Hip and Pelvis
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Pelvis and Hip
Stable base!
supports for head, arms and trunk (HAT)
supplies proximal stability
pelvis = interface between LE and spine
absorbs force from UE and ascending force from LE
central point for body sym!
Sacrum
triangle shaped
located between 5th lumbar vertebrae and coccyx
5 sacral vertebrae
Pelvis
2 hip bones, 3 distinct portions
Pubic Symphysis (anterior)
fibrocartilaginous disk that provides direct connection of 2 hip bones
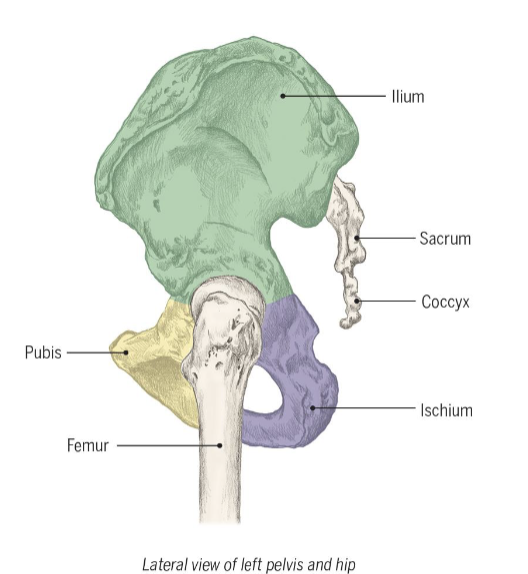
Acetabulum
where ilium, ischium, and pubis meet and form the socket for head of femur
Bony Landmarks of Pelvis
Iliac Crest
Anterior Superior iliac spine (ASIS)
Posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS)
Greater Sciatic notch
Ischial tuberosity
Iliac Crest
rounded edge superior border
Anterior Superior Iliac Spine (ASIS)
most anterior point
Posterior Superior Iliac Spine (PSIS)
most posterior point of iliac crest
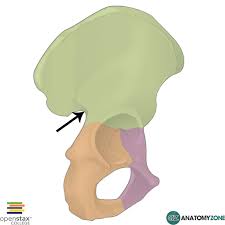
Greater sciatic notch
where blood vessels and nerves come through
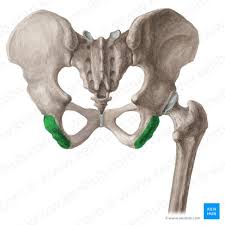
Ischial tuberosity
prime point for contact with seating surface
femur
longest bone in body
angle of inclination, important for stability!
120-130 angle
Joints of pelvis and hip
sacroiliac joint
hip joint
absorbs and transfer forces
Sacroiliac Joint (SI)
stabilizes pelvis under strain of opposing forces
type: synovial joint
Hip Joint
ball and socket
triaxial
movements: flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, external and internal rotation
Ligaments of Hip Joint
Iliofemoral ligament, pubofemoral ligament, ischiofemoral ligament
round ligament
Iliofemoral, ischiofemoral, and pubofemoral ligaments
are ligaments that provide stability to the hip joint by connecting the femur to the pelvis and restricting excessive motion
round ligament ( ligament capitis femoris)
direct support to the femoral head within the acetabulum
Ankylosing Spondylitis
inflammatory condition in spine
fuses skeletal structures
begins in SI joint and progresses into vertebrae
significant mobility limitations of spine and pain
Pelvic Floor (diaphragm)
inferior muscular wall of pelvic cavity that supports pelvic organs and maintains continence
Hip Flexors
iliopsoas muscles: psoas major, iliacus
PRIME flexors of hip
flex trunk
tilt pelvis anteriorly
Iliopsoas
hip flexion
Gluteus maximus
largest gluteal muscle
hip extension, hyperextension, lateral(external) rotation
high force demands, running/climbing
Hamstrings
a 2 joint muscle, crosses hip and knee
Hip abductors
gluteus medius and minimus
tensor fasciae latae
Gluteus Medius and Minimus
grouped together as lesser gluteal muscles
abduct the hip
Hip Extensors
gluteus maximus
hamstrings
Tensor Fascia Latae
a supportive layer of fascia
located on lateral thigh that helps stabilize the hip and knee during activity
connects to IT band
Iliotibial (IT) Band syndrome
overuse
repetitive strain
runners and cyclists
causes on friction between connective tissue and bony prominence causes pain and inflammation
Hip Adductors
adductor magnus
adductor longus
adductor brevis
pectineus
gracilis
span the inferior aspect of pelvis and medial femur
Hip Rotators
Piriformis
Quadratus femoris
obturator internus
obturator externus gemellus superior
gemellus inferior
span posterior sacrum to lateral femur
lie deep to glute max
Sciatica
tightness of piriformis or pressure on back of leg when seated can compress the nerve
sensory innervation of lower leg
pain and paresthesia in legs
posterior pelvic tilt
backward rotation of pelvis
flattens lumbar spine
increases thoracic flexion
Anterior pelvic tilt
forward rotation of pelvis
increase lumbar lordosis
increases extension of upper trunk
Pelvic tilt
refers to the orientation of the pelvis in a sagittal plane, which can be either anterior or posterior. This affects the curvature of the lumbar spine and overall posture.
Pelvic Obliquity
is a condition where the pelvis is tilted in the frontal plane, resulting in uneven hip heights. It can lead to an imbalance in the spine and affect posture
Pelvic Rotation
transverse plane position
rotation of one side of pelvis is anterior or posterior
functional mobility
transitioning and/or transferring body from one place to another
navigating an environment (walking, running, using a wheelchair)
Bowel, bladder, and sexual function Incontinence
loss of control of bowels or bladder
results of pelvic floor weakness
Stress incontinence
abdominal pressure increases from bodily function
causes involuntary leaking of urine or feces
Urge incontinence
inability to control the bladder or bowels until appropriate
proximal hip fractures
femoral neck fracture
intertrochanteric fracture
Total hip arthroplasty (THA)
replaces both the femoral head and the acetabulum
Hemiarthoplasty
replaces only the femoral head