BIO120 CH10
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
what is biological tissue
collection of cells that work together to perform a function
what are the four types of tissue
epithelial, connective, nervous, muscle
cell shape is determined by
cytoskeleton
the connection between cells relies upon
cell junctions
what are cell junctions
complexes of proteins in the cell membrane where cells make contact with each other
what is the extracellular matrix
network of proteins and polysaccharides that support cells tissues and organs
what is the structure of skin tissue
epidermis and dermis
what is the epidermis
outer layer, water-resistant, protective barrier
what is the dermis
inner layer, supports epidermis with structure and nutrients, cushions body
how many layers are epithelial cells
>1 layers
what types of cell line the digestive tract and blood vessels
epithelial cells
what are the components of the epidermis
keratinocytes, basal lamina
what is the function of keratinocytes in the epidermis
specialized to protect underlying tissues and organs
what is the function of basal laminate in epidermis
underlies and supports all epithelial tissues
cytoskeletal elements
microfilaments, microtubules
animal cells have what type of cytoskeletal elements that plant cells don’t have
intermediate filaments
all cytoskeletal elements are made of what?
long chains (polymers) of protein subunits
what are microfilaments (how are they made)
double helix of actin polymers
what are microtubules:
hollow tube formed by tubular dimers
what are intermediate filaments
a strong fiber made of protein subunits
what are all cytoskeletal elements made of
polymers, but differ in size
what type of cytoskeletal structure is the smallest
microfilaments
what do microfilaments do
reinforce the cell membrane and its proteins, help cells maintain their shape
what do intermediate filaments do
provide cells with mechanical strength, attach to cell junctions to provide structural support for cells
what are intermediate filaments made of
polymers of proteins that link to form strong cable-like structures
where do intermediate filaments attach?
they attach to cell junctions
what does anchoring to cell junctions do for cells and tissue
anchoring to cell junctions creates structural continuity between cells and strengthens all epithelial tissue
what type of cytoskeletal element is crucial for cell types subjected to physical stress (like skin)
intermediate filaments
what is made of polymers of protein dimers
microtubules
what contains two tubulin proteins, alpha and beta
dimers
what are dimers made of
two tubules proteins, alpha and betaw
what do dimers do for cells
maintain cell shape and internal structure
where are dimers tethered
to organelles to guide internal arrangement
what is attached to centrosome
microtubules
what is the centrosome
where all the microtubules begin, the center of the cell, heart of the tubules radiating outward
what are the two tubules proteins called in dimers
alpha and beta
cells change rapidly (T or F)
false, cells change slowly
what is added to the cytoskeletal structure at a rate that depends on the amount of tubular and actin that is available
protein subunits
what are continuously growing and shrinking during an organism’s lifespan
microtubules and microfilaments
what does the rate of microtubule and microfilament growth depend on
amount of tubular and actin that is available
what instigates faster assembly on one or both ends of a filament or tubule
high concentration of protein subunits in a cell
which end of a tubule or filament is the rapid assembly side
the plus side
which end of a tubule or filament is the slow assembly side
the minus end
microtubules are capable of rapid _________ and less rapid _________
depolymerization , polymerization
what is dynamic instability
when microtubules are able to grow and shrink constantly
why is dynamic instability good for cells
it allows spindles to find and attach to chromosomes during cell division
what is polymerization
the building up of the microtubuels
what are motor proteins and what do they do
associate with tubules and microfilaments to cause movement
movement of vesicles within the cell requires ____________ and ____________ to associate with motor proteins like Kinesin
microfilaments and microtubules
what things allow muscle cells to contract to facilitate movement
myosin and microfilaments
which direction does kinesis transport cargo toward on a microtubule
toward the plus end
what do microtubules do to help transportation of molecules thru the cell
provide tracts to facilitate transportation
what makes up cilia
microtubules
what are cilia
rod-like structures that extend outside of cells
what is the primary use for cilia
sensory purposes, to receive environment signs that inform cell function and movement
how do chlamydomonas move
motion of two long cilia
how do paramecium move
short cilia that beat in coordinated fashion
why do epithelial cells have cilia in airway
they sweep fluid and Debris and pathogens out of airway
tissues are held together and joined as unit bc of
cell junctions
what do cell junctions do
physically connect cells together and anchor them to extracellular matrix
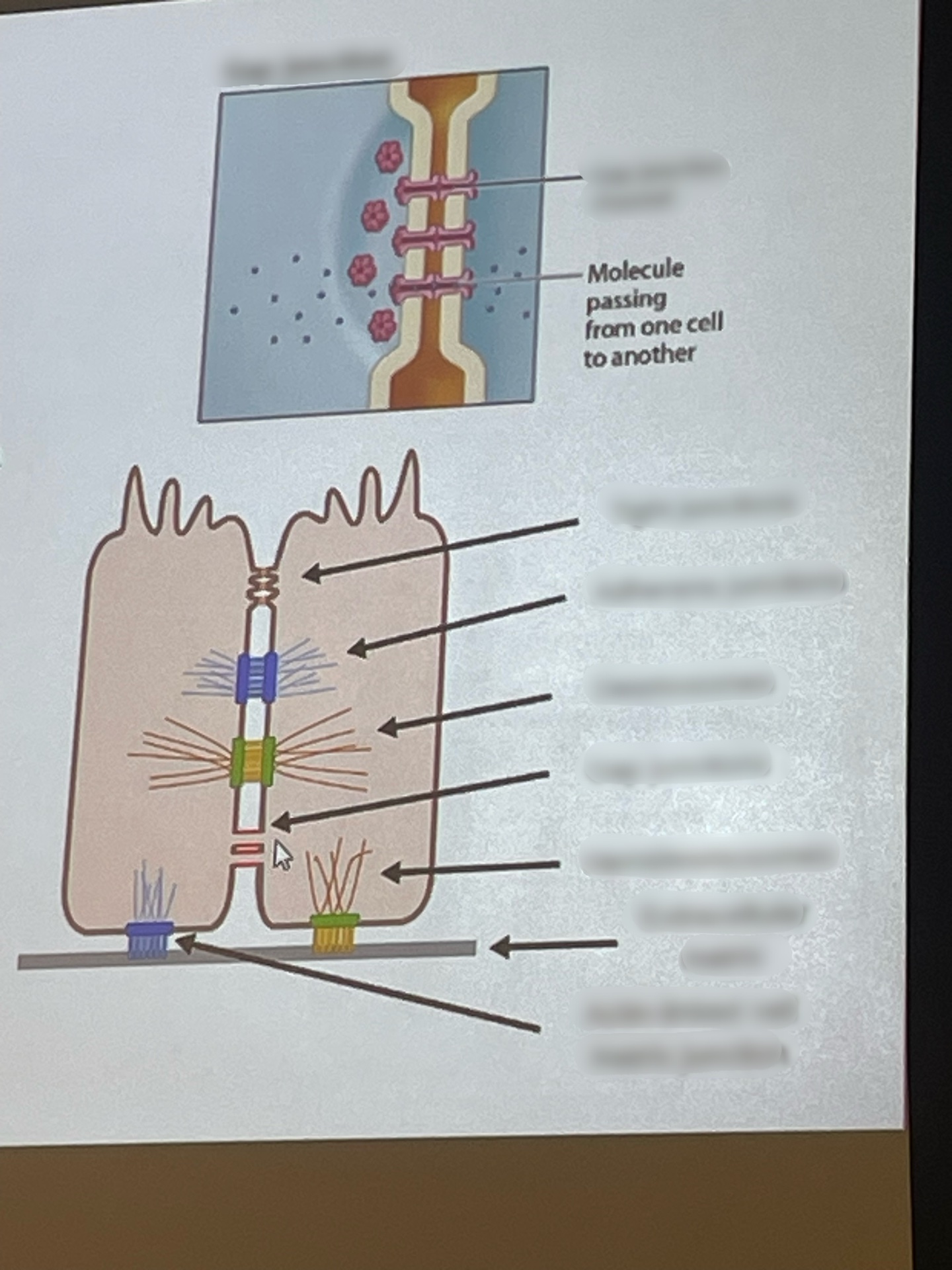

cell junctions physically connect cells together and anchor them to the __________-
extracellular matrix
what is cell adhesion
cells of the same type stick together bc of surface proteins recognize each other
what is an a cadherin
important type of cell adhesion molecule (can only bind to other cadherins)
what type of protein is a cadherin
calcium dependent adherence protein
how do cadherins bind to other cells
they are transmembrane proteins that bind to other cadherins on the outside of another cell
what are adherens junctions
beltlike structures that allow cadherins to link to other cells
how do cadherins use adherens junctions to link to other cells
They are anchored through the membrane of the cell and grab on to the cadherins poking thru the other cell’s membrane
what are desmosomes
cell junctions that allow cells to attach to other cells
how do cadherins in desmosomes work
cadherins in the desmosomes of one cell bind to cadherins in the desmosome of another cell
how are desmosomes different from adherens junctions
desmosomes are more button like and tightly packed while adherens junctions are more belt-like and more spread out

what are epithelial cells attached to
each other and the extracellular matrix (basal laminate)
how are cells anchored to the basal laminate
with a type of desmosome called Hemidesmosome
what are integrins
a type of hemidesmosome that participates in cell adhesion
what do tight junctions do
prevents the movement of substances thru the spaces between cells
which junctions don’t prevent the movement of materials between cells
adherens junctions and desmosomes
what are tight junctions
band of interconnected strands of membrane proteins
are all junctions involved in cell adhesion
no not all
WHAT are gap junctions (NOT what they do)
complex of membrane proteins called connexins
what do gap junctions do
allow material to pass between cytoplasm of cells and allow communication between cells
what are connexins
membrane proteins in gap junctions
what shape are connexins
ring of proteins
what do connexins connect to
connect to a similar ring of proteins in the adjacent cell
two connexion rings form a channel for molecules to pass thru
how do ions move in the heart
ions pass thru cell junctions that connect to cardiac muscle cells
what allows rapid communication between heart cells
movement between cells
what is plasmodesmata
passages thru the cell wall of plant cells
do animal cells have plasmodesmata
no only plant cells
what does plasmodesmata do
allow cells to exchange ions and small molecules
what does the extracellular matrix do for organisms
provides the molecular framework that determines structure of organisms
what is the extracellular matrix made of
proteins and polysaccharides at a cells surface
what is the ECM of plants
cell wall
main component of plant cell wall is
polysaccharide cellulose
how many layers are in plant cell walls
3 layers
what are the three layers of plant cell walls
middle lamella, primary cell wall, secondary cell wall
what is the function of middle lamella
allows plant cells to stick together
which cell wall layer is synthesized first
middle lamellawh
what is middle lamella made of
gluelike complex carbs
what’s the primary cell wall made of mostly
cellulose with some molecules like pectinw
which layer of plant cell wall is thin and flexible
primary cell wall
what layer of cells walls is not always constructed in all plant cells
secondary cell wallw