Chemotherapy induced nausea/vomiting
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What are the risk factors for chemotherapy induced nausea/vomiting?
§ Female
§ Young age
§ History of morning/motion sickness
§ History of nausea during chemotherapy
§ Anxiety
§ Radiation with chemotherapy
§ Emetogenic potential
Classify the 5 types of CINV:
Type | Definition |
Acute | Occurs ≤24 hours after chemotherapy administration; peaks after 5-6 hours
|
Delayed | Occurs ≥24 hours after chemotherapy administration; often peaks between 48-72 hours
|
Breakthrough | Post chemotherapy despite optimal antiemetic regimen used; requires rescue therapy
|
Anticipatory | Triggered by sensory stimuli associated with chemotherapy before administration
|
Refractory | Occurs in subsequent chemotherapy cycles despite maximum antiemetic usage
|
What are the non-pharmacological treatment options for chemotherapy nausea/vomiting?
§ Eating small, frequent meals
§ Avoiding foods that cause heartburn/spicy food.
§ Avoiding strong odors
§ Taking antiemetics before food
§ Acupressure
§ Acupuncture
§ Music therapy
§ Support groups
§ Music therapy/relaxation
What are the pharmacologic treatment options for chemotherapy nausea/vomiting?
-5-HT3 antagonists
-Substance P/NK-1 RA
-Dopamine antagonists
-Atypical antipsychotics
-BZDs
-Corticosteroids
-Cannabinoids
5-HT-3 antagonists:
o MOA:
§ selectively blocks 5-HT3 peripherally on vagal nerve terminals and centrally in chemoreceptor trigger zone.
o Adverse Drug Reactions:
§ Headache, constipation, QTc prolongation, fatigue.
o Medications:
§ Ondansetron (Zofran):IV, PO, ODT.
§ Granisetron (Sancuso): IV, SubQ, PO, Patch.
§ Palonosetron (Aloxi): IV
o Efficacy:
§ They all have equal efficacy.
§ Corticosteroids increase efficacy by 25%
o QTC prolongation:
§ The oral medications have less risk than the IV medication for QTc prolongation.
Which type of Chemotherapy Induced Nausea/Vomiting is 5-HT3 used to treat?
Acute
§ Delayed ( palonosetron)
§ Breakthrough
If no NK1-RA or Olanzapine used:
Palonosetron or granisetron extended release are the preferred agents.
Substance P/NK-1 receptor antagonists:
· MOA:
o Selectively inhibits substance P to NK-1 receptors in CNS.
· Adverse Drug Reactions:
o Fatigue, diarrhea, hiccups, hypersensitivity ( greater in fosaprepitant).
· Medications:
o Aprepitant ( Cimvanti, Emend): PO, IV ; used for Days 1-3
o Fosaprepitant (Emend): IV ; used for Day 1
o Netupitant (Akynzeo): PO; used for Day 1
o Rolapitant (Varubi): PO; used for Day 1
· Metabolism:
o It is a CYP3A4 inhibitor , so you will have to decrease the dose of Dexamethasone if given with NK-1 Receptor Antagonists.
Which chemotherapy induced nausea/vomiting are NK-1 antagonist used to prevent?
o Acute and delayed nausea/vomiting but used in combination with 5-HT3 and Dexamethasone.
What happens when you give an NK-1 Receptor Antagonist to patients on Warfarin?
o It will decrease the INR.
Women who take contraceptives, what will happen to their contraceptives while taking a NK-1 Receptor Antagonist?
o The NK-1 Receptor Antagonist will decrease the efficacy of contraceptives.
Dopamine receptor antagonists:
· MOA:
o Block D2 receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone.
· Adverse Drug Reactions:
o Drowsiness, anticholinergic effects, EPS, orthostatic hypotension, diarrhea, tardive dyskinesia ( metoclopramide)
· Medications:
o Prochlorperazine: PO, IV, PR
o Promethazine: PO, IV, PR
o Metoclopramide: PO ; short-termed use
What Chemotherapy induced nausea/vomiting are dopamine antagonist used to treat?
o Breakthrough
Atypical antipsychotics:
· Olanzapine:
o MOA:
§ Antagonist of multiple receptors including dopamine, serotonin, histamine, and acetylcholine muscarinic.
o Dose:
§ 2.5 -10 mg once daily at bedtime.
o Frequency:
§ Daily for 1-4 days.
o Adverse Drug Reactions:
§ Drowsiness, fatigue, constipation, increased appetite/weight, hyperglycemia, QTc prolongation, EPS.
What chemotherapy induced nausea/vomiting is olanzapine used to treat?
§ Acute and delayed in combination with other drugs, breakthrough.
True/False: drowsiness is the main side effect of olanzapine, so you should take this medication at night/bedtime.
-True
Benzodiazepines:
· Lorazepam:
o MOA:
§ GABA receptor modulator; anxiolytic.
o Dosing:
§ 0.5-1 mg
o Frequency:
§ Q6hrs or right before infusion appointment.
o Adverse Drug Reactions:
§ Sedation, amnesia, hypotension, respiratory depression.
What chemotherapy nausea/vomiting is lorazepam used to treat?
Anticipatory
Corticosteroids:
· Dexamethasone:
o MOA:
§ Unknown
o Dose if taking with an NK-1 Receptor Antagonist:
§ Day 1: 12 mg
§ Days 2-4: 8 mg
Dose if not taking NK-1 RA:
Day 1: 20 mg
Day 2-4: 8 mg
o Frequency:
§ Can give once daily or twice a day for 4 days.
o Adverse Drug Reactions:
§ Insomnia, hyperglycemia, mood instability, increased appetite, hypertension, stomach upset.
Which chemotherapy induced nausea/vomiting is dexamethasone used to treat?
§ Acute and delayed in combination with other agents.
o If chemotherapy protocol has corticosteroids in plan:
do not need to add additional steroids.
Cannibinoids:
· Dronabinol:
o MOA:
§ Unknown , activates CB1 receptor leading to inhibitory effects on cerebral cortex.
o Dosing:
§ 5mg/m^2
o Frequency:
§ 1-3 hours before chemo then 4-6 doses/day.
o Adverse Drug Reactions:
§ Dysphoria, hallucinations, sedation, disorientation. Vertigo.
What chemotherapy induced nausea/vomiting is dronabinol used to treat?
§ refractory
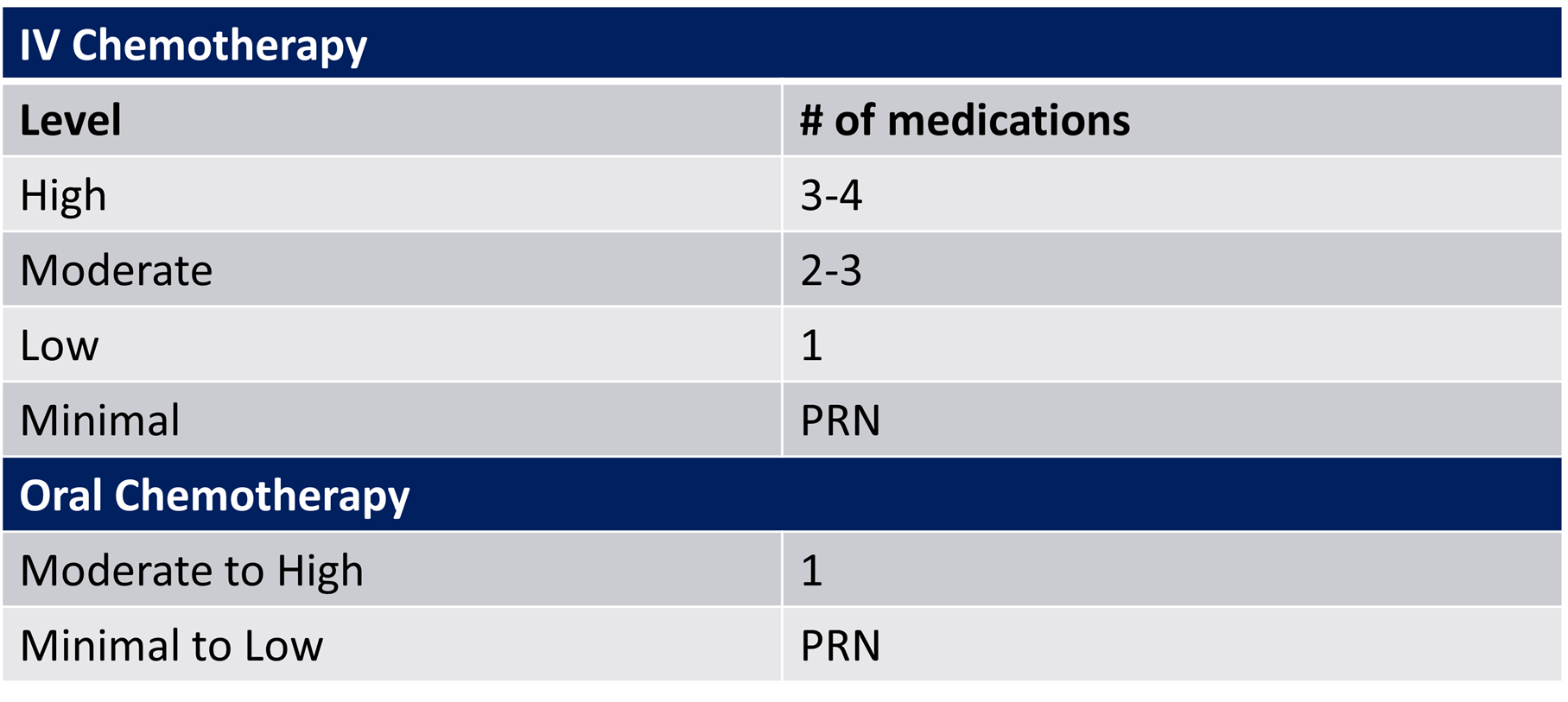
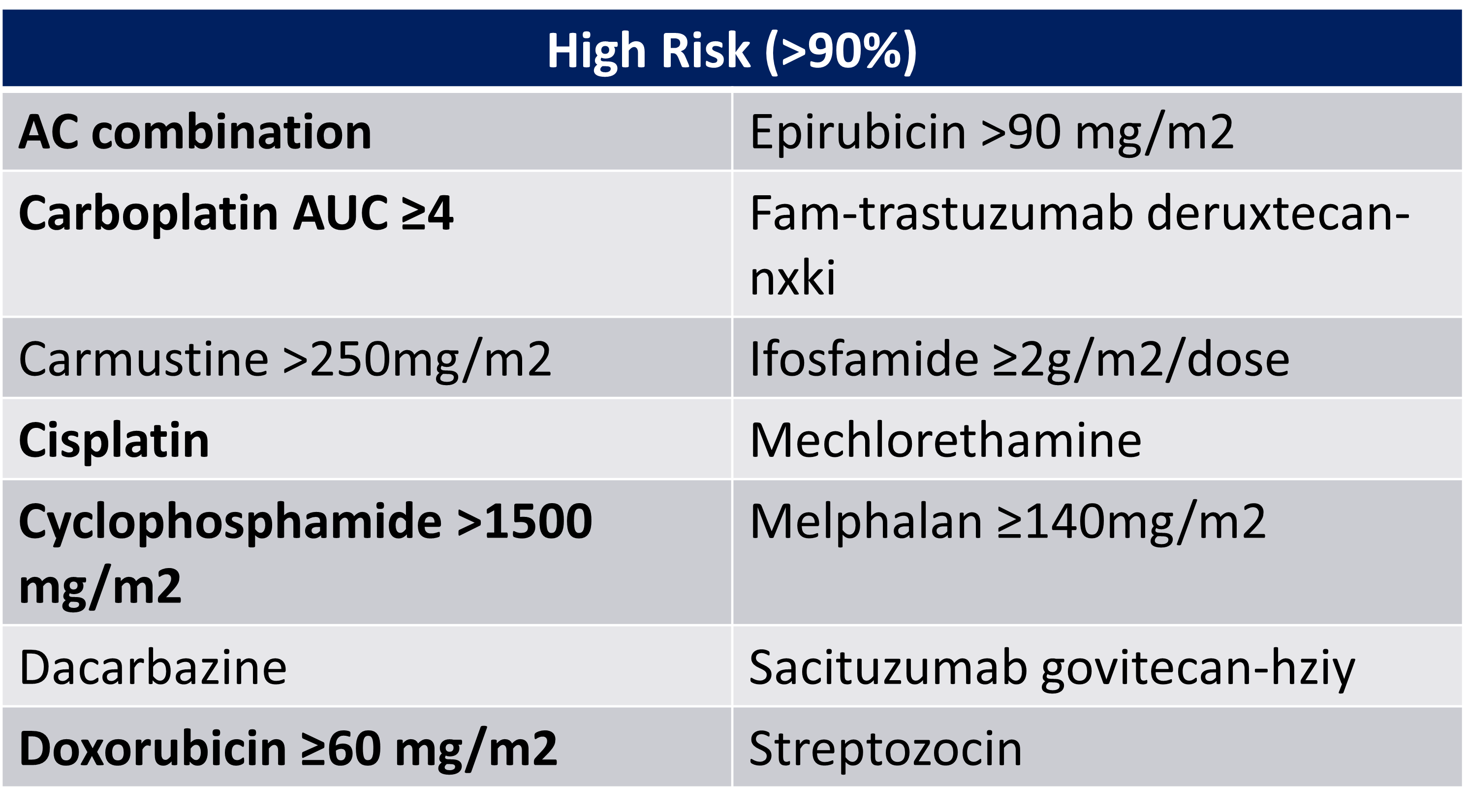
IV Emetogenic Potential High Risk:
high risk is considered > 90%
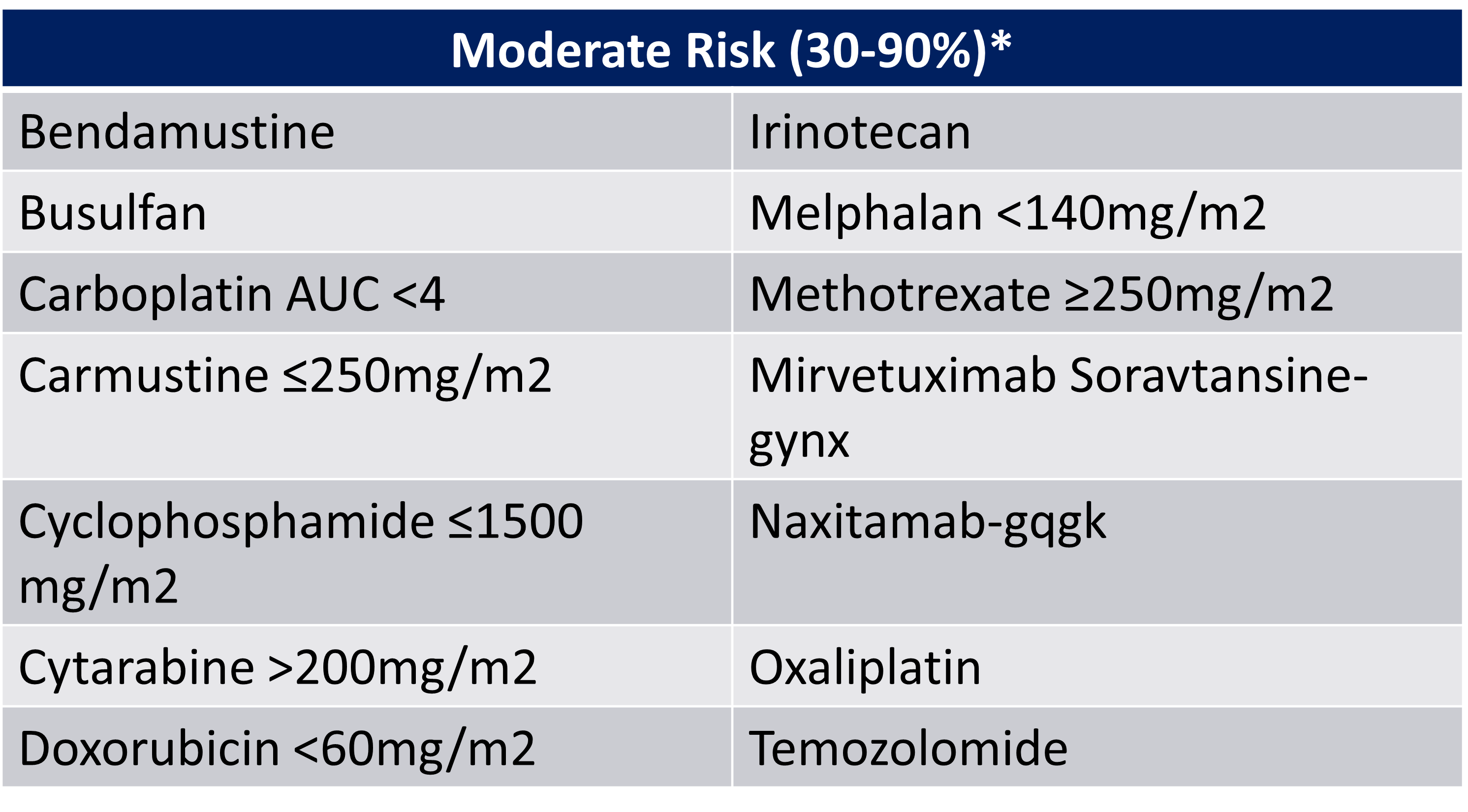
IV emetogenic potential moderate risk:
moderate risk is 30-90%
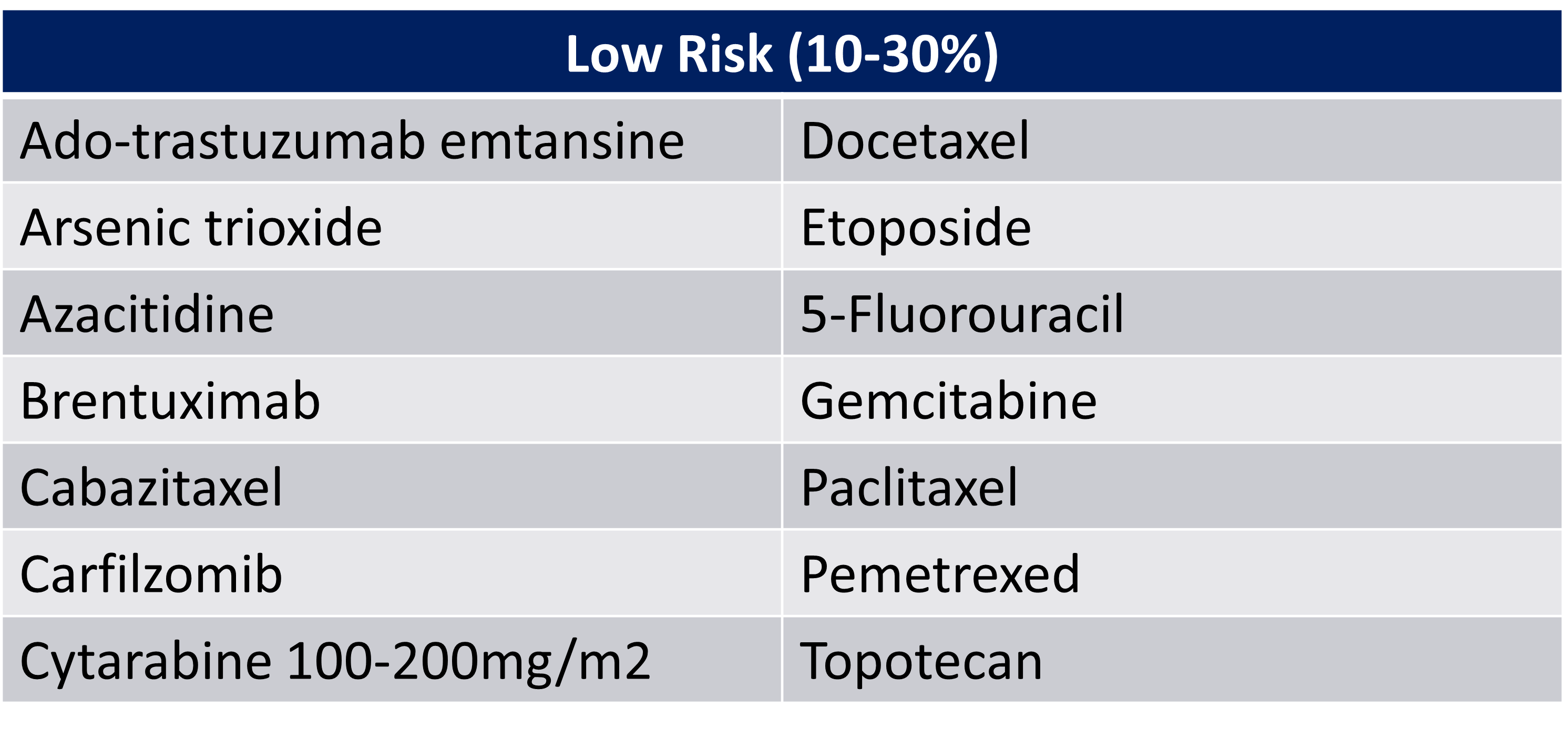
IV emetogenic potential low risk:
low risk is 10-30%
IV emetogenic potential minimal risk:
minimal risk is <10%
IV emetogenicity treatment regimens:
Emetic risk | Treatment options | Examples |
High (>90%) | 4 drug regimen day 1, 3 drugs day 2-4 Or 3 drug regimen day 1, 1 drug days 2-4 Or 3 drug regimen day 1, 2 drug days 2-4 | 1- NK1-RA 2- 5-HT3 RA 3- Dexamethasone 4- Olanzapine Followed by: Olanzapine , 5-HT3, NK-1 RA |
Moderate (30-90%) | 2 drug regimen day 1, 2 drugs day 2-3 Or 3 drug regimen day 1, 1 drug days 2-3 Or 3 drug regimen day 1, 2 drugs day 2-3 | 1- NK1 RA 2- 5-HT3 RA 3- Dexamethasone Followed by: NK-1, dexamethasone |
Low (10-30%) | 1 drug regimen day 1, breakthrough prn | 1- Dexamethasone Or 1- 5-HT3 RA |
Minimal ( < 10%) | No routine prophylaxis | PRN ondansetron |
What is the treatment for anticipatory chemotherapy induced nausea/vomiting?
· Anxiolytic (Lorazepam 0.5-1 mg po evening before anticancer therapy)
What is the treatment for breakthrough chemotherapy induced nausea/vomiting?
· Re-evaluate current regimen
· Considered different route: SubQ, topical, Rectal, IV
· Add one agent from a different class to current regimen
· Every patient should have 1-2 meds at home for breakthrough chemotherapy induced nausea/vomiting
Emetogenicity of oral agents:
§ Minimal to Low risk:
· <30%
§ Moderate to high risk:
· >30%
Which medications are started before anticancer therapy and continued daily?
· Minimal to low risk:
o PRN
o Metoclopramide
o 5-HT3 RA
o Prochlorperazine
· Moderate to high risk:
o Scheduled
o 5-HT3 RA
Oral agents emetogenic potential moderate to high risk:
-moderate to high risk is >30%
IV Chemotherapy/Oral Chemotherapy emetogenicity treatment: