creatinine?
age (higher in older patients due to lower kidney function)
sex (muscle mass)
race.......not clear if this is valid.....
BUN/Creatinine Ratio
10:1 to 20:1
if BUN is high and Cr is normal probably dehydration/protein
If both are high but ratio is normal means reduced kidney function
Urine specific gravity normal values
1.003-1.030
Urinary Tract Infection
microbial infection of any part of the urinary tract, often caused from E. coli from anus/GI
Risk factors for UTI
- female
- sexual intercourse
- indwelling catheter
- diabetes (glucosuria)
- urinary tract obstruction/urinary stasis
UTI Types
Lower UTI:
- Cystitis (bladder)
- Urethritis (urethra)
- Prostatitis (prostate)
Upper UTI:
- pyelonephritis (kidney infection)
pyelonephritis
Increased risk of developing upper UTI following lower UTI with presence of vesicoureteral reflux
can cause AKI
Uncomplicated UTI
- often asymptomatic
- female, not pregnant, no weakened immune system
- can appear as delirium in elderly patients
- lower UTI infections
S/Sx of Uncomplicated UTI
pyuria (burning upon urination)
dysuria
frequency
urgency
cloudy
WBC, RBC, nitrites in urine
bacteria in urine
Complicated UTI
occurs in individuals with other health problems, males, harder to treat, pregnant patients, upper infection
Complicated UTI S/Sx
- fever
- suprapubic pain
- flank pain
- CVA pain (often unilateral)
Patient Edu for UTI
- drink 8-10 glasses of water per day
- void q2-3hr
- females should void after sex
glomerulonephritis
inflammation of the glomeruli of the kidney
- more than just WBC/RBC/bacteria in urine (includes protein)
- severe kidney
- kidneys can't filter fluid (severe decrease in GFR)
- may need dialysis
Urinary Calculi
- kidney stones
- most common urological problem in adults
- more common in males
Causes: dehydration, excessive calcium or uric acid, urinary stasis, unknown
Urinary Calculi s/sx
flank pain
hematuria
CVA tenderness
Diagnosis of Urinary Calculi
KUB (x-ray of kidneys, ureters, bladder)
Urinalysis
Stone anlysis
Treatment of Urinary Calculi
- encourage fluid intake (3-4L/day)
- analgesic (not NSAIDs)
- give diuretics or antibiotics
- Alpha blockers: tamsulosin (flomax)
- Lithotripsy
Lithotripsy
- surgical crushing of a stone with shockwaves
- hematuria is normal after
- used for larger stones
- painful
Most common type of kidney stones and how to treat
- calcium oxalate stones (70-80% of cases)
- restrict oxalate
Foods high in oxalate
spinach, rhubarb, beets, nuts, dark chocolate, tea, wheat bran, strawberries
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- benign growth of cells within the prostate gland
- by age 60, 50% of males have BPH
- PSA levels will be elevated
Meds for BPH
- Alpha Blocker: tamsulosin (flomax) to relax muscles in neck of bladder
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitor: finasteride (proscar) blocks an enzyme that changes testosterone to another hormone that causes growth of prostate
S/Sx of BPH
- sensation of not emptying bladder completely
- frequency with urination
- interruption of urine stream
- difficulty postponing urination
- weakness of urine stream
- need to strain to begin urination
- frequency of urination at night (nocturia)
BPH treatment
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP):
TURP
Insertion site: tip of penis, through urethra to trim away excess
prostrate
TURP nursing care
- hematuria is normal after for 12 hours
- assess for signs of hemorrhage
- dribbling after the catheter removal is normal in post-op
- patient should report retrograde ejaculation