Lesson 04- Meiosis and Reproduction
1/36
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is Meiosis?
Meiosis is a two-part cell division process in organisms that sexually reproduce.
What is the chiasma?
point where crossing over occurs.
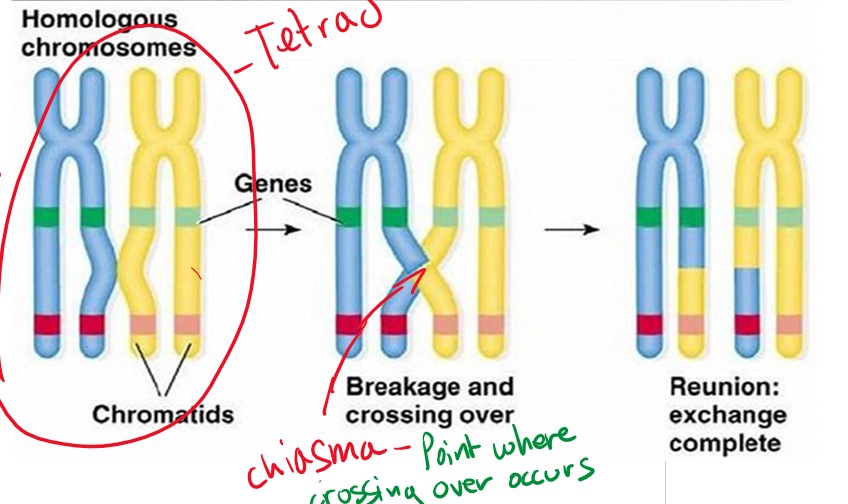
What are gametes?
Cells that carry the potential to create new life by combining with the gamete of an opposite sex. Meiosis produces them with ½ the number of chromosomes as the parent cell so that they can combine.
What is produced at the end of the meiotic process?
Four daughter cells.
What are daughter cells?
cells that have ½ the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
What happens during meiosis interphase?
The cell increases in mass, synthesizes DNA and protein, and duplicates its chromosomes in preparation for cell division.
What is prophase 1?
Chromosomes condense and attach to the nuclear envelope and go toward the metaphase plate. Genetic recombination may occur (via crossing over).
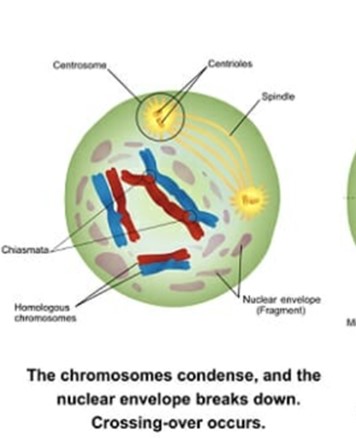
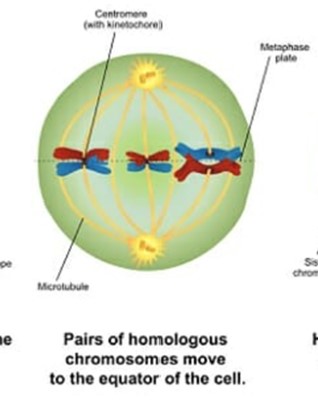
What is Metaphase 1?
Chromosomes align horizontally, and for the homologous (same structures/features) chromosomes, the centromeres are positioned toward opposite poles of the cell.
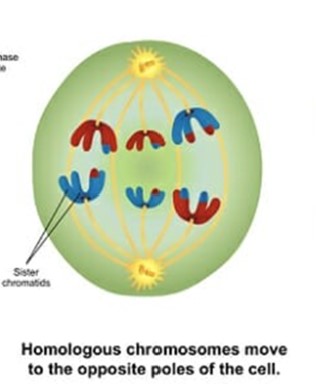
What is Anaphase 1?
homologous chromosomes separate and move toward opposite cell poles. The sister chromatids (identical copies of a chromosome made before a cell divides) remain attached after this move to opposite poles.
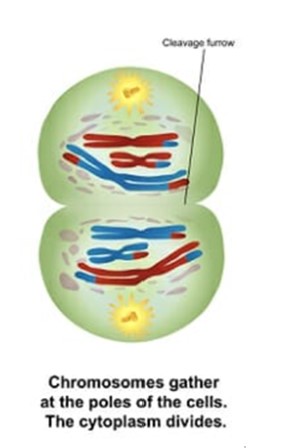
What is Telophase 1?
Cytoplasm divides, producing two cells with a haploid number of chromosomes. Sister chromatids remain together. While different cell types may prepare differently for meiosis 2, the genetic material in all cells does not undergo replication in meiosis 2.
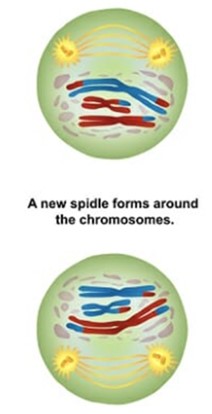
What is prophase 2?
chromosomes begin migrating towards the metaphase II plate. The chromosomes do not replicate again.
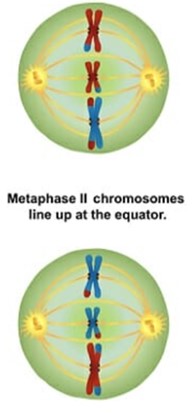
What is metaphase 2?
Chromosomes align at the metaphase II plate while the kinetochore fibers of the chromosomes are oriented towards opposite poles.
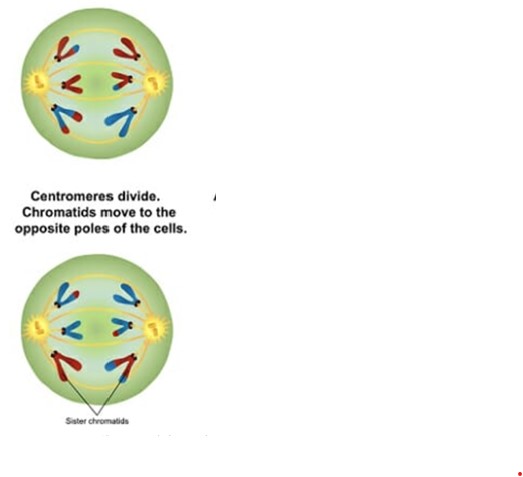
What is Anaphase II?
Sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite ends of the cell. The two cell poles grow further appart.
What is Telophase II?
New nuclei form around daughter chromosomes and the cytoplasm divides and forms two cells in cytokinesis.
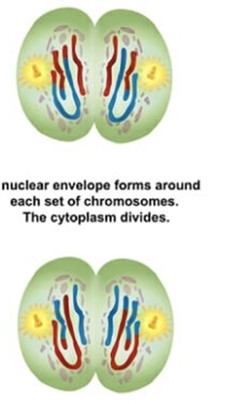
What is each of the four daughter cells called?
A haploid cell.
What is a zygote?
Haploid gametes unite to form this, in all humans, the sex cells contain 23 chromosomes and all other cells contain 46 chromosomes.
What does meiosis ensure?
That genetic variation occurs through genetic recombination that happens between homologous chromosomes.
What are some errors that could happen in meiosis?
Miscarriage, genetic disorders, chromosomal non-disjunction.
What is Chromosomal non-disjunction?
Chromosomes do not separate as they should’ve, and the gametes do not have the correct number of chromosomes. When it happens in the sex chromosomes, usually it is not as severe as when it happens in the autosomes.
What is negative to sexual reproduction?
Doesn’t allow rapid population growth.
What are the two goals of meiosis?
To produce gametes, and genetic variation by crossing over DNA.
What do gametes contain?
One chromosome of each kind.
True/False: The diploid number of chromosomes is restored after fertilization so that an animal’s body cell contains the diploid number of chromosomes.
True
True/False: In animals, the haploid cells produced by meiosis mature and become gametes.
True
True/False: There is only separation of sister chromatids in mitosis, not meiosis.
False
What are somatic cells?
Any cells except egg and sperm cells.
If a liver cell has 90 chromosomes, and that is 2n, how many chromosomes would the sperm cells have?
45
What does the first division in meiosis create?
Diploids, second is for haploids.
What is an allele?
A different version of the gene.
Is there DNA replication in Meiosis II?
Only in Meiosis I.
What type of cells make up an embryo?
Stem cells
How does an embryo form?
Needs contact with nutrients from diffusion
The cells migrate outward, forming a hollow sphere called a blastocyst (In mammals- Blastula in other animals.)
Totipotent
Means the cells can turn into any cell in the body.
Gastrulation
The cells in the blastocyst migrate into a hollow tube called the gastrula.
Pluripotent
They could turn into anything except Germ cells.
what is Aneuploidy
Odd number of chromosomes in a set.
What is trisomy and monosomy
mono- lack cromosomes, tri- three chromosomes