M6+7 Grefen- Cooperation I, II + III
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
what is hamilton’s rule of cooperation and how can we use it to classify social behaviours depending on the values involved?
an action will be favoured by natural selection when rb-c>0, where:
r is the fraction of relatedness between the actor and the recipient (proportion of own genes that will be passed on via the recipient’s offspring)
b is the benefit to the recipient (how many more offspring the recipient will be able to produce)
c is the cost to the actor (how many fewer offspring the actor will be able to produce)- if c is negative, the action also benefits the actor

what are direct, indirect and inclusive fitness?
direct fitness- the offspring the actor has
indirect fitness- the offspring the recipient has X the relatedness between the actor and recipient (how many of the actor’s genes will be passed down via the recipient’s offspring)
inclusive fitness- the sum of the direct and indirect fitness

what are fraternal and egalitarian cooperation and what are some examples?
fraternal cooperation is between cooperators that are closely related, eg:
the cells within a multicellular organism cooperate
the individuals within a population can cooperate (or may not, depending on degree of relatedness)
egalitarian cooperation is between cooperators of that are unrelated or distantly related, eg:
different genes contribute to a genome
different genomes (nuclear, mitochondrial…) contribute to a complex cell
populations of different species can cooperate
what is unenforced direct benefit cooperation? give an example
a kind of direct cooperation- no real reason/benefit to cheat
it’s just very beneficial to cooperate, so no enforcement is needed
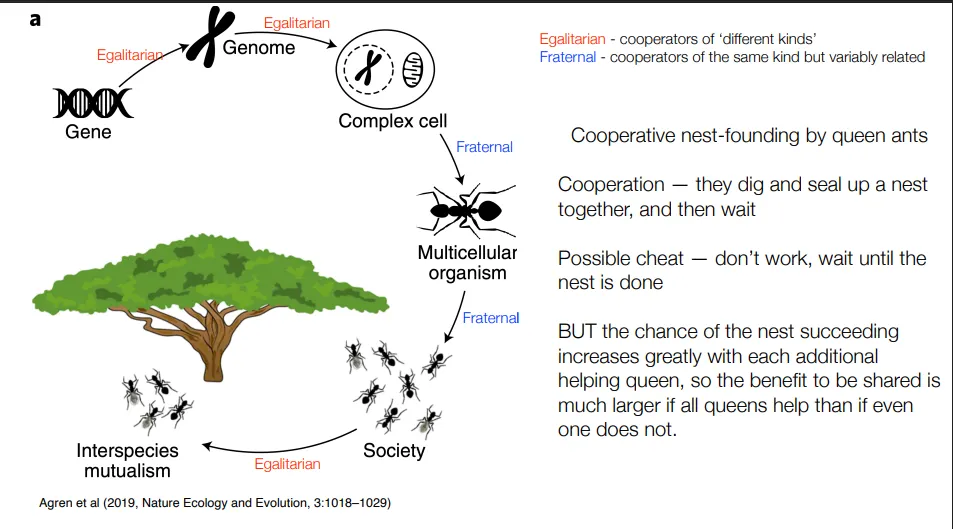
eg. cooperative nest founding by queen ants:
burrowing through soil to form a nest is difficult, so it helps to have multiple queens doing so (they then fight to the death)
possible cheat- to not work and wait until the nest is done
but the chance of a successful nest increases greatly with each additional queen, so not cooperating isn’t beneficial
what is reciprocity cooperation? give an example
a kind of direct, enforced cooperation- two partners do repeated actions that help eachother with consequences for cheating
each action looks altruistic, but the exchange becomes direct benefit
eg. cleaner fish:
cleaner gets to feed on ectoparasites and don’t get eaten, big fish ‘client’ gets cleaned
possible cheat- client eats the cleaner, cleaner takes a bit of the client
but the client would then not find another cleaner, and the cleaner would lose clients, so there are consequences for breaking reciprocity
‘prisoners dilemma’
what is policing cooperation? give an example
a kind of direct, enforced cooperation- cheating is prevented by systematic action
eg. worker laying of male eggs in eusocial insects
queen mates with many males
this produces female workers which all collaborate to raise subsequent offspring as relatives
possible cheat- a laying worker could lay its own eggs (to produce males that can mate with the queen)
but worker-laid eggs get routinely removed by workers very effectively (because they have a greater regression relatedness to queen-laid eggs than worker-laid eggs in a multi-father population), so cheating is unsuccessful
the best route to passing on your genes is by raising queen-laid eggs, so slacking is also not beneficial
what is imposed incentive cooperation? give an example
a kind of direct,enforced cooperation- cooperation is encouraged by one individual to others via rewards, punishments and sanctions
eg. soybeans and Rhizobium
soybean plants supply Rhizobium bacteria with oxygen and carbohydrates in return for fixed nitrogen
possible cheat- Rhizobia could stop fixing nitrogen
but the soybean plants withhold oxygen from Rhizobium that do not fix enough nitrogen- this is an imposed incentive
what is limited dispersal cooperation? include the calculations
also called population viscosity
a theoretical kind of indirect cooperation- offspring don’t move far from where they were born, so they are surrounded by close relatives and can all help eachother
however, this has been shown to not be a valid theory, as the degree of relatives helping eachother is cancelled by the local resource competition between them
applied to hamilton’s rule:
an altruistic action is favoured by selection if rb-c > 0
however the gain to the recipient must be balanced by a cost (of b - c) to another group of individuals (which the actor may also be related to)
relatedness to this ‘density-dependent group’ is called r_e
so hamiltons rule becomes rb - c - r_e(b - c) > 0
if the cost is spread across the whole population (isn’t density dependent), r_e = 0, so hamilton’s rule stays the same
if the actor is closely related to the density-dependent group (in the case of limited dispersal), r = r_e, so the expanded rule cancels down to rc - c > 0
in this case, the benefit b to the recipient becomes irrelevant, so there is no reason to be altruistic (theory isn’t valid)
overall altruistic actions are favoured with low comp/high r (and vice versa):
high relatedness to the recipient, where the cost comes to a wider, less related population (global competition)
what is kin discrimination cooperation? give an example
a kind of indirect cooperation- individuals are able to recognise their relatives, so they can be altruistic to just their kin and pass on their genes indirectly
eg. long-tailed tits (and other birds)
long-tailed tits try to mate on their own, but if they fail, they try to help at another nest- most of the time they select a relative to help
the more helpful the individual is, the more likely they are to be discriminant in helping only relatives
what is greenbeard cooperation? give an example
a semi-theoretical kind of indirect cooperation- a gene that can cause the individual to have a distinctive trait (a green beard), recognise it in other individuals, and behave altruistically to other bearers
eg. invasive fire ants (potential example?)
workers carrying the b allele kill young queens which don’t have it (BB), relying on a chemical odour